what is reciprocating mud pump pricelist

This website is using a security service to protect itself from online attacks. The action you just performed triggered the security solution. There are several actions that could trigger this block including submitting a certain word or phrase, a SQL command or malformed data.

This website is using a security service to protect itself from online attacks. The action you just performed triggered the security solution. There are several actions that could trigger this block including submitting a certain word or phrase, a SQL command or malformed data.

There are three types of mud pumps, depending on the type of client and the size they want. For general, mud pumps, there are three basic types of mud pumps, depending on the type of client and budget. The piston pump is another compressed mud pump, which is a pushed electric compressor mud pumps and by compressed air.@@@@@
Electric mud pumps are largely divided into three categories, among them the electric mud pumps and the semi-trash mud pumps. The piston inflated mud pumps are also classified in terms of the type of mud pumps, among them are electric mud pumps and semi-trash mud pumps. In addition, the piston inflates mud and mud pumps will be inflated by the piston, which is inflated mud pumps.

If you are supplying pump supplies, you can find the most favorable prices at Alibaba.com. Whether you will be working with piston type or diaphragm type systems, reciprocating or centrifugal, Alibaba.com has everything you need. You can also shop for different sizes drilling mud pump price wholesale for your metering applications. If you operate a construction site, then you could need to find some concrete pump solutions that you can find at affordable rates at Alibaba.com. Visit the platform and browse through the collection of submersible and inline pump system, among other replaceable models.
A drilling mud pump price comes in different makes and sizes, and you buy the tool depending on the application. The pump used by a filling station is not the one you use to fill up your tanks. There are high flow rate low pressure systems used to transfer fluids axially. On the other hand, you can go with radial ones dealing with a low flow rate and high-pressure fluid. The mixed flow pump variety combines radial and axial transfer mechanisms and works with medium flow and pressure fluids. Depending on what it will be pumping, you can then choose the drilling mud pump price of choice from the collection at Alibaba.com.
Alibaba.com has been an excellent wholesale supplier of drilling mud pump price for years. The supply consists of a vast number of brands to choose from, comes in different sizes, operations, and power sources. You can get a pump for residential and large commercial applications from the collection. Whether you want a water pump for your home, or run a repair and maintenance business, and need a supply of dr drill mud pump prices, you can find the product you want from the vast collection at Alibaba.com.ther it is for refrigeration, air conditioning, transfer, or a simple car wash business, anything you want, Alibaba.com has it.

The 2,200-hp mud pump for offshore applications is a single-acting reciprocating triplex mud pump designed for high fluid flow rates, even at low operating speeds, and with a long stroke design. These features reduce the number of load reversals in critical components and increase the life of fluid end parts.
The pump’s critical components are strategically placed to make maintenance and inspection far easier and safer. The two-piece, quick-release piston rod lets you remove the piston without disturbing the liner, minimizing downtime when you’re replacing fluid parts.

A mud pump is a reciprocating piston/plunger pump designed to circulate drilling fluid under high pressure (up to 7,500 psi (52,000 kPa)) down the drill string and back up the annulus. A duplex mud pump is an important part of the equipment used for oil well drilling.
Duplex mud pumps (two piston/plungers) have generally been replaced by the triplex pump, but are still common in developing countries. Two later developments are the hex pump with six vertical pistons/plungers, and various quintuplex’s with five horizontal piston/plungers. The advantages that Duplex mud pumps have over convention triplex pumps is a lower mud noise which assists with better Measurement while drilling and Logging while drilling decoding.
Use duplex mud pumps to make sure that the circulation of the mud being drilled or the supply of liquid reaches the bottom of the well from the mud cleaning system. Despite being older technology than the triplex mud pump, the duplex mud pumps can use either electricity or diesel, and maintenance is easy due to their binocular floating seals and safety valves.
A mud pump is composed of many parts including mud pump liner, mud pump piston, modules, hydraulic seat pullers, and other parts. Parts of a mud pump:housing itself
Duplex pumps are used to provide a secondary means of fuel transfer in the event of a failure of the primary pump. Each pump in a duplex set is sized to meet the full flow requirements of the system. Pump controllers can be set for any of the following common operating modes:Lead / Lag (Primary / Secondary): The lead (primary) pump is selected by the user and the lag (secondary pump operates when a failure of the primary pump is detected.
Alternating: Operates per Lead / Lag (Primary / Secondary) except that the operating pump and lead / lag status alternate on consecutive starts. A variation is to alternate the pumps based on the operating time (hour meter) of the lead pump.
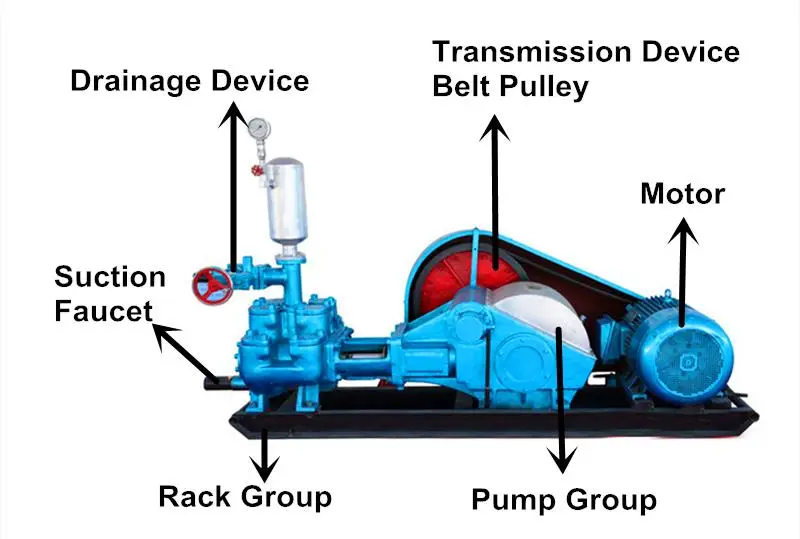
The crank gear and connecting rods drive a rotary movement that is transferred by the motor transmission. The pressure is produced by the piston in the cylinder due to which the mud is sucked. Following the operation, the suction valve is closed when it moves to left. As the pressure increase in the pipeline, the valve is forced to open and mud is released.
In accordance with the operating liquid displacer type being incorporated, the pumps are subdivided into piston units and plunger-type units. The liquid discharge uniformity is independent of head. The pumping plants are used actively for the processes with the liquids containing solid inclusions in high amounts. Incorporating the self-suction function in piston unit, the liquid is sucked and discharged twice in mud pumps during the single shaft turn, making themselves the double-action pumps whereas, the mud plunger pumps are single-action pumps where the liquid is sucked and discharged only once during a shaft turn.
The single direct-action three-piston pumps prove to be better than other types of drilling. These pumps demonstrate much more uniformity in mud delivery, lesser weight, and easy mounting when compared with two-cylinder units.
Depending on the number of cylinders, the pumping plants are classified into the following categories, single-cylinder, double-cylinder, three-cylinder and multi-cylinder pumping plants. These cylinders may be vertical or horizontal. Comparatively, the multi-cylinder pumping plants will cost higher but don’t feature any significant advantages other than the single-cylinder.
When drilling, there might occur the necessity of mud pumping out- and flushing-out, so there are various types of pumps available for such operations which are required to be installed on drilling rigs.
Sucker-rod pumps: In sucker-rod pumps, the pumpjack is a driver. This pump is installed at the bottom of the well. The reciprocating movements of the pumpjack are converted into liquid flow by the pump, which results in delivery of liquid on the surface. These pumps move oil with various admixtures demonstrating high level of capacity.
Screw pumps:The screw pumps are small-sized and are generally used to deliver mud into a centrifuge. These pumps have the rotor and stator as the major structural components and the material used to manufacture these components suit right for smooth pumping of liquids with solid inclusions and high level of viscosity. The pumped liquid flows with stable pressure, shaft slowly and the flow is free of vortexes. These pumps comparatively require minimum service.
Well pumps: These pumps are submerged into wells. The ground part of the plant is a transformer substation equipped for start and adjustment. The pump has a vertical structure, with a fixed cylinder and single-action. A plunger and valve are moving parts. The pumped liquid may contain water content of up to 99% at the temperature as high as 130ºC.
All the mud pumps have few general advantages that include the capability to process liquids and substances with high level of viscosity and with admixtures. Also, enabling the smooth flow of substances, free of pulsations or suspensions mixing are counted under the major advantages of incorporating mud pumps. The pumps have high suction power and small weight, easing out the transportation and installation at remote oil fields. They are highly reliable and also affordable.
There are various types of mud pumps available for different purposes. So, it is important to incorporate the right one for your purpose. A Professional help in getting the right mud pump would be a good and safe option.

This website is using a security service to protect itself from online attacks. The action you just performed triggered the security solution. There are several actions that could trigger this block including submitting a certain word or phrase, a SQL command or malformed data.

Welcome to Pickett Oilfield’s mud pumps web page. Our company has been in the oil & gas drilling equipment industry for over 38 years, supplying new and used mud pumps and mud pump parts to customers in practically every producing region in the world. We are here to serve all your drilling equipment needs – if you don’t see it on this site, just give us a call or email. We can get it, if you need it!
Pickett Oilfield, LLC offers prospective buyers and extensive selection of quality new and used oil & gas drilling equipment, including mud pumps and parts to choose from at competitive prices. Browse our inventory of mud pumps and mud pump parts for sale at competitive rates.For more information or to request a quote, please Contact Us at 936-336-5154 or email to Sales@PickettOilfield.com.

A well-placed suction stabilizer can also prevent pump chatter. Pump chatter occurs when energy is exchanged between the quick opening and closing of the reciprocating pump’s valves and the hammer effect from the centrifugal pump. Pump isolation with suction stabilizers is achieved when the charge pumps are isolated from reciprocating pumps and vice versa. The results are a smooth flow of pumped media devoid of agitating energies present in the pumped fluid.

A mud pump is a reciprocating piston or plunger device designed to pump drilling fluid under high pressures and volumes down the drill string of a drilling rig. The main functions of drilling fluid are to provide hydrostatic pressure to prevent formation fluids from entering and to stabilize the bore, to keep the drill bit cool and clean, to carry drill cuttings back out to the surface, and to suspend the drill cuttings while drilling is paused or during the pullback process.
Mud pumps consist of two main sub-assemblies- the fluid end and the power end. The fluid end performs the pumping process with valves, pistons, and liners, or plungers and stuffing boxes- depending upon the type used. These components are considered expendables, and are designed to be easily replaced in the field. The power end contains the eccentric or crankshaft, along with the connecting rods, and cross heads/slides.
Tulsa Triplex is a Tulsa Rig Iron company. We manufacture pumps from 100 to 600 horsepower that are designed to be easily maintained and are capable of being completely rebuilt. Our pumps feature a smaller footprint and lighter weight than competing models, making them completely legal load size and weight in most instances. They are available as a bare pump, with chainbox, or a complete skidded package.

A mud pump (sometimes referred to as a mud drilling pump or drilling mud pump), is a reciprocating piston/plunger pump designed to circulate drilling fluid under high pressure (up to 7,500 psi or 52,000 kPa) down the drill string and back up the annulus. A mud pump is an important part of the equipment used for oil well drilling.
Mud pumps can be divided into single-acting pump and double-acting pump according to the completion times of the suction and drainage acting in one cycle of the piston"s reciprocating motion.
Mud pumps come in a variety of sizes and configurations but for the typical petroleum drilling rig, the triplex (three piston/plunger) mud pump is used. Duplex mud pumps (two piston/plungers) have generally been replaced by the triplex pump, but are still common in developing countries. Two later developments are the hex pump with six vertical pistons/plungers, and various quintuplexes with five horizontal piston/plungers. The advantages that these new pumps have over convention triplex pumps is a lower mud noise which assists with better measurement while drilling (MWD) and logging while drilling (LWD) decoding.
The fluid end produces the pumping process with valves, pistons, and liners. Because these components are high-wear items, modern pumps are designed to allow quick replacement of these parts.
To reduce severe vibration caused by the pumping process, these pumps incorporate both a suction and discharge pulsation dampener. These are connected to the inlet and outlet of the fluid end.
The power end converts the rotation of the drive shaft to the reciprocating motion of the pistons. In most cases a crosshead crank gear is used for this.
Displacement is calculated as discharged liters per minute. It is related to the drilling hole diameter and the return speed of drilling fluid from the bottom of the hole, i.e. the larger the diameter of drilling hole, the larger the desired displacement. The return speed of drilling fluid should wash away the debris and rock powder cut by the drill from the bottom of the hole in a timely manner, and reliably carry them to the earth"s surface. When drilling geological core, the speed is generally in range of 0.4 to 1.0 m^3/min.
The pressure of the pump depends on the depth of the drilling hole, the resistance of flushing fluid (drilling fluid) through the channel, as well as the nature of the conveying drilling fluid. The deeper the drilling hole and the greater the pipeline resistance, the higher the pressure needed.
With the changes of drilling hole diameter and depth, the displacement of the pump can be adjusted accordingly. In the mud pump mechanism, the gearbox or hydraulic motor is equipped to adjust its speed and displacement. In order to accurately measure the changes in pressure and displacement, a flow meter and pressure gauge are installed in the mud pump.
The construction department should have a special maintenance worker that is responsible for the maintenance and repair of the machine. Mud pumps and other mechanical equipment should be inspected and maintained on a scheduled and timely basis to find and address problems ahead of time, in order to avoid unscheduled shutdown. The worker should attend to the size of the sediment particles; if large particles are found, the mud pump parts should be checked frequently for wear, to see if they need to be repaired or replaced. The wearing parts for mud pumps include pump casing, bearings, impeller, piston, liner, etc. Advanced anti-wear measures should be adopted to increase the service life of the wearing parts, which can reduce the investment cost of the project, and improve production efficiency. At the same time, wearing parts and other mud pump parts should be repaired rather than replaced when possible.

Nana Chiloda, Ahmedabad Shed No 43 Sai Industrial Estate 2 Near Railway Crossing Sardar Patel Ring Road Ranasan Toll Plaza, Nana Chiloda, Ahmedabad - 382330, Dist. Ahmedabad, Gujarat
The l-series of l. K-duplex mud pumps is the result of over two decades of incessant research and development by a young team of pains taking engineers, workingread more...
Near Jayram Transport, Mantarwadi, Uruli Devachi, Pune Sr No 52. Sambhaji Maharaj Nagar, Near Jayram Transport, Mantarwadi, Uruli Devachi, Pune - 412308, Dist. Pune, Maharashtra
Zoo Road Bye Lane 6, Guwahati, Dist. Kamrup House No. 5, First Floor Hridaya Ranjhan Path, Zoo Road Bye Lane 6, Guwahati - 781003, Dist. Kamrup, Assam
the l-series of l. K-duplex mud pumps is the result of over two decades of incessant research and development by a young team of pains taking engineers, working with an "india-can-doit" mood. They are backed by their close association with advanced pump technology and actualread more...
Gnana Bharathi, Bengaluru No. 2/6, Keerthi Bakery Road, Nagadevanahalli Jnanabharathi Post, Gnana Bharathi, Bengaluru - 560056, Dist. Bengaluru, Karnataka
We provide a qualitative range of mud pumps, which are immensely used in construction, agriculture, waste water management and many other industries. These High Pressure Duplex Double Acting Mud Pumps are primarily reciprocating plunger devices designed forread more...
Nizampura, Vadodara 31,NIZAMPURA,JAIPRAKASH SOCIETY OPP NEW ERA HIGH SCHOOL,VADODARA,,,Gujarat,390002, Nizampura, Vadodara - 390002, Dist. Vadodara, Gujarat
Established in year 1996, Maskill Enterprises is the leading Wholesaler Trader of Submersible Pump, Self Priming Pump and Double Wall Corrugated Pipe.
" GSL" Make Reciprocating Duplex Double Acting Mud Pump idle for water well drilling, core drilling, shallow crude oil drilling. Also sutable for Cement Slurry, Crude Oil, Boiler Feed, Sweage Mud pumps are suitble for mounting on skid, Trailer and on drilling rigs.
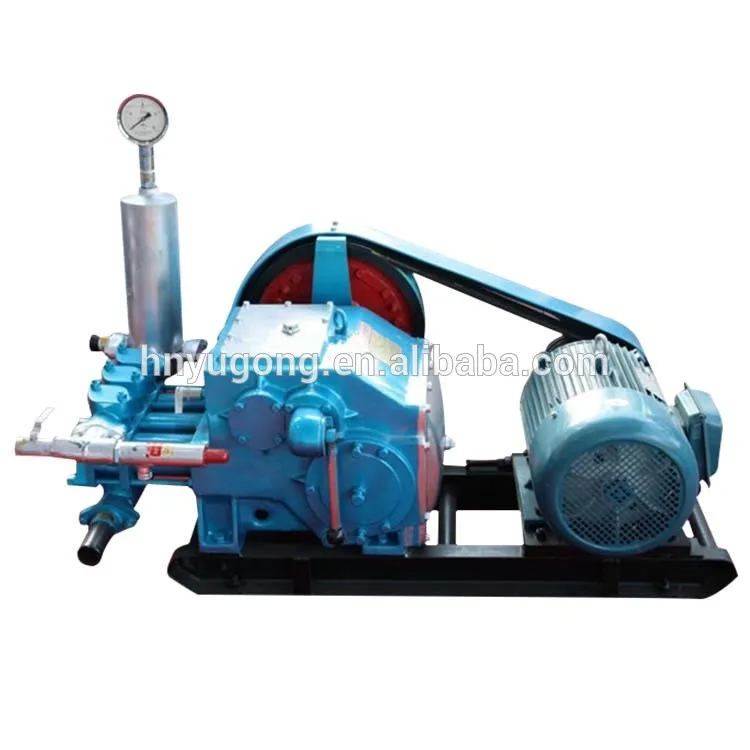

A mud pump is a reciprocating piston/plunger device used to circulate drilling fluid (mud) on a drilling rig under high pressure down the drill string and back up the annulus. It is an important part of the oil well drilling equipment.

When choosing a size and type of mud pump for your drilling project, there are several factors to consider. These would include not only cost and size of pump that best fits your drilling rig, but also the diameter, depth and hole conditions you are drilling through. I know that this sounds like a lot to consider, but if you are set up the right way before the job starts, you will thank me later.
Recommended practice is to maintain a minimum of 100 to 150 feet per minute of uphole velocity for drill cuttings. Larger diameter wells for irrigation, agriculture or municipalities may violate this rule, because it may not be economically feasible to pump this much mud for the job. Uphole velocity is determined by the flow rate of the mud system, diameter of the borehole and the diameter of the drill pipe. There are many tools, including handbooks, rule of thumb, slide rule calculators and now apps on your handheld device, to calculate velocity. It is always good to remember the time it takes to get the cuttings off the bottom of the well. If you are drilling at 200 feet, then a 100-foot-per-minute velocity means that it would take two minutes to get the cuttings out of the hole. This is always a good reminder of what you are drilling through and how long ago it was that you drilled it. Ground conditions and rock formations are ever changing as you go deeper. Wouldn’t it be nice if they all remained the same?
Centrifugal-style mud pumps are very popular in our industry due to their size and weight, as well as flow rate capacity for an affordable price. There are many models and brands out there, and most of them are very good value. How does a centrifugal mud pump work? The rotation of the impeller accelerates the fluid into the volute or diffuser chamber. The added energy from the acceleration increases the velocity and pressure of the fluid. These pumps are known to be very inefficient. This means that it takes more energy to increase the flow and pressure of the fluid when compared to a piston-style pump. However, you have a significant advantage in flow rates from a centrifugal pump versus a piston pump. If you are drilling deeper wells with heavier cuttings, you will be forced at some point to use a piston-style mud pump. They have much higher efficiencies in transferring the input energy into flow and pressure, therefore resulting in much higher pressure capabilities.
Piston-style mud pumps utilize a piston or plunger that travels back and forth in a chamber known as a cylinder. These pumps are also called “positive displacement” pumps because they literally push the fluid forward. This fluid builds up pressure and forces a spring-loaded valve to open and allow the fluid to escape into the discharge piping of the pump and then down the borehole. Since the expansion process is much smaller (almost insignificant) compared to a centrifugal pump, there is much lower energy loss. Plunger-style pumps can develop upwards of 15,000 psi for well treatments and hydraulic fracturing. Centrifugal pumps, in comparison, usually operate below 300 psi. If you are comparing most drilling pumps, centrifugal pumps operate from 60 to 125 psi and piston pumps operate around 150 to 300 psi. There are many exceptions and special applications for drilling, but these numbers should cover 80 percent of all equipment operating out there.
The restriction of putting a piston-style mud pump onto drilling rigs has always been the physical size and weight to provide adequate flow and pressure to your drilling fluid. Because of this, the industry needed a new solution to this age-old issue.
As the senior design engineer for Ingersoll-Rand’s Deephole Drilling Business Unit, I had the distinct pleasure of working with him and incorporating his Centerline Mud Pump into our drilling rig platforms.
In the late ’90s — and perhaps even earlier — Ingersoll-Rand had tried several times to develop a hydraulic-driven mud pump that would last an acceptable life- and duty-cycle for a well drilling contractor. With all of our resources and design wisdom, we were unable to solve this problem. Not only did Miller provide a solution, thus saving the size and weight of a typical gear-driven mud pump, he also provided a new offering — a mono-cylinder mud pump. This double-acting piston pump provided as much mud flow and pressure as a standard 5 X 6 duplex pump with incredible size and weight savings.
The true innovation was providing the well driller a solution for their mud pump requirements that was the right size and weight to integrate into both existing and new drilling rigs. Regardless of drill rig manufacturer and hydraulic system design, Centerline has provided a mud pump integration on hundreds of customer’s drilling rigs. Both mono-cylinder and duplex-cylinder pumps can fit nicely on the deck, across the frame or even be configured for under-deck mounting. This would not be possible with conventional mud pump designs.
Centerline stuck with their original design through all of the typical trials and tribulations that come with a new product integration. Over the course of the first several years, Miller found out that even the best of the highest quality hydraulic cylinders, valves and seals were not truly what they were represented to be. He then set off on an endeavor to bring everything in-house and began manufacturing all of his own components, including hydraulic valves. This gave him complete control over the quality of components that go into the finished product.
The second generation design for the Centerline Mud Pump is expected later this year, and I believe it will be a true game changer for this industry. It also will open up the application to many other industries that require a heavier-duty cycle for a piston pump application.

This rig features a Mission 4-by-5 centrifugal pump. Courtesy of Higgins Rig Co.Returning to the water well industry when I joined Schramm Inc. last year, I knew that expanding my mud pump knowledge was necessary to represent the company"s mud rotary drill line properly. One item new to me was the centrifugal mud pump. What was this pump that a number of drillers were using? I had been trained that a piston pump was the only pump of any ability.
As I traveled and questioned drillers, I found that opinions of the centrifugal pumps varied. "Best pump ever built," "What a piece of junk" and "Can"t drill more than 200 feet with a centrifugal" were typical of varying responses. Because different opinions had confused the issue, I concluded my discussions and restarted my education with a call to a centrifugal pump manufacturer. After that conversation, I went back to the field to continue my investigation.
For the past eight months, I have held many discussions and conducted field visits to understand the centrifugal pump. As a result, my factual investigation has clearly proved that the centrifugal pump has a place in mud rotary drilling. The fact also is clear that many drilling contractors do not understand the correct operational use of the pump. Following are the results of my work in the field.
High up-hole velocity - High pump flow (gpm) moves cuttings fast. This works well with lower viscosity muds - reducing mud expense, mixing time and creating shorter settling times.
Able to run a desander - The centrifugal"s high volume enables a desander to be operated off the pump discharge while drilling without adding a dedicated desander pump.
6. Sticky clays will stall a centrifugal pump"s flow. Be prepared to reduce your bit load in these conditions and increase your rpm if conditions allow. Yes, clays can be drilled with a centrifugal pump.
7. Centrifugal pumps cannot pump muds over 9.5 lbs./gal. Centrifugal pumps work best with a 9.0 lbs./gal. mud weight or less. High flow rate move cuttings, not heavy mud.
The goal of this article has been to increase awareness of the value of the centrifugal pump and its growing use. Although the centrifugal pump is not flawless, once its different operating techniques are understood, drilling programs are being enhanced with the use of this pump.
If you wish to learn more, please talk directly to centrifugal pump users. Feel free to call me at 314-909-8077 for a centrifugal pump user list. These drillers will gladly share their centrifugal pump experiences.

What are the main differences between centrifugal and reciprocating industrial pumps? From pump construction and design to operation and reliability, centrifugal and reciprocating pumps offer different benefits and therefore have different ideal applications. Here we break down some of those differences to help you select the pump that best suits your needs.
The first machine that could be classified was a mud lifting machine that appeared in a late 15th century treatise by the Italian Renaissance engineer Francesco di Giorgio Martini. However, the first true incarnation of a centrifugal pump was developed about 200 years later by French-born inventor Denis Papin. Papin’s version used straight vanes for local drainage and was the first modern attempt at creating a centrifugal pump.
The evolution of the reciprocating pump reaches further back into history than its centrifugal counterpart. Greek inventor and mathematician Ctesibius invented what was then called a water organ in about 200 BC. This invention used an air pump with valves on the bottom, a water tank between the valves, and a row of pipes on top. This design was the blueprint for the modern reciprocating pump.
Centrifugal pumps leverage a simple design concept based on a rotating impeller that imparts kinetic energy to the fluid with a static pump casing that collects it, slows it down, and converts it into pressure, commonly referred to as discharge head. The resulting flow is steady and continuous because the impeller spins at a constant rotational speed across 360 degrees in the pump casing. Centrifugal pumps use either a single impeller, a single impeller with high-speed options, or multiple impellers for increased capacity. This impeller-based design means fluid movement and volumes can be controlled based on the needs of the application, and this simplified construction with few moving parts lends itself to a longer service life with little or no degradation over time.
Reciprocating pumps, on the other hand, use a reciprocating crankshaft mechanism that leverages either pistons or plungers to draw in and draw out a fixed volume of fluid. The complexity of the crankshaft and piston/plunger design does require maintenance throughout the course of the pump’s life and can be prone to wear-and-tear from use in the field.
With centrifugal pump flow and control, a steady, continuous flow of fluid is achieved from constant impeller rotation. High-viscosity fluids are not ideal for use with centrifugal pumps. A valve installed on the pump discharge is used to control the pump output, which means overall pump efficiency is considerably low compared to reciprocating pumps — about 30% to 70% — due to friction losses in operation.
The flow of a reciprocating pump is intermittent and pulsating as a result of the reciprocating mechanism, which allows reciprocating pumps to pump higher-viscosity fluids — in fact, overall pump performance is actually increasedwhen using higher-viscosity fluids. Reciprocating pumps also function at a much higher level of efficiency — in the range of 65% to 85% — thanks to fluctuations in both the speed and stroke length of the piston or plunger.
The cost of a centrifugal pump is generally higher than that of a reciprocating pump, due to the use of precision-engineered components necessary for high-speed applications. (For example, the Sundyne OH6 integrally geared high-speed pump can go as high as 24,000 rpm.) Reciprocating pumps operate at lower speeds and cost less.
Another benefit of centrifugal pumps, however, is their smaller size and low weight. Due to their smaller footprint and less heavy foundation, installation cost is low. Reciprocating pumps, on the other hand, typically have a larger footprint, and a heavier foundation is required. Their installation cost is comparably high.
Overhung centrifugal pumps use a single impeller installed on a shaft that is suspended at one end of the pump by a single bearing, thus resulting in the pump being “overhung” from its single support bearing.
Between bearing centrifugal pumps also use a single impeller, but instead deploy a bearing at each end of the shaft, with the impeller mounted in between the bearings. This configuration generally results in slightly greater efficiency compared to overhung centrifugal pumps.
Vertical suspended centrifugal pumps are single-stage pumps that are designed to be mounted vertically. These pumps are often used in harsh environmental conditions or applications where pumps are placed under duress for extended periods.
With reciprocating pumps, there are three classifications most commonly seen with industrial applications per API 674, which defines minimum and maximum speeds, pulsation and vibratory control compliance, and testing requirements. The three common classifications of reciprocating pumps include:
Piston reciprocating pumps use a high-pressure seal that reciprocates in conjunction with the piston. With a piston pump, high-pressure operation can be achieved without impacting flow rate.
Plunger reciprocating pumps use a stationary high-pressure seal in conjunction with a plunger mechanism. The stationary nature of the seal allows for use in higher-pressure applications compared with piston-style pumps.
Diaphragm reciprocating pumpsoperate through the reciprocating action of a rubber, thermoplastic, or teflon diaphragm with valves fixed to either side of the diaphragm.
Centrifugal pumps create the highest levels of efficiency and value in applications and services that feature lower-viscosity fluids such as waters, solvents, oils, acids, bases, and other thin liquids. With reciprocating pumps, ideal use centers on high-pressure applications in the oil and gas, chemical processing, mining, and production industries.
IPEC has more than 70 years of industrial pump solution knowledge, expertise, and service. Our partnerships with industry standard brands Sundyne, Marelli, Fybroc, Yamada, and Milton Roy allow us to offer the most innovative, state-of-the-art centrifugal and reciprocating pumps on the market today to help you achieve superior process optimization and productivity.

Editor"s Note: This is the second of five parts of our feature, The History of Pumps. This timeline was developed through research, credible sources and the knowledge of friends in the industry, The history of pumps is long and illustrious. This account represents highlights of some of the major historical and technological developments. We welcome your contributions.
200 BC Greek inventor and mathematician Ctesibius invents the water organ, an air pump with valves on the bottom, a tank of water in between them and a row of pipes on top. This is the principal design that is now known as the reciprocating pump.
200 BC Archimedean screw pump is designed by Archimedes is considered one of the greatest inventions of all time and is still in use today for pumping liquids and granulated solids in both the industrialized world and in the third world—where it is a preferred way to irrigate agricultural fields without electrical pumps.
1475 According to Reti, the Brazilian soldier and historian of science, the first machine that could be characterized as a centrifugal pump was a mud lifting machine that appeared in a treatise by the Italian Renaissance engineer Francesco di Giorgio Martini.
1588 Sliding vane water pump technology is described by Italian engineer Agostino Ramelli in his book “The Diverse and Artifactitious Machines of Captain Agostino Ramelli,” which also included other pump and engine designs.
1636 Pappenheim, a German engineer, invents the double deep-toothed rotary gear pump, which is still used to lubricate engines. This gear pump made it possible to dispense with the reciprocating slide valves used by Ramelli. Pappenheim drove his machine by an overshot water wheel set in motion by a stream and was used to feed water fountains. The emperor Ferdinand II granted him a “privilege” - the equivalent of a patent - in respect of this invention.
1675 Sir Samuel Moreland—an English academic, diplomat, spy, inventor and mathematician—patents the packed plunger pump, capable of raising great quantities of water with far less proportion of strength than a chain or other pump. The piston had a leather seal. Moreland"s pump may have been the first use of a piston rod and stuffing box (packed in a cylinder) to displace water.
1738 In fluid dynamics, Bernoulli"s principle states that for an inviscid flow, an increase in the speed of the fluid occurs simultaneously with a decrease in pressure or a decrease in the fluid"s potential energy. It is named after the Dutch-Swiss mathematician Daniel Bernoulli, who published it in a book “Hydrodynamica.” The principle is applied to various types of fluid flow and is loosely known as Bernoulli"s equation.
1782 James Watt—who invented the steam engine"s connecting rod crank mechanism, which made it possible to convert the piston"s reciprocating motion into rotary motion—designs an oscillating piston machine in which a wing-shaped rotary blade made a near complete revolution uncovering inlet ports in a chamber separated by a curved radial wall.
1790 Briton Thomas Simpson harnesses steam power to pumping engines for municipal water applications and founds the London company Simpson and Thompson Co. (predecessor to Worthington Simpson).
1845 Henry R. Worthington invents the first direct-acting steam pumping engine. Worthington Pump designed its first products to power canal boats and U.S. naval vessels. Worthington later pioneered pump designs for boiler feed, oil pipeline and hydro-electric applications.
1851 John Gwynne files his first centrifugal pump patent. His early pumps were used primarily for land drainage, and many can still be seen today in pump house museums. They were usually powered by Gwynnes" steam engines. By the end of the 19th century, Gwynne was producing pumps of all sizes to cover all industrial applications, from small electric pumps to those rated at 1,000 tons per minute. His company had also begun to produce scientific pumps, e.g., porcelain pumps for chemical works. In the 1930s they were producing almost 1,000 different models.
1860 Adam Cameron founds the Cameron Steam Pump Works, and becomes another pioneer in reciprocating steam pump engines. Like Worthington, Cameron"s first products were used to power merchant marine and U.S. naval vessels. Cameron pumps were later applied in water resources, oil pipeline and refining and boiler feed.
1871 Johannes Klein receives a patent on his “boiler feed apparatus.” With Friedrich Schanzlin and Jakob Becker, he founds the company “Frankenthaler Maschinen- & Armatur-Fabrik Klein, Schanzlin & Becker” (now known as KSB) to manufacture boiler feed equipment and valves.
1886 Jens Nielsen, founder of Viking Pump Company, invents the internal gear pumping principal while designing a pump to remove excess water that was seeping into his limestone quarry from a nearby creek.
1886 United Centrifugal Pumps is incorporated. It becomes the world"s foremost supplier of high-pressure crude oil and refined product pipeline pumps.
1899 Robert Blackmer invents rotary vane pump technology, a pump design that was an important departure from the old gear principle and predecessor to today"s sliding vane pumps.
1902 Aldrich Pump Company begins manufacturing the world"s first line of reciprocating positive displacement pumps for steel mills and mine dewatering.
1908 Hayward Tyler creates its first electric motor for use under water and develops the wet stator motor for use as a boiler circulation glandless motor-pump.
1911 Jens Nielsen builds the first internal gear pump, founding the Viking Pump Company. The Viking Rotary “Gear-Within-A-Gear” pump (the first of its kind) is placed on the market.
1912 Durion, a universally corrosion-resistant material, is invented by the Duriron Castings Company (later known as Durco Pump) and is applied to process equipment.
1915 Albert Baldwin Wood invents the Wood trash pump. Wood spearheads the reclamation from swamp and the efforts to develop much of the land now occupied by the city of New Orleans. Some of Wood"s pumps have been in continuous use for more than 80 years without need of repairs. New ones continue to be built from his designs.
1916 While Armais Sergeevich Arutunoff first invented submersible pumps in Russia in 1916, their use in the United States did not begin until the 1950s. Arutunoff first designed his pump for use in ships, water wells and mines. He altered the design to work in oil wells. Thanks to further refinements to Arutunoff"s design, there are more types of submersible pumps, allowing use in other applications such as pumping drinking water, creating fountains and pumping wastewater.
1921 Harry LaBour founds LaBour Pump Company. A pioneer in the development of pumps for the chemical industry, LaBour developed corrosion-resistant alloys to incorporate into his pumps. Until his time, sulfuric acid was always pumped with lead pumps, the only known material that could handle certain concentrations of the acid.
1921 Jeumont-Schneider begins manufacturing water and slurry pumps in Jeumont, France. It later develops solids-handling pumps and segmental ring section multistage pumps.
1924 Durco Pump introduces the world"s first pump specifically designed for chemical processing. It would go on to establish undisputed global leadership in ANSI pump design.
1926 O.H. Dorer receives a patent for the first inducer, which reduces the required NPSH. Inducers did not become incorporated into standard pump lines until the 1960s.
1929 Pleuger incorporates in Berlin, Germany. Its first offerings are submersible motor pumps for dewatering in the construction of underground railways and subways. Pleuger pioneers the first successful application of submersible motor pumps in offshore service.
1929 Stork Pompen produces the first concrete volute pump for drainage, integrating the pump housing in the civil construction of the pumping station.
1930 While inventing a compressor for jet engines, aviation pioneer René Moineau discovers that this principle could also work as a pumping system.The University of Paris awarded Moineau a doctorate of science for his thesis on “the new capsulism.” His pioneering dissertation laid the groundwork for the progressing cavity pump.
1933 The original version of the Bush Pump is designed as a closed-top cylinder pump. In 1960 the design was modernized. The base of the well was from then on bolted to the well casing and got its current name, The Zimbabwe Bush Pump, the National Standard for hand pumps in Zimbabwe. After Zimbabwe"s independence in 1980, the government creates its own modernized version of the pump, B-type Zimbabwe Bush Pump. The pump is today regarded as a national treasure. In 1997, it was pictured on a postal stamp.
1933 J.C. Gorman and Herb Rupp introduce a pump with a “non-clogging” feature. It outperforms any other self-priming centrifugal pump previously invented. The company Gorman-Rupp is established.
1936 Robert Sheen invents the metering pump. The core of his invention was a method of controlled volume that was inherent to the pump. The first pumps were assembled in the basement of his father, Milton Roy Sheen"s, home, where the initial patterns for castings were made.
1937-1939 Smith Precision Products Company (Smith Pumps) designs three pumps, two of which (models 300 and 200) were specifically designed for LP-gas transfer.
1939 Dorr-Oliver Pump Company develops the Oliver Diaphragm Slurry pump for slurry transfer. Originally designed for mining slurry transfer with their associated acids, it developed into a Primary Sludge Underflow Pump for the wastewater industry starting in the 1970s after the Clean Water Act.
1940 Reuben Smith, of Smith Precision Products Company (Smith Pumps), receives the first approval for an LP-gas pump from the California Industrial Accident Commission. This was for the model 4X pump and the approval was a "suitable for use" certificate.
1942 The Gorman-Rupp team creates the first commercially available solids-handling trash pump to respond to the contractor"s need for a pump to withstand the considerable rigors of pumping out trash-laden septic tanks, cesspools and outhouses.
1944 During World War II, Goulds extra-quiet trim pumps are installed in every U.S. Navy submarine. That year, 157 Goulds men went to war and 157 women took their places on the Goulds manufacturing floor. Goulds earned the prestigious Army-Navy “E” Award that year for outstanding production of war materials.
1947 Flygt"s Sixten Englesson, a master of engineering, develops a prototype for the first submersible drainage pump, which is later known as the “parrot cage,” or B-pump, used in mining for construction.
1948 Smith Precision Products Company receives the patent for the first mechanical seal supplied for liquefied gas transfer pumps. It was first put into production in 1947.
1950 Vanton develops the Flex-i-liner sealless self-priming rotary pump which handles corrosive, abrasive and viscous fluids as well as those that must be transferred free of product contamination.
1954 Smith Precision Products Company (Smith Pumps) begins working with the Underwriters Laboratories to develop their first Standard for liquefied gas pumps, UL-51, which is still in use today.
In 1955, Jim Wilden invented air-operated double-diaphragm pump technology. It had the right air valve and diaphragms needed and was tough and versatile enough to meet the stringent demands of the mining and heavy-construction industries. During the 1980s, Wilden introduced plastic AODD pumps that have the ability to stand up to the harsh operating conditions and corrosive media transferred throughout the global chemical market. Photo courtest of Wilden.
1960s New lines of industrial pumps are developed by Goulds Pumps, including large double suction pumps, higher pressure pumps and non-metallic pumps. In home water systems, the jet water system is improved and a complete line of submersible pumps is completed.
1965 Warren Rupp"s heavy-duty, diverse AODD pump is introduced to the industrial market to address the vigorous demands of the steel mills and other industrial market applications.
Below: Marvin and Kathryn Summerfield founded Cascade Pump Company in 1948. They are pictured here at an industry tradeshow in the early 1950s. Photo courtesy of Cascade Pump Company.
1968 The ownership of Stenberg-Flygt AB is transferred to the American multinational enterprise ITT (International Telephone & Telegraph Corporation). Prior to this transfer, Stenberg-Flygt AB, AB Flygts Pumpar and Flygt International AB are consolidated as a single company.
1980s Gorman-Rupp unveils the nutating pump, a special purpose small pump used in health care applications; additional energy-efficient, self-priming centrifugal pumps; a series of lightweight portable pumps and high-pressure pumps with the first digital-control panels.
1985 Sims manufactures the first structural composite pump, all Simsite Vertical Pit Pump. Sims later won the Innovative Product Award for these products in 1990.
In 1933, J.C. Gorman and Herb Rupp introduced a pump which had a "non-clogging" feature. Their competitors claimed the pump would not work in a savage public awareness campaign to discredit the new design, which resulted in about $100,00 worth of "free advertising." At least one customer was willing to try it. National Ice Company purchased the first pump, and the company Gorman-Rupp was established. Photo courtesy of Gorman-Rupp Company.
1994 Two new major products are introduced by Goulds Pumps, the Industrial Model 3298 Magnetic Drive Pump and the Water Technologies Model GS “Global Submersible.”
1994 Sims receives the honor of approval from the United States Navy for composite centrifugal pump intervals. Simsite was tested and qualified for centrifugal pump replacement parts and was the first composite to be certified.
1994 Baha Abulnaga invents the slurry and froth pump with a split vane impeller. The split impeller helps to reduce recirculation in slurry pumps by dividing the space between the main vanes without reducing the passageway at the narrowest point, which is the eye of the impeller. In froth pumps, it helps to break up air bubbles that form and tend to block the flow.
1995 Sims manufactures the largest structural composite pumps in the world - two Simsite vertical turbine pumps for Potomac Electric Power Company. They are 40 feet long and 3 feet in diameter.
2006 Sims manufactures the largest structural composite centrifugal impeller in the world. This huge impeller was installed in a cooling tower pump for Puerto Rican Electrical Power Company. It is 50 inches in diameter and consumes 2,000 horsepower.




 8613371530291
8613371530291