triplex mud pump drawing free sample

Choose a used Emsco FB-1600 Triplex Mud Pump from our inventory selection and save yourself some money on your next shallow drilling oilfield project. This Emsco FB-1600 Triplex Mud Pump is used and may show some minor wear.
We offer wholesale pricing on new Emsco FB-1600 Triplex Mud Pump and pass the savings on to you. Contact us to compare prices of different brands of Mud Pump. This equipment is brand new and has never been used.
Our large network often has surplus Emsco FB-1600 Triplex Mud Pump that go unused from a surplus purchase or a project that was not completed. Contact us to see what Emsco FB-1600 Triplex Mud Pump we have in inventory. The surplus Emsco FB-1600 Triplex Mud Pump are considered new but may have some weathering depending on where it was stored. Surplus oilfield equipment is usually stored at a yard or warehouse.
We have refurbished Mud Pumpthat have been used and brought up to functional standards. It is considered a ready to use, working Mud Pump. Please contact us for more information about our refurbished Emsco FB-1600 Triplex Mud Pump. These Mud Pump have been used and brought up to functional standards. It is considered a working Mud Pump. Please contact us for more information about the product.

Since the NOV A1700-PT Triplex Mud Pump was built approximately 60 years ago, the industry has widely accepted the three cylinder or triplex style pump. Triplex mud pumps are manufactured worldwide, and many companies have emulated the original design and developed an improved form of the triplex pump in the past decade.
NOV A1700-PT Triplex Mud Pumps have many advantages they weight 30% less than a duplex of equal horsepower or kilowatts. The lighter weight parts are easier to handle and therefore easier to maintain. The other advantages include;They cost less to operate
One of the more important advantages of triplex over duplex pumps, is that they can move large volumes of mud at the higher pressure is required for modern deep hole drilling.
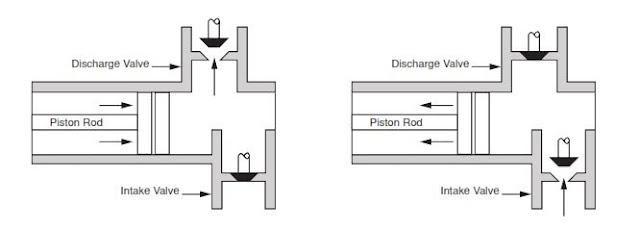
NOV A1700-PT Triplex Mud Pump is gradually phasing out duplex units. In a triplex pump, the pistons discharge mud only when they move forward in the liner. Then, when they moved back they draw in mud on the same side of the piston. Because of this, they are also called “single acting.” Single acting triplex pumps, pump mud at a relatively high speeds. NOV A1700-PT Triplex Mud Pump has three pistons each moving in its own liner. It also has three intake valves and three discharge valves. It also has a pulsation dampener in the discharge line.

Besides the production,Tecno Meccanica Emiliana is able to offer3D CAD/CAM design service. This allows us to design and produce parts even starting from simple drawings or samples already made and free of designs.

Rig pump output, normally in volume per stroke, of mud pumps on the rig is one of important figures that we really need to know because we will use pump out put figures to calculate many parameters such as bottom up strokes, wash out depth, tracking drilling fluid, etc. In this post, you will learn how to calculate pump out put for triplex pump and duplex pump in bothOilfield and Metric Unit.
The 2,200-hp mud pump for offshore applications is a single-acting reciprocating triplex mud pump designed for high fluid flow rates, even at low operating speeds, and with a long stroke design. These features reduce the number of load reversals in critical components and increase the life of fluid end parts.
The pump’s critical components are strategically placed to make maintenance and inspection far easier and safer. The two-piece, quick-release piston rod lets you remove the piston without disturbing the liner, minimizing downtime when you’re replacing fluid parts.

Pumps tend to be one of the biggest energy consumers in industrial operations. Pump motors, specifically, require a lot of energy. For instance, a 2500 HP triplex pump used for frac jobs can consume almost 2000 kW of power, meaning a full day of fracking can cost several thousand dollars in energy costs alone!
So, naturally, operators should want to maximize energy efficiency to get the most for their money. Even a 1% improvement in efficiency can decrease annual pumping costs by tens of thousands of dollars. The payoff is worth the effort. And if you want to remotely control your pumps, you want to keep efficiency in mind.
In this post, we’ll point you in the right direction and discuss all things related to pump efficiency. We’ll conclude with several tips for how you can maintain pumping efficiency and keep your energy costs down as much as possible.
In simple terms, pump efficiency refers to the ratio of power out to power in. It’s the mechanical power input at the pump shaft, measured in horsepower (HP), compared to the hydraulic power of the liquid output, also measured in HP. For instance, if a pump requires 1000 HP to operate and produces 800 HP of hydraulic power, it would have an efficiency of 80%.
Remember: pumps have to be driven by something, i.e., an electric or diesel motor. True pump system efficiency needs to factor in the efficiency of both the motor AND the pump.
Consequently, we need to think about how electrical power (when using electric motors) or heat power (when using combustion engines) converts into liquid power to really understand pump efficiency.
Good pump efficiency depends, of course, on pump type and size. High-quality pumps that are well-maintained can achieve efficiencies of 90% or higher, while smaller pumps tend to be less efficient. In general, if you take good care of your pumps, you should be able to achieve 70-90% pump efficiency.
Now that we have a better understanding of the pump efficiency metric, let’s talk about how to calculate it. The mechanical power of the pump, or the input power, is a property of the pump itself and will be documented during the pump setup. The output power, or hydraulic power, is calculated as the liquid flow rate multiplied by the "total head" of the system.
IMPORTANT: to calculate true head, you also need to factor in the work the pump does to move fluid from the source. For example, if the source water is below the pump, you need to account for the extra work the pump puts in to draw source water upwards.
*Note - this calculation assumes the pump inlet is not pressurized and that friction losses are minimal. If the pump experiences a non-zero suction pressure, or if there is significant friction caused by the distance or material of the pipe, these should be factored in as well.
You"ll notice that the elevation head is minimal compared to the discharge pressure, and has minimal effect on the efficiency of the pump. As the elevation change increases or the discharge pressure decreases, however, elevation change will have a greater impact on total head.
Obviously, that’s a fair amount of math to get at the pump efficiency, considering all of the units conversions that need to be done. To avoid doing these calculations manually, feel free to use our simple pump efficiency calculator.
Our calculations use static variables (pump-rated horsepower and water source elevation) and dynamic variables (discharge flow and pressure). To determine pump efficiency, we need to measure the static variables only once, unless they change.
If you want to measure the true efficiency of your pump, taking energy consumption into account, you could add an electrical meter. Your meter should consist of a current transducer and voltage monitor (if using DC) for electrical motors or a fuel gauge for combustion. This would give you a true understanding of how pump efficiency affects energy consumption, and ultimately your bank account.
Up until this point, we’ve covered the ins and outs of how to determine pump efficiency. We’re now ready for the exciting stuff - how to improve pump efficiency!
One of the easiest ways to improve pump efficiency is to actually monitor pumps for signs of efficiency loss! If you monitor flow rate and discharge (output power) along with motor current or fuel consumption, you’ll notice efficiency losses as soon as they occur. Simply having pump efficiency information on hand empowers you to take action.
Another way to increase efficiency is to keep pumps well-maintained. Efficiency losses mostly come from mechanical defects in pumps, e.g., friction, leakages, and component failures. You can mitigate these issues through regular maintenance that keeps parts in working order and reveals impending failures. Of course, if you are continuously monitoring your pumps for efficiency drops, you’ll know exactly when maintenance is due.
You can also improve pump efficiency by keeping pumps lubricated at all times. Lubrication is the enemy of friction, which is the enemy of efficiency (“the enemy of my enemy is my friend…”).
A fourth way to enhance pump efficiency is to ensure your pumps and piping are sized properly for your infrastructure. Although we’re bringing this up last, it’s really the first step in any pumping operation. If your pumps and piping don’t match, no amount of lubricant or maintenance will help.
In this post, we’ve given you the full rundown when it comes to calculating and improving pump efficiency. You can now calculate, measure, and improve pump efficiency, potentially saving your business thousands of dollars annually on energy costs.
For those just getting started with pump optimization, we offer purpose-built, prepackaged solutions that will have you monitoring pump efficiency in minutes, even in hazardous environments.

CAD blocks: Pumpen HVAC pipes libraries dwg blocks bloques blocos blocchi blocco blocs bl�cke family families symbols details parts models modellen geometry elements entourage cell cells drawing bibliotheque theme category collections content kostenlos insert scale landscaping

This invention relates to apparatus useful in connection with the drilling of wells, such as oil wells, wherein a mud pump is used to circulate drilling mud under pressure through a drill string, down to and around the drill bit and out the annulus of the bore hole of the well to a mud reservoir; the apparatus of the present invention being useful for simultaneously degassing drilling mud and supercharging the mud pump.
In the drilling of deep wells, such as oil wells, it is common practice to penetrate the earth with a drill bit supported on a drill string in the bore of the well being drilled. In order to lubricate the drill bit, protect the well against blowouts, etc., it is conventional practice to circulate mud under pressure through the drill string down to and around the drill bit and up the annulus between the drill string and the bore of the well. Mud flowing from the well is passed through a suitable device such as a shaker, etc., in order to remove drill cuttings, etc., and is then delivered to a mud reservoir, such as a mud tank, for recirculation to the mud pump for pressured injection into the well.
It is also conventional practice to use a mud pump, such as a duplex or triplex mud pump comprising reciprocating pistons mounted in cylinders for pressuring the incoming drilling mud and delivering it to the well bore under pressure. The operation and construction of mud pumps is well known to those of ordinary skill in the art, as illustrated, for example, by the textbook "Mud Pump Handbook" by Samuel L. Collier (Gulf Publishing Company, Houston, Tex., 1983).
It is known, as explained in the Collier handbook, that the efficiency of a mud pump can be significantly improved by supercharging the pump; that is, by delivering drilling mud under pressure to the mud pump inlet to the cylinders containing the reciprocating pumping pistons.
It is also known to remove occluded gasses such as air, methane, etc., from drilling mud before it is delivered to the mud pump as illustrated, for example, by Burgess U.S. Pat. No. 3,973,930, Burgess U.S. Pat. No. 3,999,965 and Burgess U.S. Pat. No. 4,084,946.
Other drilling mud degassing devices are known to the art, such as those disclosed in Phillips et al. U.S. Pat. No. 4,088,457, Brown et al. U.S. Pat. No. 4,113,452, Egbert U.S. Pat. No. 4,365,977, Gowan et al. U.S. Pat. No. 4,397,659, etc.
Mud pumps used for delivering drilling mud under pressure to the bore hole of a well are conventionally of the type wherein a reciprocating piston in a cylinder is used to pressure drilling mud delivered to the cylinder for delivery to the well bore. Normally, two or three such cylinders are used, such pumps being conventionally referred to as duplex and triplex pumps. During each stroke of the piston, the piston is initially accelerated by an appropriate drive means, such as a crank shaft, from a starting position to a midcylinder position, and then decelerated to a final position within the cylinder. This constantly changing rate of motion of a reciprocating piston can result in knocking, cavitation, etc., all of which impair the efficiency of the pump. It is known to use centrifugal pumps, commonly known as superchargers, in order to deliver drilling mud to the inlet of the cylinder under pressure in order to alleviate such problems and improve the efficiency of operation of the pump.
It is undesirable to recirculate drilling mud containing occluded gases to a well bore, and therefore it is common practice to remove a significant portion of occluded gas from the drilling mud before it is recirculated to the mud pump. Normally, separate pieces of equipment that operate independently of each other are used for supercharging the mud pump and for degassing the drilling mud.
It has been discovered in accordance with the present invention that a drilling mud degasser of the type disclosed in the Burgess patents can be modified to simultaneously degas drilling mud and to supercharge the mud pump to which the degassed mud is to be delivered.
This is accomplished in accordance with the present invention through the provision of a device for simultaneously supercharging a mud pump having pistons reciprocably mounted in cylinders while degassing drilling mud to be delivered to said pistons comprising:
vacuum chamber means for continuously accelerating and centrifuging drilling mud under vacuum to thereby substantially completely remove occluded gas from the drilling mud,
a first conduit interconnecting said vacuum chamber with a drilling mud reservoir for delivering drilling mud to be degassed to said vacuum chamber means,
a first valve controlled branch conduit interconnecting said second conduit with said drilling mud reservoir for delivering drilling mud to said drilling mud reservoir when the pressure in said second conduit exceeds a predetermined value, and
a second branch conduit containing normally closed flow control means interconnecting said second conduit with said first conduit and said drilling mud reservoir operable on loss of pressure in said second conduit to permit flow of drilling mud directly from said drilling mud reservoir to said second conduit.
In the accompanying drawing, the FIGURE is a schematic elevation view, with parts broken away, showing a preferred embodiment of the present invention.
Referring now to the drawing, there is shown a supercharging drilling mud degasser 10 of the present invention which comprises a degassing chamber designated generally by the number 12, a power source such as an electric powered motor or a hydraulically powered motor designated generally by the number 14, a vacuum blower such as a regenerative vacuum blower, designated generally by the number 16, a gear box designated generally by the number 18, an evacuation pump designated generally by the number 20 and a drilling mud chamber designated generally by the number 22.
In accordance with this construction, there is provided a drilling mud degasser of the type shown in Burgess U.S. Pat. No. 4,084,946, housed in a cylindrical pressure vessel 24. The motor 14 is supported on vacuum blower 16 which, in turn, is supported by vacuum motor support 26 and vacuum blower brackets 28. To facilitate movement of the degasser 10, motor handling brackets 30 may be provided on the top of the motor 14 to which the hook of a crane or other appropriate means (not shown) may be attached.
Drilling mud pump impeller 42 is fixed to the centrifuge tube 40 for rotation therewith within the housing 46 of drilling mud evacuation pump 20. Cross braces 48 mounted in the cylindrical vessel 24 support lower stops 50 and upper stops 52 for an annular float 56 that surrounds the slots of the centrifuge tube 40 and partially closes them, such that the free area of the slots will be determined by the relative position of the annular float 56.
A drilling mud inlet 60 is connected to the bottom of the housing 46 for the evacuation pump 20 for the delivery of degassed drilling mud thereto. Drilling mud is delivered to the slotted centrifuge tube 40 by an inlet conduit 62 which preferably terminates inside the housing 46 for the evacuation pump 20. The top of the inlet line 62 is spaced from the bottom of the slotted centrifuge tube 40 so that the rotating centrifuge tube 40 can rotate freely without bearing upon the top of the inlet line 62. The resultant "controlled seepage" of fluid from the inlet tube 62 into the evacuation pump 20 provides a low pressure area for high effeciency scanvenging of occluded gases. Also, there is no need for bearings and seals at the bottom of the slotted centrifuge tube 40.
With this construction there is also provided an outlet line or conduit 66 connected with the discharge side of the evacuation pump 20 and extending through the wall of the cylinder 24 for connection with a suitable first conduit 68 leading, for example, to a triplex pump 70 for injecting drilling mud under pressure into a well penetrating a subterranean formation in order to lubricate the drill bit, protect the well against blow outs, etc., it is conventional practice to circulate mud under pressure through the drill string down to and around the drill bit and up the annulus beteen the drill string and the bore of the well. Mud flowing from the well is passed through a suitable device such as a shaker, etc. (not shown) in order to remove drill cuttings, etc., and is then delivered to a mud reservoir, such as a mud tank 84, for recirculation to the mud pump 70 in the manner described herein for pressured injection into the well.
The first conduit 68 may comprise, for example, a connecting pipe 72 interconnecting the outlet line 66 with the flexible hose 74 which, in turn, is connected to a mud pump inlet line 76. The flexible hose 74, which is provided for ease in alignment, may be secured to the connecting pipe 72 by a clamp 78 of any suitable construction and to the mud pump inlet line 76 by a clamp 80 of any suitable construction.
A second conduit 82 interconnects a drilling mud reservoir such as a mud tank 84 with the inlet conduit 62 leading to the slotted centrifuge tube 40 for the degasser 10.
Preferably, the second conduit 82 is provided with valve means such as a butterfly valve 86 which may be used to close the second conduit 82 when both the drilling mud degasser 10 and the mud pump 70 are to be idled for any appreciable time.
A first branch conduit 88 interconnects the first conduit 68 with the mud tank 84 and contains pressure sensitive control means such as a spring biased relief valve 90 in order to permit drilling mud to recycle from the first conduit 68 to the mud tank 84 when the pressure in the first conduit 68 exceeds a predetermined value.
A second branch conduit 92 interconnects the first conduit 68 with the inlet conduit 62 and the second conduit 82. The second branch conduit 92 contains normally closed flow control means such as a check valve 94 to permit flow of drilling mud directly from the mud tank 84 to the mud pump 70 if the pressure in the first conduit 68 falls below a predetermined value.
During drilling operations, rotation of an appropriate vacuum blower such as a regenerative vacuum blower by the drive shaft 32 for the motor 14 will generate a vacuum in the degassing chamber 12 such that drilling mud sprayed from the slots in the centrifuge tube 40 will tend to impact upon the inner sides of the degassing chamber 12 thereby initiating degassing of the drilling mud fed through the inlet line 62. Rotation of the centrifuge tube 40 will impart upward accelerating rotary motion to partially degassed drilling mud delivered thereto through the line 62 and the resultant spraying of the thus centrifuged drilling mud through the slots in the centrifuge tube 40 will result in a sheet of drilling mud being sprayed onto and impacting on the inner walls of the degassing chamber 12 to thus substantially complete the removal of gas from the drilling mud. The thus degassed drilling mud will flow downwardly past cross braces 48 and into inlet 60 leading through the housing 46 of the evacuation pump 20 where the impeller 42 will repressure the now degassed drilling mud for discharge through the outlet line 66 which is interconnected with a triplex pump 70 by first conduit 68 for supercharging the pump 70, which further pressures the degassed drilling mud for injection into a well bore penetrating a subterranean formation.
In order to prevent the entrainment of drilling mud droplets in the gases withdrawn through the gas evacuation suction pipe 98, a splatter plate 100 is provided in the degassing chamber 12 and a combination of a foam separation impeller 36 with a splatter disk 102 is provided adjacent the top of the degassing chamber 12 so that gas liberated in the vacuum chamber must follow a sinuous path arriving at the upper chamber gas evacuation suction pipe 98.
In accordance with the present invention, the motor 14 is operated such that drilling mud delivered to the first conduit 68 will be at a predetermined appropriate supercharging pressure for the mud pump 70, (e.g. a pressure of about 20 to 30 psig).
The pressure sensitive control means, such as a spring biased relief valve 90, is set to open at a predetermined pressure about 5 to 10 psi higher than the desired pressure in the first conduit 68 so that, if the indicated pressure limit is exceeded, the pressure relief valve 90 will open in order to permit drilling mud to recycle to the mud tank 84.
This will happen if the mud pump 70 malfunctions and also when the mud pump 70 is turned off, as will happen from time to time. For example, it is necessary to turn off the mud pump 70 during drilling operations when a new stand of drill pipe is to be added to the drill string. It is also necessary to turn off the mud pump 70 when the drill string is being withdrawn from the well bore in order to replace the drill bit, while well logging operations are in progress, if it is necessary to "fish" for a piece of equipment lost down the hole, etc. However, if the drilling mud in the mud tank 84 is permitted to remain quiescent for more than a limited period of time, the drilling mud may start to gel and/or to stratify. This problem is conventionally avoided by providing a separate agitator (not shown) for the mud tank 84 in order to stir the drilling mud when the mud pump 70 is idle. However, through the provision of the present invention, there is no need for a separate agitator for the mud tank 84 because recirculation of drilling mud through the first branch conduit 88 will impart a "roiling" motion or agitation to the drilling mud in mud tank 84 to inhibit gelling and/or stratification of the drilling mud while the mud pump 70 is idle.
Loss of pressure in the first conduit 68 can occur in the event of malfunction of the degasser 10 or in the event it is desired to shut the degasser 10 down for a limited period of time. In this event, drilling mud flows directly from the mud tank 84 through the second conduit 82, the second branch conduit 92 and the flexible hose 74 to the mud pump 70 so that the mud pum 70 is not "starved" for drilling mud to be injected into the well.




 8613371530291
8613371530291