overshot weaving definition brands

Overshot is a magical structure. The first time you weave it you can hardly believe the cloth that grows on your loom. Traditionally used to weave bed coverings, overshot has many beautiful applications in today"s world, from useful household textiles to breathtaking works of art. This versatile weave is subject to endless variations. Here are a few of our favorite tips and a few truly spectacular projects, too! If you are inspired, come visit us and learn from a master weaver, Joanne Hall. See details below about her workshop.
A slouchy bag by FiberMusings on Weavolution pairs leftover BFL singles with sturdy Cottolin to create a fashionable yet functional multi-colored bag. The draft is a design from Ann Weaver"s Handweavers Pattern Dictionary, and it"s a great way to integrate Overshot techniques while making an eye-catching accessory!
Another project that caught our eye recently was a shower curtain shared by GailR@30 shared on Weaving Today - it"s nothing short of amazing (click here to see for yourself)! Consisting of thirteen different overshot pattern threadings woven in thirteen different treadlings, 169 different design effects are created based on designs from Osma Gallinger Tod"s book The Joy of Handweaving. As Gail noted on her project page, a great way to make each design stand out is to separate them with twill bands (even though it might mean a little more work in the process!)
Or, you may choose to elevate your weaving like the work of art it most certainly is, as Evaweave did with her Overshot Study pieces. These two miniature silk rugs look lovely in a frame, don"t you think? The overshot pattern was adapted from Overshot Weaving by Ellen Lewis Saltzman, complementing one another perfectly.
Think overshot is too difficult to try? Deb Essen thinks otherwise! Fiber artist, designer, and teacher, Deb is a passionate weaver who specializes in using overshot name drafts to create "secret messages" in cloth.
On her website, she explains: "Overshot is a weave structure and a draft is the weaver"s guide to creating patterns in cloth. Overshot name drafts assign the letters of a name or phrase to the shafts on a loom, creating a pattern that is unique. The one-of-a-kind patterns become a secret hidden message in the cloth and only those knowing the secret can break the code."
Deb lets you in on the secret with her clever kits, each with a hidden message. We"re particularly fond of her That"s Doable kit, which features Mountain Colors hand-painted yarns and, as the name would imply, is our first choice for those new to overshot weaving.

In its simplest form – overshot is a weaving technique that utilizes at least 2 different types of weft yarns and floats to create a pattern. These patterns are often heavily geometric.
Ground weft– plain weave pattern that is used between each row of your overshot pattern. This plain weave gives the textile structure and allows for large areas of overshot to be woven without creating an overly sleazy fabric. Without the use of a ground weft on an overshot pattern, the weaving would not hold together because there would not be enough warp and weft intersections to create a solid weaving.
They were most popular though in southern Appalachia and continued to be so even after textile technologies advanced. When other parts of colonial America moved to jacquard weaving, the weavers of southern Appalachia continued to weave their overshot coverlets by hand.
Since the overshot coverlets were most often woven at home on smaller looms they usually had a seam down the middle where two woven panels were sewn together.
The thing about overshot is that no matter the application, it is pretty impressive. Perhaps that is just my opinion, but due to how complex it can look, I feel that it is pretty safe to say.
Just because it was originally used for coverlets, does not mean it can only be used for coverlets. Changing aspects of the pattern like the colors used, or the way you use your ground weft can drastically change the look and feel of your weaving.
In the image below you can see the ground weft is not the same color throughout. Instead, I wove the ground weft as discontinuous so that I could add extra pattern and design into the weavings. In this case, you may be wondering how to deal with your weft yarns when they are in the middle of the weaving and not at the selvage.
The discontinuous weft yarns will float onto the back of the weaving until you are ready for them in their next pick. This does make your overshot weaving one sided since it will have vertical floats on the back. Keep this in mind if you want to try this technique out.
Also seen in the image above, the overshot yarn that I used was not all one color! This is a really simple way to get extra dimension and interest in your overshot if that is something you are looking for.
This makes it simple to be able to only weave overshot in certain parts of your weaving. If you want to do this then you can continue to weave your plain weave across the entire width of your weaving, but only weave overshot in specific areas. This creates a overshot section that functions similar to inlay.
Since the overshot pattern is strongly influenced by the weft yarns that are used it is important to choose the right yarns. Your weaving will be set up to the specification needed for a balanced plain weave. Make sure you understand EPI in order to get the right warp sett for your overshot weaving.
The ground weft used is almost always the same yarn as your warp. This allows the overshot weft to really be able to shine without contrasting warp and weft plain weave yarns.
In order to get the full effect of the overshot, it must be thick enough that when you are weaving your pattern it covers up the ground weft between each pass. If it is not thick enough to do this, it will still be overshot, but the full effect will not be seen.
What this warp thread does is serve as an all-purpose selvedge that does not correspond with your pattern. Instead, you would make sure to go around this warp thread every time to make sure that you are able to weave fully to the selvedge. Without this, your overshot weft will float awkwardly on the back of your weaving whenever the pattern does not take it to the edge.
I have mentioned this book multiple times because it really is such a great resource for any weaver looking to weave patterns of all types. It contains 23 pages of different overshot patterns (among so many other patterns) that you can set up on your floor or table loom.
Like a lot of different types of weaving, it is possible to do it on almost any type of loom that you have. The difference being that it might take you a little bit longer or require a bit more effort than if you did it on a traditional floor loom.
Weaving overshot on a frame loom or rigid heddle loom will require the use of string heddles and pick-up sticks that you have to manually use to create a shed.

Over three years ago, when my David Louet floor loom was still somewhat new to me, I wrotethis post on overshot. If you read it, you will discover that my initial relationship with overshot was not a very positive one.
Back then, I was a little harder on myself as a learning weaver. By now, I’ve realised that weaving, just like life, is a journey that has a beginning but no end. Back then, I thought that my ultimate goal was to be a “master weaver”.
The happy ending to the initial overshot sob story is that I can weave overshot now. Quite well, in fact! And I also teach it. And I happen to love it, very, very much. Don’t you love a happy ending?
I don’t think there was any particular moment where I thought to myself “I can weave overshot now!” I didn’t even weave any overshot for quite some time after that initial attempt. But slowly it tempted me back, and we started over. It was just a matter of sticking with it, employing some specific techniques and practice, practice, practice until it feels like an old friend.
My love of overshot has only increased with my more recent discovery of American Coverlets. I loved the look of the coverlets and the history behind them before I realised that so many of them were woven in the wonderfully humble 4 shaft overshot.
I’ve put a lot of research time into coverlets this year and have made it a big weaving goal of mine to weave my first coverlet, which is quite an undertaking, but I relish the thought.
Now that I have quite a lot of experience weaving overshot, I want to share my best overshot tips with you in hope that you too will fall in love with this wonderful weave structure.
To weave overshot you need a warp yarn, a tabby yarn and a pattern weft yarn. Using the same yarn for warp and tabby works perfectly. For the pattern weft, I like to use a yarn that is twice the size of the tabby/warp yarn. I have experimented with using doubled strands of tabby/warp yarn in a contrasting colour, but it just doesn’t look as good. A thicker pattern yarn is the way to go.
What will the size of your item be? A miniature overshot pattern may get lost in a blanket, but may be perfect for a scarf. As a general rule, a good way to estimate the size of one repeat of your pattern just by looking at the draft is to see how many repeats are in one threading repeat. Also consider the thickness of your yarns and the sett you intend to weave.
Just to give you an idea, my current project is woven at 20 ends per inch with 8/2 cotton for warp and tabby and fingering weight wool for the pattern weft. The weaving draft has 50 threads in one threading repeat. My design repeats on the loom are around 2.5″ wide and just under 5″ long, which is a great size for the 30″ x 99″ throw I’m weaving.
This is a non negotiable for overshot if you want neat edges and less headaches! You get used to using floating selvedges very quickly, so don’t stress if you have no experience with them.
There are 6 treadles needed for overshot, even though you weave on 4 shafts. The two extra treadles are for the tabby weave. I always set up my pattern treadles in the centre of the loom – two on the left and two on the right. Then I set up a “left” tabby and a “right” tabby treadle. To do this on my 8 shaft loom I leave a gap between the pattern treadles and the tabby treadles so that my feet can “see” and differentiate between a pattern and tabby treadle.
I like to advance little and often. You will find your own preference or “sweet spot” for weaving, but I find that with overshot I advance a lot more frequently at a much smaller amount than I do usually.
An example of this is that I wove an overshot sampler right before Is started my main project (the throw). It was a narrow warp (around 8″) and a different overshot threading and treadling than I’m using for the project.
I personally do not use a temple. Some weavers will say they won’t weave without one. I’ve tried using a temple on many of my projects, particularly if I’m getting broken edge warp threads (signs of tension problems and too much draw in). But I will avoid using one wherever I can get away with it, and I don’t use one for weaving overshot.
I find that if I’m careful with weft tension and warping evenly, I do not get excessive draw in. It is something I’m constantly aware of while weaving and remind myself of tip 4 so that my weft picks are not pulling in at the edges.

Cloth is woven on a grid of vertical warps and horizontal wefts. But, with a bit of knowledge about designing weaving drafts, you can use these rectilinear elements to create smoothly flowing lines in your woven fabric.
In this article, I focus on designing with overshot blocks in order to create flowing curves large enough to be seen at a distance. I will also discuss "weaving as overshot" which is a method of applying overshot techniques to other weave structures and, finally, finish up with some strategies for designing curves in any weave structure.
In the twill draft above, the diagonal lines are only three threads apart, which might be too subtle an effect. To make the scale of your design larger, you can use a diagonal progression of weave-structure blocks instead of individual threads. The following draft shows an example of a diagonal progression using overshot blocks on four shafts.
Overshot is a weave structure creating a plain-weave cloth with decorative supplementary weft floats. These floats lie on top of (float over) the ground cloth. If you pull out all of the pattern weft threads, you are left with a plain weave cloth formed by the warp and the tabby weft. There are never any warp floats because of the tabby weft.
Weaving software is very helpful for testing hues and values for weft yarns to use with your warp. If you choose to weave overshot with a single shuttle, choose a contrasting value to the warp for a subtle design but faster weaving.
If you put the curve in your threading, the waves travel across the fabric horizontally, in the direction of the weft. You can see this in the overshot draft below.
Another disadvantage to putting the curves in the threading is that it limits your ability to improvise curved designs organically at the loom. It"s easy to change treadling patterns during weaving. Changing the threading, however, is a much more involved process.
I learned how to make curves by studying a traditional overshot draft called Blooming Leaf (page 133 in A Handweaver"s Pattern Book by Marguerite Davison). In this draft, the treadling maintains a diagonal progression but the scale changes to make the shape "bloom" and undulate.
[Note: When I create overshot drafts, I place the first pattern block on treadle three; I like to weave the tabby picks with my left foot (alternating between treadles one and two) and use my right foot (on the remaining treadles) to weave the pattern weft and create the design.]
Now that you know how to create curves, undulations, and reflected curves, you have the tools you need to create any kind of curve or diagonal line in four-shaft overshot. For a challenge, try making a long curve followed by a short curve, like a meandering river.
The methods described above also work for overshot on six, eight, ten, or more shafts. As you add additional shafts to your design, you gain the ability to create smoother and more dramatic curves.
Below is an example of an eight-shaft overshot threading; in this case a diagonal progression with a point and mirror symmetry. My treadling in this draft is an S-shaped curve. This is just one example of the many different curves you can weave on this threading.
Because the underlying structure of overshot is plain weave, any threading which can produce plain weave can theoretically be woven as overshot, alternating tabby and pattern weft.
I wove the draft above using a 20/2 silk sett at 30 epi. I chose to sett the yarn this densely so I could weave both an overshot and twill version on the same warp. You can see the resulting cloth in the picture below.
How do I weave as overshot when my sett is more appropriate for twill? I use a tabby weft that is much finer than the warp, in this case 140/2 silk from Lunatic Fringe.
Other times I choose to weave as overshot because the floats show off the pattern-weft yarn, such as the handspun wool used as the pattern weft in the cloth below.
It is easy and fun to make up a curved treadling at the loom, especially when weaving as overshot. Even after forty-two years of weaving, I still enjoy working with long, non-repeating treadlings; watching the curves grow and change as I weave. Instead of memorizing a sequence and repeating it carefully, I watch the design and think about where I want the next curve to go.
A side benefit of weaving long, undulating curves instead of small, repeated patterns is that a small variation in a repeat will stand out, but design variations are normal in organic curves.
The drape of overshot fabric is not as fluid as that of a twill fabric. So for a scarf or shawl I might choose a structure other than overshot. Fine silk, however, has such nice drape that I can weave as overshot and still get good results.
With weaving software, it is easy to create curved overshot designs. Simply draw a freehand curve in the treadling—smoothing it out if necessary—and then add the tabby shots. Once you have the general idea from designing drafts, you can improvise new curved designs at the loom.
For other weave structures, creating a profile draft can be helpful. A profile draft is a design template that represents the woven design at one level of abstraction. To convert a profile draft into a weaving draft, you replace each block in a profile draft with the appropriate block of a given weave structure. You can, therefore, express a single profile draft in many different weave structures: overshot, summer-and-winter, Bronson lace, huck lace, double weave, etc.
Profile drafts with smooth, flowing curves are also useful for learning how to design graceful lines. Weaving software helps because you can quickly create and edit drafts. None of the weaving programs I"m familiar with have an option to create "graceful" or "smooth" curves. So you"ll have to train your hand and eye, but this comes with practice.
I like smooth, flowing curves that are visible at a distance. So I look for structures that give me the maximum number of pattern blocks to design with. Generally I use weave structures where I have as many pattern blocks as there are shafts on my loom. On a four-shaft loom, I use crackle, overshot, advancing and network-drafted twills, advancing points, turned taqueté, rep, and shadow weave.
If you work with graph paper, remember to check the repeats, i.e., transitions, in the threading and treadling to make sure there aren"t gaps or discontinuous areas that affect the flow of your curve. In weaving software, you can do this easily by zooming out the view to check the draft over several repeats.

It"s making me smile to get this question since I just finished recording a DVD on block weaves. I sure hope I make this very clear in the video, but here goes a short version. The first definition you"ll need to understand is the definition of block weaves. These are weaves in which the same warp and weft threads can make two different-looking interlacements, one that we identify as pattern ("figure") and the other as background (think about how you see a rose motif in some overshot drafts on a background of plain weave). Overshot is a block weave, and so is Atwater-Bronson lace and summer and winter and many more.
Summer and winter and Atwater-Bronson lace are like this. You can design a large center table or a heart or a large diamond of lace or summer-and-winter pattern-weft floats against a background, for example. But with overshot, you are limited to the potential width of the pattern-weft float in determining the width of any block. With unit weaves, all the interlacement takes place within each unit. With overshot, the pattern weft doesn"t interlace in the block at all; it just passes over it. So overshot is a block weave but not a unit weave. Atwater-Bronson lace and summer and winter are unit weaves. All unit weaves are block weaves, but not all block weaves are unit weaves. Unit weaves can be used without limitation with profile drafts (block designs), whereas non-unit block weaves have certain limitations (overshot, crackle, M"s and O"s, spot Bronson).

This post is the third in a series introducing you to common weaving structures. We’ve already looked at plain weave and twill, and this time we’re going to dive into the magic of overshot weaves—a structure that’s very fun to make and creates exciting graphic patterns.
Overshot is a term commonly used to refer to a twill-based type of weaving structure. Perhaps more correctly termed "floatwork" (more on that later), these textiles have a distinctive construction made up of both a plain weave and pattern layer. Requiring two shuttles and at least four shafts, overshot textiles are built using two passes: one weaves a tabby layer and the other weaves a pattern layer, which overshoots or floats, above.
Readers in the United States and Canada may be familiar with overshot textiles through woven coverlets made by early Scottish and English settlers. Using this relatively simple technique, a local professional weaver with a four-shaft loom could easily make a near-infinite variety of equally beautiful and complex patterns. If you’d like to learn more about overshot coverlets and some of the traditions that settlers brought with them, please see my reading list at the bottom of this article!
As it is twill-based, overshot will be very familiar to 4 shaft weavers. It’s made up of a sequence of 2-thread repeats: 1-2, 2-3, 3-4, and 1-4. These sequences can be repeated any number of times to elongate and create lines, curves, and shapes. These 2-thread repeats are often referred to as blocks or threading repeats, IE: 1-2 = block 1/A, 2-3 = block 2/B.
There are three ways weft appears on the face of an overshot cloth: as a solid, half-tone, or blank. In the draft image I’ve shared here, you can see an example of each—the solid is in circled in blue, the half-tone in red, and the blank yellow. Pressing down the first treadle (shafts 1 and 2), for example, creates solid tones everywhere there are threads on shafts 1 and 2, half-tones where there is a 1 or 2 paired with 3 or 4, and nothing on the opposite block, shafts 3 and 4. Of course, there’s not really nothing—the thread is simply traveling on the back of the cloth, creating a reverse of what’s on the face.
Because overshot sequences are always made up of alternating shafts, plain weave can be woven by tying two treadles to lift or lower shafts 1-3 and 2-4. When I weave two-shuttle weaves like overshot, I generally put my tabby treadles to the right and treadle my pattern picks with my left foot and my tabby with my right. In the draft image I’ve shared above, I’ve omitted the tabby picks to make the overarching pattern clearer and easier to read. Below is a draft image that includes the tabby picks to show the structure of the fabric.
Traditional overshot coverlets used cotton or linen for warp and plain weave wefts, and wool pattern wefts—but there’s no rule saying you have to stick to that! In the two overshot patterns I’ve written for Gist, I used both Mallo and Beam as my pattern wefts.
In the Tidal Towels, a very simple overshot threading creates an undulating wave motif across the project. It’s easy and repetitive to thread, and since the overshot section is relatively short, it’s an easy way to get a feel for the technique.
The Bloom Table Squares are designed to introduce you to a slightly more complex threading—but in a short, easy-to-read motif. When I was a new weaver, one of the most challenging things was reading and keeping track of overshot threading and treadling—but I’ve tried to make it easy to practice through this narrow and quick project.
Overshot works best with a pattern weft that 2-4 times larger than your plain weave ground, but I haven’t always followed that rule, and I encourage you to sample and test your own wefts to see how they look! In the samples I wove for this article, I used 8/2 Un-Mercerized Cotton weaving yarn in Beige for my plain weave, and Duet in Rust, Mallo in Brick, and Beam in Blush for my pattern wefts.
The Bloom Table Squares are an excellent example of what weavers usually mean when they talk about traditional overshot or colonial overshot, but I prefer to use the term "floatwork" when talking about overshot. I learned this from the fantastic weaver and textile historian Deborah Livingston-Lowe of Upper Canada Weaving. Having researched the technique thoroughly for her MA thesis, Deborah found that the term "overshot" originated sometime in the 1930s and that historical records variably called these weaves "single coverlets’ or ‘shotover designs.’ Deborah settled on the term "floatwork" to speak about these textiles since it provides a more accurate description of what’s happening in the cloth, and it’s one that I’ve since adopted.
This book contains the collected drafts and work of Frances L. Goodrich, whose interest in coverlets was sparked when a neighbor gifted her one in the 1890s. Full of charming hand-painted drafts, this book offers a glimpse into North Carolina’s weaving traditions.
Amanda Ratajis an artist and weaver living and working in Hamilton, Ontario. She studied at the Ontario College of Art and Design University and has developed her contemporary craft practice through research-based projects, artist residencies, professional exhibitions, and lectures. Subscribe to herstudio newsletteror follow her onInstagramto learn about new weaving patterns, exhibitions, projects, and more.

Weave structures often have specific threading and treadling patterns that are unique to that particular weave structure and not shared with others. This book takes you out of the traditional method of weaving overshot patterns by using different treadling techniques. This will include weaving overshot patterns as Summer/Winter, Italian manner, starburst, crackle, and petit point just to name a few. The basic image is maintained in each example but the design takes on a whole new look!
Each chapter walks you through the setup for each method and includes projects with complete drafts and instructions so it’s easy to start weaving and watch the magic happen! Try the patterns for scarves, table runners, shawls, pillows and even some upholstered pieces. Once you"ve tried a few projects, you"ll be able to apply what you"ve learned to any piece you desire!
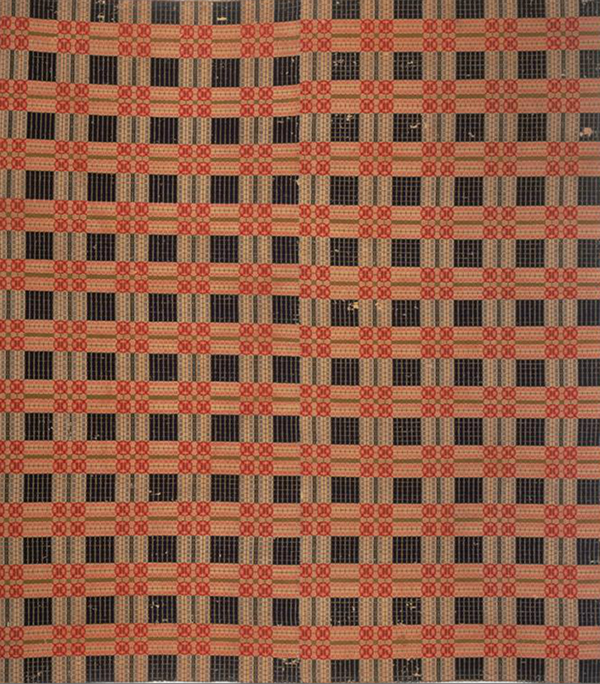
Overshot is known as a coverlet structure, but it’s also ideal for placemats, runners, blankets, fashion accessories, table linens, rugs, and much more. Just about anything you want to weave can be done in overshot.
Our class project is a series of coordinated placemats and table runners, woven in inexpensive, easy to get materials you may already have in your stash. You’ll choose from three different threadings composed of classic overshot motifs, then treadle them in star fashion, rose fashion, and many other ways.
Don’t feel like weaving placemats, runners, OR samples, or don’t have a loom available? No problem! You can still participate in the class without weaving at all. The lessons, videos, Q&As, and pen and paper exercises will help cement your understanding of overshot even if you don’t take it to the loom right away.
Don’t have that kind of loom? No worries! You can still read, watch, listen, and do all the pen and paper exercises. Your deeper understanding of overshot will be beneficial when you do have a loom to use it on or decide to explore how to weave it on the loom you already have on your own.

Overshot weave is the topic this week. Even if you haven’t heard of overshot before, I’m guessing you will still recognize it. Have you ever seen a historical coverlet before? That is overshot. Typically 2 colors. ALL about the pattern. That’s the one! Overshot.
Overshot is a partnership between 2 shuttles. The first shuttle is all about the pattern. She flits all over the fabric making big leaps and seemingly impossible designs. The second shuttle is all plain weave. She’s the reliable one, making sure the fabric will actually hold together.
Overshot Weave – Overshot is a weaving pattern that was very common in Southern Appalachia. I found a great article with some history about overshot from Comfort Cloth Weaving. Here’s the link.
Weaving Draft – A weaving draft is like sheet music. It tells you how to set up the loom and then the order in which to toss the shuttles in order to recreate a specific pattern. Once you can read a draft, the weaving world is your oyster!
Great news – I have created a free .pdf that follows along with this weaving pattern series! It provides an overview of each weaving pattern. Tells you how to recognize it and what it is used for. Plus, I’ve included a few notes on how to create the pattern on your loom. It’s a fabulous resource! Click here to get your copy today. Happy Weaving!

Very Good: A book that does not look new and has been read but is in excellent condition. No obvious damage to the cover, with the dust jacket (if applicable) included for hard covers. No missing or damaged pages, no creases or tears, and no underlining/highlighting of text or writing in the margins. May be very minimal identifying marks on the inside cover. Very minimal wear and tear. See the seller’s listing for full details and description of any imperfections.See all condition definitionsopens in a new window or tab

Now let’s consider another common use. I am weaving a set of placemats, using a pointed twill; for each one, I will change the treadling without changing the tie-up, the tie-up without changing the treadling, and changing both the tie-up and treadling.
When I weave a pointed twill that has 6 steps in the treadling-as-the-order-of-treadles, I prefer my order of treadles to be straight, it makes my weaving faster than having to go back and forth with the conventional tie-up.

Peachy Keen met up with artist Jessica R. Smith at her home studio in Savannah, GA, where she is a professor of fibers at the Savannah College of Art & Design. Smith is the is the co-author with Susan Falls of the recently released book Overshot: The Political Aesthetics of Woven Textiles from the Antebellum South and Beyond.
We discuss how her 12-year-relationship with SCAD colleague and professor of anthropology Susan Falls has produced multiple collaborations, culminating in their current book project, Overshot. Smith gives us the lowdown on their research process as a team and some of the surprising finds they made as they explored the history, presentation, context, and materiality of woven “overshot” coverlets.
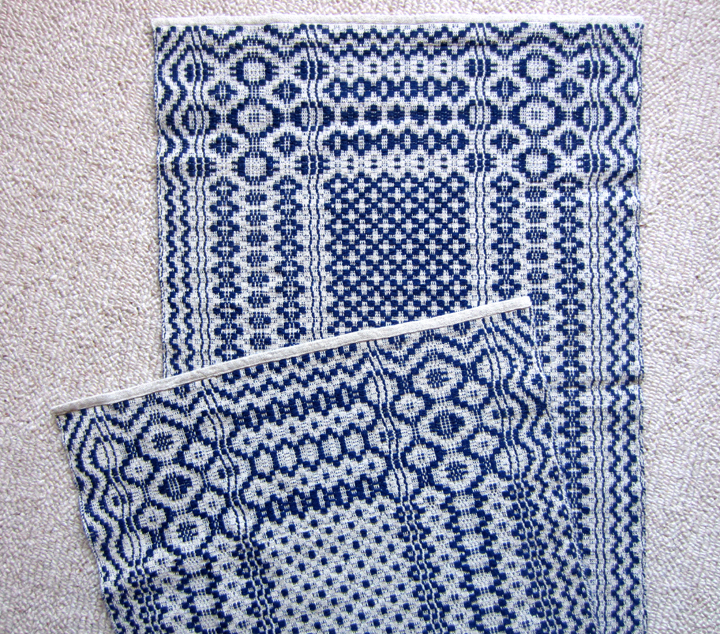

The threading here is the traditional point twill. Waffle weave are not only on point twill threading’s, but also on Rose path and broken twill threading, as well as Huck, Monk’s Belt, and Overshot. The tie-up involves tying two treadles for plain weave, and tying the rest to lift (or sink) three shafts or one. This creates the floats, which can be seen in the close up view of fabric. The treadling is tromp as writ, which simply means treadling in the same pattern as the threading draft, that means treadling one through four and reverse. A combination of warp and weft floats create the “waffles.”

The origin of the technique itself may have started in Persia and spread to other parts of the world, according to the author, Hans E. Wulff, of The Traditional Crafts of Persia. However, it is all relatively obscured by history. In The Key to Weavingby Mary E. Black, she mentioned that one weaver, who was unable to find a legitimate definition of the technique thought that the name “overshot” was a derivative of the idea that “the last thread of one pattern block overshoots the first thread of the next pattern block.” I personally think it is because the pattern weft overshoots the ground warp and weft webbing.
Overshot gained popularity and a place in history during the turn of the 19th century in North America for coverlets. Coverlets are woven bedcovers, often placed as the topmost covering on the bed. A quote that I feel strengthens the craftsmanship and labor that goes into weaving an overshot coverlet is from The National Museum of the American Coverlet:
Though, popular in many states during the early to mid 19th centuries, the extensive development of overshot weaving as a form of design and expression was fostered in rural southern Appalachia. It remained a staple of hand-weavers in the region until the early 20th century. In New England, around 1875, the invention of the Jacquard loom, the success of chemical dyes and the evolution of creating milled yarns, changed the look of coverlets entirely. The designs woven in New England textile mills were predominantly pictorial and curvilinear. So, while the weavers of New England set down their shuttles in favor of complex imagery in their textiles, the weavers of Southern Appalachia continued to weave for at least another hundred years using single strand, hand spun, irregular wool yarn that was dyed with vegetable matter, by choice.
And, due to the nature of design, overshot can be woven on simpler four harness looms. This was a means for many weavers to explore this technique who may not have the financial means to a more complicated loom. With this type of patterning a blanket could be woven in narrower strips and then hand sewn together to cover larger beds. This allowed weavers to create complex patterns that spanned the entirety of the bed.
What makes overshot so incredibly interesting that it was fundamentally a development of American weavers looking to express themselves. Many of the traditional patterns have mysterious names such as “Maltese Cross”, “Liley of the West”, “Blooming Leaf of Mexico” and “Lee’s Surrender”. Although the names are curious, the patterns that were developed from the variations of four simple blocks are incredibly intricate and luxurious.
This is only the tip of the iceberg with regard to the history of this woven structure. If you are interested in learning more about the culture and meaning of overshot, check out these resources!
The National Museum of the American Coverlet- a museum located in Bedford, Pennsylvania that has an extensive collection of traditional and jacquard overshot coverlets. Great information online and they have a “Coverlet College” which is a weekend series of lectures to learn everything about the American coverlet. Check out their website - coverletmuseum.org
Textile Art of Southern Appalachia: The Quiet Work of Women – This was an exhibit that traveled from Lowell, Massachusetts, Morehead, Kentucky, Knoxville, Tennessee, Raleigh, North Carolina, and ended at the Royal Museum in Edinburgh, Scotland. The exhibit contained a large number of overshot coverlets and the personal histories of those who wove them. I learned of this exhibit through an article written by Kathryn Liebowitz for the 2001, June/July edition of the magazine “Art New England”. The book that accompanied the exhibit, written by Kathleen Curtis Wilson, contains some of the rich history of these weavers and the cloth they created. I have not personally read the book, but it is now on the top of my wish list, so when I do, you will be the first to know about it! The book is called Textile Art of Southern Appalachia: The Quiet Work of Women and I look forward to reading it.

In the video, I mention learning how to weave Krokbragd. If you are interested in learning about this weaving technique, I encourage you to check out our course at the School of SweetGeorgia, Weaving Krokbragd, taught by Debby Greenlaw.
The overshot weaving project shown is woven on a 16″ Ashford Table Loom 8 shaft, The yarns used are Ashford 100% mercerised cotton in 10/2 and 5/2. (We don’t have this yarn currently listed on our site, but we’re able to order it in for you. Send us an email at: info@sweetgeorgiayarns.com!) The pattern is Overshot Sampler from the book Next Steps in Weaving by Pattie Graver




 8613371530291
8613371530291