oil rig mud pump system quotation

This website is using a security service to protect itself from online attacks. The action you just performed triggered the security solution. There are several actions that could trigger this block including submitting a certain word or phrase, a SQL command or malformed data.

If you are supplying pump supplies, you can find the most favorable prices at Alibaba.com. Whether you will be working with piston type or diaphragm type systems, reciprocating or centrifugal, Alibaba.com has everything you need. You can also shop for different sizes drilling mud pump price wholesale for your metering applications. If you operate a construction site, then you could need to find some concrete pump solutions that you can find at affordable rates at Alibaba.com. Visit the platform and browse through the collection of submersible and inline pump system, among other replaceable models.
A drilling mud pump price comes in different makes and sizes, and you buy the tool depending on the application. The pump used by a filling station is not the one you use to fill up your tanks. There are high flow rate low pressure systems used to transfer fluids axially. On the other hand, you can go with radial ones dealing with a low flow rate and high-pressure fluid. The mixed flow pump variety combines radial and axial transfer mechanisms and works with medium flow and pressure fluids. Depending on what it will be pumping, you can then choose the drilling mud pump price of choice from the collection at Alibaba.com.
Alibaba.com has been an excellent wholesale supplier of drilling mud pump price for years. The supply consists of a vast number of brands to choose from, comes in different sizes, operations, and power sources. You can get a pump for residential and large commercial applications from the collection. Whether you want a water pump for your home, or run a repair and maintenance business, and need a supply of dr drill mud pump prices, you can find the product you want from the vast collection at Alibaba.com.ther it is for refrigeration, air conditioning, transfer, or a simple car wash business, anything you want, Alibaba.com has it.
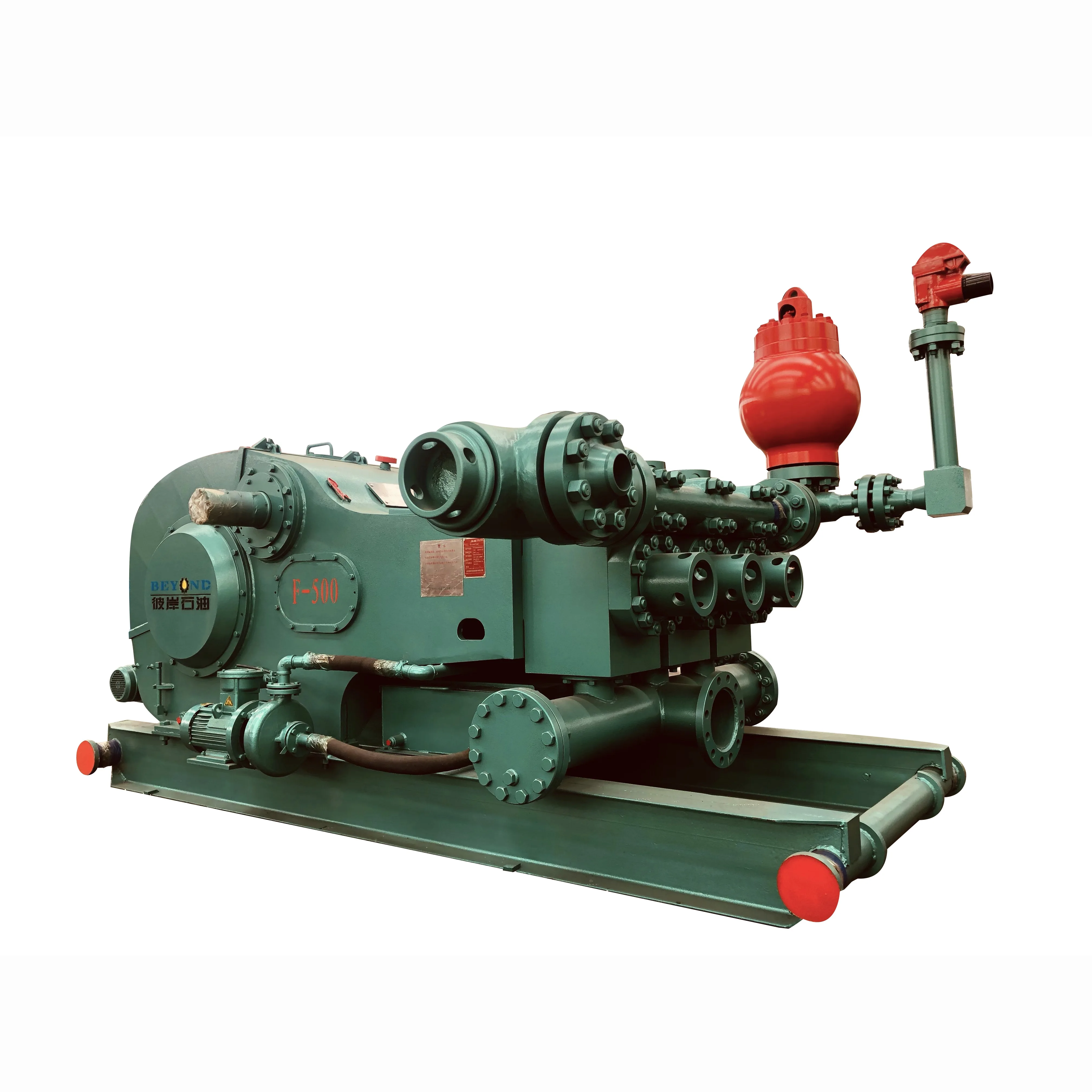

Explore a wide variety of oil rig pump on Alibaba.com and enjoy exquisite deals. The machines help maintain drilling mud circulation throughout the project. There are many models and brands available, each with outstanding value. These oil rig pump are efficient, durable, and completely waterproof. They are designed to lift water and mud with efficiency without using much energy or taking a lot of space.
The primary advantage of these oil rig pump is that they can raise water from greater depths. With the fast-changing technology, purchase machines that come with the best technology for optimum results. They should be well adapted to the overall configuration of the installation to perform various operations. Hence, quality products are needed for more efficiency and enjoyment of the machines" full life expectancy.
Alibaba.com offers a wide selection of products with innovative features. The products are designed for a wide range of flow rates that differ by brand. They provide cost-effective options catering to different consumer needs. When choosing the right oil rig pump for the drilling project, consider factors such as size, shape, and machine cost. More powerful tools are needed when dealing with large projects such as agriculture or irrigation.
Alibaba.com provides a wide range of oil rig pump to suit different tastes and budgets. The site has a large assortment of products from major suppliers on the market. The products are made of durable materials to avoid corrosion and premature wear during operations. The range of products and brands on the site assures quality and good value for money.

A Mud Pump may have many changeable parts, such as liner, piston, extension rod, pulsation dampener, valve, clamp, etc. Lake Petro could provide 100% interchangeable parts of many common brands of pump. We offer Liners with Ceramic (Zirconia and Aluminium oxide) and Steel (Metal and Bi-metal) materials. Piston assembly is the important spare parts and expendable parts of oil drilling mud pumps. Mud pump valve assy include valve body, valve seat, valve insert (valve rubber ). Pulsation Dampener is usually installed on the discharge line to reduce the fluctuation of pressure and displacement of the drilling mud pump. Fluid End Module is an important component of the hydraulic pump end of the mud pump.

One of the most expensive and troubling issues with drilling operations is the handling, processing, and circulation of drilling mud along with disposing of the unwanted drill cuttings. The drilling cuttings deposited in the half round tank and are typically removed with an excavator which must manually move the drill cuttings out of the waste bin or roll-off box and into the truck. The excavators are usually rented for this duty and the equipment charges can range from $200-300/day. Add in the cost for the day and night manpower and the real cost for a single excavator can be as much as $1800/day.
One solids control company reported the idle time for the excavator can be more than 8 hours for a 24-hour period with 8 hours of operation and 8 hours of shut down time. Fuel and time lost can cause an economic drag on rig operations. And lastly, there have been several accidents on each rig causing a potential for injury, loss of production, and lost revenue as the excavator must be repaired.
Offshore drilling rigs follow a similar process in which the mud is loaded into empty drums and held on the oil platform. When a certain number of filled drums is met, the drums are then loaded onto barges or vessels which take the drilling mud to the shore to unload and dispose of.

This website is using a security service to protect itself from online attacks. The action you just performed triggered the security solution. There are several actions that could trigger this block including submitting a certain word or phrase, a SQL command or malformed data.

Drill rigs are classified by a variety of factors. Onshore vs. Offshore begins the delineation. Land rigs vary by their size and strength, maximum drilling depth and mobility, ranging from light to super heavy models. Offshore requirements differ by the depth of water the equipment can handle, the drilling depth, and the harshness of the location. To determine which type of rig will work best for your project, we ask that you give us a call at (855)201-7193 to discuss your needs via phone or to set up a personal meeting.
Various pumps are required in the drilling process to carry fluids to and from your rig. Mud pumps specifically are a reciprocal type of pump used to circulate drilling fluid through the system. A triplex pump is often recommended to decrease the flow volume of discharged fluid in order to gain more pressure. We welcome the opportunity to discuss the scope of your project personally in order to best assess your needs. We ask that you give us a call at (855)201-7193 to review your requirements.
Miles of piping is required to dig the depths necessary to produce oil. The pipes also need rotational power which is provided by the Kelly or top drive to the bit. Other supplies required here include: collars, tools, and drill bits. Drill pipe provides a flexible transition to collars and adds additional weight to the drill bit to facilitate boring.Please give us a call at (855)201-7193 so we can discuss your needs and provide the best possible solution.
A Fracking site must be able to handle the sand, water, mud, and chemicals that go into and come out of the ground during the fracking of the well. Needs include various trucks, mixers, frac tanks to store fresh water, weir tanks, pumps, piping, and sand storage. We welcome the opportunity to discuss the scope of your project personally in order to best assess your needs. We ask that you give us a call at (855)201-7193 to review your requirements.
As production of a well decreases over time due to a drop in pressure, an artificial lift is sometimes required to boost production. That lift comes in the form of a pump jack. The pump jack uses equipment above and below the ground to push the oil to the surface. The operating principle is simple: a long heavy beam is moved up and down via an external power source working like a piston to increase pressure in the well.We welcome the opportunity to discuss the scope of your project personally in order to best assess your needs. We ask that you give us a call at (855)201-7193 to review your requirements.
Estimates say there are 150+ components and a myriad of pieces of equipment and support needs at an oil site. What you need depends on the size and complexity of your operation. From Frac Tanks to trucks to trailers and all the components in between, we’ve got you covered. . We welcome the opportunity to discuss the scope of your project personally in order to best assess your needs. We ask that you give us a call at (855)201-7193 to review your requirements.
Mud Bins are popularly used in the oil business for solidifying drilling mud and cuttings. They can also be used for construction debris and environmental clean-up.

The Driller’s Console I/O is connected to one remote rack, located in the console and connected by dual Ethernet Fiber optic cable to one Optical Link MOXA module, also located in the console, which convert the signals for use by the fiber optic cable running to the PLCs. Below is an overview of the signals exchanged between this console and the PLC system.

Having a quality mud pump is a critical part of keeping your oil well drilling system running as smoothly as possible. Dragon carries a wide range of mud pumps for systems of all kinds and jobs of all sizes. We also carry a 50 BPM mud mixing table to make drilling fluid mixing more efficient and accurate so you can always get the job done safely and correctly. View our full well service pump and mud pump selection to find the right system for your job site, or check out the rest of our drilling rigs for even more options.

Bentec completely redeveloped the concept of Mud Pumps. Being equipped with a direct-driven gearbox, an own developed motor, and a state-of-the-art pump housing, there is no need for an internal gear coming with many disadvantages and no more belt tensioning.
Bentec Mud Pumps are light weight and have a small footprint. The AC-powered motor is top or rear mounted – suitable for any drilling rig arrangement. The pump is available with 5 000 or 7 500 psi fluid ends, and all its parts that are subject to wear and tear meet API standards and are available worldwide.
A handling crane makes it easy to handle the fluid end components. Furthermore, Bentec uses a patented liner and valve clamping technology to reduce the maintenance time significantly. A quick-change liner and piston system serves for easy maintenance. A special feature of the Bentec MUD PUMP is the side-mounted gear drive.
This design eliminates the need for chain or belt tensioning systems. The two-stage helical gear feeds directly into a forged/welded crankshaft, which is balanced and provides quiet and vibration-reduced operation.
Liner cooling and gear oiler systems are included; a supercharge pump and a noise reduction package can be installed upon request. The Bentec MUD PUMP is the right choice especially when it comes to noise-sensitive environments such offshore or densely populated environments.
Beyond the supply of Mud Pumps, Bentec acts as system supplier. The pumps can be delivered together with a Bentec Power Control System and a Bentec Soft Pump System.

An integral part of onshore and offshore drilling, mud pumps circulate the drilling fluids used to facilitate drilling oil and natural gas wells. Used to stabilize pressure and support the well during the drilling process, drilling fluids also provide friction reduction and a means to remove cuttings.
While drilling with some type of fluid has been in practice for centuries, the term "drilling mud" was coined when a herd of cattle was driven through a wet field near Spindletop, and the resulting mud was used to lubricate the drillstring and drill bit. Drilling fluids have come a long way since those early days of drilling, and offshore mud pumps are constantly taxed to help operators find and develop hydrocarbons in harsher, deeper and more difficult locations.
"A mud pump delivers drilling fluid from the mud tanks, through the top drive, down the drill string and through the bit," explained Juan Lerma, Mud Pumps Product Line Manager at National Oilwell Varco. "When the mud exits the bit, it travels back to the surface carrying the cuttings made by the bit where it flows over a shale-shaker removing the cuttings, cleaning the mud and returning it to the tanks, where it"s used over and over again."
Varying according to the conditions of well being drilled, as well as the type of rock formations the bit is encountering at each depth, drilling fluids are composed of numerous ingredients, including clay, water, oil and synthetic materials. When drilling offshore, the environmental impact of drilling fluids must be more closely considered.
"A mud pump is one of the critical and required pieces of equipment for a drilling rig whether on land or offshore," Lerma stated. "Offshore, where real estate is at a premium, mud pumps are configured with a compact top-mounted drive system, reducing the overall length with a smaller package and strategically placing it in the pump room for permanent installation."
"On the other hand, space is not as much of an issue on land rigs," continued Lerma. "Here special consideration is paid to truck specifications and height restrictions for travel on roads, instead."
"Jackups semis and drillships all use the same mud pumps; however, the number of pumps installed in the pump rooms changes from rig to rig depending on the drilling specifications," explained Lerma.
Additionally, the rock formations and pressure encountered when drilling may vary; HT/HP and environmental conditions also may affect the drilling process, as well as the drilling fluids chosen and mud pumps required.
"As the drilling programs require higher flows and higher pressures, it is necessary to increase pressure ratings and either increase the number of mud pumps required or utilize larger capacity mud pumps," Lerma continued. "Most early jackups utilized two mud pumps and piping systems rated for 5000 psi work pressures and 1600 horsepower, while most of today"s jackups have 7500 psi working pressure and up to four 2200 HP pumps piping systems."
According to information gathered by premium rig data service RigLogix, National Oilwell Varco leads the pack in providing mud pumps to offshore oil rigs. Of the top six brands of mud pumps, NOV supplies four of them, garnering more than 70% of the offshore mud pump market.
Those leading NOV brands include National Oilwell, Continental Emsco (which was acquired by NOV in 1999), National and NOV. The other leading mud pump system is provided by Gardner Denver and is the third most popular type of system offshore. Additionally, Lewco, a division of Rowan, has about 4% of the offshore mud pump market, putting it fifth on the list of leading suppliers.
With more than four decades of experience providing the offshore industry with mud pumps, Lerma revealed that the company has been able to sustain such a high market share by constantly transforming the product to meet the needs of the industry. As offshore drilling programs have required higher flows and pressures, the company has strived to provide the best quality equipment, while maintaining the lowest cost of ownership.
To better serve its offshore clients, the company developed the Hex Pump in the last several years, and this new line of mud pumps has proven a success in offshore waters worldwide. Boasting 2400 HP, the Hex pump is capable of delivering up to 1,034 gallons of drilling fluids per minute, making it one of the most powerful mud pumps on the market today.
In 2004, the first two Hex Pumps were deployed on a Global Santa Fe rig working offshore West Africa, and in 2005, both the Noble Max Smith and the Noble All While started using the Hex Pump as well. In fact, the Noble Al White, working in the harsh conditions of the North Sea, was the first rig to be solely dependent on the Hex Pumps with two of them located in its pump room, and the rig now has more than 8,000 hours of successful drilling operations using the system.
Through these successes, the company has been able to lock in orders for many of the newly built and under-construction offshore rigs joining the global fleet now and in the future.
"The first drillship to use the system, Transocean"s Discoverer Clear Leader just started drilling in the Gulf of Mexico with five Hex Pump systems," said Lerma. "Additionally, the soon-to-start-drilling Discoverer Americas houses four Hex Pumps, and the soon-to-be-delivered Discoverer Inspiration will have five."
Mud pump liner selection in today"s drilling operations seldom (at best) considers electrical implications. Perhaps, with more available useful information about the relationships between mud pump liner size and operational effects on the electrical system, certain potential problems can be avoided. The intent of this paper is to develop those relationships and show how they affect an electrical system on example SCR rigs.Introduction
There, seems to be little consideration for the relationships between liner size and demand on a rig"s engine/generator set(s). Yet, consideration for this relationship can prove to be very helpful to drillers and operators in efficiency of a rig"s electrical system. In order to develop the relationships and help drillers and operators understand the importance of each, relationships between liner size, pump speed, pump pressure, and electrical power will be developed. Only basic physical laws will be used to develop the relationships; and, once developed, the relationships are readily applied to realistic examples utilizing a mud pump manufacturer"s pump data. Finally, conclusions will be drawn from the examples.DEVELOPMENT OF RELATIONSHIPS BASIC RELATIONSHIPS
where HHP= Hydraulic horsepower, GPM = Mud pump volumetric flow rate in gallons per minute, and PST Mud pump output pressure in pounds peer square inch.
Hydraulic horsepower is reflected to the mud pump motor via a multiplier for mechanical efficiency. it follows that motor horsepower is then represented by

The circulation system on the rig is the system that allows for circulation of the Drilling Fluid or Mud down through the hollow drill string and up through the annular space between the drill string and wellbore. It is a continuous system of pumps, distribution lines, storage tanks, storage pits, and cleansing units that allows the drilling fluid to fulfill its primary objectives (these will be discussed later in this lesson). The mud pumps of the circulation system and the drawworks of the hoisting systems are the two largest draws on the power from the power system
Drilling fluid is mixed in the mud pits and pumped by the mud pumps through the swivel, through the blow out preventer (not part of the circulation system) down the hollow drill pipe, through holes (Jet Nozzles) in the bit, up the annular space between drill pipe and wellbore (where it lifts the rock cuttings), to the surface, through the Solids Control Equipment (Shale Shaker, Desander, and Desilter), and back to the mud pits. A schematic of the circulation system is shown in Figure 9.05.
In this figure, fresh water-based drilling fluid (mud) is mixed with water from the Water Tank (not shown in Figure 9.05) and components from the Bulk Mud Components Storage (not shown in Figure 9.05) in the Mud Pit. The Mud Pumps then pump the mud through the swivel, kelly, kelly bushing, and rotary table down to the drill string.
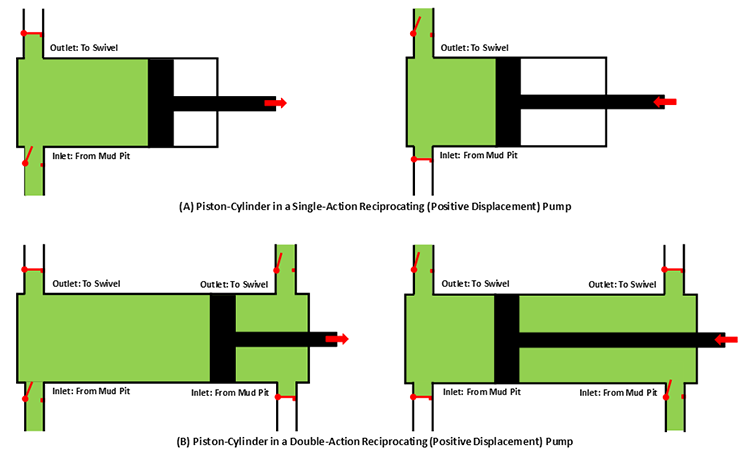
The mud pumps on a typical drilling rig are either single-action or double-action Reciprocating (Positive Displacement) Pumps which may contain two pistons-cylinders (duplex pump) or three pistons-cylinders (triplex pump). Figure 9.06 shows schematics of a single piston-cylinder in (A) a single-action and (B) a double-action reciprocating pump.
In these pumps, the positive pressure and negative pressure (suction) in the cylinder cause the valves to open and close (note: the valves in the schematic are simple representations of the actual valves). Due to the high viscosity of the drilling fluid, the inlet side of the pump may require a Charge Pump to keep fluids moving into the cylinders at high pressures and to prevent Cavitation in the pump.
From the mud pumps, the drilling fluid goes to the swivel, through the blow out preventer, and down the hollow drill string and bottom-hole assembly. The drilling fluid then goes through jet nozzles in the drill bit; at which point, it begins its return to the surface. The drilling fluid travels up the annular space between the drill pipe and the wellbore, picking up and carrying the drill cuttings up the hole.
Once the drilling fluid reaches the surface, it goes through the mud return line to the gas-mud separator and the solids control equipment. The shale shaker is where the large cuttings from the returning drilling fluid are removed. The shale shaker is a set of vibrating mesh screens that allow the mud to pass through while filtering out cuttings of different size at screen screen mesh sizes. A Mudlogger or a Well-Site Geologist may be stationed at the shale shaker to analyze the cuttings to determine the lithology of the rock and the depth within the Stratigraphic Column at which the well is currently being drilled.
The drilling fluid is then sent through a degasser to remove any gas bubbles that have been picked up during the circulation. These gasses may include natural gas from the subsurface or air acquired during the solids control. Typically, the degasser is a piece of equipment that subjects the drilling fluid to slight vacuum to cause the gas to expand for extraction. The drilling fluid is then returned to the mud pit to start the circulation process over again.
We have discussed the mechanics of how the drilling fluid is circulated during the drilling process, but we have not discussed the role of the drilling fluid. The term “mud” is often used in oil and gas well drilling because historically the most common water-based drilling fluids were mixtures of water and finely ground, bentonite clays which, in fact, are muds.
As I stated earlier, historically drilling fluids were mixtures of bentonite clay, water, and certain additives to manipulate the properties of the mud (density, viscosity, fluid loss properties, gelling qualities, etc.). Today, there are several different options available for drilling fluids. These include:
Of the listed drilling fluids, the water-based muds and the oil-based muds are the most common; foam drilling and air drilling can only be used under specialized conditions. Of the two liquid based mud systems (water-based muds and oil-based muds), water-based muds are the most common mud system. They are more environmentally friendly and are used almost exclusively to drill the shallow portions of the well where fresh water aquifers exist to minimize any contamination to those aquifers. As this implies, drilling fluids can be – and often are – switched during the course of drilling operations in single well.
In addition, water-based muds are cheaper than oil-based muds, so they are used to reduce drilling costs and commonly represent the “default” selection for a drilling fluid. In other words, water-based muds are often used unless there is a specific reason to switch to an oil-based mud.
Oil-based muds are formulated with diesel oil, mineral oil, or synthetic oils as a continuous phase and water as a dispersed phase in an emulsion. In addition, additives such as emulsifiers and gelling agents are also used. They were specifically developed to address certain drilling problems encountered with water-based muds. The reasons for using an oil-based mud include:
drilling through shales that are susceptible to swelling (in particular, highly smectite-rich shales). Shales contain a large amount of clay material and when these clays come in contact with the water in a water-based mud system, the clays may swell causing the shales to collapse into the hole. Smectite-rich shale formations are often referred to as “Gumbo” or “Gumbo Clays” in the drilling industry;
reducing torque and drag problems in deviated wells. Since oil, a lubricant, is the continuous phase in the mud system, the torque and drag between the drill pipe and the wellbore is reduced with oil-based muds;
achieving greater thermal stability at greater depths. Oil-based muds have been found to retain their stability (retain their desired properties) at greater down hole temperatures;
achieving greater resistance to chemical contamination. Many substances found down-hole (salt, CO2, H2S, etc.) are soluble in water. The introduction of these substances into the water-based mud system may have a deleterious impact on different mud properties (density, viscosity, fluid loss properties, gelling properties, etc.). These substances are not soluble in oil and, therefore, have will not impact oil-based mud properties.
The first three bullet points in this list are becoming more common problems in the oil and gas industry. The shale boom in the U.S. has made long horizontal sections in shale reservoirs targets for drilling. In addition, deviated wells and deeper wells are also becoming more common. For these reasons, the use of oil-based muds is also becoming more common.
high initial costs. Often in an active drilling campaign, if certain depth intervals require an oil-based mud, the mud is stored and reused in different wells;
slow rates of penetration. Historically, the rate of penetration has been statistically slower for oil-based muds than it is for water-based muds. The rate of penetration is the speed at which the drilling process progresses (depth versus time) and is a function of many factors other than mud type, including: weight on bit, RPM, lithologies being drilled through, bit type, bit wear, etc.;
kick detection. If gas enters the wellbore (a Kick), it may go into solution in the oil in deeper, higher pressure sections of the well and come out of solution closer to the surface;
formation evaluation. Some readings from well logs or core analysis may be sensitive to oil entering the formation of interest (for example, if oil from the oil-based mud enters the reservoir in the near-well vicinity, then tools used to detect oil saturation may read artificially high).




 8613371530291
8613371530291