puppy overshot jaw brands

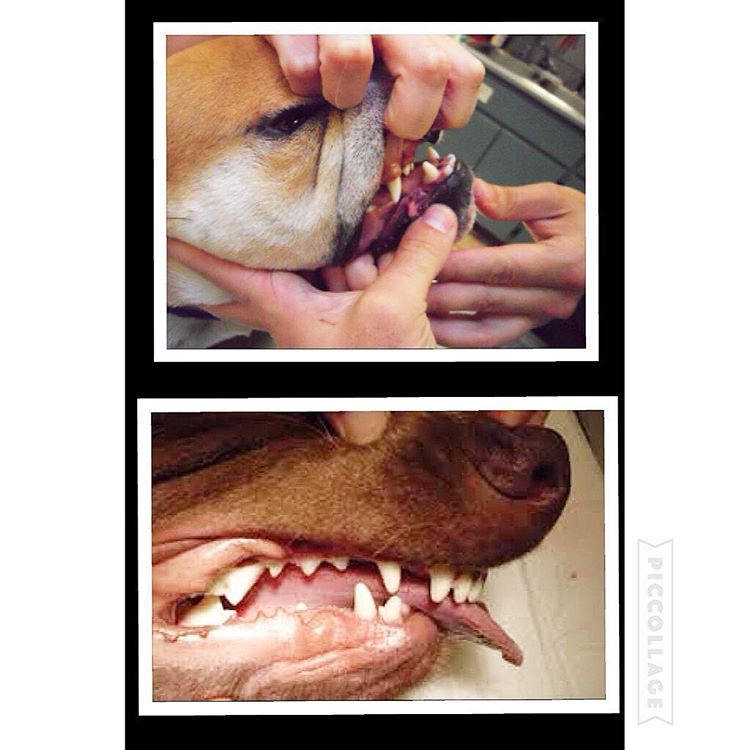
Here is a visual look into what an “undershot” and “overshot” jaw looks like. In recent years, I’ve noticed more and more dogs with this issue. Can a dog live productive life with a malocclusion: (imperfect positioning of the teeth when a jaws closed) Yes but with some issues along the way.
Let’s begin with a puppy will have 28 “puppy teeth” by the time it reaches six months old (this number can vary from breed to breed) By adulthood, most breeds will have a total of 42 teeth. As defined above a malocclusion or simply a misalignment of a dog’s teeth occurs when their bite does not fit accordingly beginning as puppy’s teeth come in and worsening as their adult teeth follow.
the upper jaw is longer than the lower one, an overshot or overbite. When a dogs mouth is closed, a gap between the upper and lower incisors (teeth) will be present. In most cases, puppies are born with a slight over/under bite and with time the problem can correct itself if the gap is not too large. What should be noted is if a dog’s bite remains over/undershot by 8-10 months old, that’s how it will remain for the remainder of its life. In overbite’s the structure may worsen as the permanent teeth come in as they are larger and can damage the soft parts of the mouth. Teeth extractions are sometimes necessary.
Structural dentition of a puppies jaw should be checked very early on to help eliminate this issue. Unfortunately most dog owners won’t notice until is late in the game. More so is the issues of backyard and/or inexplicable breeders breeding dogs with undershot/overshot jaws and potentially passing along this trait to future generations.
With an overbite, the upper jaw is longer than the lower one. When the mouth is closed, a gap between the upper and lower incisors occurs. Puppies born with an overbite will sometimes have the problem correct itself if the gap is not too large. However, a dog’s bite will usually set at ten months old. At this time improvement will not happen on its own. Your pet’s overbite may worsen as the permanent teeth come in because they are larger and can damage the soft parts of the mouth. Teeth extractions are sometimes necessary.
Problems that can arise from malocclusion are; difficulty chewing, picking up food and other objects, dogs with overshot jaws tend to pick up larger chunks of food since they can’t chew nor pick up smaller morsels which can lead to choking and future intestinal issues. These dogs are also prone to tartar and plaque build up which if left untreated can lead to other significant health issues such as heart problems. Other issues are listed below:
#dog #dogs #puppy #pup #puppies #puppylove #pets #life #family #bulldog #maltese #mastiff #chihuahua #cockerspaniel #vet #meds #instadog #instagood #instadaily
Types of malocclusionsClass 1 malocclusions occur when the upper and lower jaws are aligned (i.e. no underbite or overbite) but the teeth don’t come together properly because of crowding, misalignment, or rotation.
Class 2 malocclusionsare also known as an overbite. An overbite occurs when the maxillary (upper jaw) teeth are displaced forward relative to the mandibular (lower jaw) teeth.
Class 3 malocclusions are also known as an underbite. An underbite occurs when the mandibular (lower jaw) teeth protrude forward relative to the maxillary (upper jaw) teeth.
During your dog’s annual exam, your veterinarian will check your dog’s teeth and bite (another reason why annual exams are so important). If your puppy is developing any alignment issues, your veterinarian may suggest dental radiographs and may even refer your puppy to a veterinary dentist to correct any serious malocclusions before they become a problem.

In cats and dogs with a normal bite, the bottom canine teeth will slightly overlap their top canines. For those with a class three malocclusion, the bottom canine teeth stick out a bit further than usual, and the bottom jaw may also be longer than the top. The bottom canines and incisors may be visible at all times, even when your pet’s mouth is closed.
There are two types of malocclusions in pets: skeletal and dental. A cat or dog with a skeletal malocclusion will have a mishappen jaw, while those with a dental malocclusion will have a typical skull and jaw shape with teeth that are misaligned.
When a kitten or puppy is born, their lower jaw is smaller so they can nurse from their mother. As their milk teeth grow in during their first few weeks, their lower jaw will grow longer. In some cases, the lower jaw grows too quickly, creating a misaligned bite.
Certain breeds are predisposed to developing an underbite. In some dog breeds, particularly brachycephalic breeds like the Pug, Boxer, and French Bulldog, an “undershot” jaw is listed as a desirable trait in the AKC breed standard.
Underbites do not always have a genetic cause. If an animal suffers a traumatic jaw injury, it can affect their bite alignment. Rough play, such as a strenuous game of tug-o-war, can put stress on developing jaw. Retained milk teeth can also affect final bite alignment when adult teeth come in.
A malocclusion is detectable in pets as young as eight weeks of age. In some cases, the puppy or kitten may grow out of it. In others, though, it can cause complications by the time your pet’s adult teeth grow in, which occurs around 6-8 months of age.
Your kitten or puppy may need early intervention treatment to correct their bite. Your veterinarian may refer you to a veterinary dental surgeon to remove teeth that are causing an issue if they’re not essential. It’s also possible to reduce the height of canines that dig into oral tissue. In some cases, orthodontic appliances, similar to braces for humans, can be used to shift teeth for a more functional bite.

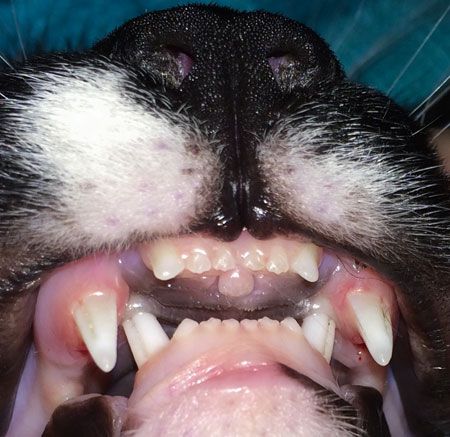
Malocclusion in dogs causes an abnormal alignment of the teeth, which results in an abnormal bite. A dog whose lower jaw is protruding and with the bottom teeth sticking out when at rest is known as an underbite dog.
We will focus on “class 3 malocclusions,” also known as an underbite. This condition happens when the lower jaw teeth protrude forward relative to the upper jaw teeth.
Class 1 malocclusion, on the other hand, occurs when the upper and lower jaws are proportionally in shape in length, but the teeth don’t come together properly.
“[A dog underbite] will be acquired, whether because something happened during gestation or something happened during growth and development. The condition can develop due to an infection, trauma, or any other event that may alter maxillofacial [face and jaw] growth.”
A dog underbite may also be caused by jaw fractures that don’t heal properly. Trauma to the face and jaw caused by bites, accidents, or getting hit by a car can cause your dog to develop an underbite.
Most malocclusions are genetic. It’s important to have your dog’s bite evaluated for non-symmetrical jaw growth by a professional, especially if your dog is brachycephalic.
Underbite in puppies may sometimes be corrected using braces. However, extraction and filling can also be applied. Treatment options for a puppy with underbites will vary depending on the type of malocclusion your pet faces, age, health status, and other factors.
Just like adult dogs, puppies with underbites are prone to health issues. If your dog has an underbite, seek medical attention to determine if your puppy’s underbite is detrimental to his health.
Most dogs that show underbite symptoms as a young puppy will likely have a dog underbite for the rest of their lives. This misalignment can sometimes self-correct as your dog develops, but if your dog is genetically predisposed, it is highly unlikely for this to happen. Dog underbite can be corrected through surgery and braces in some cases.
Genetics, accidents, dental or skeletal problems can lead to underbites in dogs. In some breeds, underbites are the result of intentional breeding practices. Breeders breed underbite dogs specifically to engineer the type of jaw structure of a bulldog or a boxer.
An underbite malocclusion can be considered normal and healthy as long as the dog can chew and eat solid food comfortably and their bite is functional. Some breeds of dogs, usually flat-faced or brachycephalic, are naturally born with underbites. These breeds have been genetically bred to have a lower jaw that is slightly longer than the upper.
Bulldogs have brachycephalic skulls, which means their faces are pushed inward. As a result, the upper jaw is usually shorter than the lower — underbite. In some bulldogs, the underbite is minor, while in others, it is extreme that they find eating difficult.

The way teeth align with each other is termed occlusion. Normal occlusion in most medium and long-nosed breeds consists of the upper (maxillary) incisors just overlapping the lower (mandibular) incisors (scissor bite). (See Photo 1.) The lower canine should be located equidistant between the last (lateral) incisor and the upper canine tooth (Photo 2). The premolar tips of the lower jaw should point between the spaces of the upper jaw teeth (Photos 3 and 4).
Malocclusion refers to abnormal tooth alignment. Overbite (overshot, class two, overjet, mandibular brachygnathism) occurs when the lower jaw is shorter than the upper (Photo 6). There is a gap between the upper and lower incisors when the mouth is closed. The upper premolars are displaced at least 25 percent toward the front when compared to the lower premolars. An underbite (undershot, reverse scissor bite, prognathism, class 3) occurs when the lower teeth protrude in front of the upper jaw teeth (Photos 7, 8) If the upper and lower incisor teeth meet each other edge to edge, the occlusion is an even or level bite (Photo 11). When the upper and lower incisors do not overlap or even meet each other when the mouth is closed, the pet has an open bite . Anterior crossbite occurs when the canine and premolar teeth on both sides of the mouth occlude normally, but one or more of the lower incisors are positioned in front of the upper incisors (Photo 12). Anterior crossbite is the most common malocclusion, is not considered genetic or hereditary and is correctable. Posterior crossbite occurs when one or more of the premolar lower jaw teeth overlap the upper jaw teeth. This is a rare condition that occurs in the larger-nosed dog breeds. A wry mouth or wrybite occurs when one side of the jaw grows longer than the other. Lingually displaced mandibular (base narrow)canines occur when the mandibular canine teeth protrude inward causing penetrating damage to the upper palate. This condition is due to either persistent primary teeth or a too-narrow mandible and can usually be corrected through an orthodontic appliance (inclined plan) used to direct the teeth into normal occlusion. Rostrally deviated canine teeth occur when the maxillary or mandibular canine is directed forward and can usually be corrected by orthodontic movement, crown reduction or extraction.

Occlusion refers to the relationship between the maxillary and mandibular teeth when they approach each other, as occurs during chewing or rest. Normal occlusion exists when the maxillary incisors just overlap the mandibular incisors (Figure 1A), the mandibular canines are equidistant from the maxillary third incisors and the maxillary canine teeth, and the premolar crown tips of the lower jaw point between the spaces of the upper jaw teeth in a saw-toothed fashion (Figure 1B). Flat-faced breeds, such as boxers, shih tzus, Boston terriers, Lhasa apsos and Persian cats, have abnormal bites that are recognized as normal for their breed in which the mandibular jaw protrudes in front of the maxillary jaw, altering the above tooth-to-tooth relationship (Figures 2A and 2B).
Malocclusion refers to abnormal tooth alignment. Skeletal malocclusion occurs when jaw anomalies result in abnormal jaw alignment that causes the teeth to be out of normal orientation. Dental malposition occurs when jaw alignment is normal but one or more teeth are out of normal orientation.
Mandibular distoclusion (also called overbite, overjet, overshot, class 2, and mandibular brachygnathism) occurs when the lower jaw is shorter that the upper and there"s a space between the upper and lower incisors when the mouth is closed. The upper premolars will be displaced rostrally (toward the nose) compared with the lower premolars. Mandibular distoclusion is never normal in any breed (Figures 3A and 3B).
Figure 4. Mandibular mesioclusion in a dog.Maxillary mandibular asymmetry (also called wry bite, especially by breeders) is a skeletal malocclusion in which one side of the jaw grows differently from the other side (Figures 5A and 5B).
The way your puppy"s top and bottom dental arches intersect with each other is known as "occlusion." The scissor bite, where the upper incisors neatly overlap the lower incisors and the premolars meet in a sawtooth fashion, is the most common and most desirable type of occlusion observed in medium- to long-muzzled dogs. The even or level bite is another common type of occlusion, but in this case the incisors meet edge to edge. Because this type of contact wears down the teeth"s surfaces, a level bite isn"t considered ideal.
Also known as parrot mouth, over shot and over jet, an overbite occurs when the upper jaw extends beyond the lower jaw. Because the upper teeth overlap the lower teeth, this type of malocclusion prevents your pup"s chompers from aligning snugly as they should. Dogs with elongated muzzles such as collies, shelties, dachshunds, and Russian wolfhounds are commonly affected. Overbites are unfortunately classified as a class II malocclusion and a major genetic fault.
You may think the condition of your puppy"s gnashers is no biggie, but depending on the severity of the malocclusion, your pup may encounter several difficulties. A minor overbite may be a purely cosmetic concern, but in severe cases, puppies may have trouble chewing and injuries may result from the lower teeth hitting the roof of the mouth. To ensure your pup"s pearly whites are growing correctly, it"s a good idea to have them thoroughly examined by your vet when your pup is around 2 to 3 months of age.
Interestingly, kitties and puppies are naturally born with an overshot upper jaw so they"re capable of nursing. Then, once they"re weaned and have started eating solid food, their mandibles go through a growth spurt, nearly reaching their adult proportions. When this growth spurt doesn"t occur and the milk teeth erupt, the upper canines may protrude over the lower ones, preventing the lower jaw from developing to its proper length, according to the Merck Veterinary Manual.
If your pup"s overbite is causing you sleepless nights, consider that not all is lost, since the jaw is still developing. In some breeds, such as the German shepherd, an overshot bite may spontaneously correct on its own as long as the gap between the upper and lower incisors is not greater than the head of a wooden match. Keep an eye on your pup"s gnashers, as improvement may continue up until the puppy is 10 months old and his jaws stop growing.
In severe overbite cases, extractions and restorative treatments can help manage and prevent injury to the pup"s soft oral tissues. If you"re planning to breed your puppy in the future, consider that overshot bites have a genetic basis and can be passed down from generation to generation. Because of this, the American Kennel Club prohibits dogs who have received interventional orthodontic treatments from competing in the conformation ring.
Adrienne Farricelli has been writing for magazines, books and online publications since 2005. She specializes in canine topics, previously working for the American Animal Hospital Association and receiving certification from the Certification Council for Professional Dog Trainers. Her articles have appeared in "USA Today," "The APDT Chronicle of the Dog" and "Every Dog Magazine." She also contributed a chapter in the book " Puppy Socialization - An Insider"s Guide to Dog Behavioral Fitness" by Caryl Wolff.

An overbite is a genetic, hereditary condition where a dog"s lower jaw is significantly shorter than its upper jaw. This can also be called an overshot jaw, overjet, parrot mouth, class 2 malocclusion or mandibular brachynathism, but the result is the same – the dog"s teeth aren"t aligning properly. In time, the teeth can become improperly locked together as the dog bites, creating even more severe crookedness as the jaw cannot grow appropriately.
Dental examinations for puppies are the first step toward minimizing the discomfort and effects of an overbite. Puppies can begin to show signs of an overbite as early as 8-12 weeks old, and by the time a puppy is 10 months old, its jaw alignment will be permanently set and any overbite treatment will be much more challenging. This is a relatively narrow window to detect and correct overbites, but it is not impossible.
Small overbites often correct themselves as the puppy matures, and brushing the dog"s teeth regularly to prevent buildup can help keep the overbite from becoming more severe. If the dog is showing signs of an overbite, it is best to avoid any tug-of-war games that can put additional strain and stress on the jaw and could exacerbate the deformation.
If the dog is young enough, however, tooth extraction is generally preferred to correct an overbite. Puppies have baby teeth, and if those teeth are misaligned, removing them can loosen the jaw and provide space for it to grow properly and realign itself before the adult teeth come in. Proper extraction will not harm those adult teeth, but the puppy"s mouth will be tender after the procedure and because they will have fewer teeth for several weeks or months until their adult teeth have emerged, some dietary changes and softer foods may be necessary.

A pooch with a protruding lower jaw and bottom teeth sticking out when at rest is referred to as an underbite dog. Before we delve into whether or not underbite on pooches can be rectified, it’s essential to understand what causes it and its variations.
However, in some instances, a puppy’s baby teeth don’t fall. Consequentially, they interfere with the permanent teeth that end up growing crookedly due to the lack of ample space. In relatively undershot bites, the incisors are the only teeth that contribute to the misalignment.
With the irresistible shorter jaws and pushed-in faces that a multitude of people find adorable, the gap into which the teeth erupt is restricted, ushering in a malocclusion. Given that skeletal underbite in pooches is significantly more problematic than dental causes, this leads to the rapid development of periodontal disease.
Typically, a dog’s lower and upper teeth intersect in a ‘scissor bite’ when the jaw is closed. However, some scenarios arise whereby the lower teeth stick out in front of the upper ones causing a reverse scissor bite. Genetic causes of a dog underbite are seen in long and medium-muzzled pooches.
In some scenarios, a puppy’s lower jaw grows more rapidly, becoming visibly longer than the upper jaw. Occurring in puppies as young as eight weeks, some upper jaw teeth get restricted behind those of the lower jaw. Consequentially, the upper jaw doesn’t grow at the normal rate.
Inform your vet immediately you spot the development of an underbite in your puppy. Early intervention can make all the difference in curbing more adverse issues.
Underbite in young dogs can be rectified using braces. Nonetheless, filling and extraction can also be applied. The treatment alternatives for a puppy with an underbite vary based on the type of malocclusion involved, their health status, and age.
As is the case with adult dogs, a puppy with an underbite is susceptible to health problems. If you notice an underbite, we recommend seeking medical attention to determine if it’s detrimental to their health. If you’re wondering whether your puppy will grow out of the underbite, the truth is, although it’s possible, the chances are slim to none if it’s genetic.




 8613371530291
8613371530291