receprecating mud pump in portuguese in stock
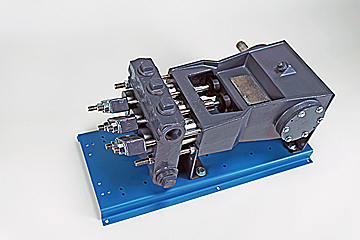
A mud pump is a reciprocating piston/plunger pump designed to circulate drilling fluid under high pressure (up to 7,500 psi (52,000 kPa)) down the drill string and back up the annulus. A duplex mud pump is an important part of the equipment used for oil well drilling.
Duplex mud pumps (two piston/plungers) have generally been replaced by the triplex pump, but are still common in developing countries. Two later developments are the hex pump with six vertical pistons/plungers, and various quintuplex’s with five horizontal piston/plungers. The advantages that Duplex mud pumps have over convention triplex pumps is a lower mud noise which assists with better Measurement while drilling and Logging while drilling decoding.
Use duplex mud pumps to make sure that the circulation of the mud being drilled or the supply of liquid reaches the bottom of the well from the mud cleaning system. Despite being older technology than the triplex mud pump, the duplex mud pumps can use either electricity or diesel, and maintenance is easy due to their binocular floating seals and safety valves.
A mud pump is composed of many parts including mud pump liner, mud pump piston, modules, hydraulic seat pullers, and other parts. Parts of a mud pump:housing itself
Duplex pumps are used to provide a secondary means of fuel transfer in the event of a failure of the primary pump. Each pump in a duplex set is sized to meet the full flow requirements of the system. Pump controllers can be set for any of the following common operating modes:Lead / Lag (Primary / Secondary): The lead (primary) pump is selected by the user and the lag (secondary pump operates when a failure of the primary pump is detected.
Alternating: Operates per Lead / Lag (Primary / Secondary) except that the operating pump and lead / lag status alternate on consecutive starts. A variation is to alternate the pumps based on the operating time (hour meter) of the lead pump.

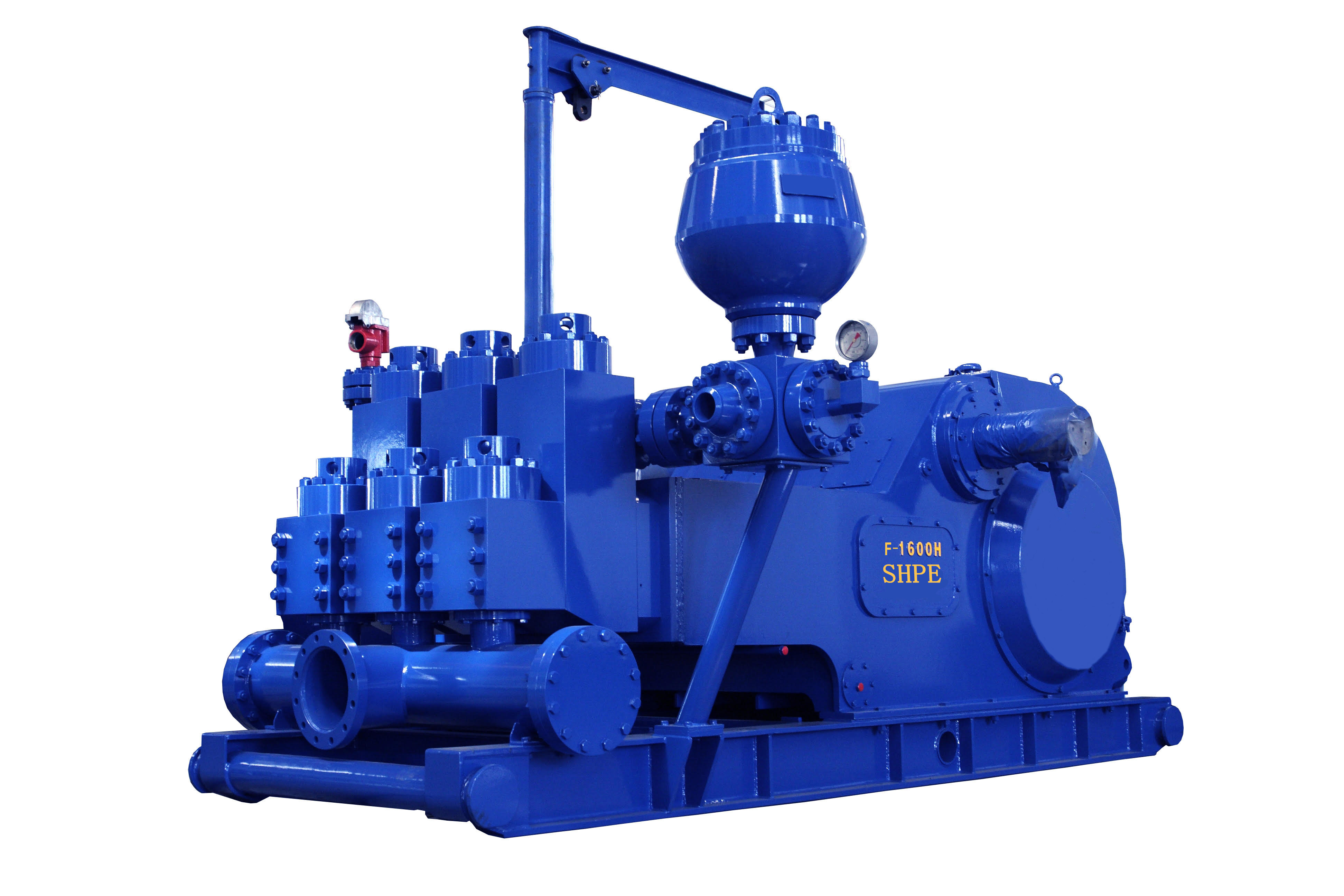
The NOV FC-1600 Triplex Mud Pump is made of rugged Fabriform construction and designed for optimum performance under extreme drilling conditions. It is compact and occupies less space, yet delivers unequaled performance. The pumps are backed by several decades of design and manufacturing experience, and are considered leaders in the field.
NOV FC-1600 Triplex Mud Pump is conservatively rated at relatively low rpm. This reduces the number of load reversals in heavily stressed components and increases the life of the fluid end parts through conservative speeds and valve operation.
The NOV FC-1600 Triplex Mud Pump design provides an inherently balanced assembly. No additional counterbalancing is required for smooth operation. No inertia forces are transmitted to the pumps’ mountings.
A Triplex Mud Pump sometimes referred to as a drilling mud pump or mud drilling pump. NOV FC-1600 Triplex Mud Pump is a reciprocating piston/plunger pump designed to circulate drilling fluid under high pressure (up to 7,500 psi) down the drill string and back up the annulus. A mud pump is an important part of the equipment used for oil well drilling.

This website is using a security service to protect itself from online attacks. The action you just performed triggered the security solution. There are several actions that could trigger this block including submitting a certain word or phrase, a SQL command or malformed data.

Triplex plunger-type mud pumps feature a reciprocating, positive displacement pump design utilizing three plungers to safely transfer high-viscosity fluids under high pressure over an extended depth. Although they have many industrial applications, these pumps have become an essential part of oil well drilling rigs where they’re used to provide smooth discharge of mud and debris from oil wells.
In addition to their use in drilling and well service operations, mud pumps are also frequently used to handle corrosive or abrasive fluids, as well as slurries containing relatively large particulates, in applications like commercial car washes, wastewater treatment, cementing, and desalination operations.
DAC Worldwide’s Representative Triplex, Plunger Mud Pump Dissectible (295-418) is an economical, conveniently-sized triplex plunger-type mud pump assembly that teaches learners hands-on maintenance activities commonly required on larger mud pump assemblies used in upstream oilfield production operations.
For example, mud pump assembly is used on well sites maintain downhole backpressure, to lubricate the rotating drill bit, and to help recycle and remove rock debris resulting from drilling activities. These heavy-duty, high-pressure pumps require regular refurbishment, inspection, and repair in the field.
DAC Worldwide’s dissectible mud pump assembly is a realistic sample that’s similar in geometry, design, and operating characteristics to the larger varieties learners will encounter on the job. DAC Worldwide chooses popular name-brand pumps for its dissectibles to ensure industrial and oil and gas training relevancy.
Using the dissectible mud pump, learners will gain hands-on experience with the operating principles, regular maintenance activities, and nomenclature/parts identification at a more convenient scale in the classroom or lab.
Technical training is most effective when learners can gain hands-on practice with industry-standard components they’ll encounter on the job. The Representative Triplex, Plunger Mud Pump Dissectible features a wide variety of common, industrial-quality components to provide learners with a realistic training experience that will build skills that translate easily to the workplace.
The Representative Triplex, Plunger Mud Pump Dissectible is a sturdy unit with a complete triplex, reciprocating, 20+ bhp plunger pump with .75" plunger, 1.5" stroke, and 3" cylinder sleeve. The unit allows for complete disassembly, assembly, and inspection, including removal of plungers, packing, and valves.
The dissectible mud pump comes with a formed-steel, powder-coated baseplate. It can also be mounted on a compatible DAC Worldwide Extended Electromechanical Workstation (903). Each unit comes with the manufacturer’s installation and maintenance manual.

Application of High Pressure Reciprocating Pumps can be noticed in pharmaceutical, waste water treatment and also in other industries. This range of pumps is suitable for heavy duty applications. These pumping systems are driven by diesel fueled engine/electric motor/gas engine. Operating pressure, diameter of pump and its weigh vary as per different models. Operating pressure of these equipments can be adjusted by using their built in speed reduction gear. Provided High Pressure Reciprocating Pumps are well known for their ergonomic appearance, functional stability and user friendly mechanism. Standard of this array of pumps has been checked as per its operating cost, longevity, performance, noise generation level, diameter and structural strength.

A mud pump (sometimes referred to as a mud drilling pump or drilling mud pump), is a reciprocating piston/plunger pump designed to circulate drilling fluid under high pressure (up to 7,500 psi or 52,000 kPa) down the drill string and back up the annulus. A mud pump is an important part of the equipment used for oil well drilling and manufactured according to API specification 7K.
The advantages of the drilling mud pump include the ability to move high-solids-content fluids laden with abrasives, the ability to pump large particles, ease of operation and maintenance, reliability, and the ability to operate over a wide range of pressures and flow rates by changing the diameter of pump liners and pistons.
The fluid end includes cylinders (module), valve assembly, cylinder liners, piston assembly, suction manifold, discharge manifold, piston rod, pulsation dampener assembly, etc.
As an important equipment for oilfield drilling operation, a drilling mud pump delivers circulating high-pressure drilling fluid or drilling mud to the bottom of the oil well, flushes the bottom of the well, breaks the rock, cools, lubricates and clean the drill bit, and carries the cuttings back to the ground.
The drilling mud is also used to suspend and carry out drill cuttings from the drill bits as it is brought in and out of the hole. This ensures that the drill bit does not clog and overheat, and makes the entire drilling operation smooth and safe.
Rotational power is supplied to the mud pump through an external power source like a diesel engine or electric motor. The power end of the mud pump converts the rotational energy through a crankshaft to a reciprocating motion of pistons.
The pistons move back and forth in mud pump liners, exerting a force on the cylinder chamber. During the retraction of the piston, valves open to allow the fluid to be drawn into the cylinder. Once the piston has fully retracted, it is pushed back into the cylinder.
At this time the intake valves are closed and the exhaust valves open, allowing the piston to force the fluid out of the cylinder under pressure. Once the piston reaches its maximum depth into the cylinder, the exhaust valves close and the process repeats.
For Fluid End: piston rod clamp, piston rod, piston assembly, cylinder cover, liner, liner flange, wear plate, cylinder, valve assembly, valve cover, valve guide, flashboard assy., cylinder cover flange, cylinder head, gaskets, studs, nuts, seal rings, pulsation dampener, bladder, discharge manifold, suction manifold, etc.

As one of the world"s leading pump manufacturers, Sulzer provides a wide range of products for engineered, configured, and standard pumping solutions as well as essential auxiliary equipment. We are renowned for our state-of-the-art products, performance reliability and efficient solutions.

A positive displacement (PD) pump is a piece of equipment that traps a fixed volume of fluid and physically moves it through a system. A reciprocating pump is a more specific type of PD pump that uses the repeated back and forth motion of a piston, plunger, or diaphragm. This cyclic motion is referred to as reciprocation and is the mechanism by which fluid is driven through the pump.
The nomenclature of a reciprocating pump is derived from the component which drives pressure. In a piston pump the primary component is a cylinder, or piston, with a seal about its outer diameter. A smooth rod known as a plunger moves through a stationary seal in a plunger pump. For a diaphragm pump, a flexible element called a diaphragm expands or contracts.
A piston, plunger, or diaphragm is a primary component of a reciprocating pump. This works inside a chamber which defines the ultimate pump volume. A connecting rod is attached to a motor crank on one end and the piston, plunger, or diaphragm on the other. A suction pipe allows fluid to be drawn into the chamber, while a delivery pipe allows fluid to be discharged. Inlet and outlet valves check the flow of fluid into and out of the chamber.
Suction phase:The piston, plunger, or diaphragm is pulled back which increases chamber volume and thereby creates a vacuum. This process opens the inlet valve and closes the outlet valve. Vacuum acting on the chamber pulls fluid through the inlet.
Compression phase: After the piston, plunger, or diaphragm has reached its maximum displacement it is then pushed back into the chamber. The inlet valve is closed and the outlet valve is opened. Fluid is then discharged under pressure through the outlet.
Reciprocating pumps are capable of producing tremendous pressure, with some designs generating more than 69Mpa (10,000psi). They also have a fixed volume of fluid displacement at a given speed which allows them to perform well in low flow applications such as dispensing and metering. Reciprocating pumps are effective in handling high viscosity fluids such as paints, oils, and resins. They can also handle fluids containing solids that might otherwise erode components of a high-speed rotary pump. Diaphragm pumps in particular can be used for handling of especially aggressive chemicals.
While there are several advantages to reciprocating pumps, a disadvantage is the production of pressure pulsations created by this reciprocating motion. Pulsation dampeners can be installed to minimize damage to the pump itself and surrounding systems. Another disadvantage versus rotary pumps, is the relative maintenance required. While mean time between maintenance (MTBM) may be less, the cost and time of repair is still relatively low.
Reciprocating pumps are used across numerous industries including Oil & Gas, Chemical Processing, Automotive, Medical, and others. These may be overlooked as they are in some cases used in equipment with which we are familiar.
A piston or plunger type pump is used when drilling in the oilfield to deliver a fluid called mud. This mud may consist of many suspended particles. It acts to cool the drill bit, prevent the drilled hole from collapse, and return drilled shavings to the surface.
High performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) is an analytical technique used to identify and quantify the components in a mixture. It is an important tool in pharmaceutical applications for evaluating formulations. The plunger pump may exceed 138Mpa (20,000psi) through a fluid column.
Chemical injection is used to inhibit deposits, limit corrosion, and keep systems flowing. This is becoming more commonly used in upstream to midstream operations in Oil & Gas. Chemicals are delivered in doses and include solvents, corrosion inhibitors, biocides, and many others.
Paint is used across industries to color and protect structures and equipment. Spraying affords even and efficient application of paint, with the pump an important part of that system.
Water blasting is a technique used for cleaning internal and external surfaces. Results are comparable to other techniques which use cleaning agents and abrasives potentially harmful to the environment. Pressure driving the water stream can reach 172Mpa (25,000psi).
The seal around the piston, stationary seal through which the plunger moves, or diaphragm must be maintained to avoid leakage. Sealing challenges for diaphragm pumps can be somewhat different, and in order to focus on piston and pump sealing challenges see below for some of the conditions that may limit seal life and cause frequent MTBM intervals:
Incorrect sealing solution:Appropriate material selection is necessary to ensure compatibility with the fluid medium and across the application temperature range. Design geometry must ensure effective sealing against pressure.
Inappropriate seal installation: Guidelines are helpful to ensure appropriate and consistent installation. In some case, tools may be needed to help facilitate the process.
Lubrication is insufficient: Insufficient lubrication can lead to excessive friction, high heat, and subsequent seal failure. Material selection is essential and lubricant injection may be needed.
Misalignment of piston to seal bore, or plunger to packing space: Eccentric loading can result in poor sealing. Centralization devices located close to the seal can help minimize this.
Excessive wear in seal bore or on plunger: Seal material or fluid media can be particularly abrasive. Hardening or coating of seal bore or plunger may be needed.
Presence of solids in medium: While reciprocating pumps are relatively capable of handling media with particulates, excluder devices may be warranted to protect seals and sealing surfaces.
Seal stacks provide redundant sealing elements and are good solutions for reciprocating pump applications. Spring energized seals (SES) or spring loaded packing can provide further benefit. One reason is they require no adjustment to the gland which can remove operator error. Another is that they allow for expansion which may occur due to thermal growth or application of system pressure.
If you have any questions about seals for reciprocating pumps, contact your local Chesterton office or our “Ask the Expert” service. They can help with material selection, geometry, and overall system design to ensure optimal performance of your equipment.
Ron Taylor is the Business Development Manager for the spring energized seal (SES) product line. He has an Engineering background in the design & development of seals and related materials. He is able to promote these through his understanding of markets including Oil & Gas, Aerospace, and Industrial.

The 2,200-hp mud pump for offshore applications is a single-acting reciprocating triplex mud pump designed for high fluid flow rates, even at low operating speeds, and with a long stroke design. These features reduce the number of load reversals in critical components and increase the life of fluid end parts.
The pump’s critical components are strategically placed to make maintenance and inspection far easier and safer. The two-piece, quick-release piston rod lets you remove the piston without disturbing the liner, minimizing downtime when you’re replacing fluid parts.

BW1500/12 mud pump for drilling rig is horizontal, four-cylinder, reciprocating single acting piston pump. Can be transformed into two different pressure and flow. Its max pressure can arrive 15Mpa.

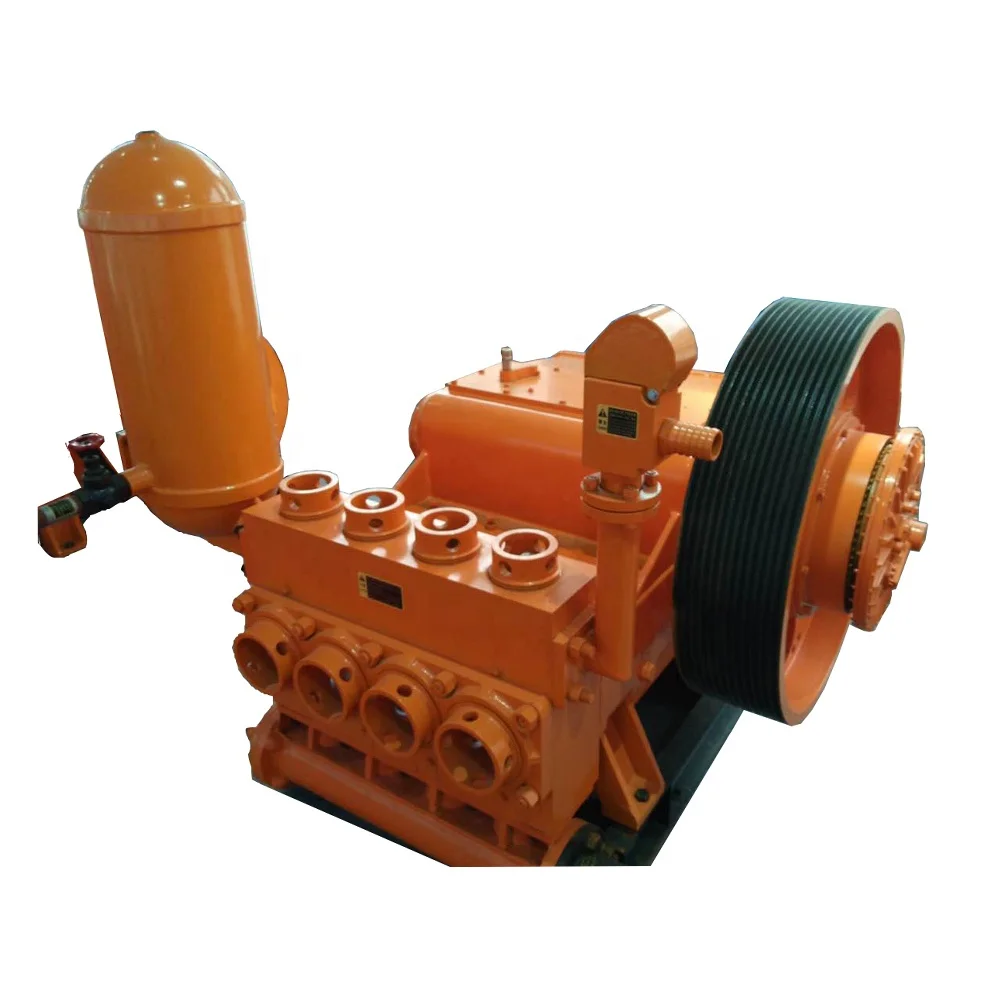
3NB Triplex and quintuplex piston reciprocating pump are mainly used in oil delivery, oil receiving, circulation mud, slim hole shallow well drilling, etc. This series of mud pumps is easy in operation and maintenance and reliable with the good absorbing property. It can directly absorb from the ground and pools (like mud pool and pool) below 2 meters with absorbing pipe below 4M under the elevation of 1000 meters without poured into, with natural absorption efficiency >95%.
It can also apply to other high-pressure liquid transportation with self-absorb. Cylinder material: alloy steel, stainless steel, duplex steel or aluminum bronze; cylinder liner material: bi-metal or ceramic; piston material: rubber or polyurethane; suction /discharge valve adopt API standard valve, ball valve, plate valve, cone valve, etc.

If you ended up on this page doing normal allowed operations, please contact our support at support@mdpi.com. Please include what you were doing when this page came up and the Ray ID & Your IP found at the

Gear pumps are one of the most common types of positive displacement pumps. They provide a constant volume of fluid that passes between the teeth of two meshing gears and the casing. The rotating gears and separation of teeth create a suction that pulls fluid in through the inlet. The gears then trap the liquid and move it around the casing to the discharge or outlet. Each revolution creates consistency in the flow of fluid.
There are two main types of rotary gear pumps, internal and external. Both types use similar principles for pumping fluids. Two gears are inside a casing in a way that the teeth lock together. As a motor turns one of the gears the locking teeth turn the other. The difference in the two designs is that an external gear pump uses side-by-side gears (typically the same size), so when the motor turns one gear, the other rotates in the opposite direction. The internal gear pump design uses two different size gears. A motor turns the small gear, which is inside the larger gear, rotating it in the same direction.
DAE Pumps offers economical rotary gear pumps of both types in a variety of sizes. No other gear pumps can match the performance and durability of our pumps. Because of the close tolerance between the gears and casing, most gear pumps are highly susceptible to wear, but DAE Pumps gear pumps outperform all others. Our pumps process a wide range of viscosities and are ideal for handling fluids at high pressures and low flow rates. DAE Pumps rotary gear pumps are widely used in chemical installations to pump high viscosity fluids. They are one of the most common types of pumps for moving corrosive liquids and hydraulic fluid power applications.
DAE pumps gear pumps provide consistency in moving a variety of slurry materials and are suitable for several industries like paints, food processing, chemicals, oil & gas, and others. Our rotary gear pumps are available in duplex steel, cast steel, and cast iron, among other materials. Contact DAE Pumps to customize a pump to your specific needs.




 8613371530291
8613371530291