drilling mud pump output in stock

Rig pump output, normally in volume per stroke, of mud pumps on the rig is one of important figures that we really need to know because we will use pump out put figures to calculate many parameters such as bottom up strokes, wash out depth, tracking drilling fluid, etc. In this post, you will learn how to calculate pump out put for triplex pump and duplex pump in bothOilfield and Metric Unit.
Bourgoyne, A.J.T., Chenevert , M.E. & Millheim, K.K., 1986. SPE Textbook Series, Volume 2: Applied Drilling Engineering, Society of Petroleum Engineers.

Pump Output per Stroke (PO): The calculator returns the pump output per stroke in barrels (bbl). However this can be automatically converted to other volume units (e.g. gallons or liters) via the pull-down menu.
A triplex mud (or slush) pump has three horizontal plungers (cylinders) driven off of one crankshaft. Triplex mud pumps are often used for oil drilling.

The 2,200-hp mud pump for offshore applications is a single-acting reciprocating triplex mud pump designed for high fluid flow rates, even at low operating speeds, and with a long stroke design. These features reduce the number of load reversals in critical components and increase the life of fluid end parts.
The pump’s critical components are strategically placed to make maintenance and inspection far easier and safer. The two-piece, quick-release piston rod lets you remove the piston without disturbing the liner, minimizing downtime when you’re replacing fluid parts.

Oil and Gas drilling process - Pupm output for Triplex and Duplex pumpsTriplex Pump Formula 1 PO, bbl/stk = 0.000243 x ( in) E.xample: Determine the pump output, bbl/stk, at 100% efficiency for a 7" by 12". triplex pump: PO @ 100%,= 0.000243 x 7 x12 PO @ 100% = 0.142884bbl/stk Adjust the pump output for 95% efficiency: Decimal equivalent = 95 + 100 = 0.95 PO @ 95% = 0.142884bbl/stk x 0.95 PO @ 95% = 0.13574bbl/stk Formula 2 PO, gpm = [3(D x 0.7854)S]0.00411 x SPM where D = liner diameter, in. S = stroke length, in. SPM = strokes per minute Determine the pump output, gpm, for a 7" by 12". triplex pump at 80 strokes per minute: PO, gpm = [3(7 x 0.7854) 1210.00411 x 80 PO, gpm = 1385.4456 x 0.00411 x 80 PO = 455.5 gpm
Example:Duplex Pump Formula 1 0.000324 x (liner diameter, in) x ( stroke lengh, in) = ________ bbl/stk -0.000162 x (rod diameter, in) x ( stroke lengh, in) = ________ bbl/stk Pump out put @ 100% eff = ________bbl/stk Example: Determine the output, bbl/stk, of a 5 1/2" by 14" duplex pump at 100% efficiency. Rod diameter = 2.0": 0.000324 x 5.5 x 14 = 0.137214bbl/stk -0.000162 x 2.0 x 14 = 0.009072bbl/stk Pump output @ 100% eff. = 0.128142bbl/stk Adjust pump output for 85% efficiency: Decimal equivalent = 85 100 = 0.85 PO@85%)= 0.128142bbl/stk x 0.85 PO@ 85% = 0.10892bbl/stk Formula 2
PO. bbl/stk = 0.000162 x S[2(D) - d] where S = stroke length, in. D = liner diameter, in. d = rod diameter, in. Example: Determine the output, bbl/stk, of a 5 1/2". by 14". duplex pump @ 100% efficiency. Rod diameter = 2.0in.: PO@100%=0.000162 x 14 x [ 2 (5.5) - 2 ] PO @ 100%)= 0.000162 x 14 x 56.5 PO@ 100%)= 0.128142bbl/stk Adjust pump output for 85% efficiency: PO@85%,= 0.128142bb/stkx 0.85 PO@8.5%= 0.10892bbl/stk Metric calculation Pump output, liter/min = pump output. liter/stk x pump speed, spm. S.I. units calculation Pump output, m/min = pump output, liter/stk x pump speed, spm. Mud Pumps Mud pumps drive the mud around the drilling system. Depending on liner size availability they can be set up to provide high pressure and low flow rate, or low pressure and high flow rate. Analysis of the application and running the Drill Bits hydraulics program will indicate which liners to recommend. Finding the specification of the mud pumps allows flow rate to be calculated from pump stroke rate, SPM. Information requiredo Pump manufacturer o Number of pumps o Liner size and gallons per revolution Weight As a drill bit cutting structure wears more weight will be required to achieve the same RoP in a homogenous formation. PDC wear flats, worn inserts and worn milled tooth teeth will make the bit drill less efficiently. Increase weight in increments of 2,000lbs approx. In general, weight should be applied before excessive rotary speed so that the cutting structure maintains a significant depth of cut to stabilise the bit and prevent whirl. If downhole weight measurements are available they can be used in combination with surface measurements to gain a more accurate representation of what is happening in the well bore.

This worksheet takes inputs for the rig pumps and (optionally) hole and pipe sizes. It outputs pump flow rates and power, also fluid velocity if diameters entered.
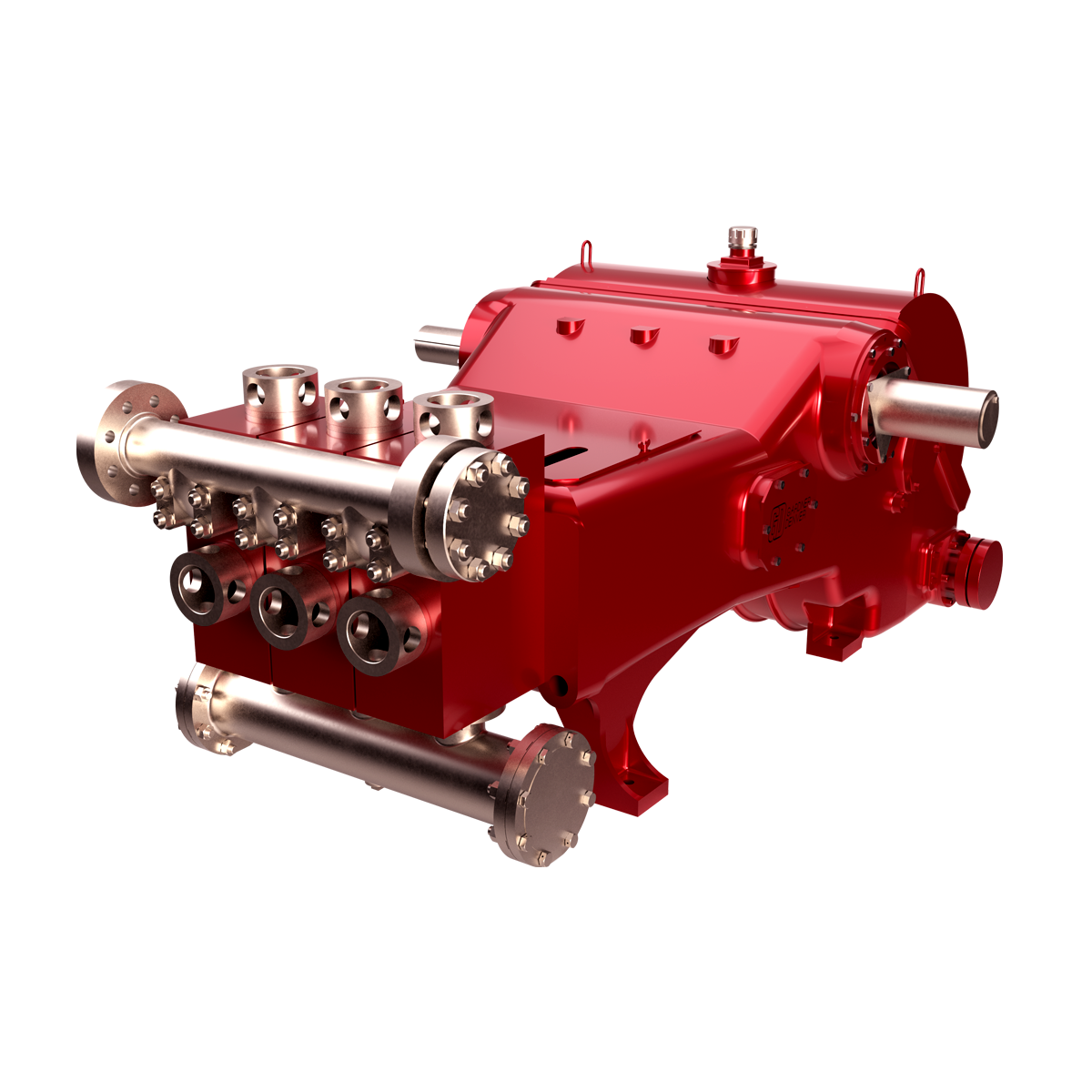
GDEP is the original creator of the drilling pump and continues to set the standard for durable, high-quality drilling pumps that can withstand the world’s toughest drilling environments. Starting with our PZ7 and rounding out with the market"s most popular pump, the PZ1600, our PZ Series of pumps are the perfect choice for today"s high-pressure drilling applications.

We stock fluid end parts for the5×6 mud pump, 5×6-1/4 FM45 mud pump, 5×8 mud pump, 5-1/2×8 mud pump, 5X10 mud pump, 4-1/2×5 mud pump, 7-1/2×8 mud pump, and 7-1/2X10 mud pump. The Gardner Denver mud pump model numbers for the above pumps are as follows: 5X6-FGFXG, 5X8-FDFXX, 5-1/2X8-FDFXX, 5X10-FDFXD, 4-1/2X5-FFFXF, 7-1/2X8-FYFXX, 7-1/2X10-FYFXD. We also handle Wheatley, Gaso, Worthington, Failing and Centerline parts and pumps. We also stock Foot Valve, Liner Puller, Valve Seat Puller, (4″ Inline Check Valve. Our Gardner Denver mud pump parts are not only competitively priced, they are also made in the USA. Oil Recommended by Gardner Denver. Call any of our experienced representatives to get the help and knowledge you deserve.

I’ve run into several instances of insufficient suction stabilization on rigs where a “standpipe” is installed off the suction manifold. The thought behind this design was to create a gas-over-fluid column for the reciprocating pump and eliminate cavitation.
When the standpipe is installed on the suction manifold’s deadhead side, there’s little opportunity to get fluid into all the cylinders to prevent cavitation. Also, the reciprocating pump and charge pump are not isolated.
The gas over fluid internal systems has limitations too. The standpipe loses compression due to gas being consumed by the drilling fluid. In the absence of gas, the standpipe becomes virtually defunct because gravity (14.7 psi) is the only force driving the cylinders’ fluid. Also, gas is rarely replenished or charged in the standpipe.
The suction stabilizer’s compressible feature is designed to absorb the negative energies and promote smooth fluid flow. As a result, pump isolation is achieved between the charge pump and the reciprocating pump.
The isolation eliminates pump chatter, and because the reciprocating pump’s negative energies never reach the charge pump, the pump’s expendable life is extended.
Investing in suction stabilizers will ensure your pumps operate consistently and efficiently. They can also prevent most challenges related to pressure surges or pulsations in the most difficult piping environments.
Sigma Drilling Technologies’ Charge Free Suction Stabilizer is recommended for installation. If rigs have gas-charged cartridges installed in the suction stabilizers on the rig, another suggested upgrade is the Charge Free Conversion Kits.
A mud pump is a reciprocating piston/plunger pump designed to circulate drilling fluid under high pressure (up to 7,500 psi (52,000 kPa)) down the drill string and back up the annulus. A duplex mud pump is an important part of the equipment used for oil well drilling.
Duplex mud pumps (two piston/plungers) have generally been replaced by the triplex pump, but are still common in developing countries. Two later developments are the hex pump with six vertical pistons/plungers, and various quintuplex’s with five horizontal piston/plungers. The advantages that Duplex mud pumps have over convention triplex pumps is a lower mud noise which assists with better Measurement while drilling and Logging while drilling decoding.
Use duplex mud pumps to make sure that the circulation of the mud being drilled or the supply of liquid reaches the bottom of the well from the mud cleaning system. Despite being older technology than the triplex mud pump, the duplex mud pumps can use either electricity or diesel, and maintenance is easy due to their binocular floating seals and safety valves.
A mud pump is composed of many parts including mud pump liner, mud pump piston, modules, hydraulic seat pullers, and other parts. Parts of a mud pump:housing itself
Duplex pumps are used to provide a secondary means of fuel transfer in the event of a failure of the primary pump. Each pump in a duplex set is sized to meet the full flow requirements of the system. Pump controllers can be set for any of the following common operating modes:Lead / Lag (Primary / Secondary): The lead (primary) pump is selected by the user and the lag (secondary pump operates when a failure of the primary pump is detected.
Alternating: Operates per Lead / Lag (Primary / Secondary) except that the operating pump and lead / lag status alternate on consecutive starts. A variation is to alternate the pumps based on the operating time (hour meter) of the lead pump.

A mud pump (sometimes referred to as a mud drilling pump or drilling mud pump), is a reciprocating piston/plunger pump designed to circulate drilling fluid under high pressure (up to 7,500 psi or 52,000 kPa) down the drill string and back up the annulus. A mud pump is an important part of the equipment used for oil well drilling and manufactured according to API specification 7K.
The advantages of the drilling mud pump include the ability to move high-solids-content fluids laden with abrasives, the ability to pump large particles, ease of operation and maintenance, reliability, and the ability to operate over a wide range of pressures and flow rates by changing the diameter of pump liners and pistons.
As an important equipment for oilfield drilling operation, a drilling mud pump delivers circulating high-pressure drilling fluid or drilling mud to the bottom of the oil well, flushes the bottom of the well, breaks the rock, cools, lubricates and clean the drill bit, and carries the cuttings back to the ground.
The drilling mud is also used to suspend and carry out drill cuttings from the drill bits as it is brought in and out of the hole. This ensures that the drill bit does not clog and overheat, and makes the entire drilling operation smooth and safe.
Rotational power is supplied to the mud pump through an external power source like a diesel engine or electric motor. The power end of the mud pump converts the rotational energy through a crankshaft to a reciprocating motion of pistons.
The pistons move back and forth in mud pump liners, exerting a force on the cylinder chamber. During the retraction of the piston, valves open to allow the fluid to be drawn into the cylinder. Once the piston has fully retracted, it is pushed back into the cylinder.




 8613371530291
8613371530291