mud pump design quotation

Manufactured to withstand the toughest drilling and environmental conditions, our K-Series triplex mud pumps are ideal for all drilling applications. This legacy product features a balanced forged-steel crankshaft and Southwest Oilfield Products ‘L” Shaped modules which is essential to minimize wear, noise, and operating vibrations. These attributes are essential when drilling deeper high pressure formations, long laterals and when handling corrosive or abrasive fluids and slurries.
Every American Block triplex mud pump is manufactured and fully load tested before leaving our manufacturing campus, and is available in sizes ranging from 800 HP to 2200 HP. The American Block K1600 HP Mud Pump is also available in a 2000 HP up-grade version, when more HP is needed in the same 1600 HP footprint.
Mud Pumps come in both electric and gas / diesel engine drive along with air motors. Most of these pumps for mud, trash and sludge or other high solids content liquid dewatering, honey wagon and pumper trucks. Slurry and mud pumps are often diaphragm type pumps but also include centrifugal trash and submersible non-clog styles.
WARNING: Do not use in explosive atmosphere or for pumping volatile flammable liquids. Do not throttle or restrict the discharge. Recommend short lengths of discharge hose since a diaphragm mud pump is a positive displacement type and they are not built with relief valves.
A mud pump is a reciprocating piston/plunger pump designed to circulate drilling fluid under high pressure (up to 7,500 psi (52,000 kPa)) down the drill string and back up the annulus. A duplex mud pump is an important part of the equipment used for oil well drilling.
Duplex mud pumps (two piston/plungers) have generally been replaced by the triplex pump, but are still common in developing countries. Two later developments are the hex pump with six vertical pistons/plungers, and various quintuplex’s with five horizontal piston/plungers. The advantages that Duplex mud pumps have over convention triplex pumps is a lower mud noise which assists with better Measurement while drilling and Logging while drilling decoding.
Use duplex mud pumps to make sure that the circulation of the mud being drilled or the supply of liquid reaches the bottom of the well from the mud cleaning system. Despite being older technology than the triplex mud pump, the duplex mud pumps can use either electricity or diesel, and maintenance is easy due to their binocular floating seals and safety valves.
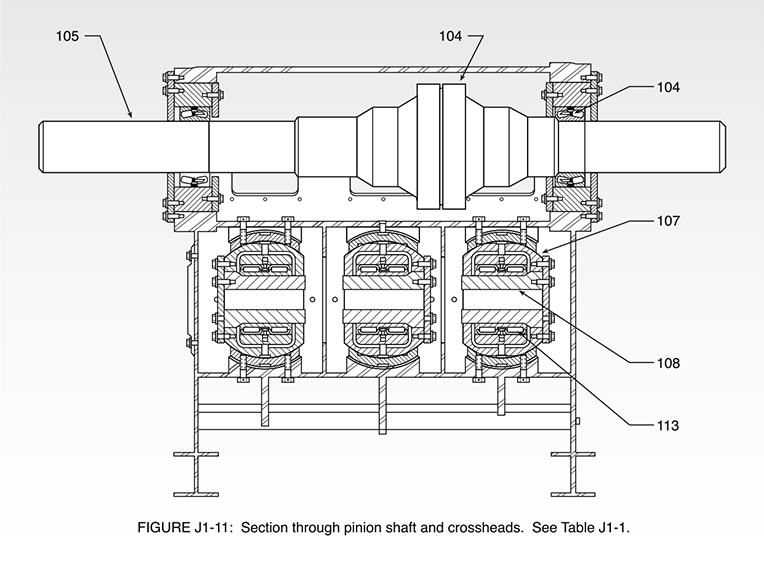
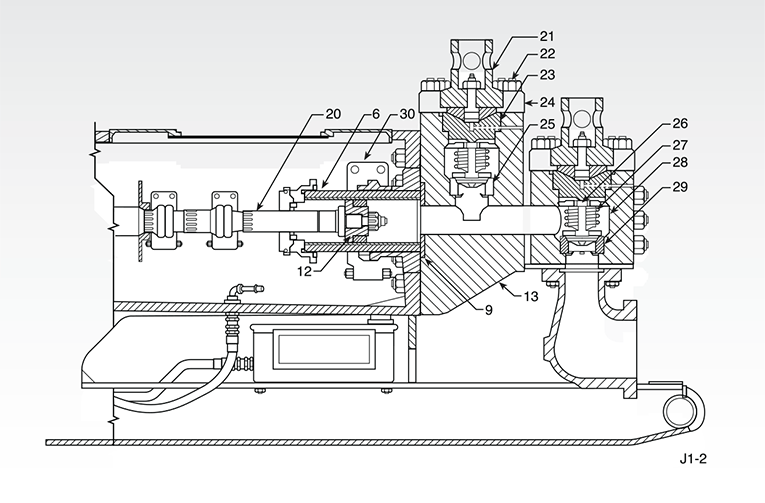
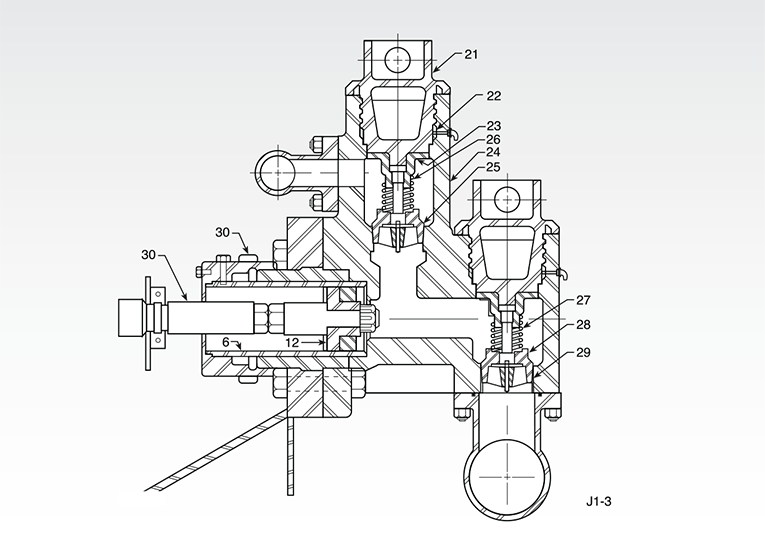
A mud pump is composed of many parts including mud pump liner, mud pump piston, modules, hydraulic seat pullers, and other parts. Parts of a mud pump:housing itself
Duplex pumps are used to provide a secondary means of fuel transfer in the event of a failure of the primary pump. Each pump in a duplex set is sized to meet the full flow requirements of the system. Pump controllers can be set for any of the following common operating modes:Lead / Lag (Primary / Secondary): The lead (primary) pump is selected by the user and the lag (secondary pump operates when a failure of the primary pump is detected.
Alternating: Operates per Lead / Lag (Primary / Secondary) except that the operating pump and lead / lag status alternate on consecutive starts. A variation is to alternate the pumps based on the operating time (hour meter) of the lead pump.
GDEP is the original creator of the drilling pump and continues to set the standard for durable, high-quality drilling pumps that can withstand the world’s toughest drilling environments. Starting with our PZ7 and rounding out with the market"s most popular pump, the PZ1600, our PZ Series of pumps are the perfect choice for today"s high-pressure drilling applications.

The synchronous reciprocating motion of drilling mud pumps operating at optimized speed, symbolize the steady but continuous operations of oil exploration and production. ShalePumps, as a recognized quality producer of high quality drilling mud pumps constantly strives to pull out an improvised and operation enhancing equipment from the assembly lines. SP-2200L drilling mud pumps are an instance of enhanced engineering and precision.
Firing optimized pump speeds, and comprising of superior materials, the drilling mud pumps are designed to operate effortlessly. To enable easy replacement of high wear components, the design incorporates a fast access mechanism, to reduce downtime.
The drilling mud pumps have been developed and manufactured by factoring in the structural demands as a result of long runs. The components are manufactured from superior materials like high strength steel frames, forged steel crankshaft, metal liners and high capacity bearings.
The combination of tested materials and engineering excellence has helped ShalePumps to consistently deliver the needs of the industry in advance. The drilling mud pumps perform in mechanical harmony to standards that overrun industry performance parameters such as displacement and pressure. At ShalePumps, the desired parameters of performance of pumps are by default, pegged higher than industry requirements.

Το work with title Full design of a drilling mud pump and flow program by Balac Srdan is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International
Srdan Balac, "Full design of a drilling mud pump and flow program", Master Thesis, School of Mineral Resources Engineering, Technical University of Crete, Chania, Greece, 2019
Drilling projects must be planned carefully as they need to be a balance of both efficiency of drilling and the project expenditure; that is, the goal is to drill the well reaching target depth with highest performance at the lowest cost.When it comes to reducing the cost of a project, mud hydraulics are one of the most important factors. By minimizing pressure loss, due to friction in drilling string and annulus, maximum efficiency of the drilling bit and the maximum usage of pump pressure is achieved.Knowing the rheology of the mud and the flow regime we can calculate pressure loss in the system. Rheology studies the flow, or rather deformation of matter, described in terms of shear rate and shear stress. Shear rate is defined as the flow velocity gradient in the direction perpendicular to the flow direction. Hence, the higher the shear rate, the higher the friction between the flowing particles. On the other hand, Fluids are described as Newtonian or non-Newtonian depending on their response to shear stress.Flow regime that appear in drilling are laminar flow, turbulent flow, and transitional flow. Pressure loss in the system can be expressed by calculating fluid velocity and Reynolds number for flow regimes. Circulating fluid must overcome friction between the fluid layers and the drill pipe, hole walls or casing walls, as well as the friction between solid particles and fluid. The major pressure loss occurs on the drilling bit nozzles. Therefore, pressure on the pump must be high enough to compensate for it; and it is equal to sum of all these forces.When it comes to the required hole cleaning and high rate of penetration, mud pumps are the most important equipment for providing the bit hydraulics. Drilling hydraulics can always be optimized by altering the pump liner, flow rate, and size of the nozzles; in accordance to the depth of drilling.In making an effective design, it is essential to have an understanding of hydraulics problems, as well as all their possible causes; in order to prepare adequate solutions to overcome delays, reduce operation costs, and reach the target.This thesis studies hydraulics as a means of assisting the design of full flow programs, that will in return give us the necessary mud pump specification for optimal drilling. Through modeling this problem, the goal is to avoid potential drilling problems in order to ensure further efficient drilling; especially in complex and inclined wells, where the hydraulic are usually more complex because of well path and geometry.

For the successful execution of your projects, it is important to find an appropriate company with a good track record. We help you in connecting with the top mud pump manufacturers and companies and get the best quotation.
We have designed affordable annual subscription plans which would help you get leads for your business. You can have a look at our pricing chart by clicking on this link: https://www.energydais.com/pricing/ . These plans are customized according to the specific needs and requirements of your business.
The most widely used mud pumps across the industry are Triplex Reciprocating Pumps. Their application has gained immense popularity with time because they are 30% lighter than duplex reciprocating pumps with relatively less operational cost. Moreover, through these pumps the discharge of mud is smooth and they are capable of moving large volume of mud at higher pressure.
Yes. We help you find the best mud pumps irrespective of your location. We simplify your search by connecting you with top mud pump manufacturers and mud pump companies in your location, according to your budget and business requirement.
The most widely used mud pumps across the industry are Triplex Reciprocating Pumps. Their application has gained immense popularity with time because they are 30% lighter than duplex reciprocating pumps with relatively less operational cost. Moreover, through these pumps the discharge of mud is smooth and they are capable of moving large volume of mud at higher pressure.
The different parts of a mud pump are Housing itself, Liner with packing, Cover plus packing, Piston and piston rod, Suction valve and discharge valve with their seats, Stuffing box (only in double-acting pumps), Gland (only in double-acting pumps), and Pulsation dampener. A mud pump also includes mud pump liner, mud pump piston, modules, hydraulic seat pullers along with other parts.
The wearing parts of a mud pump should be checked frequently for repairing needs or replacement. The wearing parts include pump casing, bearings, impeller, piston, liner, etc. Advanced anti-wear measures should be taken up to enhance the service life of the wearing parts. This can effectively bring down the project costs and improve production efficiency.

The Hex Pump is an axial piston mud pump with six vertical pistons driven by two AC motors via a gear and a specially profiled cam. In contrast to crankshaft-driven triplex pumps, the Hex pump delivers a nearly pulsation free flow. Consequently, there is no need for pulsation dampeners on either the suction or discharge side when running this pump. Other major advantages are compactness (reduced weight and footprint) and no need for replacing liner sizes to achieve high pressure or flow. The Hex 240 version with 4 1/2" liners has a rated capacity of 2540 HP, a maximum rated pressure of 7500 PSI and a maximum flow capacity of 1034 GPM.
The Hex Pump has substantially less weight than a comparable Triplex pump, and this results in increased variable deck load capacity on drilling units. The potential cost savings related to increased variable deck load capacity both on new builds and on existing rigs will be discussed in this paper. Also, the potential steel weight reduction in the substructure on drilling units will be discussed.
The Hex Pump creates a clean standpipe pressure with much lower pressure fluctuation levels than triplex pumps. Due to this, there are no need for pulsation dampeners when running the Hex Pump. This additionally leads to much better and cleaner MWD-signals for the directional driller. As a consequence, this will contribute to faster and more accurate drilling in long and complicated directional wells.
The design and development of the Hex Pump is described in SPE paper 79831, ref /1/; "Development and Performance Testing of the Hex Mud Pump", but for the understanding of this paper it is important to understand the functionality of the Hex Pump design. Some of the main items are therefore repeated in this paper. SPE paper 92507, ref. /2/, "Operational experience with use of a Hex Pump on a land rig" focuses on the improved MWD-measurements related to use of Hex Pump compared to triplex pumps. Some of the main items discussed there will also be repeated in this paper.

The mud pump piston is a key part for providing mud circulation, but its sealing performance often fails under complex working conditions, which shorten its service life. Inspired by the ring segment structure of earthworms, the bionic striped structure on surfaces of the mud pump piston (BW-160) was designed and machined, and the sealing performances of the bionic striped piston and the standard piston were tested on a sealing performance testing bench. It was found the bionic striped structure efficiently enhanced the sealing performance of the mud pump piston, while the stripe depth and the angle between the stripes and lateral of the piston both significantly affected the sealing performance. The structure with a stripe depth of 2 mm and angle of 90° showed the best sealing performance, which was 90.79% higher than the standard piston. The sealing mechanism showed the striped structure increased the breadth and area of contact sealing between the piston and the cylinder liner. Meanwhile, the striped structure significantly intercepted the early leaked liquid and led to the refluxing rotation of the leaked liquid at the striped structure, reducing the leakage rate.
Mud pumps are key facilities to compress low-pressure mud into high-pressure mud and are widely used in industrial manufacture, geological exploration, and energy power owing to their generality [1–4]. Mud pumps are the most important power machinery of the hydraulic pond-digging set during reclamation [5] and are major facilities to transport dense mud during river dredging [6]. During oil drilling, mud pumps are the core of the drilling liquid circulation system and the drilling facilities, as they transport the drilling wash fluids (e.g., mud and water) downhole to wash the drills and discharge the drilling liquids [7–9]. The key part of a mud pump that ensures mud circulation is the piston [10, 11]. However, the sealing of the piston will fail very easily under complex and harsh working conditions, and consequently, the abrasive mud easily enters the kinematic pair of the cylinder liner, abrading the piston surfaces and reducing its service life and drilling efficiency. Thus, it is necessary to improve the contact sealing performance of the mud pump piston.
As reported, nonsmooth surface structures can improve the mechanical sealing performance, while structures with radial labyrinth-like or honeycomb-like surfaces can effectively enhance the performance of gap sealing [12–14]. The use of nonsmooth structures into the cylinder liner friction pair of the engine piston can effectively prolong the service life and improve work efficiency of the cylinder liner [15–17]. The application of nonsmooth grooved structures into the plunger can improve the performance of the sealing parts [18, 19]. The nonsmooth structures and sizes considerably affect the sealing performance [20]. Machining a groove-shaped multilevel structure on the magnetic pole would intercept the magnetic fluid step-by-step and slow down the passing velocity, thus generating the sealing effect [21–23]. Sealed structures with two levels or above have also been confirmed to protect the sealing parts from hard damage [24]. The sealing performance of the high-pressure centrifugal pump can be improved by adding groove structures onto the joint mouth circumference [25]. The convex, pitted, and grooved structures of dung beetles, lizards, and shells are responsible for the high wear-resistance, resistance reduction, and sealing performance [26–28]. Earthworms are endowed by wavy nonsmooth surface structures with high resistance reduction and wear-resistance ability [29]. The movement of earthworms in the living environment is very similar to the working mode of the mud pump piston. The groove-shaped bionic piston was designed, and the effects of groove breadth and groove spacing on the endurance and wear-resistance of the piston were investigated [30]. Thus, in this study, based on the nonsmooth surface of earthworms, we designed and processed a nonsmooth striped structure on the surface of the mud pump piston and tested the sealing performance and mechanism. This study offers a novel method for prolonging the service life of the mud pump piston from the perspective of piston sealing performance.
The BW-160 mud pump with long-range flow and pressure, small volume, low weight, and long-service life was used here. The dimensions and parameters of its piston are shown in Figure 1.
A striped structure was designed and processed on the contact surface between the piston cup and the cylinder liner. The striped structure was 5 mm away from the outermost part of the lip, which ensured the lip could contact effectively with the cylinder liner. Based on the structural dimensions of the piston cup, we designed a 2-stripe structure, and the very little stripe space affected the service life of the piston [30]. Thus, the stripe space of our bionic piston was set at 5 mm. According to the machining technology, two parameters of stripe depth h and the angle between the stripes and lateral of the piston α were selected (Figure 2).
A mud pump piston sealing performance test bench was designed and built (Figure 3). This bench mainly consisted of a compaction part and a dynamic detection part. The compaction part was mainly functioned to exert pressure, which was recorded by a pressure gauge, to the piston sealed cavity. This part was designed based on a vertical compaction method: after the tested piston and the sealing liquid were installed, the compaction piston was pushed to the cavity by revolving the handle. Moreover, the dynamic detection part monitored the real-time sealing situation and was designed based on the pressure difference method for quantifying the sealing performance. This part was compacted in advance to the initial pressure P0 (0.1 MPa). After compaction, the driving motor was opened, and the tested piston was pushed to drive the testing mud to reciprocate slowly. After 1 hour of running, the pressure P on the gauge was read, and the pressure difference was calculated as , which was used to measure the sealing performance of the piston.
To more actually simulate the working conditions of the mud pump, we prepared a mud mixture of water, bentonite (in accordance with API Spec 13A: viscometer dial reading at 600 r/min ≥ 30, yield point/plastic viscosity radio ≤ 3, filtrate volume ≤ 15.0 ml, and residue of diameter greater than 75 μm (mass fraction) ≤ 4.0%), and quartz sand (diameter 0.3–0.5 mm) under complete stirring, and its density was 1.306 g/cm³ and contained 2.13% sand.
The orthogonal experimental design method was used to study the effect of factors and the best combination of factor levels [31]. Stripe depth h and angle α were selected as the factors and were both set at three levels in the sealing performance tests (Table 1).
Figure 4 shows the effects of stripe depth and angle on the sealing performance of mud pump pistons. Clearly, the stripe depth should be never too shallow or deep, while a larger angle would increase the sealing performance more (Figure 4).
The standard piston and the bionic piston were numerically simulated using the academic version of ANSYS® Workbench V17.0. Hexahedral mesh generation method was used to divide the grid, and the size of grids was set as 2.5 mm. The piston grid division is shown in Figure 8, and the grid nodes and elements are shown in Table 3. The piston cup was made of rubber, which was a hyperelastic material. A two-parameter Mooney–Rivlin model was selected, with C10 = 2.5 MPa, C01 = 0.625 MPa, D1 = 0.3 MPa−1, and density = 1120 kg/m3 [32, 33]. The loads and contact conditions related to the piston of the mud pump were set. The surface pressure of the piston cup was set as 1.5 MPa, and the displacement of the piston along the axial direction was set as 30 mm. The two end faces of the cylinder liner were set as “fixed support,” and the piston and cylinder liner were under the frictional interfacial contact, with the friction coefficient of 0.2.
To better validate the sealing mechanism of the bionic striped pistons, a piston’s performance testing platform was independently built and the sealed contact of the pistons was observed. A transparent toughened glass cylinder liner was designed and machined. The inner diameter and the assembly dimensions of the cylinder liner were set according to the standard BW-160 mud pump cylinder liners. The sealing contact surfaces of the pistons were observed and recorded using a video recorder camera.
(1)The bionic striped structure significantly enhanced the sealing performance of the mud pump pistons. The stripe depth and the angle between the stripes and the piston were two important factors affecting the sealing performance of the BW-160 mud pump pistons. The sealing performance was enhanced the most when the stripe depth was 2 mm and the angle was 90°.(2)The bionic striped structure can effectively enhance the contact pressure at the piston lips, enlarge the mutual extrusion between the piston and the cylinder liner, reduce the damage to the piston and cylinder liner caused by the repeated movement of sands, and alleviate the abrasion of abrasive grains between the piston and the cylinder liner, thereby largely improving the sealing performance.(3)The bionic striped structure significantly intercepted the leaked liquid, reduced the leakage rate of pistons, and effectively stored the leaked liquid, thereby reducing leakage and improving the sealing performance.(4)The bionic striped structure led to deformation of the piston, enlarged the width and area of the sealed contact, the stored lubricating oils, and formed uniform oil films after repeated movement, which improved the lubrication conditions and the sealing performance.
The bionic striped structure can improve the sealing performance and prolong the service life of pistons. We would study the pump resistance in order to investigate whether the bionic striped structure could decrease the wear of the piston surface.
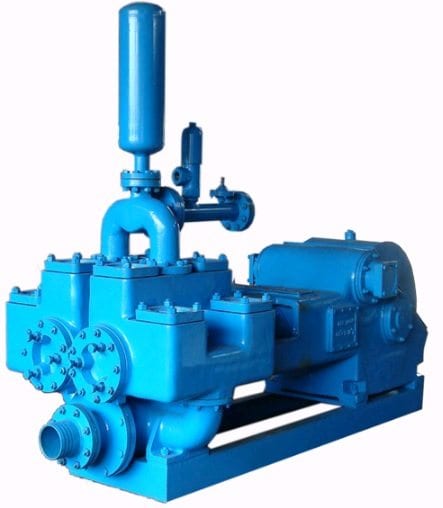

We provide a qualitative range of mud pumps, which are immensely used in construction, agriculture, waste water management and many other industries. These mud pumps are primarily reciprocating plunger devices designed for circulation of drilling fluid down the drill string and back up the annulus. Our range of pumps are suitable for pumping muddy water, sewage, polluted liquids & solids and also in swimming pool. Manufactured using latest technology, these pumps are high performing, abrasion resistant, easy to install and have long service life.

Robust Design and metallurgy ensuring long life, under any soil and abrasion content. Duplex action for maximum flow and increased pressure. Easy maintenance with both hydraulic and engine driven options.




 8613371530291
8613371530291