water well drilling mud pump pricelist

If you are supplying pump supplies, you can find the most favorable prices at Alibaba.com. Whether you will be working with piston type or diaphragm type systems, reciprocating or centrifugal, Alibaba.com has everything you need. You can also shop for different sizes drilling mud pump price wholesale for your metering applications. If you operate a construction site, then you could need to find some concrete pump solutions that you can find at affordable rates at Alibaba.com. Visit the platform and browse through the collection of submersible and inline pump system, among other replaceable models.
A drilling mud pump price comes in different makes and sizes, and you buy the tool depending on the application. The pump used by a filling station is not the one you use to fill up your tanks. There are high flow rate low pressure systems used to transfer fluids axially. On the other hand, you can go with radial ones dealing with a low flow rate and high-pressure fluid. The mixed flow pump variety combines radial and axial transfer mechanisms and works with medium flow and pressure fluids. Depending on what it will be pumping, you can then choose the drilling mud pump price of choice from the collection at Alibaba.com.
Alibaba.com has been an excellent wholesale supplier of drilling mud pump price for years. The supply consists of a vast number of brands to choose from, comes in different sizes, operations, and power sources. You can get a pump for residential and large commercial applications from the collection. Whether you want a water pump for your home, or run a repair and maintenance business, and need a supply of dr drill mud pump prices, you can find the product you want from the vast collection at Alibaba.com.ther it is for refrigeration, air conditioning, transfer, or a simple car wash business, anything you want, Alibaba.com has it.
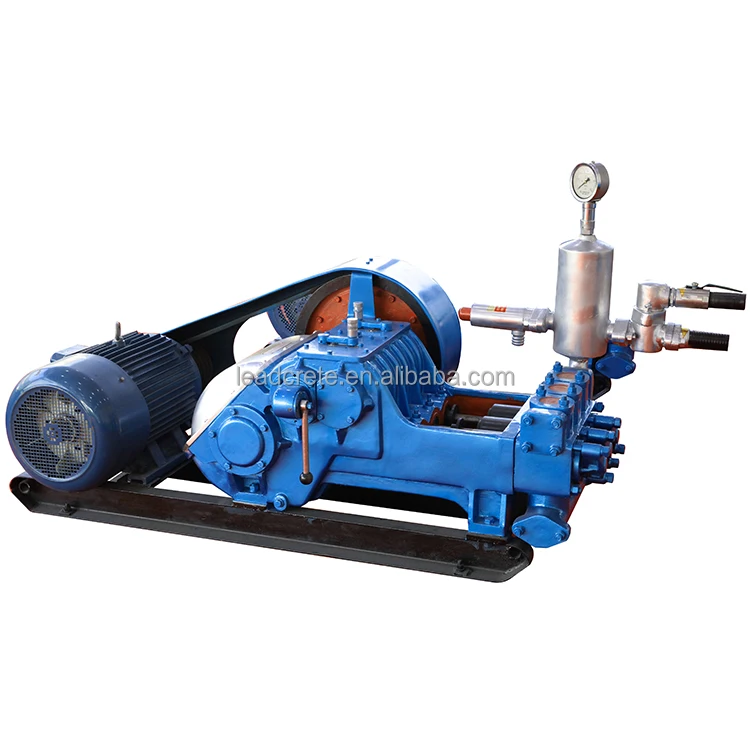

There are three types of mud pumps, depending on the type of client and the size they want. For general, mud pumps, there are three basic types of mud pumps, depending on the type of client and budget. The piston pump is another compressed mud pump, which is a pushed electric compressor mud pumps and by compressed air.
Electric mud pumps are largely divided into three categories, among them the electric mud pumps and the semi-trash mud pumps. The piston inflated mud pumps are also classified in terms of the type of mud pumps, among them are electric mud pumps and semi-trash mud pumps. In addition, the piston inflates mud and mud pumps will be inflated by the piston, which is inflated mud pumps.

The crank gear and connecting rods drive a rotary movement that is transferred by the motor transmission. The pressure is produced by the piston in the cylinder due to which the mud is sucked. Following the operation, the suction valve is closed when it moves to left. As the pressure increase in the pipeline, the valve is forced to open and mud is released.
In accordance with the operating liquid displacer type being incorporated, the pumps are subdivided into piston units and plunger-type units. The liquid discharge uniformity is independent of head. The pumping plants are used actively for the processes with the liquids containing solid inclusions in high amounts. Incorporating the self-suction function in piston unit, the liquid is sucked and discharged twice in mud pumps during the single shaft turn, making themselves the double-action pumps whereas, the mud plunger pumps are single-action pumps where the liquid is sucked and discharged only once during a shaft turn.
The single direct-action three-piston pumps prove to be better than other types of drilling. These pumps demonstrate much more uniformity in mud delivery, lesser weight, and easy mounting when compared with two-cylinder units.
Depending on the number of cylinders, the pumping plants are classified into the following categories, single-cylinder, double-cylinder, three-cylinder and multi-cylinder pumping plants. These cylinders may be vertical or horizontal. Comparatively, the multi-cylinder pumping plants will cost higher but don’t feature any significant advantages other than the single-cylinder.
When drilling, there might occur the necessity of mud pumping out- and flushing-out, so there are various types of pumps available for such operations which are required to be installed on drilling rigs.
Sucker-rod pumps: In sucker-rod pumps, the pumpjack is a driver. This pump is installed at the bottom of the well. The reciprocating movements of the pumpjack are converted into liquid flow by the pump, which results in delivery of liquid on the surface. These pumps move oil with various admixtures demonstrating high level of capacity.
Screw pumps:The screw pumps are small-sized and are generally used to deliver mud into a centrifuge. These pumps have the rotor and stator as the major structural components and the material used to manufacture these components suit right for smooth pumping of liquids with solid inclusions and high level of viscosity. The pumped liquid flows with stable pressure, shaft slowly and the flow is free of vortexes. These pumps comparatively require minimum service.
Well pumps: These pumps are submerged into wells. The ground part of the plant is a transformer substation equipped for start and adjustment. The pump has a vertical structure, with a fixed cylinder and single-action. A plunger and valve are moving parts. The pumped liquid may contain water content of up to 99% at the temperature as high as 130ºC.
All the mud pumps have few general advantages that include the capability to process liquids and substances with high level of viscosity and with admixtures. Also, enabling the smooth flow of substances, free of pulsations or suspensions mixing are counted under the major advantages of incorporating mud pumps. The pumps have high suction power and small weight, easing out the transportation and installation at remote oil fields. They are highly reliable and also affordable.
There are various types of mud pumps available for different purposes. So, it is important to incorporate the right one for your purpose. A Professional help in getting the right mud pump would be a good and safe option.

The 2,200-hp mud pump for offshore applications is a single-acting reciprocating triplex mud pump designed for high fluid flow rates, even at low operating speeds, and with a long stroke design. These features reduce the number of load reversals in critical components and increase the life of fluid end parts.
The pump’s critical components are strategically placed to make maintenance and inspection far easier and safer. The two-piece, quick-release piston rod lets you remove the piston without disturbing the liner, minimizing downtime when you’re replacing fluid parts.

Experience in developing countries has shown that the construction of drilled wells must be simple and efficient. This keeps projects affordable, maintains a certain momentum and enhances local enthusiasm.
The LS-100 is a small, portable mud rotary drilling machine made by Lone Star Bit Company in Houston, Texas. Using this small drill rig, it is possible to rapidly complete safe, reliable water wells. As discussed by Hamann (1992), advantages of the LS-100 include: comparatively low cost, portability, and speed and depth to which the rig can go relative to manual methods (see Table 2).
Disadvantages of the LS-100 drill rig are that it is limited to drilling a 6 inch borehole to a depth of 30 m (100 ft) and it cannot effectively penetrate hard rock, loose boulders or coarse gravel (an air-rotary version of the LS-100 is currently being developed to drill in these environments).
ContaminationPoor annular seals; Casing/lid often leak; Shallow water may be contaminated.Protected by sealed hole & continuous casing. Deep, safe aquifers accessible.
A small mud rotary drill rig is only a very small part of a solution to a very large problem. Success in using the drill rig depends on many factors including favourable subsurface geologic conditions, technical aptitude and experience, community support, and a commitment to maintenance, education and communication with others regarding the successes and failures of drilling.
In addition, before deciding whether or not to use the LS-100, the following factors should be seriously considered because they have a very strong bearing on the success or failure of a drilling project:Are there people in place who are already drilling using mud rotary techniques? If not, are there people with a mechanical aptitude who are willing to learn how to drill and service the machinery?
Prior to traveling to a drilling site, there are a number of tasks which should be done. While it may be sometimes necessary to embark on a drilling project without all these tasks completed, projects will have a higher success rate and a lower level of frustration if they can be done ahead of time. Ideally, people have been trained, an Action Agency and Village Water Committee(s) established, and a Drill Team Selected (see Appendix S).
the drill rig, mud pump, pump cylinders and other equipment (such as extra seals for the pump and drill) has cleared customs, is in good repair, is stored in a secure room;
Village Water Committees have been established in each prospective drilling site and that the committee and potential users are supportive of a well being constructed and are willing to take ownership of the project. Before you commit to the job, sign a "Community Water Supply Agreement" (see
Drill crews should have the following basic tools and equipment available prior to heading out to drill a well (these items are normally used to complete the construction of multiple wells):
Four 200-litre (55 gal) drums with tight fitting lids for hauling water to the drill site (water can be used up very fast during drilling and is the main cause of avoidable drilling delays).
3x4 m (8x12 ft) MINIMUM sized heavy gauge plastic sheet to line the mud pits (to prevent water loss) and to put on the ground to keep equipment clean.
10 lengths steel pump rod (1.11 cm dia 3.05 m long 1.11 cm NC threaded ends or 7/16 inch dia, 10 ft long, 7/16 NC threaded ends ) *Stainless steel preferred where water is corrosive;
Unload all tools and equipment on dry ground near the selected drilling location. If possible, orient the drill rig so that it will be shaded during the afternoon. It is very hard to clean sand from greased threads, so keep pipes off the ground by placing them on boards (or tree branches).
Fill four 200 litre (55 gallon) drums with water and ensure that villagers are ready to keep these drums full during the drilling process.Arrange the water drums next to the area where the pits are to be dug. Add 1 cup of chlorine to each drum of water to ensure that bacteria are not injected into the groundwater during drilling - unless you are using polymer to thicken your drilling fluid (see
Fence off an area behind which all observers must stand during the drilling process. Designate one of the local leaders to ensure that this safety rule is observed at all times. Have one of the drillers frequently explain what is happening while the well is being drilled.
Dig two pits (settling pit and suction pit) - see Figure 5. Keep these pits 1.5 metres away from the well guide hole so that, when the well is finished, the pump pad does not need to be built on the unstable filled-in mud pits.
If the soil in the pit is sandy or water scarce, line the pits with un-punctured plastic. Wrap the edge of the plastic over and bury it a foot or more into the ground along the flow channels to prevent drilling fluids from flowing beneath the plastic.
Dig a 6 inch deep channel between the well guide hole and the first mud pit. Put the mud pump between the drill rig and the suction mud pit (see Figure 5).
Set-up the LS-100 and mud pump following the steps outlined below (see Figure 6):Erect the drill rig over the guide hole. Orientate it so that the hoses are over the mud pits, out of the way of the operator, and that the drill table legs are parallel to the channel going from the guide hole to the mud pits. Level the ground around it and install the front and back 2 x 6 boards (see Figure 5).
one end of Suction Hose Assembly to suction port of mud pump and lower the foot valve (strainer) into a 18.93 L (5 gal) pail placed in the suction pit (Figure 5). The pail is required to avoid re-circulating cuttings back down the hole;
Make sure the crankcases on the drill rig and mud pump engines and transmissions are filled with SAE 30 oil up to the filler hole before you start them! CAUTION: change the oil after the first 5 hours operation for new machines!
The only part of the LS-100 that uses grease is the swivel. Loosen the upper and lower compression nuts of the water entry swivel, remove the 95 mm (3/8 in) bolt from the shaft, and pull out the quill. Apply grease liberally to the inside surfaces of the seals (not the outside of the seals or to the swivel housing). Reinstall the quill, insert the bolt and tighten the lock nut. Tighten the upper compression nut until it is snug. Engage the rotary and, circulating clean water, tighten the compression nut until the quill starts to bind. Then loosen slightly and lock in place using the Allan screw. Repeat tightening procedure for the lower compression nut. Then pump grease into the top and bottom fittings until it is no longer easy to inject grease. Stop if you see grease at the top or bottom of the fittings! If any leaks are observed during rig operation, loosen the set screws and tighten the compression nuts immediately (see Appendix Q to learn more about maintainance).
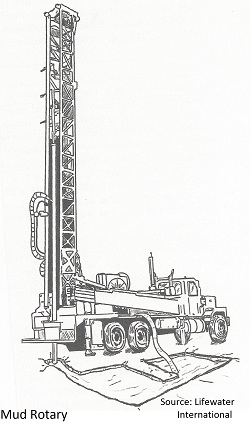
A borehole is drilled by rotating a bit at the end of drill pipe. Borehole cuttings are removed by continuous circulation of a drilling fluid as the bit penetrates the formation. The drill pipe is connected to the drill engine. Drilling fluid is pumped down through the hollow drill pipe using a centrifugal pump (mud pump) to a drill bit. The fluid flows upward in the annular space between the drill pipe and the borehole to the surface where it is channeled into a settling pit and most of the cuttings drop out. Fluid from the settling pit overflows into a second pit (suction pit). Relatively clean fluid from the second pit is then pumped back through the drill pipe and the cycle repeats.
Using water from the 208 litre (55 gallon) drums, fill the mud pits to the very top. Make sure that one person is responsible for keeping the pits full of water during the entire drilling process. This must be done to ensure that the cuttings will settle-out.
Fill the fuel tank of the mud pump and start it using the following process:Prime the pump before starting the engine by removing the discharge hose or the plug on top of the pump housing and pouring water into this opening until full. It will take a good amount of water since the Suction Hose will also be filled up.
Set the choke and run levers to the CHOKE and RUN positions respectively. These control are located on the side of the fuel tank opposite the pump side of the engine.
Pull the starting rope (several times may be necessary), and when engine starts to run, immediately return the choke lever to the OFF position. Leave the run lever in the RUN position. Note that it will take a few minutes for the pump to prime.
Increase the engine RPM until the clutch engages and the pipe starts turning. Turn the 3 way Valve so that the water will circulate from the Mud Pump through the bottom by-pass hose back to the pit. Add water as required to top-up the pits.
Then turn the valve so that water flows into the drill swivel. Make sure no water is leaking from the swivel seals. If it is, re-direct the water through the by-pass hole or stop the mud pump. Loosen set screws and tighten gland nuts quite snug and until leaking stops. Re-tighten set screws. It may be necessary to repeat this process during the drilling operation. Pump grease into the top & bottom gland nuts before tightening.
When the water begins pumping through the drill pipe, it will make a lot of splashing so make sure the drill operator is ready to lower the drill pipe into the hole fairly rapidly. After the drill has penetrated 30 cm (1 ft) or so, there will be a smooth flow of water.
Maintain a slight back pressure on the winch handle; at an easy drilling speed, the winch handle should make a full circle every 20 seconds or so. Do not exceed this speed or the water will not be able to circulate the cuttings out of the hole fast enough (causing the bit to seize) and/or the borehole walls will not be coated with enough fines to resist caving! In harder formations it should make a full circle every 40 seconds. In very hard rock, a drilling rate of 30-150 cm/hr (1 - 5 ft/hr) is to be expected.
In hard rock, insufficient pressure on the drill pipes may result in an extremely low drilling speed. Caution should be used to avoid excessive pull-down pressure (weight) exerted on the drill string because this may result in crooked holes, bent drill rods and jammed drill bits (see
Leave the drill string turning at the bottom of the hole and continue circulating drill mud until all cuttings are removed from the borehole (even if it takes 5 minutes or longer). This cleaning process is increasingly important as the hole is deepened: if not fully done in the manner described, cuttings may settle to the bottom of the borehole and make it impossible to add another length of drill pipe, cause the hole to cave-in or plug-up (see
Switch the 3-way valve so that the drilling fluid circulates back into the mud pits rather than down the drill pipe. Clamp off the drill pipe and unscrew the drill head.
Lubricate the threads of the next drill pipe and screw it into the one clamped at the well head. Screw the other end onto the output shaft. Tighten the joints with wrenches.
Switch the 3-way valve so that the drilling fluid starts to circulate back down the drill pipe. Do not lower the drill head until there is clear evidence that the mud is circulating through the pits again.
Once drilling, it is important to:monitor the drill cuttings to help determine what type of material is being drilled. Take samples of the cuttings every metre or so (at least 1 per drill pipe);
After the 10 cm (4 in) "pilot" borehole is completed to the desired depth, allow the drilling fluid to circulate for 10 minutes to remove as much cuttings as possible from the well.
After 10 minutes, raise the drill head until the slip clamp on the drill table can be engaged at the coupling of the next length of drill pipe. Turn-off the mud pump.
Continue to carefully remove the drill pipe from the well. BE SURE THE SLIP CLAMP IS FULLY ENGAGED EACH TIME AND THAT EVERYTHING IS SECURED because it is very easy to drop drill pipe and tools into the
If there is much sticky clay, the water-bearing portion of the 10 cm (4 in) hole may be filled with clean sand prior to reaming. This keeps clay from dropping into the borehole and smearing onto the borehole walls (causing severe well development problems).
After you have decided to stop drilling, allow the drilling fluid to circulate for 10 minutes to remove as much cuttings as possible from the well. Then circulate the "mud" out of the borehole by replacing it with fresh (clean)
When removing the drill pipe from the well, keep the bit rotating and water circulating. This leaves a nice smooth borehole wall behind the bit as it is coming out of the hole(2).
1 Ideally, for a 30 m (100 ft) deep borehole drilled with the LS-100, the settling pit should be 60 cm (2 ft) deep, 75 cm (2.5 ft) wide and 2 m (6 ft) long; the suction pit should be 60 cm (2 ft) deep, 75 cm (2.5 ft) wide and 1 m (3 ft) long. However, while these pits provide optimum settling capability, they require large quantities of water to be brought to the site.
2 If this is not done, the fins of the blade bit may disturb the borehole wall and cause silt/clay cuttings to "ball-up" or bridge within the borehole. In addition, drilling fluid may cause silts and clays (especially above the water table) to swell and bulge into the borehole. Getting the screen past these blockages can be very difficult and it is almost impossible to avoid severely plugging the screen.
Hamann, M. (1992) "Utilization of Small Mud Rotary Drilling Rigs for Development of Safe, Village-Level Groundwater Resources", Paper presented at the 5th African Water Technology Conference, Nairobi, Kenya, February, 1992.
Lovett, W. (1985) "Chapter 2 - Safety on the Job", pp. 9-12 in Water Well Driller"s Beginning Training Manual, Worthington, OH: National Water Well Association, ISBN 1-56034-049-5.

A mud pump (sometimes referred to as a mud drilling pump or drilling mud pump), is a reciprocating piston/plunger pump designed to circulate drilling fluid under high pressure (up to 7,500 psi or 52,000 kPa) down the drill string and back up the annulus. A mud pump is an important part of the equipment used for oil well drilling.
Mud pumps can be divided into single-acting pump and double-acting pump according to the completion times of the suction and drainage acting in one cycle of the piston"s reciprocating motion.
Mud pumps come in a variety of sizes and configurations but for the typical petroleum drilling rig, the triplex (three piston/plunger) mud pump is used. Duplex mud pumps (two piston/plungers) have generally been replaced by the triplex pump, but are still common in developing countries. Two later developments are the hex pump with six vertical pistons/plungers, and various quintuplexes with five horizontal piston/plungers. The advantages that these new pumps have over convention triplex pumps is a lower mud noise which assists with better measurement while drilling (MWD) and logging while drilling (LWD) decoding.
The fluid end produces the pumping process with valves, pistons, and liners. Because these components are high-wear items, modern pumps are designed to allow quick replacement of these parts.
To reduce severe vibration caused by the pumping process, these pumps incorporate both a suction and discharge pulsation dampener. These are connected to the inlet and outlet of the fluid end.
Displacement is calculated as discharged liters per minute. It is related to the drilling hole diameter and the return speed of drilling fluid from the bottom of the hole, i.e. the larger the diameter of drilling hole, the larger the desired displacement. The return speed of drilling fluid should wash away the debris and rock powder cut by the drill from the bottom of the hole in a timely manner, and reliably carry them to the earth"s surface. When drilling geological core, the speed is generally in range of 0.4 to 1.0 m^3/min.
The pressure of the pump depends on the depth of the drilling hole, the resistance of flushing fluid (drilling fluid) through the channel, as well as the nature of the conveying drilling fluid. The deeper the drilling hole and the greater the pipeline resistance, the higher the pressure needed.
With the changes of drilling hole diameter and depth, the displacement of the pump can be adjusted accordingly. In the mud pump mechanism, the gearbox or hydraulic motor is equipped to adjust its speed and displacement. In order to accurately measure the changes in pressure and displacement, a flow meter and pressure gauge are installed in the mud pump.
The construction department should have a special maintenance worker that is responsible for the maintenance and repair of the machine. Mud pumps and other mechanical equipment should be inspected and maintained on a scheduled and timely basis to find and address problems ahead of time, in order to avoid unscheduled shutdown. The worker should attend to the size of the sediment particles; if large particles are found, the mud pump parts should be checked frequently for wear, to see if they need to be repaired or replaced. The wearing parts for mud pumps include pump casing, bearings, impeller, piston, liner, etc. Advanced anti-wear measures should be adopted to increase the service life of the wearing parts, which can reduce the investment cost of the project, and improve production efficiency. At the same time, wearing parts and other mud pump parts should be repaired rather than replaced when possible.
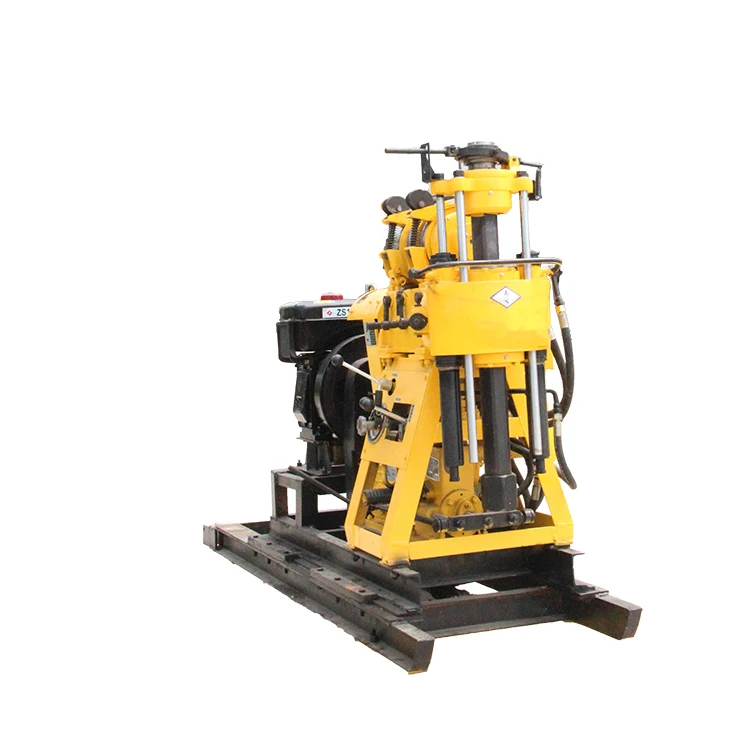

The mud pump is the heart of mud rotary drilling. This crucial piece of equipment is responsible for removing the cuttings produced when drilling a water well. Sure, on the surface, the mud pump might not be the most exciting part of a water well drilling rig. But if your crew relies on mud rotary drilling methods, your operation will literally be stuck in the mud without the proper mud pump — no matter how much horsepower and torque your drill sends down the borehole.
To better understand why the mud pump should be a key consideration when selecting a water well drill we need to take a closer look at this un-sung hero of water well drilling.
Despite its simplicity, the humble mud pump plays an important part in overall drilling efficiency. As crew members drill, the drill bit produces cuttings. These pile up in the bottom of the borehole and prevent crews from making progress – like trying to dig a hole with a shovel but throwing the dirt back into the hole every time. Mud pumps offer a solution.
Water is pumped from the mud pump to the drill pipe where it exits through the holes in the drill bit — which may be several inches or hundreds of feet deep in the borehole. Water fills the borehole, forcing the loose cuttings up and out of the hole.
Instead, we put the drilling process first. Lone Star Drills has spent decades growing its drill lineup based not just on specs, but on grueling real-world performance. No one knows better than the person in the field, so we’re constantly sending out new mud pumps and new designs to our customers across the globe and innovating our mud pumps to maximize efficiency.
But keep in mind the mud pump is only part of the overall water well drilling rig. How the whole system works together will determine water well drilling effectiveness. For example, our drills incorporate a three-way valve with a bypass so crews can quickly divert the flow of water from the mud pump, add drill pipe, reconnect water flow and continue drilling all within seconds. Drills that don’t have this feature require crews to fully shut down the mud pump to stop water flow, add drill pipe and power back on the mud pump to restart water flow — a burdensome process for deep wells that require dozens of pipe sections.
Proper mud pump pairing is the key to efficient water well drilling. That’s why Lone Star Drills offers a variety of mud pumps to match the drill for optimal performance. We offer both gasoline- and diesel-powered pumps offering up to 13 horsepower for achieving greater depths.
In addition to flushing cuttings, the mud pump helps stabilize the borehole, as the mixture of water and mud keeps it from collapsing. Using the mud pump, crews can even add bentonite to the pumped water to create a coating that binds to the borehole walls and prevents water from escaping.

BW400/10 mud pump is a horizontal three cylinder reciprocating single acting piston pump.Advanced product design, reasonable structure, high pressure, flow, multi-file variable, energy saving, light volume, efficiency, plant life, safe operation, easy maintenance.
BW series mud pump is widely used in mining, drilling, coal, railway, highway, water conservancy and hydropower, bridges, high-rise buildings, foundation reinforcement works.
They are also the main equipment of the geological survey,the main role in the process of core drilling boreholes is to supply fluid(mud or water),making it circulate during drilling and carry rock waste back to the ground,in order to achieve and maintain the bottom hole clean and lubricate drill bits and drilling tools with cooling.
Ultimately, when you reach the depth where you can’t pull up the drill string, you’ve reached the rig’s capacity. Based on this criteria, though, the max capacity rating of the SIMCO 7000, SIMCO’s largest rig would be well over 5000 feet.
Realistically, with any mud rotary drill rig, you’ve reached maximum depth capacity when you can no longer move the cuttings out of the hole. This is where having mud pump options becomes important.
Generally, there are several different versions of mud pumps available. With the SIMCO 7000 you can choose between centrifugal and piston pumps and different sizes with different depths and borehole diameters to suit your specific drilling needs.
Because each rig is built to your specifications, choosing the best mud pump for your goals takes into consideration many additional factors. Bore hole size, drilling conditions, geology, the mud mixture, and the desired depth capacity all have bearing on which mud pump will be the best fit for your personal drilling rig. By offering these different options, SIMCO helps you avoid the pitfalls of spending more money for a capacity you don’t need.
Give our sales department a call at 800-338-9925 or reach out through our contact page to learn more about the options on the SIMCO 7000 or any of our outstanding drilling systems.

The drilling rig is built on the basis of a diesel engine. The hydraulic circuit is divided into three streams, each with its own hydraulic pump. When using multiple drives at the same time and increasing the load, the operating parameters are retained.
The drilling rig has a compact, versatile design. It can be installed on different types of chassis: trailer, pickup, truck, tracked chassis, etc. At the same time, a flow switch is provided in the hydraulic system of the unit to control the movement of the chassis.
Pump for supplying drilling fluid to the bottom of the well. The piston is driven by a hydraulic cylinder, which is controlled by an electrically controlled hydraulic valve. The mud pump provides a pressure of 15 atm and pumps 400 l / min.
The trailer wheels are rotated by two hydraulic motors. A hydraulic cylinder is used to hold down the clutches. The friction drive allows for maneuvers and turns for precise positioning of the drilling rig.




 8613371530291
8613371530291