mud pump output free sample

Rig pump output, normally in volume per stroke, of mud pumps on the rig is one of important figures that we really need to know because we will use pump out put figures to calculate many parameters such as bottom up strokes, wash out depth, tracking drilling fluid, etc. In this post, you will learn how to calculate pump out put for triplex pump and duplex pump in bothOilfield and Metric Unit.
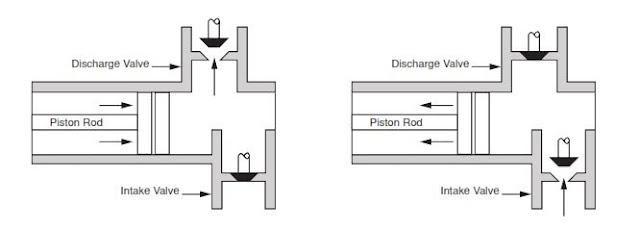
Oil and Gas drilling process - Pupm output for Triplex and Duplex pumpsTriplex Pump Formula 1 PO, bbl/stk = 0.000243 x ( in) E.xample: Determine the pump output, bbl/stk, at 100% efficiency for a 7" by 12". triplex pump: PO @ 100%,= 0.000243 x 7 x12 PO @ 100% = 0.142884bbl/stk Adjust the pump output for 95% efficiency: Decimal equivalent = 95 + 100 = 0.95 PO @ 95% = 0.142884bbl/stk x 0.95 PO @ 95% = 0.13574bbl/stk Formula 2 PO, gpm = [3(D x 0.7854)S]0.00411 x SPM where D = liner diameter, in. S = stroke length, in. SPM = strokes per minute Determine the pump output, gpm, for a 7" by 12". triplex pump at 80 strokes per minute: PO, gpm = [3(7 x 0.7854) 1210.00411 x 80 PO, gpm = 1385.4456 x 0.00411 x 80 PO = 455.5 gpm
Example:Duplex Pump Formula 1 0.000324 x (liner diameter, in) x ( stroke lengh, in) = ________ bbl/stk -0.000162 x (rod diameter, in) x ( stroke lengh, in) = ________ bbl/stk Pump out put @ 100% eff = ________bbl/stk Example: Determine the output, bbl/stk, of a 5 1/2" by 14" duplex pump at 100% efficiency. Rod diameter = 2.0": 0.000324 x 5.5 x 14 = 0.137214bbl/stk -0.000162 x 2.0 x 14 = 0.009072bbl/stk Pump output @ 100% eff. = 0.128142bbl/stk Adjust pump output for 85% efficiency: Decimal equivalent = 85 100 = 0.85 PO@85%)= 0.128142bbl/stk x 0.85 PO@ 85% = 0.10892bbl/stk Formula 2
PO. bbl/stk = 0.000162 x S[2(D) - d] where S = stroke length, in. D = liner diameter, in. d = rod diameter, in. Example: Determine the output, bbl/stk, of a 5 1/2". by 14". duplex pump @ 100% efficiency. Rod diameter = 2.0in.: PO@100%=0.000162 x 14 x [ 2 (5.5) - 2 ] PO @ 100%)= 0.000162 x 14 x 56.5 PO@ 100%)= 0.128142bbl/stk Adjust pump output for 85% efficiency: PO@85%,= 0.128142bb/stkx 0.85 PO@8.5%= 0.10892bbl/stk Metric calculation Pump output, liter/min = pump output. liter/stk x pump speed, spm. S.I. units calculation Pump output, m/min = pump output, liter/stk x pump speed, spm. Mud Pumps Mud pumps drive the mud around the drilling system. Depending on liner size availability they can be set up to provide high pressure and low flow rate, or low pressure and high flow rate. Analysis of the application and running the Drill Bits hydraulics program will indicate which liners to recommend. Finding the specification of the mud pumps allows flow rate to be calculated from pump stroke rate, SPM. Information requiredo Pump manufacturer o Number of pumps o Liner size and gallons per revolution Weight As a drill bit cutting structure wears more weight will be required to achieve the same RoP in a homogenous formation. PDC wear flats, worn inserts and worn milled tooth teeth will make the bit drill less efficiently. Increase weight in increments of 2,000lbs approx. In general, weight should be applied before excessive rotary speed so that the cutting structure maintains a significant depth of cut to stabilise the bit and prevent whirl. If downhole weight measurements are available they can be used in combination with surface measurements to gain a more accurate representation of what is happening in the well bore.

I’ve run into several instances of insufficient suction stabilization on rigs where a “standpipe” is installed off the suction manifold. The thought behind this design was to create a gas-over-fluid column for the reciprocating pump and eliminate cavitation.
When the standpipe is installed on the suction manifold’s deadhead side, there’s little opportunity to get fluid into all the cylinders to prevent cavitation. Also, the reciprocating pump and charge pump are not isolated.
The suction stabilizer’s compressible feature is designed to absorb the negative energies and promote smooth fluid flow. As a result, pump isolation is achieved between the charge pump and the reciprocating pump.
The isolation eliminates pump chatter, and because the reciprocating pump’s negative energies never reach the charge pump, the pump’s expendable life is extended.
Investing in suction stabilizers will ensure your pumps operate consistently and efficiently. They can also prevent most challenges related to pressure surges or pulsations in the most difficult piping environments.

The 2,200-hp mud pump for offshore applications is a single-acting reciprocating triplex mud pump designed for high fluid flow rates, even at low operating speeds, and with a long stroke design. These features reduce the number of load reversals in critical components and increase the life of fluid end parts.
The pump’s critical components are strategically placed to make maintenance and inspection far easier and safer. The two-piece, quick-release piston rod lets you remove the piston without disturbing the liner, minimizing downtime when you’re replacing fluid parts.

A comprehensive range of mud pumping, mixing, and processing equipment is designed to streamline many essential but time-consuming operational and maintenance procedures, improve operator safety and productivity, and reduce costly system downtime.

Centerline Manu-facturing introduces the CLM 7.5 x 10D hydraulic mud pump, a pump which utilizes common fluid end parts. Its advantages are said to be its flow capacity, rated pressure, size and weight. It is designed to pump 100 percent more rated flow than a standard 5x6 and up to 3.25 times the rated pressure. However, it only has a third of the weight and 77 percent of the length.

Pumps tend to be one of the biggest energy consumers in industrial operations. Pump motors, specifically, require a lot of energy. For instance, a 2500 HP triplex pump used for frac jobs can consume almost 2000 kW of power, meaning a full day of fracking can cost several thousand dollars in energy costs alone!
So, naturally, operators should want to maximize energy efficiency to get the most for their money. Even a 1% improvement in efficiency can decrease annual pumping costs by tens of thousands of dollars. The payoff is worth the effort. And if you want to remotely control your pumps, you want to keep efficiency in mind.
In this post, we’ll point you in the right direction and discuss all things related to pump efficiency. We’ll conclude with several tips for how you can maintain pumping efficiency and keep your energy costs down as much as possible.
In simple terms, pump efficiency refers to the ratio of power out to power in. It’s the mechanical power input at the pump shaft, measured in horsepower (HP), compared to the hydraulic power of the liquid output, also measured in HP. For instance, if a pump requires 1000 HP to operate and produces 800 HP of hydraulic power, it would have an efficiency of 80%.
Remember: pumps have to be driven by something, i.e., an electric or diesel motor. True pump system efficiency needs to factor in the efficiency of both the motor AND the pump.
Consequently, we need to think about how electrical power (when using electric motors) or heat power (when using combustion engines) converts into liquid power to really understand pump efficiency.
Good pump efficiency depends, of course, on pump type and size. High-quality pumps that are well-maintained can achieve efficiencies of 90% or higher, while smaller pumps tend to be less efficient. In general, if you take good care of your pumps, you should be able to achieve 70-90% pump efficiency.
Now that we have a better understanding of the pump efficiency metric, let’s talk about how to calculate it. The mechanical power of the pump, or the input power, is a property of the pump itself and will be documented during the pump setup. The output power, or hydraulic power, is calculated as the liquid flow rate multiplied by the "total head" of the system.
IMPORTANT: to calculate true head, you also need to factor in the work the pump does to move fluid from the source. For example, if the source water is below the pump, you need to account for the extra work the pump puts in to draw source water upwards.
*Note - this calculation assumes the pump inlet is not pressurized and that friction losses are minimal. If the pump experiences a non-zero suction pressure, or if there is significant friction caused by the distance or material of the pipe, these should be factored in as well.
You"ll notice that the elevation head is minimal compared to the discharge pressure, and has minimal effect on the efficiency of the pump. As the elevation change increases or the discharge pressure decreases, however, elevation change will have a greater impact on total head.
Obviously, that’s a fair amount of math to get at the pump efficiency, considering all of the units conversions that need to be done. To avoid doing these calculations manually, feel free to use our simple pump efficiency calculator.
Our calculations use static variables (pump-rated horsepower and water source elevation) and dynamic variables (discharge flow and pressure). To determine pump efficiency, we need to measure the static variables only once, unless they change.
If you want to measure the true efficiency of your pump, taking energy consumption into account, you could add an electrical meter. Your meter should consist of a current transducer and voltage monitor (if using DC) for electrical motors or a fuel gauge for combustion. This would give you a true understanding of how pump efficiency affects energy consumption, and ultimately your bank account.
Up until this point, we’ve covered the ins and outs of how to determine pump efficiency. We’re now ready for the exciting stuff - how to improve pump efficiency!
One of the easiest ways to improve pump efficiency is to actually monitor pumps for signs of efficiency loss! If you monitor flow rate and discharge (output power) along with motor current or fuel consumption, you’ll notice efficiency losses as soon as they occur. Simply having pump efficiency information on hand empowers you to take action.
Another way to increase efficiency is to keep pumps well-maintained. Efficiency losses mostly come from mechanical defects in pumps, e.g., friction, leakages, and component failures. You can mitigate these issues through regular maintenance that keeps parts in working order and reveals impending failures. Of course, if you are continuously monitoring your pumps for efficiency drops, you’ll know exactly when maintenance is due.
You can also improve pump efficiency by keeping pumps lubricated at all times. Lubrication is the enemy of friction, which is the enemy of efficiency (“the enemy of my enemy is my friend…”).
A fourth way to enhance pump efficiency is to ensure your pumps and piping are sized properly for your infrastructure. Although we’re bringing this up last, it’s really the first step in any pumping operation. If your pumps and piping don’t match, no amount of lubricant or maintenance will help.
In this post, we’ve given you the full rundown when it comes to calculating and improving pump efficiency. You can now calculate, measure, and improve pump efficiency, potentially saving your business thousands of dollars annually on energy costs.
For those just getting started with pump optimization, we offer purpose-built, prepackaged solutions that will have you monitoring pump efficiency in minutes, even in hazardous environments.
Kverneland, Hege, Kyllingstad, Åge, and Magne Moe. "Development and Performance Testing of the Hex Mud Pump." Paper presented at the SPE/IADC Drilling Conference, Amsterdam, Netherlands, February 2003. doi: https://doi.org/10.2118/79831-MS

Triplex mud pumps pump drilling mud during well operations. An example of a typical triplex mud pump 10 shown in FIG. 1A has a power assembly 12, a crosshead assembly 14, and a fluid assembly 16. Electric motors (not shown) connect to a pinion shaft 30 that drives the power assembly 12. The crosshead assembly 14 converts the rotational movement of the power assembly 12 into reciprocating movement to actuate internal pistons or plungers of the fluid assembly 16. Being triplex, the pump"s fluid assembly 16 has three internal pistons to pump the mud.
As shown in FIG. 1B, the pump"s power assembly 14 has a crankshaft 20 supported at its ends by double roller bearings 22. Positioned along its intermediate extent, the crankshaft 20 has three eccentric sheaves 24-1 . . . 24-3, and three connecting rods 40 mount onto these sheaves 24 with cylindrical roller bearings 26. These connecting rods 40 connect by extension rods (not shown) and the crosshead assembly (14) to the pistons of the pump"s fluid assembly 16.
In addition to the sheaves, the crankshaft 20 also has a bull gear 28 positioned between the second and third sheaves 24-2 and 24-3. The bull gear 28 interfaces with the pinion shaft (30) and drives the crankshaft 20"s rotation. As shown particularly in FIG. 1C, the pinion shaft 30 also mounts in the power assembly 14 with roller bearings 32 supporting its ends. When electric motors couple to the pinion shaft"s ends 34 and rotate the pinion shaft 30, a pinion gear 38 interfacing with the crankshaft"s bull gear 28 drives the crankshaft (20), thereby operating the pistons of the pump"s fluid assembly 16.
When used to pump mud, the triplex mud pump 10 produces flow that varies by approximately 23%. For example, the pump 10 produces a maximum flow level of about 106% during certain crankshaft angles and produces a minimum flow level of 83% during other crankshaft angles, resulting in a total flow variation of 23% as the pump"s pistons are moved in differing exhaust strokes during the crankshaft"s rotation. Because the total flow varies, the pump 10 tends to produce undesirable pressure changes or “noise” in the pumped mud. In turn, this noise interferes with downhole telemetry and other techniques used during measurement-while-drilling (MWD) and logging-while-drilling (LWD) operations.
In contrast to mud pumps, well-service pumps (WSP) are also used during well operations. A well service pump is used to pump fluid at higher pressures than those used to pump mud. Therefore, the well service pumps are typically used to pump high pressure fluid into a well during frac operations or the like. An example of a well-service pump 50 is shown in FIG. 2. Here, the well service pump 50 is a quintuplex well service pump, although triplex well service pumps are also used. The pump 50 has a power assembly 52, a crosshead assembly 54, and a fluid assembly 56. A gear reducer 53 on one side of the pump 50 connects a drive (not shown) to the power assembly 52 to drive the pump 50.
As shown in FIG. 3, the pump"s power assembly 52 has a crankshaft 60 with five crankpins 62 and an internal main bearing sheave 64. The crankpins 62 are offset from the crankshaft 60"s axis of rotation and convert the rotation of the crankshaft 60 in to a reciprocating motion for operating pistons (not shown) in the pump"s fluid assembly 56. Double roller bearings 66 support the crankshaft 60 at both ends of the power assembly 52, and an internal double roller bearing 68 supports the crankshaft 60 at its main bearing sheave 64. One end 61 of the crankshaft 60 extends outside the power assembly 52 for coupling to the gear reducer (53; FIG. 2) and other drive components.
As shown in FIG. 4A, connecting rods 70 connect from the crankpins 62 to pistons or plungers 80 via the crosshead assembly 54. FIG. 4B shows a typical connection of a connecting rod 70 to a crankpin 62 in the well service pump 50. As shown, a bearing cap 74 fits on one side of the crankpin 62 and couples to the profiled end of the connecting rod 70. To reduce friction, the connection uses a sleeve bearing 76 between the rod 70, bearing cap 74, and crankpin 62. From the crankpin 62, the connecting rod 70 connects to a crosshead 55 using a wrist pin 72 as shown in FIG. 4A. The wrist pin 72 allows the connecting rod 70 to pivot with respect to the crosshead 55, which in turn is connected to the plunger 80.
In use, an electric motor or an internal combustion engine (such as a diesel engine) drives the pump 50 by the gear reducer 53. As the crankshaft 60 turns, the crankpins 62 reciprocate the connecting rods 70. Moved by the rods 70, the crossheads 55 reciprocate inside fixed cylinders. In turn, the plunger 80 coupled to the crosshead 55 also reciprocates between suction and power strokes in the fluid assembly 56. Withdrawal of a plunger 80 during a suction stroke pulls fluid into the assembly 56 through the input valve 82 connected to an inlet hose or pipe (not shown). Subsequently pushed during the power stroke, the plunger 80 then forces the fluid under pressure out through the output valve 84 connected to an outlet hose or pipe (not shown).
In contrast to using a crankshaft for a quintuplex well-service pump that has crankpins 62 as discussed above, another type of quintuplex well-service pump uses eccentric sheaves on a direct drive crankshaft. FIG. 4C is an isolated view of such a crankshaft 90 having eccentric sheaves 92-1 . . . 92-5 for use in a quintuplex well-service pump. External main bearings (not shown) support the crankshaft 90 at its ends 96 in the well-service pumps housing (not shown). To drive the crankshaft 90, one end 91 extends beyond the pumps housing for coupling to drive components, such as a gear box. The crankshaft 90 has five eccentric sheaves 92-1 . . . 92-5 for coupling to connecting rods (not shown) with roller bearings. The crankshaft 90 also has two internal main bearing sheaves 94-1, 94-2 for internal main bearings used to support the crankshaft 90 in the pump"s housing.
In the past, quintuplex well-service pumps used for pumping frac fluid or the like have been substituted for mud pumps during drilling operations to pump mud. Unfortunately, the well-service pump has a shorter service life compared to the conventional triplex mud pumps, making use of the well-service pump as a mud pump less desirable in most situations. In addition, a quintuplex well-service pump produces a great deal of white noise that interferes with MWD and LWD operations, further making the pump"s use to pump mud less desirable in most situations. Furthermore, the well-service pump is configured for direct drive by a motor and gear box directly coupling on one end of the crankshaft. This direct coupling limits what drives can be used with the pump. Moreover, the direct drive to the crankshaft can produce various issues with noise, balance, wear, and other associated problems that make use of the well-service pump to pump mud less desirable.
One might expect to provide a quintuplex mud pump by extending the conventional arrangement of a triplex mud pump (e.g., as shown in FIG. 1B) to include components for two additional pistons or plungers. However, the actual design for a quintuplex mud pump is not as easy as extending the conventional arrangement, especially in light of the requirements for a mud pump"s operation such as service life, noise levels, crankshaft deflection, balance, and other considerations. As a result, acceptable implementation of a quintuplex mud pump has not been achieved in the art during the long history of mud pump design.
What is needed is an efficient mud pump that has a long service life and that produces low levels of white noise during operation so as not to interfere with MWD and LWD operations while pumping mud in a well.
A quintuplex mud pump is a continuous duty, reciprocating plunger/piston pump. The mud pump has a crankshaft supported in the pump by external main bearings and uses internal gearing and a pinion shaft to drive the crankshaft. Five eccentric sheaves and two internal main bearing sheaves are provided on the crankshaft. Each of the main bearing sheaves supports the intermediate extent of crankshaft using bearings. One main bearing sheave is disposed between the second and third eccentric sheaves, while the other main bearing sheave is disposed between the third and fourth eccentric sheaves.
One or more bull gears are also provided on the crankshaft, and the pump"s pinion shaft has one or more pinion gears that interface with the one or more bull gears. If one bull gear is used, the interface between the bull and pinion gears can use herringbone or double helical gearing of opposite hand to avoid axial thrust. If two bull gears are used, the interface between the bull and pinion gears can use helical gearing with each having opposite hand to avoid axial thrust. For example, one of two bull gears can be disposed between the first and second eccentric sheaves, while the second bull gear can be disposed between fourth and fifth eccentric sheaves. These bull gears can have opposite hand. The pump"s internal gearing allows the pump to be driven conventionally and packaged in any standard mud pump packaging arrangement. Electric motors (for example, twin motors made by GE) may be used to drive the pump, although the pump"s rated input horsepower may be a factor used to determine the type of motor.
Connecting rods connect to the eccentric sheaves and use roller bearings. During rotation of the crankshaft, these connecting rods transfer the crankshaft"s rotational movement to reciprocating motion of the pistons or plungers in the pump"s fluid assembly. As such, the quintuplex mud pump uses all roller bearings to support its crankshaft and to transfer crankshaft motion to the connecting rods. In this way, the quintuplex mud pump can reduce the white noise typically produced by conventional triplex mud pumps and well service pumps that can interfere with MWD and LWD operations.
Turning to the drawings, a quintuplex mud pump 100 shown in FIGS. 5 and 6A-6B has a power assembly 110, a crosshead assembly 150, and a fluid assembly 170. Twin drives (e.g., electric motors, etc.) couple to ends of the power assembly"s pinion shaft 130 to drive the pump"s power assembly 110. As shown in FIGS. 6A-6B, internal gearing within the power assembly 110 converts the rotation of the pinion shaft 130 to rotation of a crankshaft 120. The gearing uses pinion gears 138 on the pinion shaft 130 that couple to bull gears 128 on the crankshaft 120 and transfer rotation of the pinion shaft 130 to the crankshaft 120.
For support, the crankshaft 120 has external main bearings 122 supporting its ends and two internal main bearings 127 supporting its intermediate extent in the assembly 110. As best shown in FIG. 6A, rotation of the crankshaft 120 reciprocates five independent connecting rods 140. Each of the connecting rods 140 couples to a crosshead 160 of the crosshead assembly 150. In turn, each of the crossheads 160 converts the connecting rod 40"s movement into a reciprocating movement of an intermediate pony rod 166. As it reciprocates, the pony rod 166 drives a coupled piston or plunger (not shown) in the fluid assembly 170 that pumps mud from an intake manifold 192 to an output manifold 198. Being quintuplex, the mud pump 100 has five such pistons movable in the fluid assembly 170 for pumping the mud.
The cross-section in FIG. 10A shows a crosshead 160 for the quintuplex mud pump. The end of the connecting rod 140 couples by a wrist pin 142 and bearing 144 to a crosshead body 162 that is movable in a crosshead guide 164. A pony rod 166 coupled to the crosshead body 162 extends through a stuffing box gasket 168 on a diaphragm plate 169. An end of this pony rod 166 in turn couples to additional components of the fluid assembly (170) as discussed below.
The cross-section in FIG. 10B shows portion of the fluid assembly 170 for the quintuplex mud pump. An intermediate rod 172 has a clamp 174 that couples to the pony rod (166; FIG. 10A) from the crosshead assembly 160 of FIG. 10A. The opposite end of the rod 172 couples by another clamp to a piston rod 180 having a piston head 182 on its end. Although a piston arrangement is shown, the fluid assembly 170 can use a plunger or any other equivalent arrangement so that the terms piston and plunger can be used interchangeably herein. Moved by the pony rod (166), the piston head 182 moves in a liner 184 communicating with a fluid passage 190. As the piston 182 moves, it pulls mud from a suction manifold 192 through a suction valve 194 into the passage 190 and pushes the mud in the passage 190 to a discharge manifold 198 through a discharge valve 196.
As noted previously, a triplex mud pump produces a total flow variation of about 23%. Because the present mud pump 100 is quintuplex, the pump 100 offers a lower variation in total flow, making the pump 100 better suited for pumping mud and producing less noise that can interfere with MWD and LWD operations. In particular, the quintuplex mud pump 100 can produce a total flow variation as low as about 7%. For example, the quintuplex mud pump 100 can produce a maximum flow level of about 102% during certain crankshaft angles and can produce a minimum flow level of 95% during other crankshaft angles as the pump"s five pistons move in their differing strokes during the crankshaft"s rotation. Being smoother and closer to ideal, the lower total flow variation of 7% produces less pressure changes or “noise” in the pumped mud that can interfere with MWD and LWD operations.
Although a quintuplex mud pump is described above, it will be appreciated that the teachings of the present disclosure can be applied to multiplex mud pumps having at least more than three eccentric sheaves, connecting rods, and fluid assembly pistons. Preferably, the arrangement involves an odd number of these components so such mud pumps may be septuplex, nonuplex, etc. For example, a septuplex mud pump according to the present disclosure may have seven eccentric sheaves, connecting rods, and fluid assembly pistons with at least two bull gears and at least two bearing sheaves on the crankshaft. The bull gears can be arranged between first and second eccentric sheaves and sixth and seventh eccentric sheaves on the crankshaft. The internal main bearings supporting the crankshaft can be positioned between third and fourth eccentric sheaves and the fourth and fifth eccentric sheaves on the crankshaft.




 8613371530291
8613371530291