puppy overshot jaw for sale

Hi, I"m due to collect my new labrador puppy in 1 week and the breeder has just told me that when the pups were taken to the vet on Friday she noted my pup had a "slightly overshot jaw". He was exactly 7 weeks old at this appointment and is otherwise very healthy.
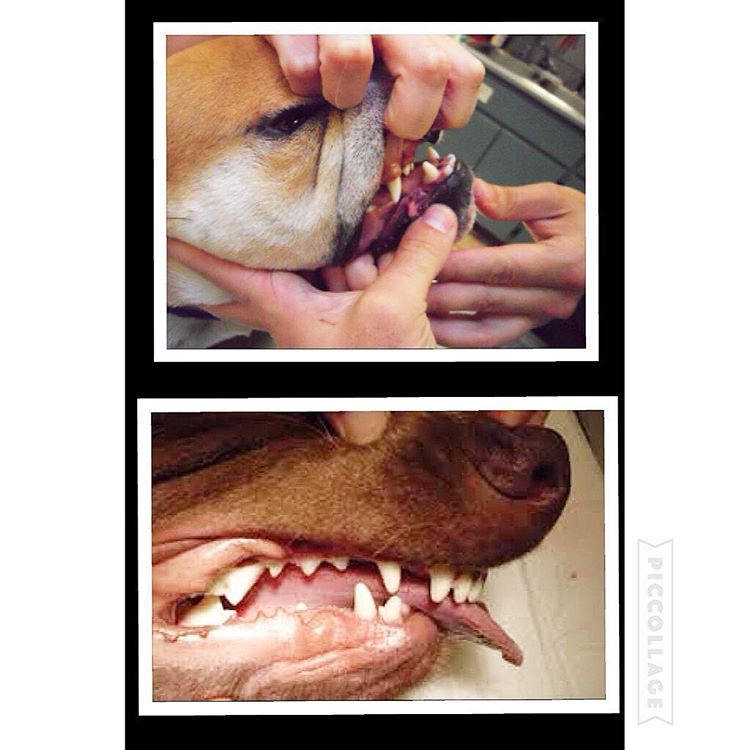
Here is a visual look into what an “undershot” and “overshot” jaw looks like. In recent years, I’ve noticed more and more dogs with this issue. Can a dog live productive life with a malocclusion: (imperfect positioning of the teeth when a jaws closed) Yes but with some issues along the way.
Let’s begin with a puppy will have 28 “puppy teeth” by the time it reaches six months old (this number can vary from breed to breed) By adulthood, most breeds will have a total of 42 teeth. As defined above a malocclusion or simply a misalignment of a dog’s teeth occurs when their bite does not fit accordingly beginning as puppy’s teeth come in and worsening as their adult teeth follow.
the upper jaw is longer than the lower one, an overshot or overbite. When a dogs mouth is closed, a gap between the upper and lower incisors (teeth) will be present. In most cases, puppies are born with a slight over/under bite and with time the problem can correct itself if the gap is not too large. What should be noted is if a dog’s bite remains over/undershot by 8-10 months old, that’s how it will remain for the remainder of its life. In overbite’s the structure may worsen as the permanent teeth come in as they are larger and can damage the soft parts of the mouth. Teeth extractions are sometimes necessary.
Structural dentition of a puppies jaw should be checked very early on to help eliminate this issue. Unfortunately most dog owners won’t notice until is late in the game. More so is the issues of backyard and/or inexplicable breeders breeding dogs with undershot/overshot jaws and potentially passing along this trait to future generations.
With an overbite, the upper jaw is longer than the lower one. When the mouth is closed, a gap between the upper and lower incisors occurs. Puppies born with an overbite will sometimes have the problem correct itself if the gap is not too large. However, a dog’s bite will usually set at ten months old. At this time improvement will not happen on its own. Your pet’s overbite may worsen as the permanent teeth come in because they are larger and can damage the soft parts of the mouth. Teeth extractions are sometimes necessary.
Problems that can arise from malocclusion are; difficulty chewing, picking up food and other objects, dogs with overshot jaws tend to pick up larger chunks of food since they can’t chew nor pick up smaller morsels which can lead to choking and future intestinal issues. These dogs are also prone to tartar and plaque build up which if left untreated can lead to other significant health issues such as heart problems. Other issues are listed below:
#dog #dogs #puppy #pup #puppies #puppylove #pets #life #family #bulldog #maltese #mastiff #chihuahua #cockerspaniel #vet #meds #instadog #instagood #instadaily

Here is a visual look into what an “undershot” and “overshot” jaw looks like. In recent years, I’ve noticed more and more dogs with this issue. Can a dog live productive life with a malocclusion: (imperfect positioning of the teeth when a jaws closed) Yes but with some issues along the way.
Let’s begin with a puppy will have 28 “puppy teeth” by the time it reaches six months old (this number can vary from breed to breed) By adulthood, most breeds will have a total of 42 teeth. As defined above a malocclusion or simply a misalignment of a dog’s teeth occurs when their bite does not fit accordingly beginning as puppy’s teeth come in and worsening as their adult teeth follow.
the upper jaw is longer than the lower one, an overshot or overbite. When a dogs mouth is closed, a gap between the upper and lower incisors (teeth) will be present. In most cases, puppies are born with a slight over/under bite and with time the problem can correct itself if the gap is not too large. What should be noted is if a dog’s bite remains over/undershot by 8-10 months old, that’s how it will remain for the remainder of its life. In overbite’s the structure may worsen as the permanent teeth come in as they are larger and can damage the soft parts of the mouth. Teeth extractions are sometimes necessary.
Structural dentition of a puppies jaw should be checked very early on to help eliminate this issue. Unfortunately most dog owners won’t notice until is late in the game. More so is the issues of backyard and/or inexplicable breeders breeding dogs with undershot/overshot jaws and potentially passing along this trait to future generations.
With an overbite, the upper jaw is longer than the lower one. When the mouth is closed, a gap between the upper and lower incisors occurs. Puppies born with an overbite will sometimes have the problem correct itself if the gap is not too large. However, a dog"s bite will usually set at ten months old. At this time improvement will not happen on its own. Your pet"s overbite may worsen as the permanent teeth come in because they are larger and can damage the soft parts of the mouth. Teeth extractions are sometimes necessary.
Problems that can arise from malocclusion are; difficulty chewing, picking up food and other objects, dogs with overshot jaws tend to pick up larger chunks of food since they can"t chew nor pick up smaller morsels which can lead to choking and future intestinal issues. These dogs are also prone to tartar and plaque build up which if left untreated can lead to other significant health issues such as heart problems. Other issues are listed below:
#dog #dogs #puppy #pup #puppies #puppylove #pets #life #family #bulldog #maltese #mastiff #chihuahua #cockerspaniel #vet #meds #instadog #instagood #instadaily

This condition is most often spotted at either the first or second puppy checks or between 6 and 8 months of age as the permanent (adult) teeth erupt. Either the deciduous or permanent lower canines occlude into the soft tissues of the roof or the mouth causing severe discomfort and, possibly, oral nasal fistulae.
Secondly, the growth of the mandible is rostral from the junction of the vertical and horizontal ramus. If the lower canines are embedded in pits in the hard palate, the normal rostral growth of the mandible(s) cannot take place normally due to the dental interlock caused by the lower canines being embedded in hard palate pits. This can cause deviation of the skull laterally or ventral bowing of the mandibles (lower jaws).
Thirdly, the permanent lower canine is located lingual to the deciduous canine. This means that if the deciduous lower canines are in a poor position it is a certainty the permanent teeth will be worse. See the radiograph below. The deciduous canines are on the outside of the jaws and the developing permanent canines are seen in the jaw as small "hats". It is clear that the eruption path of the permanent canines will be directly dorsal and not buccally inclined as is normal.
The permanent successor tooth is located lingual to the deciduous tooth and wholly within the jaw at this stage. Any use of luxators or elevators on the lingual half of the deciduous tooth will cause permanent damage to the developing enamel of the permanent tooth. See the images below showing canines (and also the third incisor) with extensive damage to the enamel. The radiograph also shows how much damage can occur to the teeth - see the top canine and adjacent incisor. Some severely damaged teeth need to be extracted while other can be repaired with a bonded composite. This damage is avoidable with careful technique using an open surgical approach.
Do not try ball therapy with deciduous (puppy) teeth. There are two main reasons for this. Puppy teeth are fragile and can easily break. More importantly, the adult canine tooth bud is developing in the jaw medial to the deciduous canine tooth (see radiograph above in the puppy section). If the deciduous crown tips outwards the root will tip inwards. This will push the permanent tooth bud further medial than it already is.
The intention of the procedure is to keep the pulp alive and allow the shortened lower canines to develop normally and contribute to the strength of the lower jaws.
The advantage of this procedure is that the whole of the root and the majority of the crown remain. The strength and integrity of the lower jaw is not weakened by the procedure and long term results are very good due to the use of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate as a direct pulp dressing.
However, many owners are concerned (rightly) about the loss of the tooth and the weakness it may cause to the lower jaw(s). It is not our preferred option. This is not an easy surgical extraction and the resulting loss of the root causes a weakness in the lower jaws. This is compounded if both lower canines are removed.
Normally a composite resin bite plane is bonded onto the upper teeth (see below) with an incline cut into the sides. The lower canine makes contact with the incline when the mouth closes and, over time, the force tips the tooth buccally. This takes around four to eight weeks. The lower canine will often migrate back into a lingually displaced position when the bite plane is removed. This can occur if the tooth height of the lower canine is too short (stunted). If the lower canine is not self-retained by the upper jaw when the mouth is shut further surgery may be required.

An overbite is a genetic, hereditary condition where a dog"s lower jaw is significantly shorter than its upper jaw. This can also be called an overshot jaw, overjet, parrot mouth, class 2 malocclusion or mandibular brachynathism, but the result is the same – the dog"s teeth aren"t aligning properly. In time, the teeth can become improperly locked together as the dog bites, creating even more severe crookedness as the jaw cannot grow appropriately.
Dental examinations for puppies are the first step toward minimizing the discomfort and effects of an overbite. Puppies can begin to show signs of an overbite as early as 8-12 weeks old, and by the time a puppy is 10 months old, its jaw alignment will be permanently set and any overbite treatment will be much more challenging. This is a relatively narrow window to detect and correct overbites, but it is not impossible.
Small overbites often correct themselves as the puppy matures, and brushing the dog"s teeth regularly to prevent buildup can help keep the overbite from becoming more severe. If the dog is showing signs of an overbite, it is best to avoid any tug-of-war games that can put additional strain and stress on the jaw and could exacerbate the deformation.
If the dog is young enough, however, tooth extraction is generally preferred to correct an overbite. Puppies have baby teeth, and if those teeth are misaligned, removing them can loosen the jaw and provide space for it to grow properly and realign itself before the adult teeth come in. Proper extraction will not harm those adult teeth, but the puppy"s mouth will be tender after the procedure and because they will have fewer teeth for several weeks or months until their adult teeth have emerged, some dietary changes and softer foods may be necessary.
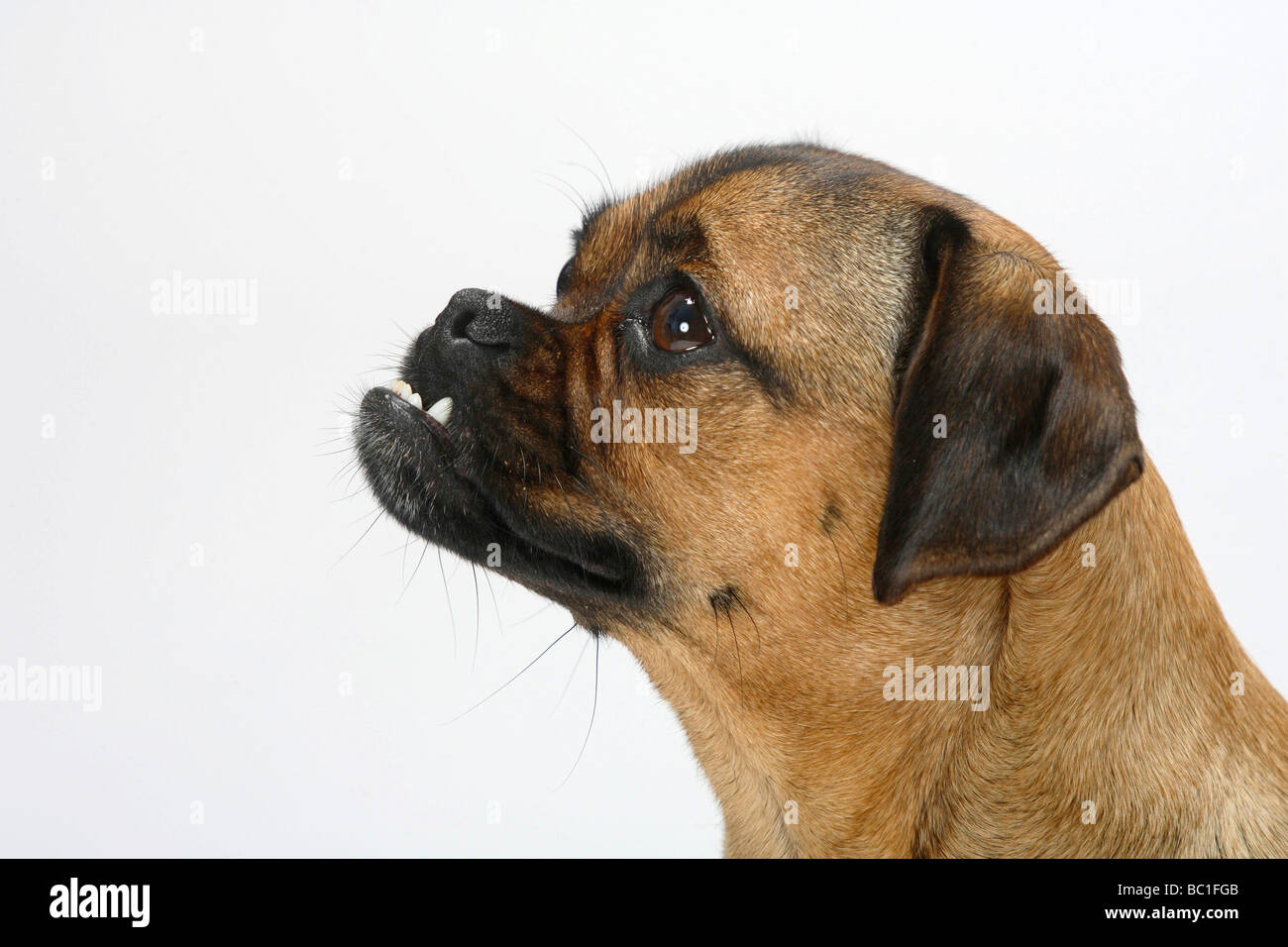

As the puppies grow, we see different body parts growing at different rates. Sometime, a German Shepherds puppy has a slights overbite at 8 weeks, when the teeth are not in a tight scissors bite, as they should per breed standard. As the puppy continued developing, this slight overbite usually resolves itself, as puppy gets through teething stage and has their adult teeth. Because overbite is a fault, breeders should never use dogs with any less-than-perfect teeth in breeding. (Luckily for us, humans, an orthodontic treatment exists and even those of us with the most un-perfect smiles, still able to reproduce. Dogs in a show world aren"t that lucky ). We have never seen an under-bite in this breed. While to many pet owners slight overbite might not seem like a serious condition, but a cosmetic defect, it is very important that your puppy"s teeth are aligned as close as possible. Severely misaligned teeth can lead to difficulty eating, gum injuries and bruising, bad breath and different types of dental problems, including tooth decay and gingivitis. Fortunately, there are ways to help fix the problem before it becomes irreversible.
An overbite is a genetic, hereditary condition where a dog"s lower jaw is significantly shorter than its upper jaw. This can also be called an overshot jaw, overjet, parrot mouth, class 2 malocclusion or mandibular brachynathism, but the result is the same – the dog"s teeth aren"t aligning properly. In time, the teeth can become improperly locked together as the dog bites, creating even more severe crookedness as the jaw cannot grow appropriately.
Dental examinations for puppies are the first step toward minimizing the discomfort and effects of an overbite. Puppies can begin to show signs of an overbite as early as 8-12 weeks old, and by the time a puppy is 10 months old, its jaw alignment will be permanently set and any overbite treatment will be much more challenging. This is a relatively narrow window to detect and correct overbites, but it is not impossible.
Small overbites often correct themselves as the puppy matures, and brushing the dog"s teeth regularly to prevent buildup can help keep the overbite from becoming more severe. If the dog is showing signs of an overbite, it is best to avoid any tug-of-war games that can put additional strain and stress on the jaw and could exacerbate the deformation.
If the dog is young enough, however, tooth extraction is generally preferred to correct an overbite. Puppies have baby teeth, and if those teeth are misaligned, removing them can loosen the jaw and provide space for it to grow properly and realign itself before the adult teeth come in. Proper extraction will not harm those adult teeth, but the puppy"s mouth will be tender after the procedure and because they will have fewer teeth for several weeks or months until their adult teeth have emerged, some dietary changes and softer foods may be necessary.

Normally, a puppy will have 28 baby teeth once it is six months old. By the time it reaches adulthood, most dog breeds will have 42 teeth. A misalignment of a dog"s teeth, or malocclusion, occurs when their bite does not fit accordingly. This may begin as the puppy"s baby teeth come in and usually worsens as their adult teeth follow.
The smaller front teeth between the canines on the upper and lower jaws are called incisors. These are used to grasp food and to keep the tongue inside the mouth. Canines (also known as cuspids or fangs) are found behind the front teeth, which are also used to grasp. Behind the canines are the premolars (or bicuspids) and their function is to shear or cut food. Molars are the last teeth found at the back of the mouth and they are used for chewing.
With an overbite, the upper jaw is longer than the lower one. When the mouth is closed, a gap between the upper and lower incisors occurs. Puppies born with an overbite will sometimes have the problem correct itself if the gap is not too large. However, a dog"s bite will usually set at ten months old. At this time improvement will not happen on its own. Your pet"s overbite may worsen as the permanent teeth come in because they are larger and can damage the soft parts of the mouth. Teeth extractions are sometimes necessary.
The way the upper teeth align with the lower teeth is called occlusion. It is normal for most breeds to have a slight overlap of the upper front teeth. When the jaw is closed, the lower canine (fang) should fit in front of the upper canine. Most cases of malocclusion have a hereditary link.

Thanks for all the advice. Tooolz, he has as far as I am aware never left the breeder. I have not yet been to see this puppy as he is some 8 hours around trip. I have a picture and a description of the anomaly - 1/2" gap. The breeders vet states (according to the breeder) that the most that would be needed is teeth to be pulled as and when, but it is very much a guessing game. The breeder has said that if that needed to be done then to take the puppy back and he would arrange for it to be done with his vet and we can share the cost. Not sure how much that would be???
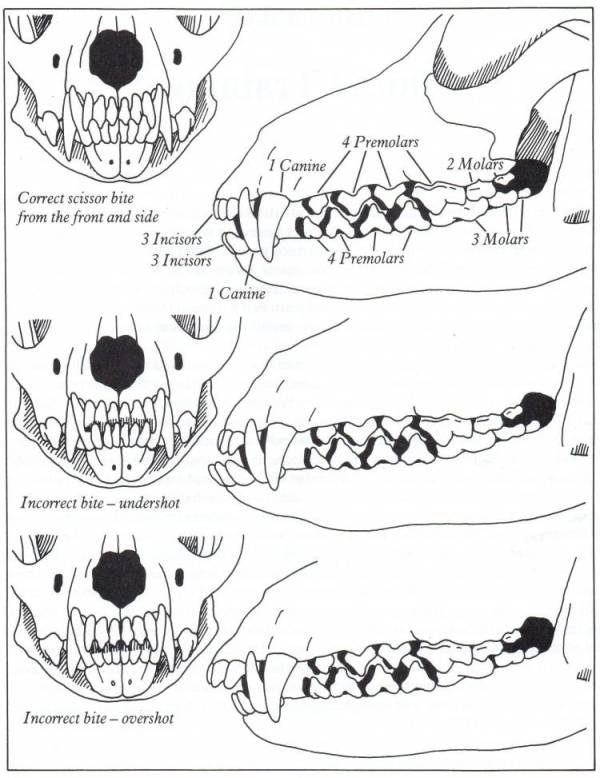
Australian Shepherds have a variety of jaw structure issues that result in misaligned teeth, called malocclusions. Breeders generally call them bad bites. There are several different defects that arise from improperly shaped jaws:
Undershot – the lower jaw extends beyond the upper, the greater the difference in length between the two jaws, the greater the degree of malocclusion seen in the teeth. Undershot bites are a disqualifying fault in Aussies.
Overshot – the lower jaw does not reach proper length in proportion to the upper, the shorter it is the greater the degree of malocclusion of the teeth. A very extreme overshot bite may be referred to as “parrot mouth.” Standards vary but very slight undershot bites may be deemed faulty but acceptable. Anything beyond what is specified in the breed standard(s) – 1/8 inch per ASCA and AKC – is disqualifying.
Wry – One side of the jaw has grown longer or failed to grow as long as the other, resulting in malocclusion of the teeth in the front of the jaw. Wry bites are not specifically addressed in the standards but in many cases are likely to result in disqualification because some portion of the lower jaw will be longer or shorter than the upper.
The mode(s) of inheritance for bad bites remain unknown. Because of the complexity of the jaw structure inheritance of bad bites is likely to be equally complex. It is clear that there is no single “bad bite gene” or even a separate gene for each kind of bad bite.
Bad bites are common in Aussies. This, in addition to their genetic complexity, makes them difficult to eliminate completely. However, breeders can lower the incidence of bad bites through selection. A dog with a bite that is undershot, disqualifying overshot, or wry should not be bred. Do not repeat breedings that produce these defects. The parents and siblings (full and half) of affected animals should not be bred close on either side of the affected dog’s pedigree nor should they be bred to mates with a family history of bad bites.

Teeth strongly developed, powerful canine teeth fitting closely. Jaws strong, with a perfect, regular and complete scissor bite, i.e. upper teeth closely overlapping lower teeth and set square to the jaws. Complete dentition important.
The correct mouth should be a “Scissor” bite, with closely overlapping top and bottom canine teeth. Any deviation from this is a fault; for example an “overshot” jaw where the top teeth overlap the bottom teeth by a significant margin, or an “undershot” jaw, where the top teeth close behind the lower incisors. An overshot jaw is more common than an undershot jaw. Neither of these faults is likely to be a problem for a Dachshund living as a pet, but he would not be able to grasp and hold his prey firmly if he was a working dog with either of these faults.
The extent of the scissor bite is sometimes a cause for discussion. Judges who own Wires have been known to observe in their critiques that the teeth of the other varieties are overshot and, conversely, judges who own Smooths or Longs have criticised Wires for having pincer bites. If the top teeth closely overlap the bottom teeth, the dog has a correct bite. A pincer bite would have edge-to-edge teeth.
Complete dentition means there should be 22 lower teeth and 20 upper teeth. There should be 6 incisors in each jaw. Occasionally, one incisor might be missing, but sometimes two are missing; both situations are faults. There should be 2 canines in each jaw – 1 on each side. There should be 8 pre-molars in each jaw – 4 on each side; missing pre-molars would also be considered to be faulty. There should be 4 molars in the upper jaw – 2 on each side – and 6 in the lower jaw – 3 on each side. Note that missing premolars is not considered to be a fault under the latest FCI Standard.
A full set of teeth means the dog can grip strongly and if you try to prise a Dachshund’s jaws apart you should be able to feel how powerful his jaws are. This applies as much in the Miniatures as the Standards; they should not have soft, toy-ish mouths, or weak jaws.
Luckily, breeders seem to have corrected the crowded teeth and narrow jaws that were seen in the Mini Wires not so long ago, but judges do need to be vigilant and observations on dentition in their critiques can be helpful.




 8613371530291
8613371530291