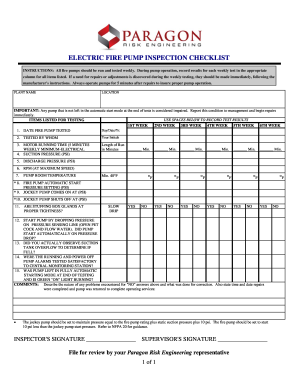
mud pump inspection checklist quotation
Created specifically for drilling equipment inspectors and others in the oil and gas industry, the Oil Rig Mud Pump Inspection app allows you to easily document the status and safety of your oil rigs using just a mobile device. Quickly resolve any damage or needed maintenance with photos and GPS locations and sync to the cloud for easy access. The app is completely customizable to fit your inspection needs and works even without an internet signal.Try Template
Fulcrum helps us improve our processes and make our work environment safer by streamlining inspections, surfacing inspection-related insights, and managing follow-up actions. Once you close the loop from action to insight to further action, the possibilities are limitless.
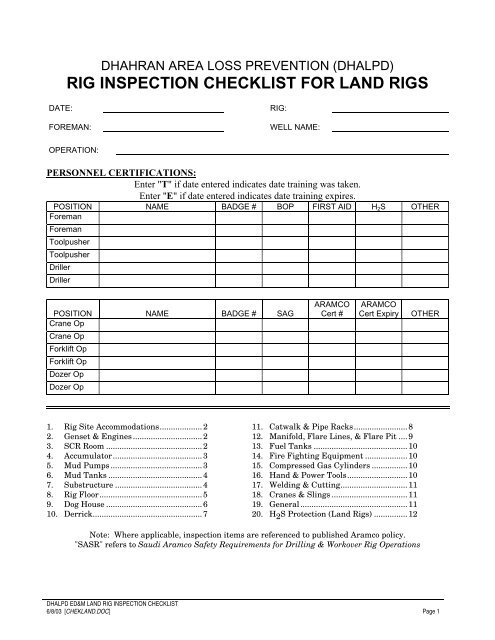
Instead of using paper checklists when out in the field, drilling contractors and rig inspection services can generate a new inspection form from anywhere and the results are saved electronically.
Specifically designed for drilling companies and others in the oil and gas industry, the easy to use drilling rig inspections app makes it easy to log information about the drill rigs, including details about the drill rigs operators, miles logged and well numbers. The inspection form app covers everything from the mud pump areas and mud mixing area to the mud tanks and pits, making it easy to identify areas where preventative maintenance is needed. The drilling rig equipment checklist also covers health and safety issues, including the availability of PPE equipment, emergency response and preparedness processes, and other critical elements of the drilling process and drill press equipment.

As it is the case with most equipment, pumps require regular maintenance to keep within peak performance benchmarks. The benefits of preventive maintenance in the HVAC industry have proven to improve asset life cycle, boost CRM, cut excessive repair costs and reduce unplanned equipment downtime.
When talking about pump failure the best remedy is having a great schedule and maintenance checklist in place. In a pump’s life cycle, environmental conditions can often be a major factor in its performance. Some other important maintenance tasks and factors to consider include:
All of these issues can be detrimental to a pump’s performance and cause defects if not resolved with regular maintenance. When considering what to include in your regular maintenance checklist a great place to start is the warranty and manufacturer standards as per pump type. Pump manufacturers often set requirements to follow to ensure the best life cycle for your equipment.
Pump efficiency point is the result of hydraulic, mechanical and volumetric parts to ensure performance is within a desired level. The level of efficiency in a pump is drawn from the units of energy that is required for performance.
However in centrifugal pumps, the inner workings of the pump will drive the motor. Essentially this means the mechanical energy is transformed to hydraulic energy and electrical energy is transformed to mechanical energy. This means that for a centrifugal pump you will find your level of efficiency sits at either 75% or higher in larger pumps and around 60% in smaller pumps.
As a part of your work order management for your pump maintenance schedule, you need to do some research behind what factors you need to consider that will be most detrimental to your pump’s health. When you create your ultimate guide to maintenance, your aim is to reduce your unplanned downtime and improve your standard of service by keeping a regular schedule.
When trying to determine the frequency of your maintenance checklist, you need to consider the factors that will impact your pump listed in the beginning of this article. If you have a higher quality pump that is used every day and is largely impacted by elemental factors, you will need to have more regular services in place. The warranty and safety standards will also have an impact here, depending on your pump type and according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
The more thorough your maintenance is, the better service you can provide. While a large maintenance schedule can seem daunting to your maintenance team, the assistance of checklists can ensure no step is missed no matter how big or small. Having a checklist in place will also provide consistency across your team and ensure each pump may receive the correct care it needs.
The main area for concern in centrifugal pumps is the lubrication. As centrifugal pumps rely heavily on correct lubrication to work, maintenance is important to ensure pumps aren’t under or over lubricated, which can cause damage. When you have over lubrication your pump will create too much heat and can result in frothing the oil.
Getting your maintenance plan right means you consider all these above factors and are able to incorporate them into your pump checklist and schedule.
For this checklist, you want to schedule a quick inspection of your pumps to avoid damage and wear. The main reason for having a daily checklist in your schedule is to catch those pesky issues that can turn into defects and pricey repairs if not caught early on.
Generally your quarterly maintenance will be done with the change of the season and can include varying tasks due to elemental factors. The severity of your pump environment will also affect the consistency and schedule of your pump maintenance program. Will your pump be exposed to extreme heat or extreme cold temperatures?
In your annual preventive plan, you will generally go into more detail and evaluate pump performance. Each year you should take a record of your annual operations and benchmarking data that might include:
For your routine maintenance schedule for your centrifugal pumps you need to make sure you have a solid system in place where you can reliably plan and train your team. Having a great software in place will also give you the ability to structure your maintenance program according to the manufacturer’s instructions and adhere to your customer contracts.
Job management software like FieldInsight gives you the ability to keep your centrifugal pump maintenance in perfect balance. With FieldInsight, you also gain access to the five primary automations in your business:
A pump that lets you down when you need it most causes obvious losses of time and money. Not so obvious, but every bit as costly, are losses you can incur with pumps that operate at less-than-peak efficiency. A pump laboring under the handicap of a suction line air leak, a corroded discharge line or a clogged impeller uses excessive energy, takes longer than necessary to do the job, and subjects parts to undue stress, causing premature failure.
A 6-inch gasoline-driven, self-priming centrifugal pump operating at 25% less than peak efficiency through an eight-hour day uses approximately 8.8 gallons more fuel than a pump operating efficiently. At $2.00 per gallon over a 40-hour week that’s $80.00 per week LOST! And that figure doesn’t include additional service costs!
Gorman-Rupp wants to keep your pump performance efficient. If you already own Gorman-Rupp pumps, you know how easy they are to service, so there is really no reason to let them deliver less than their best.
If you don’t own Gorman-Rupp pumps, you’ll find our 9-point checklist helpful because today every penny of profit counts, and we want your pumps to work as efficiently as possible.
Indications that your pump isn’t operating at peak efficiency may not be dramatic, but they’re easily recognized. Look for these signs of inefficiency:
There is a noticeable difference in pump flow. Has the discharge flow visibly decreased? Is it taking your pump longer to do the same job than it used to? The slow-up might be caused by a collapsed suction hose lining, a leaking gasket, a plugged suction line, or a damaged or worn impeller or wear plate.
Your pump isn’t re-priming as rapidly as it once did. Most commonly, slower re-prime can be attributed to excessive face clearance. If this is not the cause of your slowdown, check the following: Is the seal leaking? Are all hardware at gaskets tight? Is the suction check valve sealing properly? Is the cutwater section of the volute badly worn? Is the recirculating port clogged?
Your pump is making excessive noise. Does it sound like a bunch of marbles rattling in a can? This may be an indication of cavitation and could be caused by a suction lift that’s too high, a suction hose that’s too long or plugged or that has a collapsed lining, a clogged strainer, a combination of any of these, or perhaps a problem on the discharge side of the pump. Failing bearings can also cause excessive noise.
Your pump is clogging frequently. The suction check valve may be clogged, the strainer may be too large or too small, face clearance could be too wide, or the strainer may be stuck in mud, plugging the suction side.
Your pump is overheating. Very likely the flow of liquid into or out of the pump is being restricted. Improper impeller clearance could be slowing re-priming, or the suction strainer may be clogged.
Although this list is not a complete guide to pump inspection and service, it does cover the more common conditions that can impair pump efficiency. Keep in mind that excessive wear could also be the cause of any of the problems in the above paragraphs.
Check for air leaks. Using a vacuum gauge, make sure that the suction line, fittings and pipe plugs are airtight. Most Gorman-Rupp pumps have a tapped hole for easy connection of a vacuum gauge. Use pipe dope to seal gauge threads and pipe plugs. Replace leaky seals and badly worn hoses.
Check the suction hose lining. The rubber lining in a suction hose can pull away from the fabric, causing partial blockage of the line. If the pump develops a high vacuum but low discharge pressure, the hose lining may be blocking suction flow. Replace the hose.
Check the suction strainer. Frequent inspection and cleaning of the suction strainer is particularly important when pumping liquids containing solids. Always use the proper size strainer to prevent the pump from clogging.
Check the impeller vanes, wear plate or wear rings. The removable cover plate on many Gorman-Rupp pumps provides quick, easy inspection of the impeller and wear plate. These components should be inspected every six months or sooner, depending on pump application. They are subject to faster wear when pumping abrasive liquids and slurries. Gorman-Rupp wear plates and wear rings can be replaced without replacing expensive castings.
Check the impeller clearance. Pumping efficiency will be reduced if the clearance between impeller and wear plate or wear rings is beyond the recommended limits. If the clearance is less than recommended, components will wear by rubbing, causing excess work for the engine or motor. Check the impeller clearance against the pump manual specifications and adjust it if necessary.
Check the seal. Many Gorman-Rupp pumps are equipped with a double seal which is lubricated under pressure by a spring-loaded grease cup, or an oil-lubricated seal for long, trouble-free service. Some pumps are equipped with a single seal that is lubricated by the liquid being pumped. Sand or other solids can cause rapid wear of the seal faces. Check and replace the seal if worn. Replace the seal liner or shaft sleeve if they have scratches.
Check the bearings. Worn bearings can cause the shaft to wobble. Eventually the pump will overheat, and sooner or later it will freeze up and stop. Replace bearings at the first sign of wear.
Check the engine or motor. The pump may not be getting the power it needs to operate efficiently. The engine may need a tune-up, or the motor may need service.
If your submersible pump is operating at a reduced capacity, it could be caused by a worn impeller, excessive impeller clearance, low or incorrect voltage, or it could be running backward. A discharge head that’s too high, a clogged or kinked hose, or a clogged strainer could also be responsible for reduced flow. Use an amp meter and volt meter to determine if the pump is getting the proper power it needs to operate efficiently. Normal amp readings are provided in the manual accompanying your pump.
If your diaphragm pump isn’t pumping as it should, check the diaphragm, suction and discharge check valve flappers and seats, and replace any worn parts. Check suction hose fittings for leaks, and check the plunger rod for proper adjustment.

Pumps are often designed to operate at a single point known as the Best Efficiency Point (BEP). As components begin to wear, a pumps performance begins to decline, with operation away from this point leading to issues such as accelerated bearing or seal wear, vibration, excess temperature rise or cavitation. Quite often declining performance can start gradually, before quickly accelerating until failure if performance issues are not addressed in a timely fashion.
Corrective Maintenance is undertaken when failure has occurred. The unit may be leaking, efficiency reduced, pump stopped or motor tripped, leading to loss of production resulting in an urgent situation where parts must be sourced and fitted quicky.
Preventative Maintenance is inspection and repair scheduled at specific intervals (daily, weekly, monthly, yearly) or based on the number of hours run. Visual inspections are made externally and internally by dismantling the unit, replacing seals such as gaskets and mechanical seals, with pump parts checked for wear.
Differential Pressure:Check the operating pressure by calculating the difference between the inlet and outlet pressure of the pump ensuring it is operating on curve.
The “6 to 1 Rule” discovered by John Day Jr, (Manager of Engineering & Maintenance at Alumax South Carolina stated that the ideal ratio of Proactive Maintenance (PM) to Corrective Maintenance (CM) should be 6 to 1 - 6 PM checks to 1 RM check. If your ratio is below this then according to his theory it is being inspected too infrequently, above and inspections are too frequent.
Although Proactive Maintenance can seem to avoid the urgent costs and downtime associated with reactive maintenance, PM maintenance costs can be high due to the cost of labour in dismantling of complicated designs such as Progressing Cavity, or Triplex Plunger pumps which are often time consuming to maintain with more than one person required to undertake work.
On dismantling units, some seals require replacing regardless of condition, and excess spares can be required in case of gasket entrapment during assembly. Rental of specialist lifting equipment may be required and there can be situations where when inspected, pump parts do not require replacement.
This can be achieved through a monitoring device, where when the right data is collected, pump failure can be anticipated between 3 and 12 months in advance with an 80-95% accuracy.
With the average lead time on DN100 pumps, and units over 5 years old being 3 months or more, it is essential that spares are either on the shelf or failure is anticipated through advance ordering.
There are hazards during any maintenance activity. Always ensure the correct PPE is worn before attempting repair, that sufficient expertise is on hand and chemical data sheets of any fluid being pumped are checked prior to undertaking work. A full risk assessment should be completed in advance.
Hazardous FluidsIrritation, Chemical burns, ignitionEnsure when pump is opened the unit is cool, not pressurized, ignition sources are not present, and any fluids spilt are contained.
If inspection has been neglected for some time, then additional parts may require replacing than had the unit been inspected earlier, with some pump parts becoming beyond economical repair.
Enables planned work to be undertaken during lower activity levels and at lowest cost & risk.Pump has to be crucial within a process or above a certain size for monitoring to be cost effective
Thread Sealant –The use of semi-permanent thread sealant will ensure vitality important threaded fasteners such as bolts or screws on shafts, couplings or pump casings do not self-loosen due to vibration and become disengaged.
Interchangeable Spares –Our range of pumps are modular in design utilizing interchangeable spares, meaning on site stock holding of parts can be reduced by up to 80% further reducing slow moving stock.
Repair & Replace –Choosing to repair an existing pump within a process of vital importance, as well as replace, is a strategy we recommend for maximizing plant efficiencies and reducing downtime. Should unexpected pump failure occur, your process can be restored quickly.
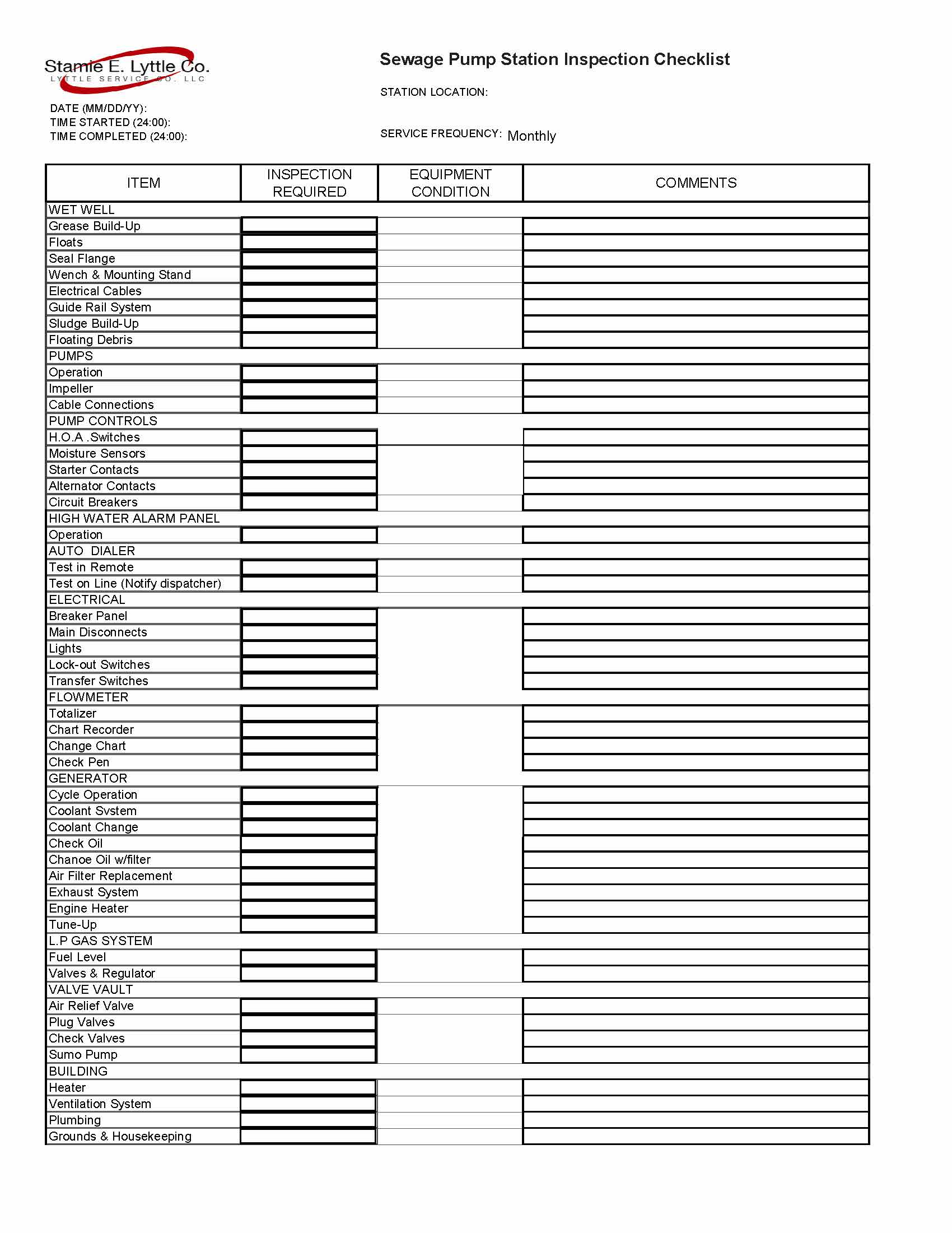
Checklists & Logs –The use of checklists and logs ensures a fully repeatable process ensuring important maintenance intervals are not missed. Logs can provide valuable insight and reveal a pattern before failure occurs enabling easier troubleshooting.
indicates which areas should be checked, but note that a units maintenance routine is dependent on several factors such as hours of operation, duty, aggressiveness of pump medium, rpm of motor, temperature, inlet conditions and location of equipment.

Is your basement dry? You might want to thank your sump pump. It works hard to keep your basement and possessions dry every rainy (or melty) season. It detects when water is threatening your basement, then pumps it out before it rises above the floor level.
But in order for your sump pump to function at its best, it’s important to give it a thorough check a couple times per year. At the very least, make it a habit to check your sump pump every spring to make sure it’s working. That way, the risk of a surprise puddle in your basement stays low. Cross these simple tasks off your cleaning to-do list and enjoy the year while staying flood-free.
While your sump pump might seem like a complicated machine, it only takes a little bit of effort and know-how to see if it’s running like it should. Check out these tips on avoiding any potential sump pump breakdowns.
Make sure your sump pump is totally upright. Your sump pump should be sitting on sold, even ground. Any sort of leaning can shift the water in the pump’s pit and put unnecessary pressure on its components.
Open it up.Take the cover off the sump pump pit or basin and have a look inside. Clear any debris, mud or rocks that you find, as any foreign items can clog your sump pump and cause an overflow.
Double-check the drain hose. Check and make sure the drain hose is connected, and that it’s not blocked or frozen. A clogged drain hose can cause your sump pump to run continuously, as it won’t be able to dispose of the water that’s filled its pit.
Clear out the inlet screen. Make sure the inlet screen is allowing water to enter your sump pump’s pit. If your inlet screen is blocked, water won’t be able to make its way into the sump pumps pit and could lead to a basement flood.
Keep it afloat. Your sump pump’s float controls when it will turn on and pump excess water out. Make sure the float component can move freely and isn’t blocked. A malfunctioning float can cause your pump to not run when it’s supposed to, or run constantly, eventually burning out your pump’s engine.
Make sure it’s flowing away from your house.The next time you hear your sump pump running, go outside and make sure its discharge pipe is pumping the water away from your home at a safe distance. If it’s too close, the water could seep back into your pump, causing your pump to run continuously and inefficiently. And the more your sump pump runs, the more likely it is to burn out early in its life span.
And while you don’t want your discharge pipe too close to your house, shed, garage or other structure, make sure it stays on your property. You’ll have some unhappy neighbors if your sump pump is pushing all your excess water onto their lot.
Give your sump pump a test run. Fill the pit with a bucket of water to turn your pump on. Watch it carefully to see if it’s getting rid of the water, then check the discharge pipe outside to make sure it’s disposed of properly. If the pump doesn’t run, make sure it’s plugged in and its power cord is in working order.
Plan for the unexpected. Having a backup battery or generator can be crucial if a strong rain storm comes complete with a power outage. And eventually, your sump pump may give out without the help of a power outage. To avoid the stress of trying to buy and install a new sump pump while the water seeps closer and closer to your basement, have a backup sump pump handy — and be sure to test it regularly, too.
Call a professional. You’ve checked the power cords, discharge pipe, inlet screen and every other piece of the pump, but still can’t figure out what’s wrong. It’s time to call a professional! Risking your basement and everything else in it isn’t worth maintaining your pride as a handyman or woman — get it fixed and fast!
Your American Family Insurance agent can help you plan for the unexpected with sump pump failure and water backup coverage, which is designed to mitigate the cost of repairs caused by water leaking into a home due to a backed-up drain or an overflowing sump. Get in touch with them and make sure you’ve got all the coverage and peace of mind you need.

Lake Petro provides high quality Mud Pump Parts including Mud Pump Liners, Mud Pump Fluid End Module, piston, Valve and Seat etc. With more than 10 years of experience in the oil and gas industry, we are dedicated to help and support our loyal clients with the most cost-effective and quality Liners and Pistons. We also provide mud pump price and mud pump for sale.
We offer Liners with Ceramic (Zirconia and Aluminium oxide) and Steel (Metal and Bi-metal) materials for all common brands of the mud pump and triplex mud pump.
All Lake Petro liner products are interchangeable with O.E.M. products. Meanwhile, we provide customized Liners according to drawings. Our liners, also with our other mud pump spares, are supplied for use in Honghua, F-Series, Bomco, Emsco and National lines of triplex drilling pumps. Let Lake Petro be your one-stop shop for your whole fleet of pumps. Please refer to “Suitable Pump Models” Lable for more details.

GDEP is the original creator of the drilling pump and continues to set the standard for durable, high-quality drilling pumps that can withstand the world’s toughest drilling environments. Starting with our PZ7 and rounding out with the market"s most popular pump, the PZ1600, our PZ Series of pumps are the perfect choice for today"s high-pressure drilling applications.

Black gold is truly the best description to sum up the value of oil. One of the most important contributors to change and industrialization, it drives the wheels of progress. ShalePumps is headquartered in Houston, the global oil capital. Headed by experts, it has a vision to support the industry with superior completion equipment. Frac operators, drilling contractors and well service companies source rely on ShalePumps for superior quality.
The key personnel of ShalePumps have a combined experience of more than a hundred years. This experience is reflected in the quality of our equipment. The fracking pumps, components and all services are much sought after for reliability and long life. This is because of the processes we follow. The design, materials, precision engineering and expertise contribute to an advanced assembly line.
After many years of thought and conscientious engineering, the team at ShalePumps is proud to add the Q5K™ 5000 HP Frac Pump to their list of many product offerings. Perfectly capable and suited for the next generation of hydraulic fracking market demands and technology. The Q5K is the only frac pump that has been designed and developed from the ground up to be capable of accepting true 5000 HP in a continuous duty frac application.
ShalePumps has consistently delivered high quality completion equipment to all stakeholders. The mission is to develop faster, rugged and efficient equipment to help the Oil and Exploration Industry. The vision is to continue leading the race with the best quality in completion equipment.

The fluid end of a duplex or triplex pump offers hundreds of opportunities for error. The results of an error in such a high-pressure system can mean (1) expensive downtime on the pump and maybe the entire rig, (2) expensive repair-replacement, and (3) possible injury or death of a crewman or a company man. Under the laws of nature, pump pistons and liners will wear, and there will be some corrosion and metallurgical imperfections, but the majority of pump failures are manmade. Theoretically, thorough training and retraining should avoid most mud pump problems. Realistically, a critical failure analysis during repair will be necessary to determine how to correct the failure. Telltale signs of trouble are distortion of piston rods, frayed piston polymer, discoloration, odor, hard-to-remove piston, rod cracks, pitting, total fracture, valve seat wear, and unsuitable external appearance.
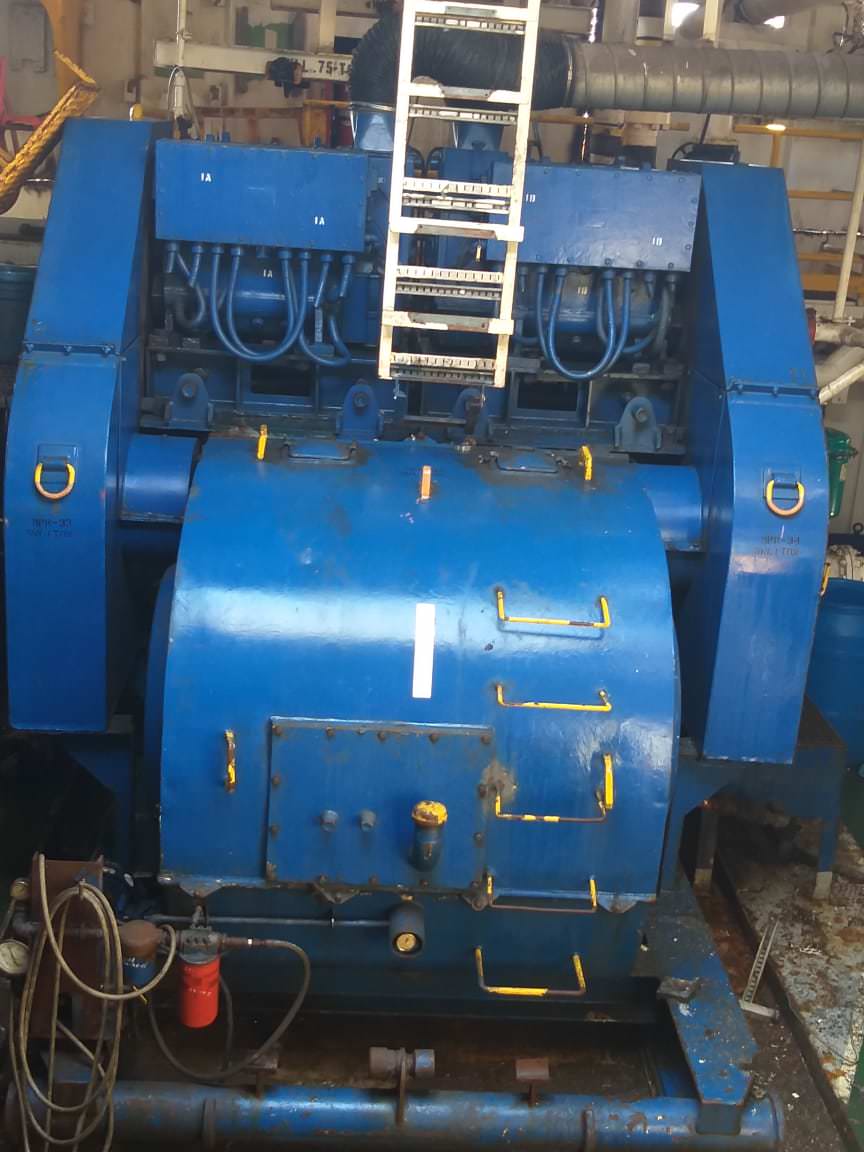

A Mud Pump may have many changeable parts, such as liner, piston, extension rod, pulsation dampener, valve, clamp, etc. Lake Petro could provide 100% interchangeable parts of many common brands of pump. We offer Liners with Ceramic (Zirconia and Aluminium oxide) and Steel (Metal and Bi-metal) materials. Piston assembly is the important spare parts and expendable parts of oil drilling mud pumps. Mud pump valve assy include valve body, valve seat, valve insert (valve rubber ). Pulsation Dampener is usually installed on the discharge line to reduce the fluctuation of pressure and displacement of the drilling mud pump. Fluid End Module is an important component of the hydraulic pump end of the mud pump.
![]()
Triplex plunger-type mud pumps feature a reciprocating, positive displacement pump design utilizing three plungers to safely transfer high-viscosity fluids under high pressure over an extended depth. Although they have many industrial applications, these pumps have become an essential part of oil well drilling rigs where they’re used to provide smooth discharge of mud and debris from oil wells.
In addition to their use in drilling and well service operations, mud pumps are also frequently used to handle corrosive or abrasive fluids, as well as slurries containing relatively large particulates, in applications like commercial car washes, wastewater treatment, cementing, and desalination operations.
DAC Worldwide’s Representative Triplex, Plunger Mud Pump Dissectible (295-418) is an economical, conveniently-sized triplex plunger-type mud pump assembly that teaches learners hands-on maintenance activities commonly required on larger mud pump assemblies used in upstream oilfield production operations.
For example, mud pump assembly is used on well sites maintain downhole backpressure, to lubricate the rotating drill bit, and to help recycle and remove rock debris resulting from drilling activities. These heavy-duty, high-pressure pumps require regular refurbishment, inspection, and repair in the field.
DAC Worldwide’s dissectible mud pump assembly is a realistic sample that’s similar in geometry, design, and operating characteristics to the larger varieties learners will encounter on the job. DAC Worldwide chooses popular name-brand pumps for its dissectibles to ensure industrial and oil and gas training relevancy.
Using the dissectible mud pump, learners will gain hands-on experience with the operating principles, regular maintenance activities, and nomenclature/parts identification at a more convenient scale in the classroom or lab.
Technical training is most effective when learners can gain hands-on practice with industry-standard components they’ll encounter on the job. The Representative Triplex, Plunger Mud Pump Dissectible features a wide variety of common, industrial-quality components to provide learners with a realistic training experience that will build skills that translate easily to the workplace.
The Representative Triplex, Plunger Mud Pump Dissectible is a sturdy unit with a complete triplex, reciprocating, 20+ bhp plunger pump with .75" plunger, 1.5" stroke, and 3" cylinder sleeve. The unit allows for complete disassembly, assembly, and inspection, including removal of plungers, packing, and valves.
The dissectible mud pump comes with a formed-steel, powder-coated baseplate. It can also be mounted on a compatible DAC Worldwide Extended Electromechanical Workstation (903). Each unit comes with the manufacturer’s installation and maintenance manual.

The article presents selected technical issues relating to drilling performed by a drillship, one type of drilling rigs. Basic problems encountered in the main function of such rigs − drilling a well − are failures of mud pumps. The authors investigate these pumps in operational conditions, aiming at development of a system for monitoring the technical condition of these pumps. Work on a diagnostic system is in progress that will permit to predict the condition of mud pump valves well in…Expand




 8613371530291
8613371530291