how to figure gpm of a mud pump 0997 free sample

Rig pump output, normally in volume per stroke, of mud pumps on the rig is one of important figures that we really need to know because we will use pump out put figures to calculate many parameters such as bottom up strokes, wash out depth, tracking drilling fluid, etc. In this post, you will learn how to calculate pump out put for triplex pump and duplex pump in bothOilfield and Metric Unit.
Bourgoyne, A.J.T., Chenevert , M.E. & Millheim, K.K., 1986. SPE Textbook Series, Volume 2: Applied Drilling Engineering, Society of Petroleum Engineers.

This website is using a security service to protect itself from online attacks. The action you just performed triggered the security solution. There are several actions that could trigger this block including submitting a certain word or phrase, a SQL command or malformed data.
When it comes to pumping terminology, one crucial term to know is GPM — a measurement that will help you determine if you’re choosing the right pump. So what is GPM, and how do you calculate it?
GPM stands for gallons per minute and is a measurement of how many gallons a pump can move per minute. It is also referred to as flow rate. GPM is variable based on another measurement known as the Head, which refers to the height the water must reach to get pumped through the system. It is also referred to as flow rate. GPM is variable based on another measurement known as the Head, which refers to the height the water must reach to get pumped through the system.
Pumps are typically measured by their GPM at a certain Head measurement. For example, a pump specification may read 150 GPM at 50 Feet of Head, which means the pump will work at 150 gallons per minute when pumping water at a height of 50 feet.
The GPM formula is 60 divided by the number of seconds it takes to fill a one gallon container. So if you took 10 seconds to fill a gallon container, your GPM measurement would be 6 GPM (60/10 seconds = 6 GPM). To most accurately calculate GPM, you use the pressure tank method and formula. For this calculation, you need to know the specifications of your pressure tank, including how many gallons it holds, the gallon drawdown and the PSI. The manufacturer specifies the gallon drawdown. Once you have that information, as well as a stopwatch to keep time, follow these steps:
For example, if it took four minutes for the pressure switch to turn off, and your gallon drawdown was 20 gallons, this would mean a GPM rate of five.
If you don’t have a pressure tank, you can also use a bucket or any other container, time how long it takes to fill up and then divide that by the volume the container holds.
GPM identifies the unique capabilities of a pump so you can select the right one for your specific needs. If you need a pump for a larger public area such as a golf course, marina or lake, you will need a pump with a much higher GPM than one used for your home’s well. Plus, choosing the correct pump is essential for reducing your costs and increasing your pump’s lifespan.
At GeoForm International, we are a leading manufacturer of high-quality submersible pumps, dredges, digester packages and aerators, all of which are made in the U.S. With our pump expertise, we know just how essential GPM is in the pumping and dredging industry from how much equipment costs to how long jobs will take.

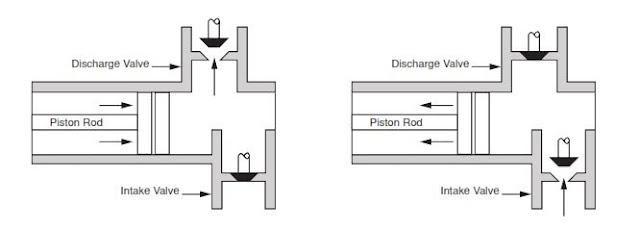
Oil and Gas drilling process - Pupm output for Triplex and Duplex pumpsTriplex Pump Formula 1 PO, bbl/stk = 0.000243 x ( in) E.xample: Determine the pump output, bbl/stk, at 100% efficiency for a 7" by 12". triplex pump: PO @ 100%,= 0.000243 x 7 x12 PO @ 100% = 0.142884bbl/stk Adjust the pump output for 95% efficiency: Decimal equivalent = 95 + 100 = 0.95 PO @ 95% = 0.142884bbl/stk x 0.95 PO @ 95% = 0.13574bbl/stk Formula 2 PO, gpm = [3(D x 0.7854)S]0.00411 x SPM where D = liner diameter, in. S = stroke length, in. SPM = strokes per minute Determine the pump output, gpm, for a 7" by 12". triplex pump at 80 strokes per minute: PO, gpm = [3(7 x 0.7854) 1210.00411 x 80 PO, gpm = 1385.4456 x 0.00411 x 80 PO = 455.5 gpm
Example:Duplex Pump Formula 1 0.000324 x (liner diameter, in) x ( stroke lengh, in) = ________ bbl/stk -0.000162 x (rod diameter, in) x ( stroke lengh, in) = ________ bbl/stk Pump out put @ 100% eff = ________bbl/stk Example: Determine the output, bbl/stk, of a 5 1/2" by 14" duplex pump at 100% efficiency. Rod diameter = 2.0": 0.000324 x 5.5 x 14 = 0.137214bbl/stk -0.000162 x 2.0 x 14 = 0.009072bbl/stk Pump output @ 100% eff. = 0.128142bbl/stk Adjust pump output for 85% efficiency: Decimal equivalent = 85 100 = 0.85 PO@85%)= 0.128142bbl/stk x 0.85 PO@ 85% = 0.10892bbl/stk Formula 2
PO. bbl/stk = 0.000162 x S[2(D) - d] where S = stroke length, in. D = liner diameter, in. d = rod diameter, in. Example: Determine the output, bbl/stk, of a 5 1/2". by 14". duplex pump @ 100% efficiency. Rod diameter = 2.0in.: PO@100%=0.000162 x 14 x [ 2 (5.5) - 2 ] PO @ 100%)= 0.000162 x 14 x 56.5 PO@ 100%)= 0.128142bbl/stk Adjust pump output for 85% efficiency: PO@85%,= 0.128142bb/stkx 0.85 PO@8.5%= 0.10892bbl/stk Metric calculation Pump output, liter/min = pump output. liter/stk x pump speed, spm. S.I. units calculation Pump output, m/min = pump output, liter/stk x pump speed, spm. Mud Pumps Mud pumps drive the mud around the drilling system. Depending on liner size availability they can be set up to provide high pressure and low flow rate, or low pressure and high flow rate. Analysis of the application and running the Drill Bits hydraulics program will indicate which liners to recommend. Finding the specification of the mud pumps allows flow rate to be calculated from pump stroke rate, SPM. Information requiredo Pump manufacturer o Number of pumps o Liner size and gallons per revolution Weight As a drill bit cutting structure wears more weight will be required to achieve the same RoP in a homogenous formation. PDC wear flats, worn inserts and worn milled tooth teeth will make the bit drill less efficiently. Increase weight in increments of 2,000lbs approx. In general, weight should be applied before excessive rotary speed so that the cutting structure maintains a significant depth of cut to stabilise the bit and prevent whirl. If downhole weight measurements are available they can be used in combination with surface measurements to gain a more accurate representation of what is happening in the well bore.




 8613371530291
8613371530291