free overshot weaving patterns quotation

Woven by Rachel SnackWeave two overshot patterns with the same threading using this downloadable weave draft to guide you. This pattern features the original draft along with one pattern variation. Some yarns shown in the draft are available to purchase in our shop: 8/2 cotton, wool singles, 8/4 cotton (comparable to the 8/4 linen shown).
please note: this .pdf does not explain how to read a weaving draft, how to interpret the draft onto the loom, or the nuances of the overshot structure.

The origin of the technique itself may have started in Persia and spread to other parts of the world, according to the author, Hans E. Wulff, of The Traditional Crafts of Persia. However, it is all relatively obscured by history. In The Key to Weavingby Mary E. Black, she mentioned that one weaver, who was unable to find a legitimate definition of the technique thought that the name “overshot” was a derivative of the idea that “the last thread of one pattern block overshoots the first thread of the next pattern block.” I personally think it is because the pattern weft overshoots the ground warp and weft webbing.
Overshot gained popularity and a place in history during the turn of the 19th century in North America for coverlets. Coverlets are woven bedcovers, often placed as the topmost covering on the bed. A quote that I feel strengthens the craftsmanship and labor that goes into weaving an overshot coverlet is from The National Museum of the American Coverlet:
Though, popular in many states during the early to mid 19th centuries, the extensive development of overshot weaving as a form of design and expression was fostered in rural southern Appalachia. It remained a staple of hand-weavers in the region until the early 20th century. In New England, around 1875, the invention of the Jacquard loom, the success of chemical dyes and the evolution of creating milled yarns, changed the look of coverlets entirely. The designs woven in New England textile mills were predominantly pictorial and curvilinear. So, while the weavers of New England set down their shuttles in favor of complex imagery in their textiles, the weavers of Southern Appalachia continued to weave for at least another hundred years using single strand, hand spun, irregular wool yarn that was dyed with vegetable matter, by choice.
Designs were focused on repeating geometric patterns that were created by using a supplementary weft that was typically a dyed woolen yarn over a cotton plain weave background. The designs expressed were often handed down through family members and shared within communities like a good recipe. And each weaver was able to develop their own voice by adjusting the color ways and the treadling arrangements. Predominately, the homestead weavers that gave life and variations to these feats of excellent craftsmanship were women. However, not every home could afford a loom, so the yarn that was spun would have been sent out to be woven by the professional weavers, who were mostly men.
And, due to the nature of design, overshot can be woven on simpler four harness looms. This was a means for many weavers to explore this technique who may not have the financial means to a more complicated loom. With this type of patterning a blanket could be woven in narrower strips and then hand sewn together to cover larger beds. This allowed weavers to create complex patterns that spanned the entirety of the bed.
What makes overshot so incredibly interesting that it was fundamentally a development of American weavers looking to express themselves. Many of the traditional patterns have mysterious names such as “Maltese Cross”, “Liley of the West”, “Blooming Leaf of Mexico” and “Lee’s Surrender”. Although the names are curious, the patterns that were developed from the variations of four simple blocks are incredibly intricate and luxurious.
This is only the tip of the iceberg with regard to the history of this woven structure. If you are interested in learning more about the culture and meaning of overshot, check out these resources!
The National Museum of the American Coverlet- a museum located in Bedford, Pennsylvania that has an extensive collection of traditional and jacquard overshot coverlets. Great information online and they have a “Coverlet College” which is a weekend series of lectures to learn everything about the American coverlet. Check out their website - coverletmuseum.org
Textile Art of Southern Appalachia: The Quiet Work of Women – This was an exhibit that traveled from Lowell, Massachusetts, Morehead, Kentucky, Knoxville, Tennessee, Raleigh, North Carolina, and ended at the Royal Museum in Edinburgh, Scotland. The exhibit contained a large number of overshot coverlets and the personal histories of those who wove them. I learned of this exhibit through an article written by Kathryn Liebowitz for the 2001, June/July edition of the magazine “Art New England”. The book that accompanied the exhibit, written by Kathleen Curtis Wilson, contains some of the rich history of these weavers and the cloth they created. I have not personally read the book, but it is now on the top of my wish list, so when I do, you will be the first to know about it! The book is called Textile Art of Southern Appalachia: The Quiet Work of Women and I look forward to reading it.
I wove my Mermaid Scarf with a PICK UP STICK on my 25-inch-wide Schacht Flip rigid heddle loom. Warp 3/2 weaving cotton, tabby weft 10/2 weaving cotton, pattern weft fingering wool singles. Watch my short freeform overshot video on my Lisa Rayner Handwoven"s Facebook page: https://www.facebook.com/lisaraynerhandwovens.
Do you wish you could weave fabric with complex Jacquard-like patterns? Do you like tapestry motifs, but want to weave wearable, drapeable cloth? You can weave such fabrics on any loom, from rigid heddle looms, backstrap looms, and even full size inkle looms, to simple shaft looms, multishaft table and floor looms, and dobby looms using the freeform overshot technique. Most looms require freeform overshot to be woven with a pick up stick.
All rights reserved. No part of this booklet may be duplicated, reprinted or shared electronically without written permission from the author, except for brief quotes and reviews. Respecting copyright supports the important work of authors. In addition, my patterns are for personal use only, not commercial use. Thank you.

Step out of the weaving comfort zone and experiment with something new! Weave structures often have specific threading and treadling patterns that are unique to that particular weave structure and not shared with others. This book takes you out of the traditional method of weaving overshot patterns by using different treadling techniques. This will include weaving overshot patterns as Summer/Winter, Italian manner, starburst, crackle, and petit point just to name a few. The basic image is maintained in each example but the design takes on a whole new look! Each chapter walks you through the setup for each method and includes projects with complete drafts and instructions so it"s easy to start weaving and watch the magic happen! Try the patterns for scarves, table runners, shawls, pillows and even some upholstered pieces. Once you"ve tried a few projects, you"ll be able to apply what you"ve learned to any piece you desire!

One of my favorite parts of working on my Ancient Rose Scarf for the March/April 2019 issue of Handwoven was taking the time to research overshot and how it fits into the history of American weaving. As a former historian, I enjoyed diving into old classics by Lou Tate, Eliza Calvert Hall, and Mary Meigs Atwater, as well as one of my new favorite books, _Ozark Coverlets, by Marty Benson and Laura Lyon Redford Here’s what I wrote in the issue about my design:_
“The Earliest weaving appears to have been limited to the capacity of the simple four-harness loom. Several weaves are possible on this loom, but the one that admits of the widest variations is the so-called ‘four harness overshot weave,’—and this is the foremost of the colonial weaves.” So wrote Mary Meigs Atwater in The Shuttle-Craft Book of American Hand-Weaving when speaking of the American coverlet and the draft s most loved by those early weavers.
Overshot, in my mind, is the most North American of yarn structures. Yes, I know that overshot is woven beyond the borders of North America, but American and Canadian weavers of old took this structure and ran with it. The coverlets woven by weavers north and south provided those individuals with a creative outlet. Coverlets needed to be functional and, ideally, look nice. With (usually) just four shaft s at their disposal, weavers gravitated toward overshot with its stars, roses, and other eye-catching patterns. Using drafts brought to North America from Scotland and Scandinavia, these early weavers devised nearly endless variations and drafts, giving them delightful names and ultimately making them their own.
When I first began designing my overshot scarf, I used the yarn color for inspiration and searched for a draft reminiscent of poppies. I found just what I was looking for in the Ancient Rose pattern in A Handweaver’s Pattern Book. When I look at the pattern, I see poppies; when Marguerite Porter Davison and other weavers looked at it, they saw roses. I found out later that the circular patterns—what looked so much to me like flowers—are also known as chariot wheels.

Introduction:I thought I would tell a bit about each of my books and maybe some of the back story about how I came to write them. If you like, just skip to my website: www.peggyosterkamp.com for details of the Holiday Sale. Buy One book and Get One Free!
My annual Holiday Sale begins today on Black Friday. “Buy one, get one free with your order”. You can request a free book with every item you buy. The website: WWW.PeggyOsterkamp.com has all the details.
Book #2: Warping Your Loom & Tying On New Warps came out in1995 and the second and third editions, in 1997 and 2002. Now it’s out of print but available as a pdf. The reason for writing the books is that the information Jim Ahrens taught us at Pacific Basin School of Textile Arts was revolutionary. That is, American handweavers were not using this information that production weavers in Europe and around the world were using. In his class, Production Weaving, he taught us those techniques and I felt the information must be passed along to future weavers. I apprenticed with him for a year and I kept a folder with all the things he taught us that year. We called it the “Chairman Jim File.”
Again, I was afraid I wouldn’t get more books written so I put a lot more in it that the title indicates—just in case. On the title page, I wrote: “A guide that makes weaving fun with new techniques from European handweavers and the textile industry.
Book #3: Weaving & Drafting Your Own Cloth, came out in its third printing in 2005. I’m not sure when the first edition was printed. Finally, I got to the weaving and drafting part of the process. In all three of these books I put in everything I knew and what Jim taught us. I call them tomes because I wrote why about everything and much more than many weavers need to know.
This book guides you through every step from weaving motions, shuttles and selvedges to finishing your cloth. When problems come your way there’s an extensive chapter on trouble shooting. The drafting chapter explains how to create your own designs as well as to use drafts in books and magazines. I wanted it to be for those weavers who think that they will never understand drafting. Also included: Drafting for Analyzing Fabric and Drafting for Multi-shaft Weaving.
Book #4: Weaving for Beginners. It came out in 2010 with the Second Edition in 2014 and just now, the Third Edition. This time I put in all the steps and left out a lot of the “whys” and had the illustrator make over 600 illustrations. I taught Beginning Weaving at our junior college for 10 or so years and this is what I taught them—all using the same efficient techniques. I hoped that someone could teach themselves with only the book. I also hoped teachers would use it for themselves to plan their classes as well as use it for a text for students. They could demonstrate something for the whole class and say what page it was on. Students could follow along as well as come back and refer to it when they got to that stage.
Jim’s techniques did not cover warping “Front-to-Back” so I asked an expert to write that chapter and I helped edit it so that I could understand it. Front-to-back is like standing on my head for me. Other experts wrote the chapter on computers. And others did chapters on hand-manipulated weaves and a beginning chapter: Rigid Heddle Weaving.

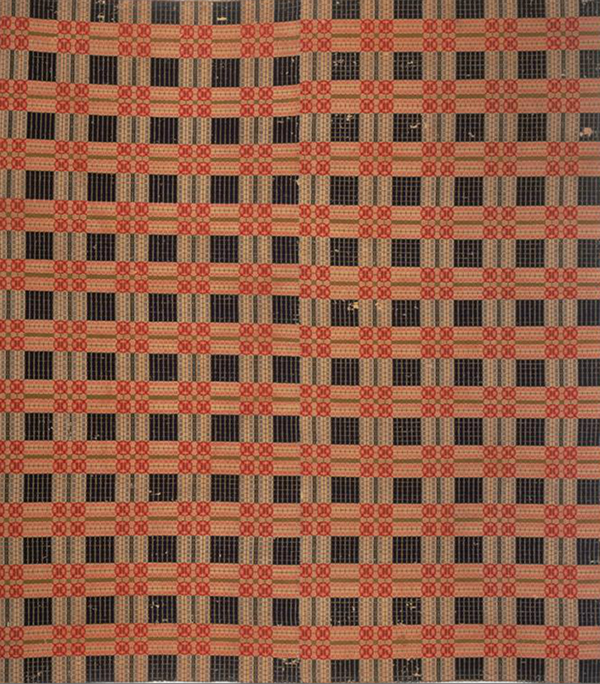
In its simplest form – overshot is a weaving technique that utilizes at least 2 different types of weft yarns and floats to create a pattern. These patterns are often heavily geometric.
Ground weft– plain weave pattern that is used between each row of your overshot pattern. This plain weave gives the textile structure and allows for large areas of overshot to be woven without creating an overly sleazy fabric. Without the use of a ground weft on an overshot pattern, the weaving would not hold together because there would not be enough warp and weft intersections to create a solid weaving.
They were most popular though in southern Appalachia and continued to be so even after textile technologies advanced. When other parts of colonial America moved to jacquard weaving, the weavers of southern Appalachia continued to weave their overshot coverlets by hand.
Since the overshot coverlets were most often woven at home on smaller looms they usually had a seam down the middle where two woven panels were sewn together.
The thing about overshot is that no matter the application, it is pretty impressive. Perhaps that is just my opinion, but due to how complex it can look, I feel that it is pretty safe to say.
Just because it was originally used for coverlets, does not mean it can only be used for coverlets. Changing aspects of the pattern like the colors used, or the way you use your ground weft can drastically change the look and feel of your weaving.
In the image below you can see the ground weft is not the same color throughout. Instead, I wove the ground weft as discontinuous so that I could add extra pattern and design into the weavings. In this case, you may be wondering how to deal with your weft yarns when they are in the middle of the weaving and not at the selvage.
The discontinuous weft yarns will float onto the back of the weaving until you are ready for them in their next pick. This does make your overshot weaving one sided since it will have vertical floats on the back. Keep this in mind if you want to try this technique out.
Also seen in the image above, the overshot yarn that I used was not all one color! This is a really simple way to get extra dimension and interest in your overshot if that is something you are looking for.
This makes it simple to be able to only weave overshot in certain parts of your weaving. If you want to do this then you can continue to weave your plain weave across the entire width of your weaving, but only weave overshot in specific areas. This creates a overshot section that functions similar to inlay.
Since the overshot pattern is strongly influenced by the weft yarns that are used it is important to choose the right yarns. Your weaving will be set up to the specification needed for a balanced plain weave. Make sure you understand EPI in order to get the right warp sett for your overshot weaving.
The ground weft used is almost always the same yarn as your warp. This allows the overshot weft to really be able to shine without contrasting warp and weft plain weave yarns.
In order to get the full effect of the overshot, it must be thick enough that when you are weaving your pattern it covers up the ground weft between each pass. If it is not thick enough to do this, it will still be overshot, but the full effect will not be seen.
What this warp thread does is serve as an all-purpose selvedge that does not correspond with your pattern. Instead, you would make sure to go around this warp thread every time to make sure that you are able to weave fully to the selvedge. Without this, your overshot weft will float awkwardly on the back of your weaving whenever the pattern does not take it to the edge.
I have mentioned this book multiple times because it really is such a great resource for any weaver looking to weave patterns of all types. It contains 23 pages of different overshot patterns (among so many other patterns) that you can set up on your floor or table loom.
Like a lot of different types of weaving, it is possible to do it on almost any type of loom that you have. The difference being that it might take you a little bit longer or require a bit more effort than if you did it on a traditional floor loom.
Weaving overshot on a frame loom or rigid heddle loom will require the use of string heddles and pick-up sticks that you have to manually use to create a shed.




 8613371530291
8613371530291