definition of kelly hose in stock

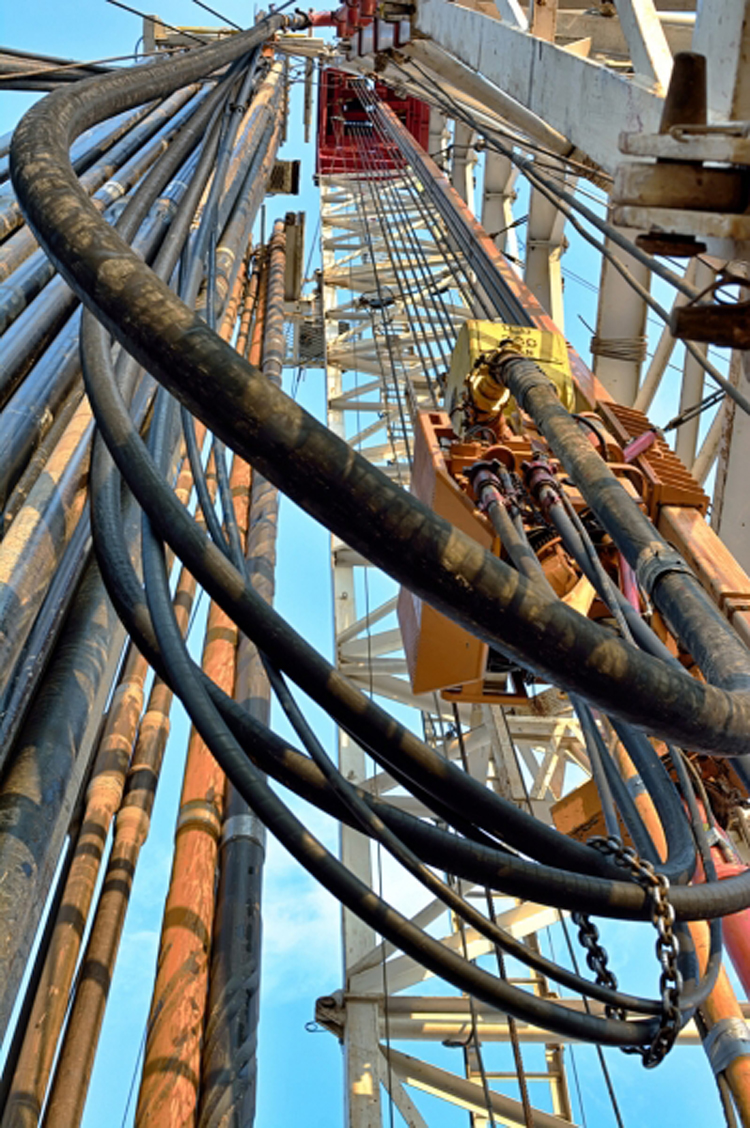
A large-diameter (3- to 5-in inside diameter), high-pressure flexible line used to connect the standpipe to the swivel. This flexible piping arrangement permits the kelly (and, in turn, the drillstring and bit) to be raised or lowered while drilling fluid is pumped through the drillstring. The simultaneous lowering of the drillstring while pumping fluid is critical to the drilling operation.

A kelly hose is a piece of mining equipment. Specifically, it refers to a piece of equipment used in the mining of fluid or semi-fluid resources, such as oil and natural gas. The main purpose of a kelly hose is to allow the drill string to be raised and lowered at the same time that drill fluid is being pumped through it. This is important, as drill fluid is critical to the mining process.
In most cases, a kelly hose is classified as a large-diameter hose. This means that the inside diameter is usually between 3 and 5 inches (about 7.6 cm and 12.7 cm). This wide diameter allows for a significant rate of flow and reduces the likelihood of a blockage occurring in the hose.
The kelly hose must also be able to withstand large amounts of pressure. This applies primarily to the pressure of the fluid flowing through the hose. For this reason, it is often made of highly durable material and is generally reinforced with steel.
In a derrick or drilling rig, the kelly hose connects the standpipe, which is the rigid metal shaft that delivers the mining fluid, to the swivel, which is the piece that supports the weight of and controls the rotation of the drill string. Its purpose is to provide a flexible drilling fluid conduit, as a rigid conduit would be unable to move with the swivel and would therefore disallow movement of the drill string and, subsequently, the bit.
The drilling fluid, sometimes called drilling mud, carried by a kelly hose is critical to operations in several ways. It keeps the bit cool, which helps reduce friction and failure. It also cleans the bit and carries away drill cuttings so they cannot damage the drill assembly. Some varieties are used for additional purposes, such as preventing corrosion and providing hydrostatic pressure. Drilling fluid is not necessarily fluid, but may, in fact, be a solid, liquid, gas or other combined form.
The kelly hose is so named because of its connection with the kelly, the actual mechanical piece that ejects the drilling fluid over the drill string. It may alternatively be called a mud hose or a rotary hose. Failure can occur, despite the rugged construction of the hose. Such failure can lead to damage to the rig or a failure to operate. Failed kelly hoses must be repaired or replaced before mining operations can safely and effectively resume.

additional terms may apply. By using this site, you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy. Wikipedia® is a registered trademark of the Wikimedia Foundation, Inc., a non-profit organization.

The kelly provides a connection between the rotary table, also called the kelly bushing, to the drill string that allows the drill string to turn around its longitudinal axis and move up and down along its length. The hole in the kelly is matched by a hole in the kelly bushing that allows for the passage of drilling fluid into the bore. A kelly is used in fluid or oil assisted bore projects.

The IADC Lexicon is © IADC. However, the documents from which the definitions were drawn may be copyrighted by the original sources, and may not be used without express permission of the copyright holders. IADC expressly recognizes the copyrights of contributors to this Lexicon, including API, OGP, ISO, NORSOK and DNV.

This website uses cookies to improve your experience while you navigate through the website. Out of these cookies, the cookies that are categorized as necessary are stored on your browser as they are essential for the working of basic functionalities of the website. We also use third-party cookies that help us analyze and understand how you use this website. These cookies will be stored in your browser only with your consent. You also have the option to opt-out of these cookies. But opting out of some of these cookies may have an effect on your browsing experience.

Flexible drilling rubber hoses play an important role in petroleum extraction. They should suffer high operating pressure, extreme operating temperature, abrasion and other inferior elements. Our special compounded synthetic rubber has been proven an effective and economical way to reject these problems. All our oilfield drill hoses are manufactured as API 7K or other related specifications.
Steel cable reinforcement loads most working pressure up to 15,000psi. The wires are usually zinc-plating or copper platting to improve steel wire resistant against rust and corrosion. Due to the thick reinforcement, the hoses should be handled or stored in correct way to avoid kicking or crushing. They will substantially decrease their rated operating pressure.
Rotary hose, Kelly hose, cement hose, mud hose, jumper hose and vibrator hose and choke & kill hoses are the most popular oilfield rubber hoses. They convey high-pressure drilling fluid from one place to another. Many end fittings are provided to satisfy different applications. Most end fittings are made according to API standards. Special order is also available.

This is the brief explanation of a Kelly rotating system on the rig. Kelly rig is on an old style rigs and nowadays it is mostly used on land operations. For offshore operation, a top drive system is used instead.
First of all, it is important for new people to look at these images before reading the information below because they show the equipment’s name and where they are on the rig.
The upper end of the drill pipe is screwed onto the saver sub. The saver sub is used to protect and minimize wearr and tear on the threads at the bottom of the Kelly. The Kelly is about 40 ft in length with a square or hexagonal shape and it is hollow throughout in order to transport the drilling mud. Kelly moves freely through a Kelly bushing even though the drill stem is rotated.
A Kelly cock valve is located at the top of a Kelly and it is a safety valve which can be closed to stop back pressure from coming back to damage other surface equipment.
A swivel attached to the hook does not rotate, but at the bottom part it supports the Kelly which is being rotated while drilling. Drilling mud is pumped from a mud pump to a stand pipe manifold, Kelly hose and then to a gooseneck connection at a swivel.
A rotary table rotates a Kelly bushing and it simultaneously rotates a Kelly and a drill string and a drill bit. A rotary table has two main functions. The first one is to provide rotation to a drill stem and a bit and the second function is to hold slip in order to support the weight of a drill stem when it is not connected to a Kelly.
Generally, a rotary drive consists of a chain and rotary-drive sprocket. A rotary-drive sprocket is a part of the draw-works. In other rig power systems, an independent electric motor or engine with a direct drive to a rotary table is utilized. For this case, the rotary is normally driven by a drive shaft instead of a chain and rotary-drive sprocket.
A master bushing severs its function as a rotary motion transmission from a rotary table to a Kelly. Additionally, it is a link between a slip and a rotary table.
A Kelly bushing (some people call “rotary Kelly bushing”) engages a master bushing via four pins and rollers inside a Kelly bushing to allow a Kelly to move up or down freely while it is rotated or in a static mode.
Drilling hose also called Oilfield drilling hose, rotary drilling hose, is hollow, thin-walled, steel or aluminium alloy piping that is used on drilling rigs. It is hollow to allow drilling fluid to be pumped down the hole through the bit and back up the annul-us. It comes in a variety of sizes, strengths, and wall thicknesses, but is typically 27 to 32 feet in length (Range 2). Longer lengths, up to 45 feet, exist (Range 3).
Oilfield drilling hoses have found their wide application in the extraction of minerals such as oil & gas drilling. With the help of the drill pipe, a drilling mud is injected into the well at a very high pressure, most often technical water, hydrogel solution or clay-based solutions. The drill hose is also used between oil tankers and drilling wells in the sea. Drilling hoses can be used on stationary and mobile drilling rigs, for drilling wells in the sea.
The drilling rotary hose is suitable for flexible connection between the top of the drilling riser and the swivel which can move vertically. It resists corrosion of hydrogen sulfide and can deliver water, oil, mud high‐pressure media.
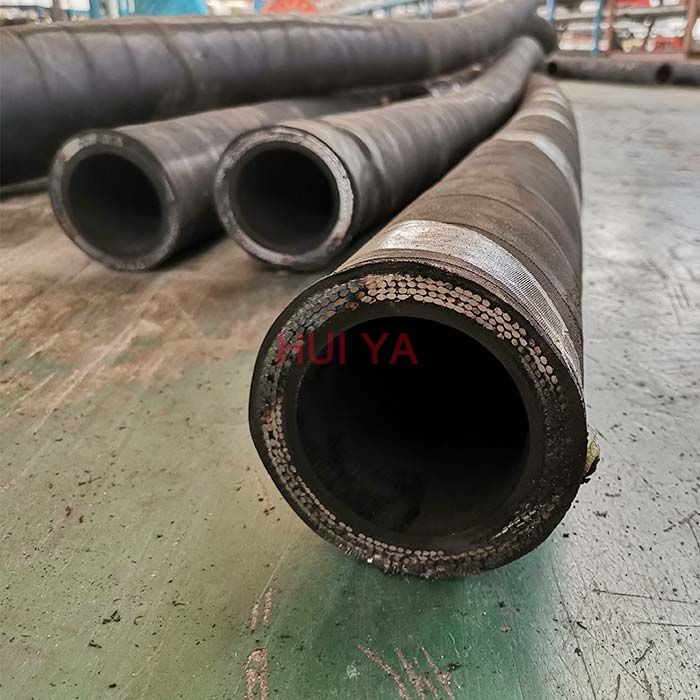
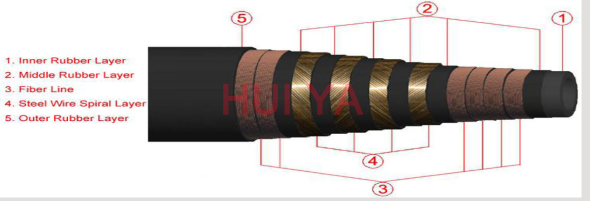
Rotary drilling hose is mainly used for conveying water-based or oil-based mud and other fluids in the working temperature of -30 °C to +82 °C. It is often used for oil fields, cement repairing, geological exploration and water conveyance for coal excavation. It is composed of three parts: tube, reinforcement and cover. The tube is made from NBR, which is resistant to abrasion, corrosion and oils. The reinforcement is made from 2-8 layers of high tensile and high strength spiraled steel wire, making the hose have solid structure and resistant to high pressure. The cover is made from high quality synthetic rubber, mainly chloroprene rubber, making the hose resistant to abrasion, corrosion, cut, weather, ozone, aging and sunlight. The hose has longer service life as a result.
Cover: high quality synthetic rubber, mainly chloroprene rubber, making the hose resistant to abrasion, corrosion, cut, weather, ozone, aging and sunlight.
As drilling operation methods evolve, become deeper, with increasing pressure and higher temperatures, JYM can provide a range of drilling and cementing hose solutions to meet these challenging conditions. Our key offering includes rotary drilling / vibrator hose grade D and E, choke and kill, cement and sour hoses. The JYM range supports the pumping of mud at very high pressure during drilling and exploration campaigns.
JINYUAN RUBBER CO., LTD. has been an important partner of many famous customers including America, East Asia, Africa and other countries and regions in the world. Oilfield drilling hoses are vital components for rig drilling systems. Rotary drilling hose, mud hose, cement hose, Kelly hose, vibrator hose are working under high-pressure. Once the hose failure, it will cause catastrophic damage to the equipment, body health and property. Our professional engineers can help you solve any problem in safe storage, handling and other technical problems. Our drilling hoses are equipped with API end fittings – flanges, NPT threads and butt-weld unions to meet requirements on the market. Bespoke end fittings are also available. Hose quality is our life. It is our aim to provide constantly high level of quality. All production processes and procedures have been strictly inspected. The final inspection before shipment is the strictest and any inferior products are not allowed in our company. When you purchase our products, we will provide considerable after-sales service. If the drill rotary hoses fail in warranty time, they can be returned without costing you one cent of shipment.

Kelly bushing is that elevated device positioned right on top of the rotary table and used to transmit torque from the rotary table to the kelly. The kelly bushing is designed to be the connection between the rotary table and the kelly. The kelly is a 4 or 6 sided steel pipe.
The purpose of the rotary table is to generate the rotary action (torque) and power necessary to rotate the drillstring and drill a well. The torque generated by the rotary table is useless if it is not transferred to the kelly (the drillstring is connected to the kelly).
Hence, through the kelly bushing the torque generated at the rotary table is transferred to the kelly. To achieve this connection, the inside profile of the kelly bushing matches the outer profile of the kelly so that the kelly fits or “sits” comfortably in the kelly bushing.
There are various designs for the kelly bushing including the split type, the pin-drive type and the square-drive type. Each of these designs has different ways in which they are connected and disconnected from the rotary table.
The internal diameter of the kelly bushing can be cut into the shape of a square (4-sided) or a hexagon (6-sided) depending on the outer shape of the kelly that will be used. The internals of a Kelly bushing is designed to resemble the outer shape of a Kelly just like the insides of a key lock is cut to exactly match the outer shape of the key.
The kelly bushing is not designed to hold tightly onto the Kelly; the kelly is still permitted to move up and down through the kelly bushing. This requirement is a must since drilling cannot progress if the kelly remains on a fixed spot. As the well is drilled deeper, the kelly also moves downward through the Kelly bushing.
The kelly bushing is sometimes used as a reference point from which depth measurements can be taken. All depths must be recorded with respect to a reference point; the kelly bushing (KB) is one of the depth references used in the oil and gas industry.
The top of the kelly bushing is normally used as the depth reference.For example, 7500ft KB means 7500ft below the kelly bushing or 7500ft measured from the top of the kelly bushing down to that point in the well.
In some other cases, depths could be recorded as 7500ft MDBKB meaning 7500ft measured depth below the kelly bushing. This is mostly used when the measured depth is different from the true vertical depth of the well, common with deviated and horizontal wells.

The rotary system includes all of the equipment used to achieve bit rotation. Originally, the main driver in the system of all rigs was the rotary table. The main parts of the rotary system with a rotary table are the swivel, kelly, and drillstring.
The rotary swivel (Fig. 1)serves two important functions in the drilling process. It is a connecting point between the circulating system and the rotary system. It also provides a fl uid seal that must absorb rotational wear while holding pressure. The upper section of the swivel has a bail for connection to the elevator hook, and the gooseneck of the swivel provides a downward-pointing connection for the rotary hose.
The kelly is the fi rst section of pipe below the swivel. The outside cross section of the kelly is square or (mostcommonly) hexagonal to permit it to be gripped easily for turning. Torque is transmitted to the kelly through kelly bushings, which fi t inside the master bushing of the rotary table. The kelly thread is right-handed on the lower end and left-handed on the upper end to permit normal right-hand rotation of the drillstring.
During drilling operations, in every connection, a new pipe is added below the kelly. To avoid premature wear in the kelly’s threads, a kelly saver sub is used between the kelly and the fi rst joint of drillpipe. Kelly cock valves are located on either end of the kelly.
Modern rigs use a topdrive to replace the kelly, kelly bushings, and rotary table. Drillstring rotation is achieved through hydraulic or electric motors. One type of topdrive is shown in Fig. 2
Topdrives are suspended from the hook and can travel up and down the derrick. This will allow drilling to be done with stands of pipes, instead of single joints, which will save considerable time. Comparing with the conventional process, where a new pipe must be added to the drillstring after the length of just one joint has been drilled, using a topdrive system, a new connection will occur only after the length of one stand (two, three, or four pipes) has been drilled.
Besides saving time, a system with a topdrive enables the driller to re-initiate fl uid circulation or drillstring rotation faster while tripping, which reduces the chance of problems such as stuck pipe.
Fig. 1 —(a) Rotary swivel (Steven M. Hain Company, Inc. 2010); used with permission from Steven M. Hain Company, Inc.; (b) rotary swivel (courtesy of OSHA).
The drillstring connects the surface equipment with the drill bit at the bottom of the well. The rotary table, or the topdrive, rotates the drillstring and, consequently, rotation is transmitted to the bit.
The drillstring is basically composed of two major portions, the drillpipes and the bottomhole assembly (BHA) (see Fig. 3). Drillpipes (Fig. 3b) are specifi ed by outside diameter, weight per foot, steel grade, and length range. Drillpipes are classifi ed by API in the following length ranges: Range 1 is 18 to 22 ft (5.5 to 6.7 m), Range 2 is 27 to 30 ft (8 to 9 m), and Range 3 is 38 to 45 ft (12 to 14 m).
Range 2 drillpipe is used most commonly. Since each joint of pipe has a unique length, the length of each joint must be measured carefully and recorded to allow a determination of total well depth during drilling operations.
The drillpipe joints are fastened together in the drillstring by means of tool joints (Fig. 3a). The portion of the drillpipe to which the tool joint is attached has thicker walls than the rest of the drillpipe to provide for a stronger joint. This thicker portion of the pipe is called the upset. If the extra thickness is achieved by decreasing the inside diameter, the pipe is said to have an internal upset. If the extra thickness is achieved by increasing the outside diameter, the pipe is said to have an external upset. A tungsten carbide hardfacing sometimes is manufactured on the outer surface of the tool joint box to reduce the abrasive wear of the tool joint by the borehole wall when the drillstring is rotated.
The BHA is the lower section of the drillstring. Even though a BHA may have many different tubulars depending on the complexity of the operation, most of the BHA is composed of drill collars (Fig. 3c). The drill collars are thick-walled, heavy steel tubulars used to apply weight to the bit. The buckling tendency of the relatively thinwalled drillpipe is too great to use it for this purpose. The smaller clearance between the borehole and the drill collars helps to keep the hole straight. Stabilizers (Fig. 4)often are used in the drill collar string to assist in keeping the drill collars centralized. Other types of tubulars used include shock absorbers and drilling jars. In addition, heavyweight drillpipes, a type of drillpipe with thicker walls, are commonly placed on top of the BHA to make the transition between the heavier drill collars and the drillpipes.
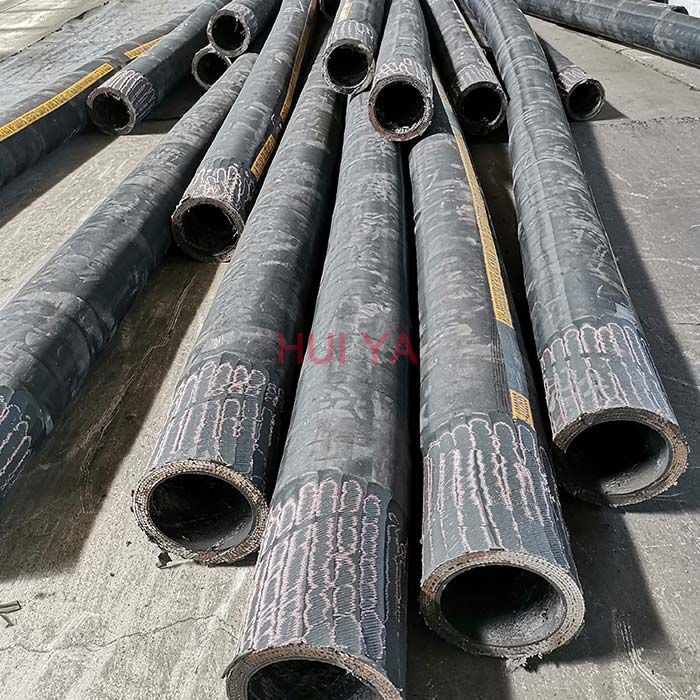

High Pressure Drilling Rotary Hoses is used in drilling and exploration work. Suitable for hydraulic fluids, such as hydraulic oil, fuel oil, lubricants, emulsion, glycol and water.Drilling hose is also used to adjust the installation mistake between drilling pipe line and stand pipe to avoid shake. To transmit high pressure oil or water based mud.
Meets the severe demands of today’s drilling methods including directional drilling, pressure pulses and elevated temperatures. Tube is designed to handle abrasive, corrosive and oil based drilling muds. The cover is designed to handle external damage from abrasion, corrosion, gouges, oil and weather.
Recommended For:Flexible hose between the riser and manifold or around the ball joint of offshore drilling rigs, specially designed to withstand high pressure.Meets the high demands of directional drilling and down linking with negative pressure pulses and elevated temperatures. This hose can also be used as a Motion Compensator hose for stabilization of rotary drilling and pumping equipment against vertical wave action on offshore drill platforms. The Motion Compensator hose is not recommended for phosphate ester fluids.




 8613371530291
8613371530291