mud pump flow rate calculator made in china

Rig pump output, normally in volume per stroke, of mud pumps on the rig is one of important figures that we really need to know because we will use pump out put figures to calculate many parameters such as bottom up strokes, wash out depth, tracking drilling fluid, etc. In this post, you will learn how to calculate pump out put for triplex pump and duplex pump in bothOilfield and Metric Unit.

Pump Output per Stroke (PO): The calculator returns the pump output per stroke in barrels (bbl). However this can be automatically converted to other volume units (e.g. gallons or liters) via the pull-down menu.
A triplex mud (or slush) pump has three horizontal plungers (cylinders) driven off of one crankshaft. Triplex mud pumps are often used for oil drilling.
When two (or more) pumps are arranged in serial their resulting pump performance curve is obtained by adding theirheads at the same flow rate as indicated in the figure below.
Centrifugal pumps in series are used to overcome larger system head loss than one pump can handle alone. for two identical pumps in series the head will be twice the head of a single pump at the same flow rate - as indicated with point 2.
With a constant flowrate the combined head moves from 1 to 2 - BUTin practice the combined head and flow rate moves along the system curve to point 3. point 3 is where the system operates with both pumps running
When two or more pumps are arranged in parallel their resulting performance curve is obtained by adding the pumps flow rates at the same head as indicated in the figure below.
Centrifugal pumps in parallel are used to overcome larger volume flows than one pump can handle alone. for two identical pumps in parallel and the head kept constant - the flow rate doubles compared to a single pump as indicated with point 2
Note! In practice the combined head and volume flow moves along the system curve as indicated from 1 to 3. point 3 is where the system operates with both pumps running
In practice, if one of the pumps in parallel or series stops, the operation point moves along the system resistance curve from point 3 to point 1 - the head and flow rate are decreased.

AfghanistanAlbaniaAlgeriaAmerican SamoaAndorraAngolaAnguillaAntarcticaAntigua and BarbudaArgentinaArmeniaArubaAustraliaAustriaAzerbaijanBahamasBahrainBangladeshBarbadosBelarusBelgiumBelizeBeninBermudaBhutanBoliviaBonaire, Sint Eustatius and SabaBosnia and HerzegovinaBotswanaBouvet IslandBrazilBritish Indian Ocean TerritoryBrunei DarussalamBulgariaBurkina FasoBurundiCabo VerdeCambodiaCameroonCanadaCayman IslandsCentral African RepublicChadChileChinaChristmas IslandCocos IslandsColombiaComorosCongoCongo, Democratic Republic of theCook IslandsCosta RicaCroatiaCubaCuraçaoCyprusCzechiaCôte d"IvoireDenmarkDjiboutiDominicaDominican RepublicEcuadorEgyptEl SalvadorEquatorial GuineaEritreaEstoniaEswatiniEthiopiaFalkland IslandsFaroe IslandsFijiFinlandFranceFrench GuianaFrench PolynesiaFrench Southern TerritoriesGabonGambiaGeorgiaGermanyGhanaGibraltarGreeceGreenlandGrenadaGuadeloupeGuamGuatemalaGuernseyGuineaGuinea-BissauGuyanaHaitiHeard Island and McDonald IslandsHoly SeeHondurasHong KongHungaryIcelandIndiaIndonesiaIranIraqIrelandIsle of ManIsraelItalyJamaicaJapanJerseyJordanKazakhstanKenyaKiribatiKorea, Democratic People"s Republic ofKorea, Republic ofKuwaitKyrgyzstanLao People"s Democratic RepublicLatviaLebanonLesothoLiberiaLibyaLiechtensteinLithuaniaLuxembourgMacaoMadagascarMalawiMalaysiaMaldivesMaliMaltaMarshall IslandsMartiniqueMauritaniaMauritiusMayotteMexicoMicronesiaMoldovaMonacoMongoliaMontenegroMontserratMoroccoMozambiqueMyanmarNamibiaNauruNepalNetherlandsNew CaledoniaNew ZealandNicaraguaNigerNigeriaNiueNorfolk IslandNorth MacedoniaNorthern Mariana IslandsNorwayOmanPakistanPalauPalestine, State ofPanamaPapua New GuineaParaguayPeruPhilippinesPitcairnPolandPortugalPuerto RicoQatarRomaniaRussian FederationRwandaRéunionSaint BarthélemySaint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da CunhaSaint Kitts and NevisSaint LuciaSaint MartinSaint Pierre and MiquelonSaint Vincent and the GrenadinesSamoaSan MarinoSao Tome and PrincipeSaudi ArabiaSenegalSerbiaSeychellesSierra LeoneSingaporeSint MaartenSlovakiaSloveniaSolomon IslandsSomaliaSouth AfricaSouth Georgia and the South Sandwich IslandsSouth SudanSpainSri LankaSudanSurinameSvalbard and Jan MayenSwedenSwitzerlandSyria Arab RepublicTaiwanTajikistanTanzania, the United Republic ofThailandTimor-LesteTogoTokelauTongaTrinidad and TobagoTunisiaTurkmenistanTurks and Caicos IslandsTuvaluTürkiyeUS Minor Outlying IslandsUgandaUkraineUnited Arab EmiratesUnited KingdomUnited StatesUruguayUzbekistanVanuatuVenezuelaViet NamVirgin Islands, BritishVirgin Islands, U.S.Wallis and FutunaWestern SaharaYemenZambiaZimbabweÅland Islands

The mud pump piston is a key part for providing mud circulation, but its sealing performance often fails under complex working conditions, which shorten its service life. Inspired by the ring segment structure of earthworms, the bionic striped structure on surfaces of the mud pump piston (BW-160) was designed and machined, and the sealing performances of the bionic striped piston and the standard piston were tested on a sealing performance testing bench. It was found the bionic striped structure efficiently enhanced the sealing performance of the mud pump piston, while the stripe depth and the angle between the stripes and lateral of the piston both significantly affected the sealing performance. The structure with a stripe depth of 2 mm and angle of 90° showed the best sealing performance, which was 90.79% higher than the standard piston. The sealing mechanism showed the striped structure increased the breadth and area of contact sealing between the piston and the cylinder liner. Meanwhile, the striped structure significantly intercepted the early leaked liquid and led to the refluxing rotation of the leaked liquid at the striped structure, reducing the leakage rate.
Mud pumps are key facilities to compress low-pressure mud into high-pressure mud and are widely used in industrial manufacture, geological exploration, and energy power owing to their generality [1–4]. Mud pumps are the most important power machinery of the hydraulic pond-digging set during reclamation [5] and are major facilities to transport dense mud during river dredging [6]. During oil drilling, mud pumps are the core of the drilling liquid circulation system and the drilling facilities, as they transport the drilling wash fluids (e.g., mud and water) downhole to wash the drills and discharge the drilling liquids [7–9]. The key part of a mud pump that ensures mud circulation is the piston [10, 11]. However, the sealing of the piston will fail very easily under complex and harsh working conditions, and consequently, the abrasive mud easily enters the kinematic pair of the cylinder liner, abrading the piston surfaces and reducing its service life and drilling efficiency. Thus, it is necessary to improve the contact sealing performance of the mud pump piston.
As reported, nonsmooth surface structures can improve the mechanical sealing performance, while structures with radial labyrinth-like or honeycomb-like surfaces can effectively enhance the performance of gap sealing [12–14]. The use of nonsmooth structures into the cylinder liner friction pair of the engine piston can effectively prolong the service life and improve work efficiency of the cylinder liner [15–17]. The application of nonsmooth grooved structures into the plunger can improve the performance of the sealing parts [18, 19]. The nonsmooth structures and sizes considerably affect the sealing performance [20]. Machining a groove-shaped multilevel structure on the magnetic pole would intercept the magnetic fluid step-by-step and slow down the passing velocity, thus generating the sealing effect [21–23]. Sealed structures with two levels or above have also been confirmed to protect the sealing parts from hard damage [24]. The sealing performance of the high-pressure centrifugal pump can be improved by adding groove structures onto the joint mouth circumference [25]. The convex, pitted, and grooved structures of dung beetles, lizards, and shells are responsible for the high wear-resistance, resistance reduction, and sealing performance [26–28]. Earthworms are endowed by wavy nonsmooth surface structures with high resistance reduction and wear-resistance ability [29]. The movement of earthworms in the living environment is very similar to the working mode of the mud pump piston. The groove-shaped bionic piston was designed, and the effects of groove breadth and groove spacing on the endurance and wear-resistance of the piston were investigated [30]. Thus, in this study, based on the nonsmooth surface of earthworms, we designed and processed a nonsmooth striped structure on the surface of the mud pump piston and tested the sealing performance and mechanism. This study offers a novel method for prolonging the service life of the mud pump piston from the perspective of piston sealing performance.
The BW-160 mud pump with long-range flow and pressure, small volume, low weight, and long-service life was used here. The dimensions and parameters of its piston are shown in Figure 1.
A mud pump piston sealing performance test bench was designed and built (Figure 3). This bench mainly consisted of a compaction part and a dynamic detection part. The compaction part was mainly functioned to exert pressure, which was recorded by a pressure gauge, to the piston sealed cavity. This part was designed based on a vertical compaction method: after the tested piston and the sealing liquid were installed, the compaction piston was pushed to the cavity by revolving the handle. Moreover, the dynamic detection part monitored the real-time sealing situation and was designed based on the pressure difference method for quantifying the sealing performance. This part was compacted in advance to the initial pressure P0 (0.1 MPa). After compaction, the driving motor was opened, and the tested piston was pushed to drive the testing mud to reciprocate slowly. After 1 hour of running, the pressure P on the gauge was read, and the pressure difference was calculated as , which was used to measure the sealing performance of the piston.
To more actually simulate the working conditions of the mud pump, we prepared a mud mixture of water, bentonite (in accordance with API Spec 13A: viscometer dial reading at 600 r/min ≥ 30, yield point/plastic viscosity radio ≤ 3, filtrate volume ≤ 15.0 ml, and residue of diameter greater than 75 μm (mass fraction) ≤ 4.0%), and quartz sand (diameter 0.3–0.5 mm) under complete stirring, and its density was 1.306 g/cm³ and contained 2.13% sand.
Figure 4 shows the effects of stripe depth and angle on the sealing performance of mud pump pistons. Clearly, the stripe depth should be never too shallow or deep, while a larger angle would increase the sealing performance more (Figure 4).
The standard piston and the bionic piston were numerically simulated using the academic version of ANSYS® Workbench V17.0. Hexahedral mesh generation method was used to divide the grid, and the size of grids was set as 2.5 mm. The piston grid division is shown in Figure 8, and the grid nodes and elements are shown in Table 3. The piston cup was made of rubber, which was a hyperelastic material. A two-parameter Mooney–Rivlin model was selected, with C10 = 2.5 MPa, C01 = 0.625 MPa, D1 = 0.3 MPa−1, and density = 1120 kg/m3 [32, 33]. The loads and contact conditions related to the piston of the mud pump were set. The surface pressure of the piston cup was set as 1.5 MPa, and the displacement of the piston along the axial direction was set as 30 mm. The two end faces of the cylinder liner were set as “fixed support,” and the piston and cylinder liner were under the frictional interfacial contact, with the friction coefficient of 0.2.
Figure 10 shows the surface pressures from the lip mouth to the root in the standard piston and the bionic piston. The surface pressure of the bionic piston surpasses that of the standard piston, and the pressure at the edge of each striped structure changes suddenly: the pressures at the striped structure of the bionic piston are far larger than at other parts. These results suggest the contact pressure between the edges of the striped structures and the cylinder liner is larger, and the four edges of the two striped structures are equivalent to a four-grade sealed lip mouth formed between the piston and the cylinder liner, which generates a multilevel sealing effect and thereby largely enhances the sealing effect of the piston.
The piston surface flow field was numerically simulated using the CFX module of the software ANSYS® Workbench V17.0. The side of the lips was set as fluid inlet, and the other side as fluid outlet, as shown in Figure 11. The inlet and outlet were set as opening models, and the external pressure difference between them was 0 Pa. The moving direction of the piston was opposite to the fluid flow direction. The fluid region was divided into grids of 0.2 mm, while the striped structures were refined to grade 2.
Figures 12 and 13 show the surface streamline clouds and sectional streamline clouds of the two pistons at the early stage of leakage when the fluid entered the interface. Clearly, compared with the standard piston, when the surface-leaked liquid from the bionic piston passed the striped structure, the streamlines were sparse and significantly decreased in number, and the flow velocity declined more. The flow velocity decreased from 0.9348 m/s to 0.7555 m/s in the bionic piston and from 0.9346 m/s to 0.9262 m/s in the standard piston. It shows that, after the blockage by the striped structures, the striped structure more significantly intercepted the leaked liquid and could reduce the leakage rate of the piston, thereby enhancing the sealing effect.
Figure 13 shows the section leakage streamline of the standard piston and the bionic piston. Clearly, compared with the standard piston, when the leaked liquid of the bionic piston flowed through the striped structures, the streamlines would reflux and reverse inside the striped structures, indicating the striped structures can efficiently store the leaked liquid and slow down the leakage.
To better validate the sealing mechanism of the bionic striped pistons, a piston’s performance testing platform was independently built and the sealed contact of the pistons was observed. A transparent toughened glass cylinder liner was designed and machined. The inner diameter and the assembly dimensions of the cylinder liner were set according to the standard BW-160 mud pump cylinder liners. The sealing contact surfaces of the pistons were observed and recorded using a video recorder camera.
(1)The bionic striped structure significantly enhanced the sealing performance of the mud pump pistons. The stripe depth and the angle between the stripes and the piston were two important factors affecting the sealing performance of the BW-160 mud pump pistons. The sealing performance was enhanced the most when the stripe depth was 2 mm and the angle was 90°.(2)The bionic striped structure can effectively enhance the contact pressure at the piston lips, enlarge the mutual extrusion between the piston and the cylinder liner, reduce the damage to the piston and cylinder liner caused by the repeated movement of sands, and alleviate the abrasion of abrasive grains between the piston and the cylinder liner, thereby largely improving the sealing performance.(3)The bionic striped structure significantly intercepted the leaked liquid, reduced the leakage rate of pistons, and effectively stored the leaked liquid, thereby reducing leakage and improving the sealing performance.(4)The bionic striped structure led to deformation of the piston, enlarged the width and area of the sealed contact, the stored lubricating oils, and formed uniform oil films after repeated movement, which improved the lubrication conditions and the sealing performance.
The bionic striped structure can improve the sealing performance and prolong the service life of pistons. We would study the pump resistance in order to investigate whether the bionic striped structure could decrease the wear of the piston surface.

The mud pump piston is a key part for providing mud circulation, but its sealing performance often fails under complex working conditions, which shorten its service life. Inspired by the ring segment structure of earthworms, the bionic striped structure on surfaces of the mud pump piston (BW-160) was designed and machined, and the sealing performances of the bionic striped piston and the standard piston were tested on a sealing performance testing bench. It was found the bionic striped structure efficiently enhanced the sealing performance of the mud pump piston, while the stripe depth and the angle between the stripes and lateral of the piston both significantly affected the sealing performance. The structure with a stripe depth of 2 mm and angle of 90° showed the best sealing performance, which was 90.79% higher than the standard piston. The sealing mechanism showed the striped structure increased the breadth and area of contact sealing between the piston and the cylinder liner. Meanwhile, the striped structure significantly intercepted the early leaked liquid and led to the refluxing rotation of the leaked liquid at the striped structure, reducing the leakage rate.
Mud pumps are key facilities to compress low-pressure mud into high-pressure mud and are widely used in industrial manufacture, geological exploration, and energy power owing to their generality [1–4]. Mud pumps are the most important power machinery of the hydraulic pond-digging set during reclamation [5] and are major facilities to transport dense mud during river dredging [6]. During oil drilling, mud pumps are the core of the drilling liquid circulation system and the drilling facilities, as they transport the drilling wash fluids (e.g., mud and water) downhole to wash the drills and discharge the drilling liquids [7–9]. The key part of a mud pump that ensures mud circulation is the piston [10, 11]. However, the sealing of the piston will fail very easily under complex and harsh working conditions, and consequently, the abrasive mud easily enters the kinematic pair of the cylinder liner, abrading the piston surfaces and reducing its service life and drilling efficiency. Thus, it is necessary to improve the contact sealing performance of the mud pump piston.
As reported, nonsmooth surface structures can improve the mechanical sealing performance, while structures with radial labyrinth-like or honeycomb-like surfaces can effectively enhance the performance of gap sealing [12–14]. The use of nonsmooth structures into the cylinder liner friction pair of the engine piston can effectively prolong the service life and improve work efficiency of the cylinder liner [15–17]. The application of nonsmooth grooved structures into the plunger can improve the performance of the sealing parts [18, 19]. The nonsmooth structures and sizes considerably affect the sealing performance [20]. Machining a groove-shaped multilevel structure on the magnetic pole would intercept the magnetic fluid step-by-step and slow down the passing velocity, thus generating the sealing effect [21–23]. Sealed structures with two levels or above have also been confirmed to protect the sealing parts from hard damage [24]. The sealing performance of the high-pressure centrifugal pump can be improved by adding groove structures onto the joint mouth circumference [25]. The convex, pitted, and grooved structures of dung beetles, lizards, and shells are responsible for the high wear-resistance, resistance reduction, and sealing performance [26–28]. Earthworms are endowed by wavy nonsmooth surface structures with high resistance reduction and wear-resistance ability [29]. The movement of earthworms in the living environment is very similar to the working mode of the mud pump piston. The groove-shaped bionic piston was designed, and the effects of groove breadth and groove spacing on the endurance and wear-resistance of the piston were investigated [30]. Thus, in this study, based on the nonsmooth surface of earthworms, we designed and processed a nonsmooth striped structure on the surface of the mud pump piston and tested the sealing performance and mechanism. This study offers a novel method for prolonging the service life of the mud pump piston from the perspective of piston sealing performance.
The BW-160 mud pump with long-range flow and pressure, small volume, low weight, and long-service life was used here. The dimensions and parameters of its piston are shown in Figure 1.
A mud pump piston sealing performance test bench was designed and built (Figure 3). This bench mainly consisted of a compaction part and a dynamic detection part. The compaction part was mainly functioned to exert pressure, which was recorded by a pressure gauge, to the piston sealed cavity. This part was designed based on a vertical compaction method: after the tested piston and the sealing liquid were installed, the compaction piston was pushed to the cavity by revolving the handle. Moreover, the dynamic detection part monitored the real-time sealing situation and was designed based on the pressure difference method for quantifying the sealing performance. This part was compacted in advance to the initial pressure P0 (0.1 MPa). After compaction, the driving motor was opened, and the tested piston was pushed to drive the testing mud to reciprocate slowly. After 1 hour of running, the pressure P on the gauge was read, and the pressure difference was calculated as , which was used to measure the sealing performance of the piston.
To more actually simulate the working conditions of the mud pump, we prepared a mud mixture of water, bentonite (in accordance with API Spec 13A: viscometer dial reading at 600 r/min ≥ 30, yield point/plastic viscosity radio ≤ 3, filtrate volume ≤ 15.0 ml, and residue of diameter greater than 75 μm (mass fraction) ≤ 4.0%), and quartz sand (diameter 0.3–0.5 mm) under complete stirring, and its density was 1.306 g/cm³ and contained 2.13% sand.
Figure 4 shows the effects of stripe depth and angle on the sealing performance of mud pump pistons. Clearly, the stripe depth should be never too shallow or deep, while a larger angle would increase the sealing performance more (Figure 4).
The standard piston and the bionic piston were numerically simulated using the academic version of ANSYS® Workbench V17.0. Hexahedral mesh generation method was used to divide the grid, and the size of grids was set as 2.5 mm. The piston grid division is shown in Figure 8, and the grid nodes and elements are shown in Table 3. The piston cup was made of rubber, which was a hyperelastic material. A two-parameter Mooney–Rivlin model was selected, with C10 = 2.5 MPa, C01 = 0.625 MPa, D1 = 0.3 MPa−1, and density = 1120 kg/m3 [32, 33]. The loads and contact conditions related to the piston of the mud pump were set. The surface pressure of the piston cup was set as 1.5 MPa, and the displacement of the piston along the axial direction was set as 30 mm. The two end faces of the cylinder liner were set as “fixed support,” and the piston and cylinder liner were under the frictional interfacial contact, with the friction coefficient of 0.2.
Figure 10 shows the surface pressures from the lip mouth to the root in the standard piston and the bionic piston. The surface pressure of the bionic piston surpasses that of the standard piston, and the pressure at the edge of each striped structure changes suddenly: the pressures at the striped structure of the bionic piston are far larger than at other parts. These results suggest the contact pressure between the edges of the striped structures and the cylinder liner is larger, and the four edges of the two striped structures are equivalent to a four-grade sealed lip mouth formed between the piston and the cylinder liner, which generates a multilevel sealing effect and thereby largely enhances the sealing effect of the piston.
The piston surface flow field was numerically simulated using the CFX module of the software ANSYS® Workbench V17.0. The side of the lips was set as fluid inlet, and the other side as fluid outlet, as shown in Figure 11. The inlet and outlet were set as opening models, and the external pressure difference between them was 0 Pa. The moving direction of the piston was opposite to the fluid flow direction. The fluid region was divided into grids of 0.2 mm, while the striped structures were refined to grade 2.
Figures 12 and 13 show the surface streamline clouds and sectional streamline clouds of the two pistons at the early stage of leakage when the fluid entered the interface. Clearly, compared with the standard piston, when the surface-leaked liquid from the bionic piston passed the striped structure, the streamlines were sparse and significantly decreased in number, and the flow velocity declined more. The flow velocity decreased from 0.9348 m/s to 0.7555 m/s in the bionic piston and from 0.9346 m/s to 0.9262 m/s in the standard piston. It shows that, after the blockage by the striped structures, the striped structure more significantly intercepted the leaked liquid and could reduce the leakage rate of the piston, thereby enhancing the sealing effect.
Figure 13 shows the section leakage streamline of the standard piston and the bionic piston. Clearly, compared with the standard piston, when the leaked liquid of the bionic piston flowed through the striped structures, the streamlines would reflux and reverse inside the striped structures, indicating the striped structures can efficiently store the leaked liquid and slow down the leakage.
To better validate the sealing mechanism of the bionic striped pistons, a piston’s performance testing platform was independently built and the sealed contact of the pistons was observed. A transparent toughened glass cylinder liner was designed and machined. The inner diameter and the assembly dimensions of the cylinder liner were set according to the standard BW-160 mud pump cylinder liners. The sealing contact surfaces of the pistons were observed and recorded using a video recorder camera.
(1)The bionic striped structure significantly enhanced the sealing performance of the mud pump pistons. The stripe depth and the angle between the stripes and the piston were two important factors affecting the sealing performance of the BW-160 mud pump pistons. The sealing performance was enhanced the most when the stripe depth was 2 mm and the angle was 90°.(2)The bionic striped structure can effectively enhance the contact pressure at the piston lips, enlarge the mutual extrusion between the piston and the cylinder liner, reduce the damage to the piston and cylinder liner caused by the repeated movement of sands, and alleviate the abrasion of abrasive grains between the piston and the cylinder liner, thereby largely improving the sealing performance.(3)The bionic striped structure significantly intercepted the leaked liquid, reduced the leakage rate of pistons, and effectively stored the leaked liquid, thereby reducing leakage and improving the sealing performance.(4)The bionic striped structure led to deformation of the piston, enlarged the width and area of the sealed contact, the stored lubricating oils, and formed uniform oil films after repeated movement, which improved the lubrication conditions and the sealing performance.
The bionic striped structure can improve the sealing performance and prolong the service life of pistons. We would study the pump resistance in order to investigate whether the bionic striped structure could decrease the wear of the piston surface.

This article will focus on understanding of MWD signal decoding which is transmitted via mud pulse telemetry since this method of transmission is the most widely used commercially in the world.
As a basic idea, one must know that transmitted MWD signal is a wave that travels through a medium. In this case, the medium is mud column inside the drill string to mud pumps. Decoding is about detecting the travelling wave and convert it into data stream to be presented as numerical or graphical display.
The signal is produced by downhole transmitter in the form of positive pulse or negative pulse. It travels up hole through mud channel and received on the surface by pressure sensor. From this sensor, electrical signal is passed to surface computer via electrical cable.
Noise sources are bit, drill string vibration, bottom hole assemblies, signal reflection and mud pumps. Other than the noises, the signal is also dampened by the mud which make the signal becomes weak at the time it reaches the pressure sensor. Depth also weaken the signal strength, the deeper the depth, the weaker the signal detected.
BHA components that have moving mechanical parts such as positive mud motor and agitator create noise at certain frequency. The frequency produced by these assemblies depends on the flow rate and the lobe configuration. The higher the flow rate and the higher the lobe configuration creates higher noise frequency.
Normally, the noise frequency created by these BHA components are relatively much higher than MWD signal frequency, so that, practically this noise type is not disturbing decoding. In a certain situation, this noise frequency can be annoying which disrupts decoding. To cure this, one must alter the noise frequency by altering the flow rate.
Thruster, normally made up above MWD tool, tends to dampen the MWD signal significantly. It has a nozzle to use mud hydraulic power to push its spline mandrel – and then push the BHA components beneath it including the bit – against bottom of the hole. When the MWD signal is passing through the nozzle, the signal loses some of its energy. Weaker signal will then be detected on surface.
The pressure sensor on the pipe manifold detects 2 identical signals, one from the original MWD transmitter and another one comes from signal reflection, which are separated in some milliseconds. The result seen by the surface computer is the sum of those two signals. Depending on the individual signal width and the timing when the reflected signal arrives at the pressure sensor, surface computer may see a wider signal width or two identical signals adjacent to each other.
Important to note that the surface computer has been programmed to detect a signal with certain signal width and certain signal separation. When the computer sees this wider signal and/or two signals which are not correctly separated, the computer will set these signal as false ones and will not be decoded or decoded incorrectly.
The common sources of signal reflection are pipe bending, change in pipe inner diameter or closed valve. These are easily found in pipe manifold on the rig floor. To avoid the signal reflection problem, the pressure sensor must be mounted in a free reflection source area, for example close to mud pumps. The most effective way to solve this problem is using dual pressure sensors method.
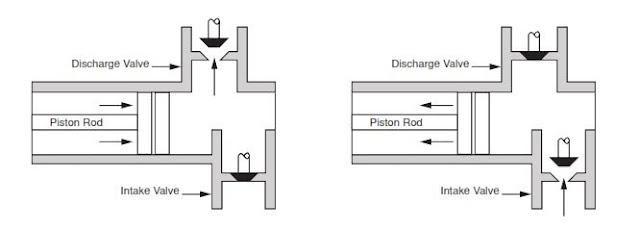
Mud pump is positive displacement pump. It uses pistons in triplex or duplex configuration. As the piston pushes the mud out of pump, pressure spikes created. When the piston retracts, the pressure back to idle. The back and forth action of pistons produce pressure fluctuation at the pump outlet.
Pressure fluctuation is dampened by a dampener which is located at the pump outlet. It is a big rounded metal filled with nitrogen gas and separated by a membrane from the mud output. When the piston pushes the mud the nitrogen gas in the dampener will be compressed storing the pressure energy; and when the piston retracts the compressed nitrogen gas in the dampener release the stored energy. So that the output pressure will be stable – no pressure fluctuation.
The dampener needs to be charged by adding nitrogen gas to certain pressure. If the nitrogen pressure is not at the right pressure, either too high or too low, the pump output pressure fluctuation will not be stabilized. This pressure fluctuation may match the MWD frequency signal and hence it disturbs decoding, it is called pump noise.
When the pump noise occurs, one may simply change the flow rate (stroke rate) so that the pump noise frequency fall outside the MWD frequency band – and then apply band pass frequency to the decoder.
The formula to calculate pump noise frequency is 3*(pump stroke rate)/60 for triplex pump and 2*(pump stroke rate)/60 for duplex pump. The rule of thumb to set up dampener pressure charge is a third (1/3) of the working standpipe pressure.
Sometime the MWD signal is not detected at all when making surface test although the MWD tool is working perfectly. This happen whenever the stand pipe pressure is the same with the pump dampener pressure. Reducing or increasing test flow rate to reduce or increase stand pipe pressure helps to overcome the problem.
When the MWD signal wave travels through mud as the transmission medium, the wave loses its energy. In other words, the wave is giving some energy to the mud.
The mud properties that are affecting MWD signal transmission is viscosity and weight. The increasing mud weight means there is more solid material or heavier material in the mud. Sometimes the mud weight increment is directly affecting mud viscosity to become higher. The MWD signal wave interacts with those materials and thus its energy is reduced on its way to surface. The more viscous the mud and the heavier the mud, the weaker the signal detected on surface.
Aerated mud often used in underbalance drilling to keep mud influx into the formation as low as possible. The gas injected into the mud acts as signal dampener as gas bubble is compressible. MWD signal suffers severely in this type of mud.
Proper planning before setting the MWD pulser gap, flow rate and pump dampener pressure based on mud properties information is the key to overcome weak signal.
The further the signal travels, the weaker the signal detected on the surface. The amount of detected signal weakness ratio compare to the original signal strength when it is created at the pulser depends on many factors, for example, mud properties, BHA component, temperature and surface equipment settings.

Researchers have shown that mud pulse telemetry technologies have gained exploration and drilling application advantages by providing cost-effective real-time data transmission in closed-loop drilling operations. Given the inherited mud pulse operation difficulties, there have been numerous communication channel efforts to improve data rate speed and transmission distance in LWD operations. As discussed in “MPT systems signal impairments”, mud pulse signal pulse transmissions are subjected to mud pump noise signals, signal attenuation and dispersion, downhole random (electrical) noises, signal echoes and reflections, drillstring rock formation and gas effects, that demand complex surface signal detection and extraction processes. A number of enhanced signal processing techniques and methods to signal coding and decoding, data compression, noise cancellation and channel equalization have led to improved MPT performance in tests and field applications. This section discusses signal-processing techniques to minimize or eliminate signal impairments on mud pulse telemetry system.
At early stages of mud pulse telemetry applications, matched filter demonstrated the ability to detect mud pulse signals in the presence of simulated or real noise. Matched filter method eliminated the mud noise effects by calculating the self-correlation coefficients of received signal mixed with noise (Marsh et al. 1988). Sharp cutoff low-pass filter was proposed to remove mud pump high frequencies and improve surface signal detection. However, matched filter method was appropriate only for limited single frequency signal modulated by frequency-shift keying (FSK) with low transmission efficiency and could not work for frequency band signals modulated by phase shift keying (PSK) (Shen et al. 2013a).
In processing noise-contaminated mud pulse signals, longer vanishing moments are used, but takes longer time for wavelet transform. The main wavelet transform method challenges include effective selection of wavelet base, scale parameters and vanishing moment; the key determinants of signal correlation coefficients used to evaluate similarities between original and processed signals. Chen et al. (2010) researched on wavelet transform and de-noising technique to obtain mud pulse signals waveform shaping and signal extraction based on the pulse-code information processing to restore pulse signal and improve SNR. Simulated discrete wavelet transform showed effective de-noise technique, downhole signal was recovered and decoded with low error rate. Namuq et al. (2013) studied mud pulse signal detection and characterization technique of non-stationary continuous pressure pulses generated by the mud siren based on the continuous Morlet wavelet transformation. In this method, generated non-stationary sinusoidal pressure pulses with varying amplitudes and frequencies used ASK and FSK modulation schemes. Simulated wavelet technique showed appropriate results for dynamic signal characteristics analysis.
As discussed in “MPT mud pump noises”, the often overlap of the mud pulses frequency spectra with the mud pump noise frequency components adds complexity to mud pulse signal detection and extraction. Real-time monitoring requirement and the non-stationary frequency characteristics made the utilization of traditional noise filtering techniques very difficult (Brandon et al. 1999). The MPT operations practical problem contains spurious frequency peaks or outliers that the standard filter design cannot effectively eliminate without the possibility of destroying some data. Therefore, to separate noise components from signal components, new filtering algorithms are compulsory.
Early development Brandon et al. (1999) proposed adaptive compensation method that use non-linear digital gain and signal averaging in the reference channel to eliminate the noise components in the primary channel. In this method, synthesized mud pulse signal and mud pump noise were generated and tested to examine the real-time digital adaptive compensation applicability. However, the method was not successfully applied due to complex noise signals where the power and the phases of the pump noises are not the same.
Jianhui et al. (2007) researched the use of two-step filtering algorithms to eliminate mud pulse signal direct current (DC) noise components and attenuate the high frequency noises. In the study, the low-pass finite impulse response (FIR) filter design was used as the DC estimator to get a zero mean signal from the received pressure waveforms while the band-pass filter was used to eliminate out-of-band mud pump frequency components. This method used center-of-gravity technique to obtain mud pulse positions of downhole signal modulated by pulse positioning modulation (PPM) scheme. Later Zhao et al. (2009) used the average filtering algorithm to decay DC noise components and a windowed limited impulse response (FIR) algorithm deployed to filter high frequency noise. Yuan and Gong (2011) studied the use of directional difference filter and band-pass filter methods to remove noise on the continuous mud pulse differential binary phase shift keying (DBPSK) modulated downhole signal. In this technique, the directional difference filter was used to eliminate mud pump and reflection noise signals in time domain while band-pass filter isolated out-of-band noise frequencies in frequency domain.
Other researchers implemented adaptive FIR digital filter using least mean square (LMS) evaluation criterion to realize the filter performances to eliminate random noise frequencies and reconstruct mud pulse signals. This technique was adopted to reduce mud pump noise and improve surface received telemetry signal detection and reliability. However, the quality of reconstructed signal depends on the signal distortion factor, which relates to the filter step-size factor. Reasonably, chosen filter step-size factor reduces the signal distortion quality. Li and Reckmann (2009) research used the reference signal fundamental frequencies and simulated mud pump harmonic frequencies passed through the LMS filter design to adaptively track pump noises. This method reduced the pump noise signals by subtracting the pump noise approximation from the received telemetry signal. Shen et al. (2013a) studied the impacts of filter step-size on signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) distortions. The study used the LMS control algorithm to adjust the adaptive filter weight coefficients on mud pulse signal modulated by differential phase shift keying (DPSK). In this technique, the same filter step-size factor numerical calculations showed that the distortion factor of reconstructed mud pressure QPSK signal is smaller than that of the mud pressure DPSK signal.
Study on electromagnetic LWD receiver’s ability to extract weak signals from large amounts of well site noise using the adaptive LMS iterative algorithm was done by (Liu 2016). Though the method is complex and not straightforward to implement, successive LMS adaptive iterations produced the LMS filter output that converges to an acceptable harmonic pump noise approximation. Researchers’ experimental and simulated results show that the modified LMS algorithm has faster convergence speed, smaller steady state and lower excess mean square error. Studies have shown that adaptive FIR LMS noise cancellation algorithm is a feasible effective technique to recover useful surface-decoded signal with reasonable information quantity and low error rate.
Different techniques which utilize two pressure sensors have been proposed to reduce or eliminate mud pump noises and recover downhole telemetry signals. During mud pressure signal generation, activated pulsar provides an uplink signal at the downhole location and the at least two sensor measurements are used to estimate the mud channel transfer function (Reckmann 2008). The telemetry signal and the first signal (pressure signal or flow rate signal) are used to activate the pulsar and provide an uplink signal at the downhole location; second signal received at the surface detectors is processed to estimate the telemetry signal; a third signal responsive to the uplink signal at a location near the downhole location is measured (Brackel 2016; Brooks 2015; Reckmann 2008, 2014). The filtering process uses the time delay between first and third signals to estimate the two signal cross-correlation (Reckmann 2014). In this method, the derived filter estimates the transfer function of the communication channel between the pressure sensor locations proximate to the mud pump noise source signals. The digital pump stroke is used to generate pump noise signal source at a sampling rate that is less than the selected receiver signal (Brackel 2016). This technique is complex as it is difficult to estimate accurately the phase difference required to give quantifiable time delay between the pump sensor and pressure sensor signals.
As mud pulse frequencies coincide with pump noise frequency in the MPT 1–20 Hz frequency operations, applications of narrow-band filter cannot effectively eliminate pump noises. Shao et al. (2017) proposed continuous mud pulse signal extraction method using dual sensor differential signal algorithm; the signal was modulated by the binary frequency-shift keying (BFSK). Based on opposite propagation direction between the downhole mud pulses and pump noises, analysis of signal convolution and Fourier transform theory signal processing methods can cancel pump noise signals using Eqs. 3 and 4. The extracted mud pulse telemetry signal in frequency domain is given by Eqs. 3 and 4 and its inverse Fourier transformation by Eq. 4. The method is feasible to solve the problem of signal extraction from pump noise,
These researches provide a novel mud pulse signal detection and extraction techniques submerged into mud pump noise, attenuation, reflections, and other noise signals as it moves through the drilling mud.




 8613371530291
8613371530291