overshot jaw price

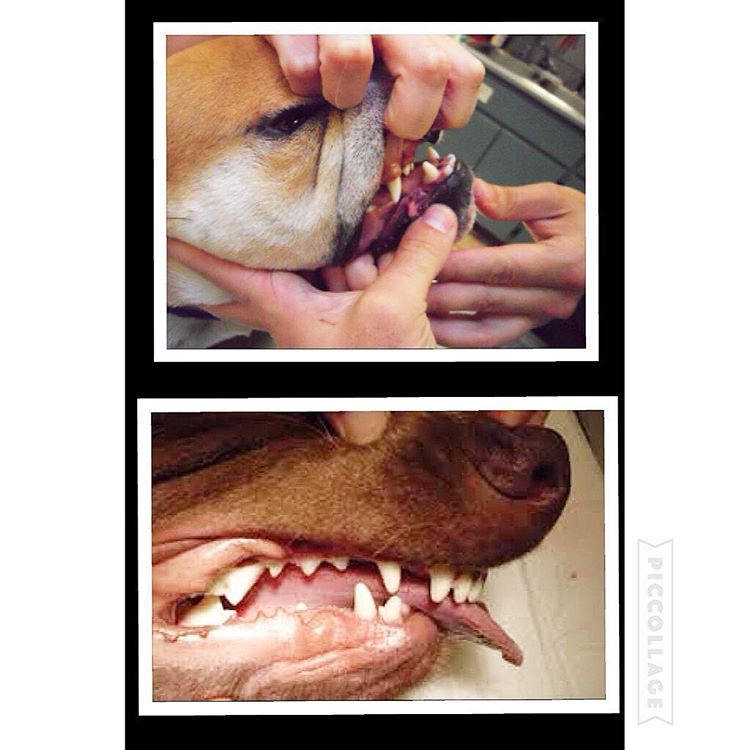
Enzo is a short-haired Havanese and he was born with his lower jaw shorter than the upper jaw. This is called an Overbite, also referred to as an Overshot Jaw, a Parrot Mouth or Mandibular Brachygnathism. This malocclusion is a genetic change and can be seen in a number of breeds, oftentimes collie related breeds and dachshunds. Occasionally this change happens because of differences in the growth of the upper and lower jaws, and in many cases it doesn’t cause any significant problems other than cosmetically.
Dr. Robin Riedinger evaluated Enzo at his first visit when he was just 11 weeks of age and while the lower jaw was too short, there was no evidence of damage and no indication that this was causing a problem for Enzo. When there is abnormal occlusion of the teeth, it is important to monitor closely for trouble caused by the teeth being aligned improperly. Malocclusions can lead to gum injuries, puncturing of the hard palate, abnormal positioning of adjacent teeth, abnormal wear and bruising of the teeth, permanent damage and subsequent death of one or more teeth, and in the long run, premature loss of teeth. Some malocclusions can be severe enough to interfere with normal eating and drinking.
Within three weeks, when Enzo was only 3.5 months old, it was clear that our doctors would need to intervene. The left and right sides of Enzo’s upper jaw (maxilla) were growing at different rates because the lower canine teeth were being trapped by the upper canine teeth. This is called Dental Interlock. Because the teeth are ‘locked’ in place, the lower jaw cannot grow symmetrically and this creates a number of other problems. Early intervention is critical.
The solution for Dental Interlock is to extract the teeth from the shorter jaw; in this case, the lower ‘baby’ canines and thereby allow the lower jaw (mandible) to grow in the best way possible. This procedure is most effective when the Dental Interlock is discovered early and the extractions are performed quickly. In some cases, this can be as early as ten weeks of age. Dr. Riedinger consulted with a local veterinary dental specialist to confirm the treatment plan and to get advice on extracting the deciduous teeth without damaging the developing adult canines. Dental radiographs are essential to proper extraction technique and also to ensure that there are no other abnormalities below the gumline.
Enzo came through his procedure extremely well. He was given pain medications for comfort and had to eat canned foods and avoid chewing on his toys for the next two weeks to ensure that the gum tissue healed properly. As he continues to grow we will be monitoring how his jaw develops and Dr. Riedinger will also be watching the alignment of his adult canine teeth when they start to emerge around six months of age. Hopefully this early intervention will minimize problems for Enzo in the future.
An overbite is a genetic, hereditary condition where a dog"s lower jaw is significantly shorter than its upper jaw. This can also be called an overshot jaw, overjet, parrot mouth, class 2 malocclusion or mandibular brachynathism, but the result is the same – the dog"s teeth aren"t aligning properly. In time, the teeth can become improperly locked together as the dog bites, creating even more severe crookedness as the jaw cannot grow appropriately.
Dental examinations for puppies are the first step toward minimizing the discomfort and effects of an overbite. Puppies can begin to show signs of an overbite as early as 8-12 weeks old, and by the time a puppy is 10 months old, its jaw alignment will be permanently set and any overbite treatment will be much more challenging. This is a relatively narrow window to detect and correct overbites, but it is not impossible.
Small overbites often correct themselves as the puppy matures, and brushing the dog"s teeth regularly to prevent buildup can help keep the overbite from becoming more severe. If the dog is showing signs of an overbite, it is best to avoid any tug-of-war games that can put additional strain and stress on the jaw and could exacerbate the deformation.
If the dog is young enough, however, tooth extraction is generally preferred to correct an overbite. Puppies have baby teeth, and if those teeth are misaligned, removing them can loosen the jaw and provide space for it to grow properly and realign itself before the adult teeth come in. Proper extraction will not harm those adult teeth, but the puppy"s mouth will be tender after the procedure and because they will have fewer teeth for several weeks or months until their adult teeth have emerged, some dietary changes and softer foods may be necessary.

Undershot is a class III malocclusion that is also referred to as mandibular prognathism, maxillary brachygnathism, mandibular mesioclusion, or an underbite. This malocclusion is characterized by a shorter upper jaw and a longer lower jaw, resulting in lower teeth that are in front of the upper teeth. While this condition is normal for some breeds, such as Bulldogs, in many breeds it is unusual. An undershot jaw occurs when the lower jaw grows faster than normal and becomes longer than the upper jaw, and is usually evident around 8 weeks of age in puppies. This misalignment can cause soft tissue trauma, such as to the lips. When the incisors meet instead of fitting next to each other, it is called a level bite. When the malocclusion causes the lower incisors to be placed in front of the upper incisors, it is called a reverse scissors bite.
The cause of overshot and undershot jaws in dogs relate to the increased or decreased rate of growth of the upper and lower jaws in relation to one another. This can occur due to a: Genetic disorder Trauma; Systemic infection ;Nutritional disorder; Endocrine disorder; Abnormal setting of puppy teeth; Early or late loss of puppy teeth.
After a quick physical exam, your vet may have to sedate your dog in order to perform a thorough oral exam. This will assess your dog’s skull type and teeth location in relation to the teeth on the opposite jaw. Often, the placement of the upper and lower incisors in relation to one another can determine what type of malocclusion your dog has. Your vet will note any areas of trauma due to teeth striking those areas, and any cysts, tumors, abscesses, or remaining puppy teeth that may be present. A dental X-ray can also help to assess the health of the jaws and teeth. These diagnostic methods will lead to a diagnosis of an overshot or undershot jaw in your dog.
Treatment of a jaw misalignment will depend on the severity of the condition. If your dog has a misalignment, but can still bite and chew food without problems, no treatment may be needed. If the misalignment is caught early in a puppy’s life, it may only be temporary and may correct itself over time. However, there are times when intervention may be needed. If your puppy’s teeth are stopping the normal growth of his jaws, then surgery to remove those puppy teeth may be performed. This may allow the jaws to continue to grow, but will not make them grow. For older dogs who are experiencing pain and trauma due to misaligned jaws and teeth, oral surgery is generally performed to extract teeth that are causing trauma, to move teeth so that they fit, or to create space for a misaligned tooth to occupy. Other therapies include crown reductions or braces.
If your dog is genetically programmed to have an overshot or undershot jaw, intervention can help, but will not slow or stop the abnormal growth of either jaw. Prevent jaw misalignments in puppies by not breeding dogs who have overshot or undershot jaws.
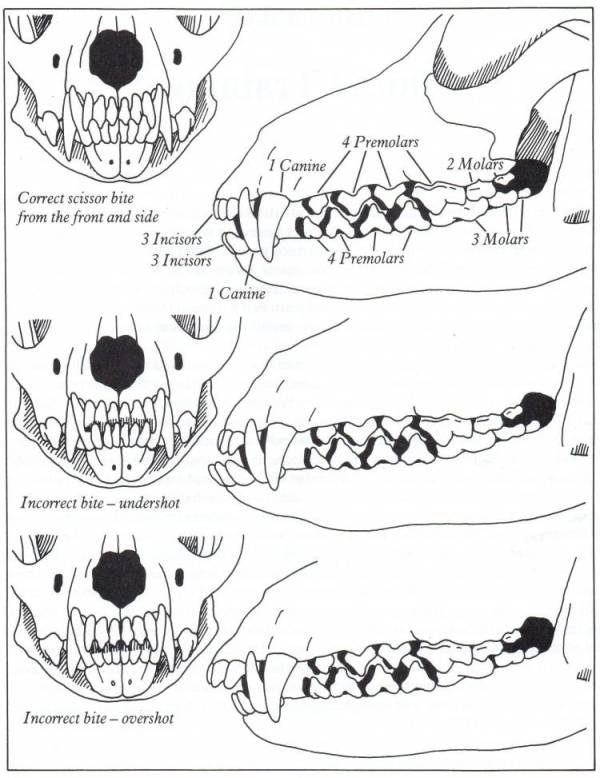
The ‘carnassial’ teeth are the large specialised pair of teeth towards the back of the mouth on each side, which work together like the blades of a pair of scissors. The upper carnassial is the fourth premolar, while the lower one is the first molar The upper jaw is the maxilla, and the lower jaw is the mandible.
Malocclusion is the termed used for an abnormal bite. This can arise when there are abnormalities in tooth position, jaw length, or both. The simplest form of malocclusion is when there are rotated or crowded teeth. These are most frequently seen in breeds with shortened muzzles, where 42 teeth need to be squeezed into their relatively smaller jaws. Affected teeth are prone to periodontal disease (inflammation of the tissues supporting the teeth, including the gums and jawbone), and early tooth loss.
Class II malocclusions (‘overshot’) arise when the lower jaw is relatively short compared with the upper jaw. This type of occlusion is NEVER considered normal and can result in significant and painful trauma to the upper gums, hard palate and teeth from the lower canines and incisors.
Class III malocclusions (‘undershot’, ‘prognathism’) occur when the lower jaw is relatively long compared with the upper jaw. The upper incisors may either meet the lower ones (level bite) or sit behind them (reverse scissor bite). While this is very common, and considered normal for some breeds, it can cause problems if the upper incisors are hitting the floor of the mouth or the lower teeth (similar problems to rostral crossbite). If the lower canines are striking the upper incisors, the accelerated dental wear often results in dead or broken teeth.
Class IV malocclusions (‘wry bite’) occur when there is a deviation of one or both jaws in any direction (up and down, side to side or front to back). These may be associated with mild to severe problems with chewing, damage to teeth and oral tissues, and chronic pain.
Normal development of the teeth and jaws is largely under genetic control, however environmental forces such as nutrition, trauma, dental interlock and other mechanical forces can also affect the final outcome.
Most malocclusions involving jaw length (skeletal) abnormalities are genetic in origin. We need to recognise this as it has enormous implications if you are planning to breed, as once a malocclusion is established in a line, it can be heartbreaking work to try and breed it back out.
The exact genes involved in jaw development are not yet well understood. We do know that the upper and lower jaws grow at different rates, at different times, and are under separate genetic control. In fact, the growth of one only affects the growth of the other if there is physical contact between them via the teeth. This contact is called ‘dental interlock’.
When the upper and lower teeth are locked against each other, the independent growth of either jaw is severely limited. This can occasionally work in the dog’s favour, for example if the lower jaw is slightly long compared with the upper jaw, the corner incisors may lock the lower canines in position behind them, limiting any further growth spurts of the lower jaw.
However, in many cases, dental interlock interferes with jaw development in a negative way. A classic example we see regularly in our practice is when a young puppy has a class II malocclusion (relatively short lower jaw) and the lower deciduous canines are locked behind the upper deciduous canines, or trapped in the tissues of the hard palate. In these cases, even if the lower jaw was genetically programmed to catch up to the upper jaw, it cannot physically do so.
Extraction of these teeth will not stimulate jaw growth, but will allow it to occur if nature (ie genetic potential) permits. It also relieves the painful trauma caused by the teeth to the hard palate whenever the pup closes its mouth (and we all know how sharp those baby teeth are!!). More information on interceptive orthodontics can be found later in this book.
Although diet often gets the blame for development of malocclusions, the role of nutrition is actually much less significant than is often believed. Obviously gross dietary deficiencies will affect bone and tooth development, for example severe calcium deficiency can lead to ‘rubber jaw’. However, the vast majority of puppies are on balanced, complete diets and have adequate nutrient intake for normal bone and tooth development.
One myth I have heard repeated by several owners is that strict limitation of a puppy’s dietary intake can be used to correct an undershot jaw. This is simply NOT true. Limiting calories will NOT slow the growth of the lower jaw relative to the upper jaw (both jaws receive the same nutrient supply). Such a practice is not only ineffective, it can be detrimental for the puppy’s overall growth and development.
Trauma, infection and other mechanical forces may affect growth and development of the jaws and teeth. Developing tooth buds are highly sensitive to inflammation and infection, and malformed teeth may erupt into abnormal positions (or not erupt at all!). Damage to developing teeth can also occur if the jaw is fractured.
Extraction of lower canine teeth – the roots of these teeth make up about 70% of the front of the jaw, and so there is a potential risk of jaw fracture associated with their removal. Some dogs also use these teeth to keep the tongue in position, so the tongue may hang out after extraction.
This is the term we use when we remove deciduous teeth to alter the development of a malocclusion. The most common form of this is when we relieve dental interlock that is restricting normal jaw development. Such intervention does not make the jaw grow faster, but will allow it to develop to its genetic potential by removing the mechanical obstruction.
Extraction of deciduous lower canines and incisors in a puppy with an overbite releases the dental interlock and gives the lower jaw the time to ‘catch up’ (if genetically possible).
As jaw growth is rapid in the first few months of life, it is critical to have any issues assessed and addressed as soon as they are noticed, to give the most time for any potential corrective growth to occur before the adult teeth erupt and dental interlock potentially redevelops. Ideally treatment is performed from eight weeks of age.
Extraction of deciduous teeth is not necessarily as easy as many people imagine. These teeth are very thin-walled and fragile, with long narrow roots extending deep into the jaw. The developing adult tooth bud is sitting right near the root, and can be easily damaged. High detail intraoral (dental) xrays can help us locate these tooth buds, so we can reduce the risk of permanent trauma to them. Under no circumstances should these teeth be snapped or clipped off as this is not only inhumane, but likely to cause serious infection and ongoing problems below the surface.
Sometimes, the tooth will be in a favourable position but caught behind a small rim of jawbone – again early surgical intervention may be successful in relieving this obstruction. If the tooth is in an abnormal position or deformed, it may be unable to erupt even with timely surgery.
Impacted or embedded teeth should be removed if they are unable to erupt with assistance. If left in the jaw, a dentigerous cyst may form around the tooth. These can be very destructive as they expand and destroy the jawbone and surrounding teeth. Occasionally these cysts may also undergo malignant transformation (ie develop into cancer).
Firstly, if there are two teeth in one socket (deciduous and adult), the surrounding gum cannot form a proper seal between these teeth, leaving a leaky pathway for oral bacteria to spread straight down the roots of the teeth into the jawbone. Trapping of plaque, food and debris between the teeth also promotes accelerated periodontal disease. This not only causes discomfort and puts the adult tooth at risk of early loss, but allows infection to enter the bloodstream and affect the rest of the body.
Broken teeth also become infected, with bacteria from the mouth gaining free passage through the exposed pulp chamber inside the tooth, deep into the underlying jawbone. This is not only painful, but can lead to irreversible damage to the developing adult tooth bud, which may range from defects in the enamel (discoloured patches on the tooth) through to arrested development and inability to erupt. The infection can also spread through the bloodstream to the rest of the body. Waiting for the teeth to fall out is NOT a good option!

Extraction therapy of puppy teeth is recommended as young as possible (6-9 weeks of age), to relieve the pain of tooth-to-palate contact as well as to allow the lower jaws to grow to their genetic potential. Unfortunately, most lower jaws will remain too short. Therefore, these pets must be re-evaluated at 5.5 months of age to select the best therapy: orthodontic therapy, extraction of the lower canine teeth or crown reduction (shortening the teeth) and pulp capping.

Secondly, the growth of the mandible is rostral from the junction of the vertical and horizontal ramus. If the lower canines are embedded in pits in the hard palate, the normal rostral growth of the mandible(s) cannot take place normally due to the dental interlock caused by the lower canines being embedded in hard palate pits. This can cause deviation of the skull laterally or ventral bowing of the mandibles (lower jaws).
Thirdly, the permanent lower canine is located lingual to the deciduous canine. This means that if the deciduous lower canines are in a poor position it is a certainty the permanent teeth will be worse. See the radiograph below. The deciduous canines are on the outside of the jaws and the developing permanent canines are seen in the jaw as small "hats". It is clear that the eruption path of the permanent canines will be directly dorsal and not buccally inclined as is normal.
The permanent successor tooth is located lingual to the deciduous tooth and wholly within the jaw at this stage. Any use of luxators or elevators on the lingual half of the deciduous tooth will cause permanent damage to the developing enamel of the permanent tooth. See the images below showing canines (and also the third incisor) with extensive damage to the enamel. The radiograph also shows how much damage can occur to the teeth - see the top canine and adjacent incisor. Some severely damaged teeth need to be extracted while other can be repaired with a bonded composite. This damage is avoidable with careful technique using an open surgical approach.
Do not try ball therapy with deciduous (puppy) teeth. There are two main reasons for this. Puppy teeth are fragile and can easily break. More importantly, the adult canine tooth bud is developing in the jaw medial to the deciduous canine tooth (see radiograph above in the puppy section). If the deciduous crown tips outwards the root will tip inwards. This will push the permanent tooth bud further medial than it already is.
The intention of the procedure is to keep the pulp alive and allow the shortened lower canines to develop normally and contribute to the strength of the lower jaws.
The advantage of this procedure is that the whole of the root and the majority of the crown remain. The strength and integrity of the lower jaw is not weakened by the procedure and long term results are very good due to the use of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate as a direct pulp dressing.
However, many owners are concerned (rightly) about the loss of the tooth and the weakness it may cause to the lower jaw(s). It is not our preferred option. This is not an easy surgical extraction and the resulting loss of the root causes a weakness in the lower jaws. This is compounded if both lower canines are removed.
Normally a composite resin bite plane is bonded onto the upper teeth (see below) with an incline cut into the sides. The lower canine makes contact with the incline when the mouth closes and, over time, the force tips the tooth buccally. This takes around four to eight weeks. The lower canine will often migrate back into a lingually displaced position when the bite plane is removed. This can occur if the tooth height of the lower canine is too short (stunted). If the lower canine is not self-retained by the upper jaw when the mouth is shut further surgery may be required.
It really depends on how overshot his mouth is as to whether it will affect him eating properly.Sometimes an overshot jaw can be occompanied by a twisted jaw too. As long as he can eat it really won"t affect him at all.
Yes I believe undershot is when the lower jaw protudes beyond the upper jaw and overshot is when the upper jaw protrudes over the lower jaw. It is my understanding that the overshot can be more of a problem but of course depends on the severity or degree to which it occurs. Hopefully there are some breeders out there with more knowledge on this that can explain.
looking-for-a-friend - if you are not planning to show your pup, and he is obviously managing to eat and enjoy life, then I can"t see that the jaw will be a problem. Sometimes they can correct, depending on the severity - right up to 3 years of age. I would expect some reduction in his price though.
We had a newf who had a serious overshot jaw. The bottom teeth went up into the roof of his mouth and they had to be ground down so they didn"t cause any more damage. He had a hard time picking things up off the ground because his nose got in the way before his bottom teeth...
If he"s already overshot, there"s always the chance it could get worse. or it could get better! You never know. But this is probably not the worst problem a puppy could have.
Hmmm, a good breeder should give a price reduction on something like this as it definitely means the dog can"t be shown. When my parents got thir pyrenees puppy over 40 years ago, the breeder called to apologise and say Lani turned out to have a slightly undershot jaw that would not likely correct. They offered another choice of puppy in the next litter or another not yet chosen in the current litter, or half off the price of Lani who then also had to be sold under a spay contract. My parents already had their hearts set on Lani and never planned to show and had intended to spay anyway, so none of this was an issue. She lived to a ripe age for a pyr, around 12 or 13, and was adored by us all.
So on the one hand, unless a truly serious problem for the puppy, there should be no issue for you at all. And yes, by all accounts they do *sometimes* correct, and as well, a perfect scissors bite in a puppy sometimes gets undershot or overshot as the dog grows. The breeders discuss these issues from time to time over on one of the breeder email lists that I subscribe to.
Teeth will become easier to clean. Your risks for tooth decay and gum disease will decrease. You’ll also feel less strain on your teeth, jaws, and facial muscles.
Removal of one or more teeth on the lower jaw may also help improve the appearance of an underbite if overcrowding of the teeth is contributing to the issue. A dentist may also use a grinding device to shave down or smooth teeth that are large or stick out.

The average overbite is around 2 – 4mm. This is a normal range and both your upper and lower teeth will be aesthetically appealing. If your overbite is smaller, your lower teeth will be more noticeable. When there is a significantly reduced overbite or none at all, it’s referred to as an anterior open bite. With an anterior open bite, there’s usually a gap between your upper and lower teeth when your jaws are closed.
To make things worse, overbites can be exacerbated by early childhood habits like thumb sucking. Sucking your thumb puts pressure on your upper teeth. In turn, this forces them forward and places pressure on your lower jaw, forcing your jaw backward.
This type of overbite occurs when your teeth aren’t properly aligned. In such cases, your lower jaw may be well balanced with your upper jaw, but the misalignment of your teeth causes your lower jaw to force back towards your neck. Typically, nonsurgical treatments work well for this type of overbite correction for adults.A Skeletal Overbite
With this type of overbite, your lower jaw is too small to fit your upper jaw. As a result, the upper rows of teeth push forward over your small jaw. Skeletal overbites usually require surgical solutions to realign the jaw.
What’s more, an overbite can result in tooth wear and damage, and even sleep apnoea. Jaw pain is another consequence of an uncorrected overbite. Misaligned jaws can lead to chronic jaw pain and even headaches, contributing to the development of Temporomandibular Joint Disorder (TMD).
Typically, a dentist will refer you to an orthodontist for overbite correction. Overbites tend to be easier to treat in children, since a child’s jaw is still developing, however overbite correction for adults is quite common.
Your orthodontist will start with x-rays, to determine what kind of overbite you have and the relationship between your jaw and teeth. From here, they will develop a treatment plan.

It is important that the horse"s incisor bite be checked with the head in the normal resting position and not raised up high. Raising the head high, or extending the poll joint, will cause the lower jaw (mandible) to slide backwards (caudally) slightly (approx 3- 10 mm). Conversely, when the head is lowered and the poll flexes, the lower jaw (mandible) slides forward.
This backward and forward sliding of the jaw when the head is raised and lowered is knownas Rostro-Caudal Movement (RCM). It is a normal process which is required for normal chewing and comfort to the horse when ridden. So even though most of the jaw movement when eating is from side to side (lateral movement), there is also a small amount of backwards and forwards movement of the lower jaw (RCM).
The condition can result from the top jaw (maxilla) developing too long, or the bottom jaw (mandible) developing too short. Usually it is the lower jaw that is too short. But anything which interferes with the match up of the top and bottom jaws can cause a horse to be parrot mouthed.
The real problems with being parrot mouthed are due to the fact that horses" teeth are hypsodont teeth — that means that they have long crowns up in the bone and continue to erupt or move into the mouth throughout life — up to a point where there is no more tooth left to erupt into the mouth. If they are not opposing another tooth, they continue to erupt into the mouth to a point where they are a problem and dig into the opposite jaw etc.
As the elongating tooth or teeth become more prominent, they may cause the tooth to be moved or forced out of its normal position and they also may restrict the whole jaw"s normal RCM (rostro-caudal movement) whilst eating or when ridden.
When being ridden the hooks and ridges restrict the free gliding movement of the jaw (RCM) during flexion and other changes in head position. Thus these affected horses may be not as light in the mouth as they should be during collection, or they may work behind the bit, or they may have a bad head toss at transitions.
The floating must be certain to address the associated overgrowths of teeth which arise and encourage the backwards displacement of the Mandible (jaw). These overgrowths include lipping of the incisors, hooks on the cheek teeth and excessive transverse ridges on the cheek teeth. Obviously the sharp enamel points must also be addressed.
The results of these orthodontic techniques are more functional than cosmetic, and there are possible side effects. The wiring requires many general anaesthetics as the jaw grows, so the orthodontic wiring programme becomes quite expensive and will need to continue for months to years. It needs to be commenced when the foals are young, but the foal needs to be able to eat creep feeds such as pellets and chaff.

With much more crossbreeding happening these days, we have seen a rise in jaw problems in dogs. This will often become apparent in the puppy. The top (maxilla) and the bottom (mandible) jaws are under control from two different sets of genes, so when we see breeding between different head shaped dogs we sometimes see the two jaws at different positions.
The most common problem we see in jaw development is an undershot jaw. This is also called prognathism or a Class 3 Malocclusion. This is where the mandibles are relatively too long for the maxilla. A classic breed to suffer from this problem is the Boxer or a Shih Tzu. This malocclusion causes the teeth to not line up properly. As they are designed to damage tissue, any tissue, they do! In dogs with an undershot jaw it is not uncommon for the upper incisors (the front teeth) to touch or dig into the bottom jaw, behind the lower incisors. Although this is arguably cute, the teeth over time can cause a great deal of discomfort and even end up damaging the bone and teeth of the lower jaw.
The opposite problem which we are seeing more and more of is an overbite. Also, called brachygnathism or a Class 2 Malocclusion. This is where the top jaw is relatively too long for the mandibles. This can result in a much bigger problem for those dogs affected. Even as puppies the lower deciduous canines can be in such a position that they strike the roof of the mouth. Anyone who has played with puppies knows that these are sharp and painful teeth. Every time these puppies close their mouths it hurts. This also will occur with the following adult canine teeth too. However, they are much larger and can cause much more of a problem with the dog’s mouth.




 8613371530291
8613371530291