calculate mud pump efficiency brands

Rig pump output, normally in volume per stroke, of mud pumps on the rig is one of important figures that we really need to know because we will use pump out put figures to calculate many parameters such as bottom up strokes, wash out depth, tracking drilling fluid, etc. In this post, you will learn how to calculate pump out put for triplex pump and duplex pump in bothOilfield and Metric Unit.

Pumps tend to be one of the biggest energy consumers in industrial operations. Pump motors, specifically, require a lot of energy. For instance, a 2500 HP triplex pump used for frac jobs can consume almost 2000 kW of power, meaning a full day of fracking can cost several thousand dollars in energy costs alone!
So, naturally, operators should want to maximize energy efficiency to get the most for their money. Even a 1% improvement in efficiency can decrease annual pumping costs by tens of thousands of dollars. The payoff is worth the effort. And if you want to remotely control your pumps, you want to keep efficiency in mind.
In this post, we’ll point you in the right direction and discuss all things related to pump efficiency. We’ll conclude with several tips for how you can maintain pumping efficiency and keep your energy costs down as much as possible.
In simple terms, pump efficiency refers to the ratio of power out to power in. It’s the mechanical power input at the pump shaft, measured in horsepower (HP), compared to the hydraulic power of the liquid output, also measured in HP. For instance, if a pump requires 1000 HP to operate and produces 800 HP of hydraulic power, it would have an efficiency of 80%.
Remember: pumps have to be driven by something, i.e., an electric or diesel motor. True pump system efficiency needs to factor in the efficiency of both the motor AND the pump.
Consequently, we need to think about how electrical power (when using electric motors) or heat power (when using combustion engines) converts into liquid power to really understand pump efficiency.
Good pump efficiency depends, of course, on pump type and size. High-quality pumps that are well-maintained can achieve efficiencies of 90% or higher, while smaller pumps tend to be less efficient. In general, if you take good care of your pumps, you should be able to achieve 70-90% pump efficiency.
Motor efficiency is also an important factor here. Motor efficiency depends on the fuel type, whether electricity or hydrocarbon, which in turn depends on availability and cost.
AC motors can achieve 90%+ efficiency when converting electrical to mechanical energy. Combustion engines are much less efficient, with typical efficiency ratings coming in at ~20% for gasoline and ~40% for diesel. Your choice of engine or motor type will depend on the availability and cost of fuel or electricity in your area.
Now that we have a better understanding of the pump efficiency metric, let’s talk about how to calculate it. The mechanical power of the pump, or the input power, is a property of the pump itself and will be documented during the pump setup. The output power, or hydraulic power, is calculated as the liquid flow rate multiplied by the "total head" of the system.
IMPORTANT: to calculate true head, you also need to factor in the work the pump does to move fluid from the source. For example, if the source water is below the pump, you need to account for the extra work the pump puts in to draw source water upwards.
*Note - this calculation assumes the pump inlet is not pressurized and that friction losses are minimal. If the pump experiences a non-zero suction pressure, or if there is significant friction caused by the distance or material of the pipe, these should be factored in as well.
You"ll notice that the elevation head is minimal compared to the discharge pressure, and has minimal effect on the efficiency of the pump. As the elevation change increases or the discharge pressure decreases, however, elevation change will have a greater impact on total head.
Obviously, that’s a fair amount of math to get at the pump efficiency, considering all of the units conversions that need to be done. To avoid doing these calculations manually, feel free to use our simple pump efficiency calculator.
Our calculations use static variables (pump-rated horsepower and water source elevation) and dynamic variables (discharge flow and pressure). To determine pump efficiency, we need to measure the static variables only once, unless they change.
If you want to measure the true efficiency of your pump, taking energy consumption into account, you could add an electrical meter. Your meter should consist of a current transducer and voltage monitor (if using DC) for electrical motors or a fuel gauge for combustion. This would give you a true understanding of how pump efficiency affects energy consumption, and ultimately your bank account.
Up until this point, we’ve covered the ins and outs of how to determine pump efficiency. We’re now ready for the exciting stuff - how to improve pump efficiency!
One of the easiest ways to improve pump efficiency is to actually monitor pumps for signs of efficiency loss! If you monitor flow rate and discharge (output power) along with motor current or fuel consumption, you’ll notice efficiency losses as soon as they occur. Simply having pump efficiency information on hand empowers you to take action.
Another way to increase efficiency is to keep pumps well-maintained. Efficiency losses mostly come from mechanical defects in pumps, e.g., friction, leakages, and component failures. You can mitigate these issues through regular maintenance that keeps parts in working order and reveals impending failures. Of course, if you are continuously monitoring your pumps for efficiency drops, you’ll know exactly when maintenance is due.
You can also improve pump efficiency by keeping pumps lubricated at all times. Lubrication is the enemy of friction, which is the enemy of efficiency (“the enemy of my enemy is my friend…”).
A fourth way to enhance pump efficiency is to ensure your pumps and piping are sized properly for your infrastructure. Although we’re bringing this up last, it’s really the first step in any pumping operation. If your pumps and piping don’t match, no amount of lubricant or maintenance will help.
Pipes have physical limits to how much fluid they can move at a particular pressure. If pipes aren’t sized properly, you’ll lose efficiency because your motor will have to work harder. It’s like air conditioning - if your ductwork isn’t sized appropriately for your home, you’ll end up paying more on your energy bill.
In this post, we’ve given you the full rundown when it comes to calculating and improving pump efficiency. You can now calculate, measure, and improve pump efficiency, potentially saving your business thousands of dollars annually on energy costs.
For those just getting started with pump optimization, we offer purpose-built, prepackaged solutions that will have you monitoring pump efficiency in minutes, even in hazardous environments.

This worksheet takes inputs for the rig pumps and (optionally) hole and pipe sizes. It outputs pump flow rates and power, also fluid velocity if diameters entered.

NOTE: Max RPM in the above equation varies according to type of pump, size of stroke, and other variables. Duplex pumps often run about 100 RPM Max. while triplex pumps will run somewhere between 100 RPM Max and 400 RPM Max.
I have a reciprocating pump and I know what my max rated rod load is (in foot pounds). I also know what size plunger size my pump has. What PSI will my pump produce?
Specific Gravity is used when sizing a centrifugal pump. Liquids with a specific gravity greater than 1.0 are heavier than water and conversely, liquids with a specific gravity lower than 1.0 are lighter weight than water and will generally float on water.

I’ve run into several instances of insufficient suction stabilization on rigs where a “standpipe” is installed off the suction manifold. The thought behind this design was to create a gas-over-fluid column for the reciprocating pump and eliminate cavitation.
When the standpipe is installed on the suction manifold’s deadhead side, there’s little opportunity to get fluid into all the cylinders to prevent cavitation. Also, the reciprocating pump and charge pump are not isolated.
The suction stabilizer’s compressible feature is designed to absorb the negative energies and promote smooth fluid flow. As a result, pump isolation is achieved between the charge pump and the reciprocating pump.
The isolation eliminates pump chatter, and because the reciprocating pump’s negative energies never reach the charge pump, the pump’s expendable life is extended.
Investing in suction stabilizers will ensure your pumps operate consistently and efficiently. They can also prevent most challenges related to pressure surges or pulsations in the most difficult piping environments.

Pump Output per Stroke (PO): The calculator returns the pump output per stroke in barrels (bbl). However this can be automatically converted to other volume units (e.g. gallons or liters) via the pull-down menu.
A triplex mud (or slush) pump has three horizontal plungers (cylinders) driven off of one crankshaft. Triplex mud pumps are often used for oil drilling.

The ratio of the actual output volume of a positive displacement pump divided by the theoretical geometric maximum volume of liquid that the pump could output under perfect conditions. Inefficiencies are caused by gaseous components (air and methane) being trapped in the liquid mud, leaking and noninstantaneously sealing valves in the pumps, fluid bypass of pump swab seals, and mechanical clearances and "play" in various bearings and connecting rods in the pumps. This efficiency is usually expressed as a percentage, and ranges from about 92% to 99% for most modern rig pumps and cement pumps. For critical calculations, this efficiency can be determined by a rigsite version of the "bucket and stopwatch" technique, whereby the rig crew will count the number of pump strokes required to pump a known volume of fluid. In cementing operations, displacement is often measured by alternating between two 10-bbl displacement tanks.

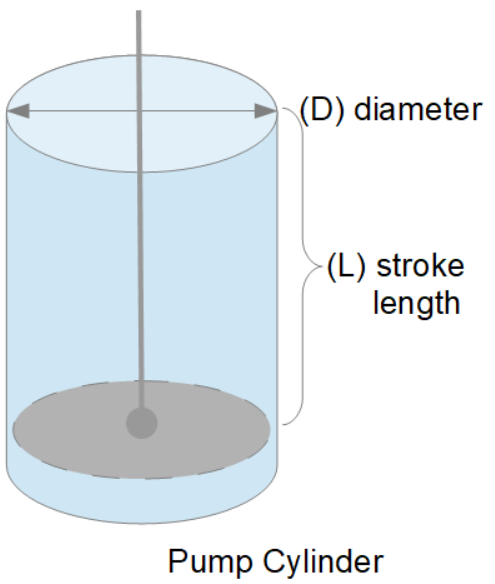
Oil and Gas drilling process - Pupm output for Triplex and Duplex pumpsTriplex Pump Formula 1 PO, bbl/stk = 0.000243 x ( in) E.xample: Determine the pump output, bbl/stk, at 100% efficiency for a 7" by 12". triplex pump: PO @ 100%,= 0.000243 x 7 x12 PO @ 100% = 0.142884bbl/stk Adjust the pump output for 95% efficiency: Decimal equivalent = 95 + 100 = 0.95 PO @ 95% = 0.142884bbl/stk x 0.95 PO @ 95% = 0.13574bbl/stk Formula 2 PO, gpm = [3(D x 0.7854)S]0.00411 x SPM where D = liner diameter, in. S = stroke length, in. SPM = strokes per minute Determine the pump output, gpm, for a 7" by 12". triplex pump at 80 strokes per minute: PO, gpm = [3(7 x 0.7854) 1210.00411 x 80 PO, gpm = 1385.4456 x 0.00411 x 80 PO = 455.5 gpm
Example:Duplex Pump Formula 1 0.000324 x (liner diameter, in) x ( stroke lengh, in) = ________ bbl/stk -0.000162 x (rod diameter, in) x ( stroke lengh, in) = ________ bbl/stk Pump out put @ 100% eff = ________bbl/stk Example: Determine the output, bbl/stk, of a 5 1/2" by 14" duplex pump at 100% efficiency. Rod diameter = 2.0": 0.000324 x 5.5 x 14 = 0.137214bbl/stk -0.000162 x 2.0 x 14 = 0.009072bbl/stk Pump output @ 100% eff. = 0.128142bbl/stk Adjust pump output for 85% efficiency: Decimal equivalent = 85 100 = 0.85 PO@85%)= 0.128142bbl/stk x 0.85 PO@ 85% = 0.10892bbl/stk Formula 2
PO. bbl/stk = 0.000162 x S[2(D) - d] where S = stroke length, in. D = liner diameter, in. d = rod diameter, in. Example: Determine the output, bbl/stk, of a 5 1/2". by 14". duplex pump @ 100% efficiency. Rod diameter = 2.0in.: PO@100%=0.000162 x 14 x [ 2 (5.5) - 2 ] PO @ 100%)= 0.000162 x 14 x 56.5 PO@ 100%)= 0.128142bbl/stk Adjust pump output for 85% efficiency: PO@85%,= 0.128142bb/stkx 0.85 PO@8.5%= 0.10892bbl/stk Metric calculation Pump output, liter/min = pump output. liter/stk x pump speed, spm. S.I. units calculation Pump output, m/min = pump output, liter/stk x pump speed, spm. Mud Pumps Mud pumps drive the mud around the drilling system. Depending on liner size availability they can be set up to provide high pressure and low flow rate, or low pressure and high flow rate. Analysis of the application and running the Drill Bits hydraulics program will indicate which liners to recommend. Finding the specification of the mud pumps allows flow rate to be calculated from pump stroke rate, SPM. Information requiredo Pump manufacturer o Number of pumps o Liner size and gallons per revolution Weight As a drill bit cutting structure wears more weight will be required to achieve the same RoP in a homogenous formation. PDC wear flats, worn inserts and worn milled tooth teeth will make the bit drill less efficiently. Increase weight in increments of 2,000lbs approx. In general, weight should be applied before excessive rotary speed so that the cutting structure maintains a significant depth of cut to stabilise the bit and prevent whirl. If downhole weight measurements are available they can be used in combination with surface measurements to gain a more accurate representation of what is happening in the well bore.

We connect our flow meter to the vibrating hose at the discharge end of the mud pump. We run our survey while you resume drilling, or while you circulate to condition the wellbore before running casing. By eliminating the need for remediation jobs we can save you very valuable rig time.
Pump OutputDuplex Pump OutputLitres/Stroke @ 90% Efficiency (2” Rod Diameter)Liner Diamerter (mm)StrokeLength(mm)101 108 114 121 127 133 140 146 152 159 165 170 178 184 190 197 203 209 216203 5.40 6.19 6.99 7.78 8.73 6.69 10.6 11.5 12.7 13.8 15 16.2 17.4 18.9254 6.67 7.62 8.58 6.69 10.8 12.0 13.3 14.6 15.9 17.3 18.7 20.0 21.9 23.6305 7.78 9.90 10.10 11.40 12.9 14.3 15.9 17.3 19.1 20.7 22.6 24.3 26.2 28.3 30.4356 14.6 16.4 18.0 19.9 21.8 23.8 25.9 28.0 30.2 32.4 35.0 37.4 39.9381 15.6 17.3 19.2 21.1 23.2 25.3 27.5 29.7 32.3 34.7 37.4 39.9 42.8406 16.7 18.6 20.5 22.6 24.8 27.0 29.4 32.3 34.5 37.0 39.7 42.8 45.6 48.6457 18.4 20.7 22.7 25.3 27.8 30.2 32.7 35.6 38.5 41.3 44.5 47.7 51.1 54.4508 20.3 22.7 25.1 28.0 30.5 33.4 36.4 39.4 46.2 45.9 49.4 53.1 56.8 60.4559 49.8 53.5 57.3 61.1 65.1 69.2 73.5610 71.1 75.6 80.2Note: For pump output in m 3 /stroke, move the decimal point 3 places to the left.Duplex Mud PumpsThe pistons on a duplex mud pump work in both directions, so that the rear cylinder has thepump rod moving through its swept volume and occupying some volume. The difference incalculations for a duplex vs. a triplex pump is that the displacement volume of this pump rodmust be subtracted from the volume in one of the cylinders, plus the difference in number ofpumping cylinders; 4 for a duplex and 3 for a triplex. Duplex pumps generally have longerstrokes (in the 10 to 18 in. range) and operate at lower rate; in the 40 to 80 stroke/minrange.The general equation to calculate output of a duplex pump is:Pump output (litres/stroke) = ,Where:ID = ID of the linerOD = OD of the rodL = Length of the pump strokeEff = Pump efficiency (decimal)1800, 505 – 3 rd Street SW Calgary, Alberta, Canada T2P 3E6 Telephone: 403.547.2906 Fax: 403.547.3129Email: info@hitechfluid.com Web: www.hitechfluid.com




 8613371530291
8613371530291