using a rotary table on a milling machine made in china

This website is using a security service to protect itself from online attacks. The action you just performed triggered the security solution. There are several actions that could trigger this block including submitting a certain word or phrase, a SQL command or malformed data.

This website is using a security service to protect itself from online attacks. The action you just performed triggered the security solution. There are several actions that could trigger this block including submitting a certain word or phrase, a SQL command or malformed data.

A turret milling machine is a vertical mill, meaning the spindle — the area that performs the cuts — is positioned vertically. The turret milling machine is
considered a versatile unit, because it can create a wide array of shapes. It has a quill that can be raised or lowered to create different cutting depths. Turret milling machines are only effective if they are kept at a relatively small size, because the quill is difficult to operate with larger units.

Domestic Market16.00%CNC Lathe; CNC Machining Center; CNC Milling Machine; Press Brake; Milling Machine; Lathe; CNC Turning Center; Drilling Machine; Sawing Machine
South America12.00%CNC Lathe; CNC Machining Center; CNC Milling Machine; Press Brake; Milling Machine; Lathe; CNC Turning Center; Drilling Machine; Sawing Machine
North America10.00%CNC Lathe; CNC Machining Center; CNC Milling Machine; Press Brake; Milling Machine; Lathe; CNC Turning Center; Drilling Machine; Sawing Machine
Eastern Asia10.00%CNC Lathe; CNC Machining Center; CNC Milling Machine; Press Brake; Milling Machine; Lathe; CNC Turning Center; Drilling Machine; Sawing Machine
South Asia9.00%CNC Lathe; CNC Machining Center; CNC Milling Machine; Press Brake; Milling Machine; Lathe; CNC Turning Center; Drilling Machine; Sawing Machine
Southeast Asia8.00%CNC Lathe; CNC Machining Center; CNC Milling Machine; Press Brake; Milling Machine; Lathe; CNC Turning Center; Drilling Machine; Sawing Machine
Mid East7.00%CNC Lathe; CNC Machining Center; CNC Milling Machine; Press Brake; Milling Machine; Lathe; CNC Turning Center; Drilling Machine; Sawing Machine
Eastern Europe6.00%CNC Lathe; CNC Machining Center; CNC Milling Machine; Press Brake; Milling Machine; Lathe; CNC Turning Center; Drilling Machine; Sawing Machine
Western Europe6.00%CNC Lathe; CNC Machining Center; CNC Milling Machine; Press Brake; Milling Machine; Lathe; CNC Turning Center; Drilling Machine; Sawing Machine
Africa4.00%CNC Lathe; CNC Machining Center; CNC Milling Machine; Press Brake; Milling Machine; Lathe; CNC Turning Center; Drilling Machine; Sawing Machine
Northern Europe4.00%CNC Lathe; CNC Machining Center; CNC Milling Machine; Press Brake; Milling Machine; Lathe; CNC Turning Center; Drilling Machine; Sawing Machine
Oceania3.00%CNC Lathe; CNC Machining Center; CNC Milling Machine; Press Brake; Milling Machine; Lathe; CNC Turning Center; Drilling Machine; Sawing Machine
Southern Europe3.00%CNC Lathe; CNC Machining Center; CNC Milling Machine; Press Brake; Milling Machine; Lathe; CNC Turning Center; Drilling Machine; Sawing Machine
Central America2.00%CNC Lathe; CNC Machining Center; CNC Milling Machine; Press Brake; Milling Machine; Lathe; CNC Turning Center; Drilling Machine; Sawing Machine

The mill rotary table is one of the main accessories of milling machine. As a precision work positioning device, it is widely used for indexing drilling, milling, circumferential cutting, boring, etc. The rotary turn table for milling machine is made from HT200 casting with high quality. It has already passed the ISO9001 quality system certification. They are are very popular on the market for their superior performance, excellent design and reasonable cost.
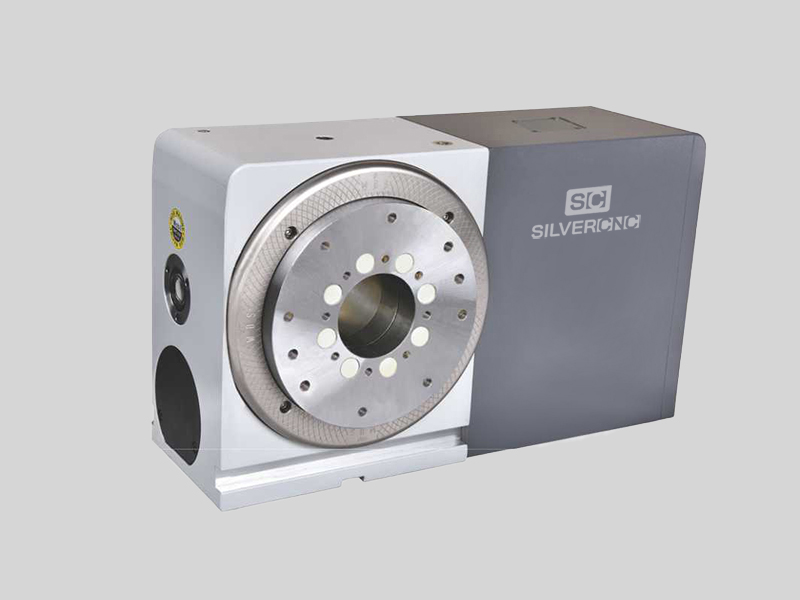

The rotary table is an accessory for the CNC floor type boring and milling machine. It can be working together with the floor type boring milling machine for milling angle, reverse boring, polyhedral machining, and other complex machining processes. It could do five sides machining if the main machine equipped the angle milling head.
CNC rotary table is a common part of CNC milling machine, often used as a servo axis of CNC milling machine, namely C axis of vertical CNC milling machine and B axis of horizontal CNC milling machine. The CNC rotary table includes the foot of the turntable, a round turntable surface, four rolling bearing parts arranged on the upper surface of the foot of the turntable, and a center with a self-aligning bearing installed at the center of the upper surface of the foot of the turntable. Support, each rolling bearing component includes a rolling bearing and a support that supports the rolling bearing through the axle. The center of the lower surface of the turntable is provided with a vertical downward axle. The turntable is installed on the foot of the turntable. The inner ring of the self-aligning bearing is fixed, and the rotating surface of the rolling bearing is in rolling contact with the lower surface of the turntable surface.
The CNC rotary table has an inclinometer with two orthogonal test axes as the test tool. The inclinometer is set at the center of the turntable surface to be leveled, so that the two orthogonal test axes of the inclinometer are parallel to the turntable surface, by adjusting the milling machine turntable. The leveling mechanism under the base makes the tilt angle value output by the two test shafts of the inclinometer turntable in the leveling state.
CNC rotary table and swing head are the key components of multi-coordinate CNC machine tools. Traditional rotary tables and swing heads using high-precision worm gears and other transmissions are not only difficult to manufacture, costly, but also difficult to achieve the speed and accuracy required for high-speed machining. Therefore, it is necessary to develop a new electromagnetic drive system for the CNC milling machine turntable and swing head in a different way to realize the zero-drive drive of the rotational motion coordinates of the CNC machine tool.
1. The CNC turntable uses modular design technology. The PAN turntable and TILT turntable are independent components, which are easy to disassemble and can be controlled by linkage or individually.
2. The use of AC servo motor drives the harmonic wave reducer transmission system to ensure that the equipment not only runs stably at low speeds, but also has fast dynamic response performance.
3. The automatic control system is composed of a PC and a motion controller based on DSP, which ensures the openness and convenience of expansion of the automatic control system.
4. The control software developer platform uses the Windows platform, which can make full use of various data visualization development tools, which greatly simplifies the progress of experimentation, research, and research and development.

Rotary table in market mainly includes 4 kinds of mechanism that is worm gear, roller cam, DD driver and harmonic structure. The following is the introduction:
1. worm gear: it’s one of the most popular structrue in NC rotary table because of its irreversibility and costs.The worm is generally made of bronze, but the wear resistance is poor. In order to improve the service life, some manufacturers use the alloy steel.
2.roller cam: This is the most popular deceleration mode in the Chinese market. Compared with worm gear, it has many advantages, such as wear resistance, high transmission efficiency , good price and basically no maintenance. Chinese consumers like it very much.
3.DD motor: it’s the most efficient rotary table with the highest precision. It has the highest precision because it has no mechanical structure, which is directly driven by motor , no reducer. It has high technical difficulty and high price. It is generally used for five axis machine tools.
4. Harmonic driver: Harmonic reducer is a new transmission structure in gear reducer. It uses flexible gear to produce controllable elastic deformation and cause relative staggered teeth between rigid wheel and flexible wheel to transmit power and motion. This kind of transmission is essentially different from the general gear transmission, and has particularity in meshing theory, set calculation and structural design.

Kunming Machine Tool Company Ltd, China, (KMTC) has developed a variety of ‘China"s first" high performance machine tools, leading the development of machinery and the machine tool industry in China. As a market leader in metrology, Renishaw has provided KMTC with advanced solutions in machine calibration and performance evaluation, including XL-80 laser interferometer, QC20-W telescoping ballbar system, XR20-W rotary axis calibrator and AxiSet™ Check-Up.
KMTC has a very strict quality control where each machine has to be calibrated twice: in manufacture and at the client site before it goes into production. Some large machine tools need to be dismantled after first calibration in manufacture, and calibrated again after re-assembly on site. Mr. Yang, supervisor of KMTC Metrology Centre, says “We used to adopt laser interferometers from another supplier before we started the partnership with Renishaw. Although the other supplier"s system performance was good, it was a problem when travelling to customer sites as we had to carry the full system kit in 3 large cases. We found many advantages when we switched to Renishaw"s first generation ML10 laser interferometer system which was compact and portable. We now widely use Renishaw"s latest XL-80 laser interferometer system in our production and benefit from its extended functionality.” KMTC has purchased 18 laser interferometer systems.
In KMTC"s current machine tool models, the accuracy and resolutions are up to 3 µm/m and down to 1 µm/m respectively. KMTC engineers are now able to finish the calibration on an axis of 2 to 3 metres travel distance in 30 minutes.
Axis length can be up to 60 metres on some models. Renishaw"s XL-80 laser interferometer offers accuracy of ±0.5 µm/m at normal environmental temperature. It can provide a resolution of 1 nm at a speed of 4 m/s as well as measuring distance up to 80 metres, which is long enough to satisfy most of the machine tools manufactured.
Rotary axes are becoming more popular in use with the growth in 5-axis machine tools. Conventional rotary axis assessment is not only time consuming but also requires skilled operators. Mr Yang said “We used to adopt a multi-tooth indexing table working with a quasi laser tube or a 24 face prism with auto-collimator to measure positioning accuracy of rotary axes. During the measurement, the upper half of the multi-tooth indexing table is lifted off manually and turned to a defined measuring angle. Then, we counter rotate the rotary table by the same angle to re-align with the laser tube. As a result, the errors can be measured. The accuracy of this approach is quite high, up to ±0.2 arc seconds but the tradeoff is time consumed; even an experienced technician has to spend one day to complete the measurement. The 24 face prism projects images on its reflective surface via the light tube. However the limitation is the measuring angle interval must be a multiple of 15 degrees.
The Renishaw XR20-W rotary axis calibrator has transformed the way we calibrate rotary axes on machine tools. The XR20-W works with the XL-80 laser, allowing the measurement to be completed within 2 hours, reducing labour costs. The operation is quite simple, available with a software user interface in Chinese language, where operators with basic computer knowledge are able to get started quickly."
The Renishaw XR20-W rotary axis calibrator employs wireless operation where data capture is synchronized to axis movement, with accuracy up to ±1 arc second, allowing automated measurement at any defined angle interval. All calibrators are factory calibrated and delivered with traceable certification. The XR20-W also supports off-axis measurement, allowing measurement even when the calibrator is not directly installed on the rotary axis pivot point. It is one of the frequently used functions by KMTC.
“The XR20-W features many improvements over its RX10 predecessor, including Bluetooth wireless technology which makes the data capture process more reliable. Renishaw has a strong reputation in metrology so some of our customers specifically request that we use Renishaw"s calibration products for commissioning, despite us explaining that traditional methods, such as multi-tooth indexing table, are able to offer comparable accuracy too", concluded Mr Yang.
Apart from laser interferometers, KMTC has also started to incorporate use of the Renishaw QC20-W ballbar system into its production. With a simple and quick ballbar test a user can identify the overall performance of their machine tool, as well as diagnosing problems. This enables customers to measure conventional 3-axis machine tools in accordance with ISO 230-4.
Renishaw has launched Ballbar Trace software, which it offers to existing ballbar users for free. This provides verification for 4 and 5-axis machine tools in accordance with ISO 10791-6 using XCal-View data analysis software.
KMTC also uses Renishaw"s AxiSet Check-Up to perform a fast and accurate health check of rotary axis pivot points on multi-axis machine tools, and automatically update parameters and compensations for rotary axis pivot point position errors. This has greatly improved the precision performance of 5-axis machine tools.
Renishaw sales engineers are always very helpful and provide invaluable technical knowledge and support. They always respond to us quickly and provide useful suggestions. They are happy to share information about updates and notify us of new products, which is one of the key reasons why KMTC and Renishaw maintain such a long term partnership.
KMTC is capable of developing systems with technology and specification comparable with the top manufacturers in the global machine tool market. Mr. Liang Feng Peng, Vice President of KMTC said "We have produced parts such as bearings and accessories for some German manufacturers. In future, KMTC will continue the development in industries such as wind power, automotive, aerospace and engineering machinery. At the same time, we will allocate more resources in horizontal machining centres. We have recently provided a custom solution of automatic production lines for a well-known automobile parts manufacturer."
Manufacturers encountering technical issues during machine tool measurement need support and guidance to help them achieve optimum measurement results. “KMTC has been collaborating with Renishaw for more than 10 years. Renishaw sales engineers are always very helpful and provide invaluable technical knowledge and support. They always respond to us quickly and provide useful suggestions. They are happy to share information about updates and notify us of new products, which is one of the key reasons why KMTC and Renishaw maintain such a long term partnership." Mr Yang said.
Kunming Machine Tool Company Ltd (KMTC), a subsidiary of Shenji Group, is a leading machine tool manufacturer in China. Established in 1939, KMTC has successfully developed over 400 products over 70 years, among which was China"s first precise horizontal machine centre and high precision jig borer. KMTC is in the ‘Top 100 Chinese Companies of Excellent Quality". Its product lines cover jig borer, floor boring and milling machines, planer boring and milling machines, horizontal boring and milling machines, gantry boring and milling machines, horizontal machining centres and machine tool accessories.
Kunming Machine Tool Company Ltd, China, (KMTC) has developed a variety of ‘China’s first’ high performance machine tools, leading the development of machinery and the machine tool industry in China. As a market leader in metrology, Renishaw has provided KMTC with advanced solutions in machine calibration and performance evaluation, including XL-80 laser interferometer, QC20-W telescoping ballbar system, XR20-W rotary axis calibrator and AxiSet™ Check-Up.

Japan was pretty much on board making quality stuff by the early 1970"s. We started seeing Honda motorcycles in the early 60"s. At first the Japanese machines had more bells and whistles than the made in US or European machines and were generally high quality. However, the early Japanese machinese were on the light duty side. When put under a load the Jap stuff was a bit wimpy compared to the domestic machines. Under light loads the Jap machinese were fine. This changed by the 80"s and the "best" Jap machinese were as good as any. Today, I"m proud to own Japanese stuff but still drive Fords.
Not so sure about Taiwan. My 9 x 42 JET mill was made in 1999 in Taiwan and has performed fine for me. I think the Taiwan stuff is somewhere between Japan and China from a quality point.
My 13 x 40 JET lathe was made in China and was bought new in 1999. It has served me well and I expect (hope) it will continue. Chinese machines are not that bad in my opinion. Those screwless vices and parallel sets that ENCO sells are great. The Chinese crash and burn when it comes to cutting tools and house hold items. I do not believe the Chinese use real high speed steel in their cutting tools. Their cutting tools are fine for machining low carb steels and nonferrous materials but not when machining D-2. Beware of anything made in China and purchased in your local hardware store.
I think you will be fine with you mill and the vise and turn table that came with it. My advise for running Asian made machines and tools is take it easy. Their short commings will surface when under stress like taking heavier cuts than the machines was intended or capable of. People get into trouble when they think there equipment is indestructable.

This website is using a security service to protect itself from online attacks. The action you just performed triggered the security solution. There are several actions that could trigger this block including submitting a certain word or phrase, a SQL command or malformed data.
When autocomplete results are available use up and down arrows to review and enter to select. Touch device users, explore by touch or with swipe gestures.
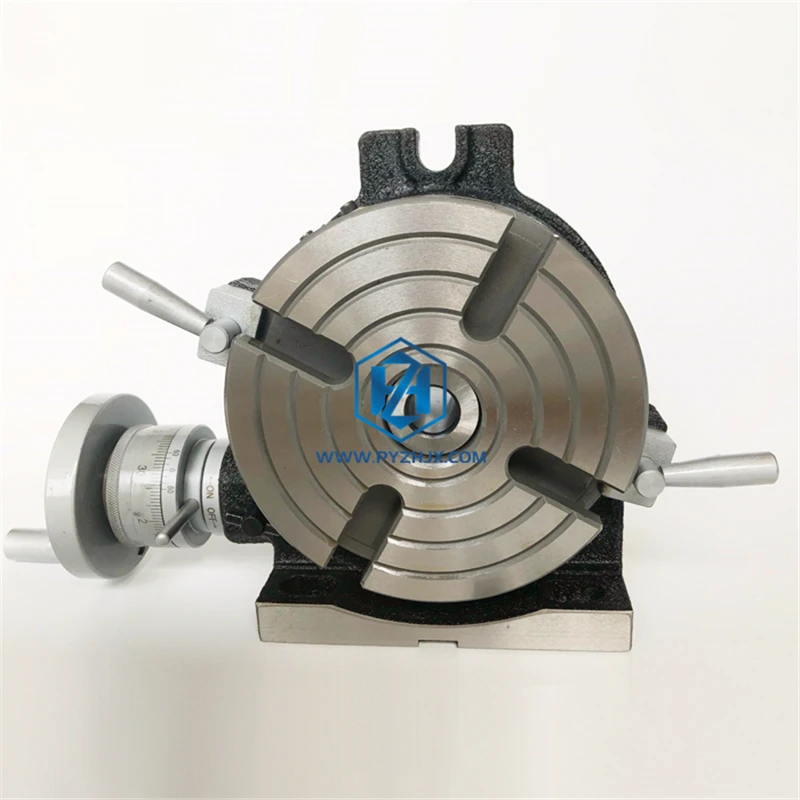

Have you already know about us? If you want to choose the machine you want in our CNC milling machine series. Consider the options for CNC machine tools. Contact us by phone, email or submit a quotation form. Your custom CNC machine price will be sent to your inbox. It"s that simple! Explore our affordable CNC machines today!
If you are still hesitating or have more questions, please feel free to contact us by email. We have more than ten years of experience in CNC machine experts to answer your questions, and you can also subscribe to our news, you will receive it from time to time. Our product updates and CNC machine industry dynamics.

Floor boring machine is available with drilling, boring, reaming, countersinking, milling, slotting and threading. Add-ons with rotary table, angle head, universal milling head and spindle support sleeve enable reverse boring and multi surface process. Recommend for heavy machinery, vehicle, machinery engineering, aviation, aerospace, vessel, power generation, millitary, nuclear, metallurgy and environmen protection industries.
HT serial planner machine adopt domestic and foreign advanced technic to design the structure and technology , to make the machine to be a high-grade CNC machine ,it is suitable for milling ,boring/drilling ,threading ,cutting ,turning and machining three dimensional curved ,many machining processes could be finished under once clamped .the machine was widely used in all kinds of different fields ,including oil equipment ,valve ,electrical equipment ,metallurgical and mine , construction machinery ,ships ,rail traffic ,and many other mechanical machining industries ,it should be your first choice to machine the valve ,box-type , monoblock ,machine base ,and many other work pieces.itemunitHT110HHT130H

Lathe slides are designed to resist only turning forces which is usually directly down onto the slide. You are milling which puts loads on the slide it wouldn"t normally see. Make sure that the gibs on your slides are snugged up to reduce any lift or lash and if you don"t intend moving the slide during your milling, lock it up tight.
Another thing I would do it add some support to the rear of the table. If you can fix an angle or block to the base and clamp it down then you"ll find it a lot more rigind.
Finally your clamping of the part leaves a lot to be desired. You"re milling a long way from the clamp and if that flat bar is even slightly bowed it will hinge all over the place. You could put a second clamp on it ir if you don"t have the room for that without fouling the cutter try at least putting some low level stops in the dis-used slots to prevent hinging. Another thing you could do is put a piece of paper under the part near each edge of the table. That will improve clamping forces a lot.
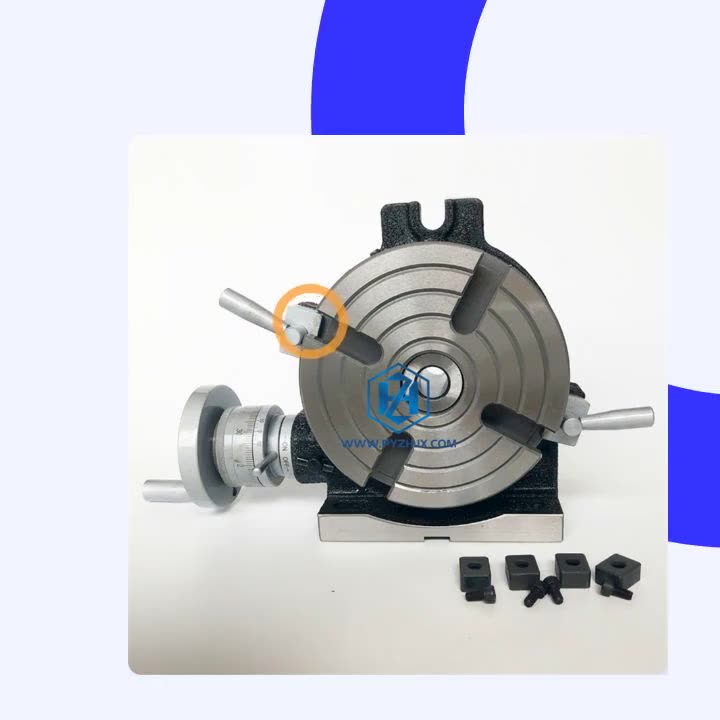

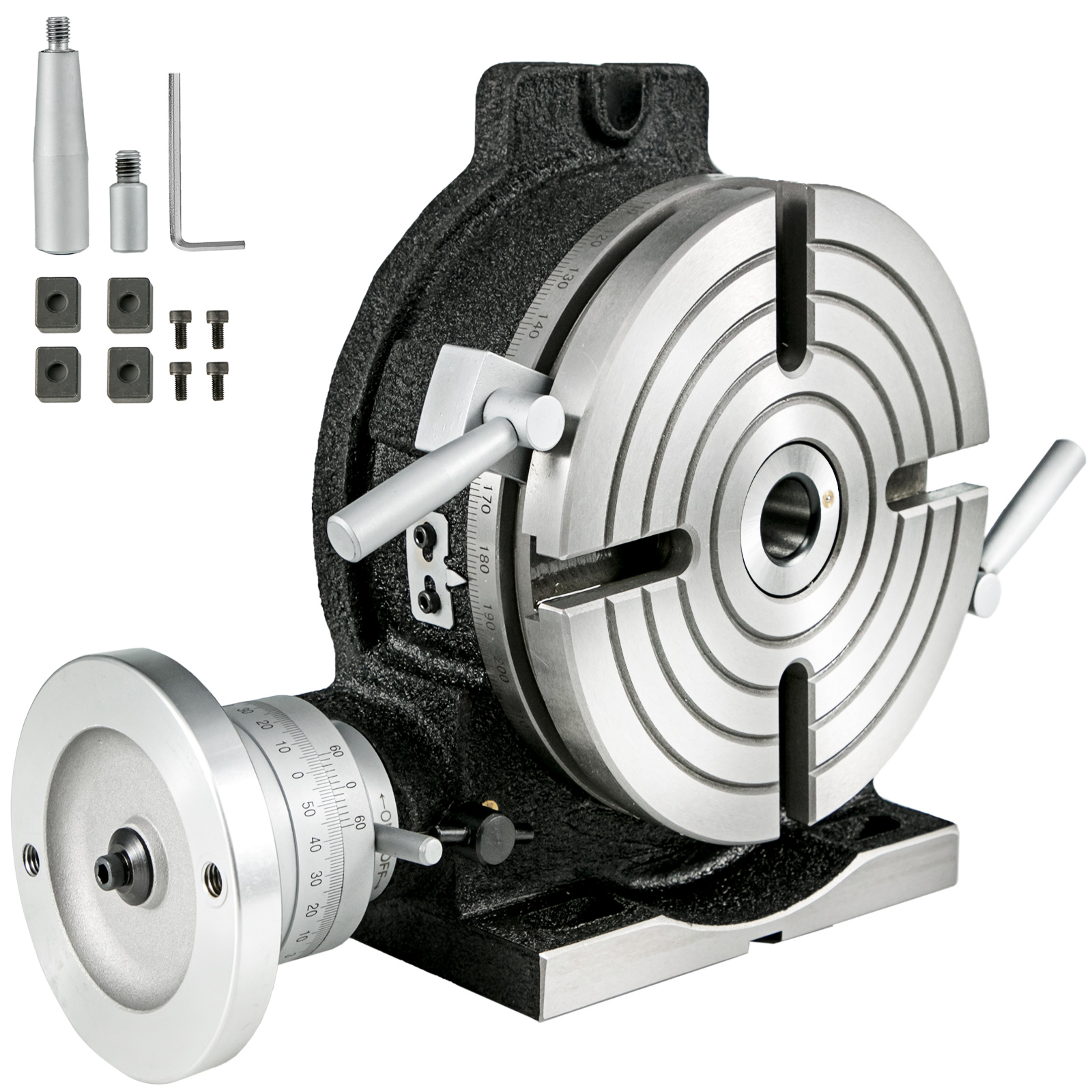
A rotary table is a precision work positioning device used in metalworking. It enables the operator to drill or cut work at exact intervals around a fixed (usually horizontal or vertical) axis. Some rotary tables allow the use of index plates for indexing operations, and some can also be fitted with dividing plates that enable regular work positioning at divisions for which indexing plates are not available. A rotary fixture used in this fashion is more appropriately called a dividing head (indexing head).
The table shown is a manually operated type. Powered tables under the control of CNC machines are now available, and provide a fourth axis to CNC milling machines. Rotary tables are made with a solid base, which has provision for clamping onto another table or fixture. The actual table is a precision-machined disc to which the work piece is clamped (T slots are generally provided for this purpose). This disc can rotate freely, for indexing, or under the control of a worm (handwheel), with the worm wheel portion being made part of the actual table. High precision tables are driven by backlash compensating duplex worms.
The ratio between worm and table is generally 40:1, 72:1 or 90:1 but may be any ratio that can be easily divided exactly into 360°. This is for ease of use when indexing plates are available. A graduated dial and, often, a vernier scale enable the operator to position the table, and thus the work affixed to it with great accuracy.
Rotary tables are most commonly mounted "flat", with the table rotating around a vertical axis, in the same plane as the cutter of a vertical milling machine. An alternate setup is to mount the rotary table on its end (or mount it "flat" on a 90° angle plate), so that it rotates about a horizontal axis. In this configuration a tailstock can also be used, thus holding the workpiece "between centers."
With the table mounted on a secondary table, the workpiece is accurately centered on the rotary table"s axis, which in turn is centered on the cutting tool"s axis. All three axes are thus coaxial. From this point, the secondary table can be offset in either the X or Y direction to set the cutter the desired distance from the workpiece"s center. This allows concentric machining operations on the workpiece. Placing the workpiece eccentrically a set distance from the center permits more complex curves to be cut. As with other setups on a vertical mill, the milling operation can be either drilling a series of concentric, and possibly equidistant holes, or face or end milling either circular or semicircular shapes and contours.
* To create large-diameter holes, via milling in a circular toolpath, on small milling machines that don"t have the power to drive large twist drills (>0.500"/>13 mm)
* With the addition of a compound table on top of the rotary table, the user can move the center of rotation to anywhere on the part being cut. This enables an arc to be cut at any place on the part.
Additionally, if converted to stepper motor operation, with a CNC milling machine and a tailstock, a rotary table allows many parts to be made on a mill that otherwise would require a lathe.

when I was young, strong, healthy, and thought nothing of lifting it, a 10" H & V was my first choice. I still think it was a good choice for the work I mostly do, and this is where you may decide to compromise. If you do small work, an 8" table is much lighter and more convenient to set up. Stood vertical, it interferes less with the spindle to reach center. I don"t think a 6" is a good choice unless you know you will only be working miniature stuff. You use a considerable percentage of a small table just for set ups and hold down clamps on a lot of work, and a small table does not leave much room.
I like 90:1 gear ratio for circular milling, which is presumably your primary interest with a rotary table. My 10" table is 90:1, and that is a pretty good ratio for milling diameters (hand cranking) out to 12" or so. My 20" table is also only 90:1, and out near or past the rim (I do one part at 32" diameter) that always seems _very_ coarse.
If most of your work is small, round to begin with, and will actually be dividing work, where you index the table, lock it, and then drill a hole or mill a slot with the machine axis drive, you might find a dividing head more useful. For instance, I"ve made gears on a vertical rotary table, and in a spin index. On the table, you need an insert collet chuck or other arrangement in the center hole to get the work out far enough to clear the cutter. It"s a lot more convenient on a dividing head. OTOH, I don"t find it fun or convenient to do much circular milling on a dividing head if the work diameter is much over a few inches.
Dividing heads typically are 40:1, so faster to index, position to positon. But the milling capability on a radius is limited by the "coarse" ratio to smaller diameters, as is the usual work holding (collet or chuck) arrangement. A dividing head will tilt from below horizontal to past vertical, so you can mill, drill, bore or shape profiles at any angle in between.
an 8" H & V with dividing plates and set up, can usually be arranged somehow to do most of the work you might want to do on it. It is relatively light to move, and convenient to set up with reasonable space (spindle clearance, e.g.)limitations to be considered. A little bigger (10") is better, if you will ever need the capacity.




 8613371530291
8613371530291