earthquake gas safety valve free sample
Seismic shut-off valves are a simple, but effective way to ensure you never experience a gas fire after an earthquake. They are designed for earthquakes, accidents and any event of impact. We have installed thousands of automatic gas shut off valves to the manufacture’s specification to ensure safe, trouble free use.
The seismic valves work on a simple, consistent and accurate principle. A sensor moves when the valve is subjected to a 5.4 magnitude or larger earthquake, releasing the valve float which blocks the line and prevents gas going in to the building. The valve is then manually reset once a safety inspection has been done and you’re sure there are no leaks in the building.
Each valve is tested and certified before leaving the factory to meet approval from the State Board of Architect and LA Counties stringent requirements. They are tested to ASCE 25-97, State of California 12-23-1 & ANSI Z21.70-1981 Standards for Seismic Gas Valves.
Some cities and counties in California have regulations that require the installation of automatic gas shut-off devices, which may include excess flow gas shut-off valves and/or seismic gas shut-off valves. Regulations vary, but generally apply to new building construction, or significant alterations or additions to existing buildings.
If a customer installs an automatic gas shut-off valve, it should be one that is certified by the State of California and it should be installed by a licensed plumbing contractor in accordance to the manufacturers instructions.PG&Edoes not install or service seismic actuated or excess flow gas shut-off valves, or recommend specific contractors for customer applications.
Non-emergency shut-offs will occur if the automatic gas shut-off is not installed according to manufacturer’s specifications. For example, the impact of heavy vehicles can trigger a non-emergency shut-off. They operate on movement and shut off the supply of gas to a building, when triggered by a 5.4 magnitude or larger Earthquake.

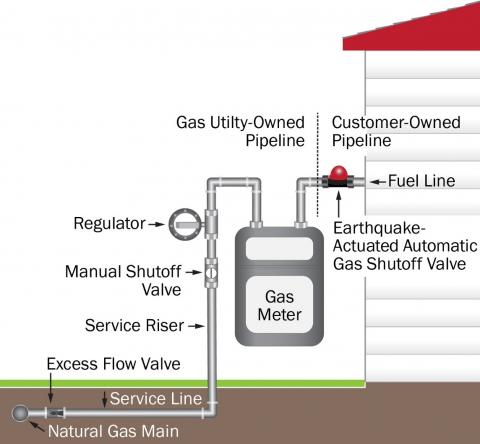
Homes that are equipped with a gas line that runs from the utility line to the home should have an automatic gas shut-off valve (ASV) (Figure 1), which is a valve that shuts off the flow of gas into a home due to an earthquake or other event that causes a rupture of the gas line, thus reducing the chance of explosion or fires from leaking gas. Shaking or movement of a building or the appliances in the home in the event of an earthquake or other natural disaster can cause damage to the gas piping and appliances, causing the accidental release of natural gas, which can lead to fires or explosions. Structural weaknesses, the absence of appliance anchors, and lack of flexible pipe connectors can all contribute to a greater possibility of gas leaks (Danville 2021).
All homes that have natural gas have a manual shutoff valve located on the gas meter that can be closed using a wrench to stop the flow of natural gas into the home in the event of an emergency (Figure 5). However, the home’s occupants may not be available to close the line in the event of a natural disaster or may not be aware of a rupture of the line due to some other cause such as digging. If an automatic gas shutoff valve is installed on the line, it can stop the flow of gas quickly in the event of an emergency with no human intervention needed, preventing large gas spills from occurring and potentially causing fires or explosions.
There are two types of automatic gas shut-off devices: earthquake-actuated gas shut-off valves (also known as seismic valves) and excess flow valves. The differences between the two valves are summarized in Table 1 and described below. Requirements for shutoff valves for natural gas lines vary by jurisdiction. The requirement typically applies to new building construction and significant alterations or additions to existing buildings (PG&E 2021). Because an earthquake valve is triggered by movement, not an actual line break, while it will prevent gas leakage from the initial quake or aftershocks, it will shut off the gas even if no rupture occurs to the gas line. In contrast, an excess flow valve is triggered by sudden high flow on the line, indicating a leak has occurred; earthquake movement alone won"t trigger it. Utilities note that restoration of utility gas service after an emergency will take time, whether the gas valve has been shut manually or automatically, because the utility may require that its crews inspect the gas meter and equipment to verify there are no leaks in the line, clear active lines of residual gas, restore service to the lines, and relight pilot lights (PG&E 2021).
Stops flow of gas on the service line between the main line and the meter when it detects high gas flow and/or loss of line pressure depending on valve model.
Sensors on the gas line detect a large increase in gas flow rate due to a rupture of the service line (for any cause, such as earthquakes, tree roots, excavation equipment, severed line in house)
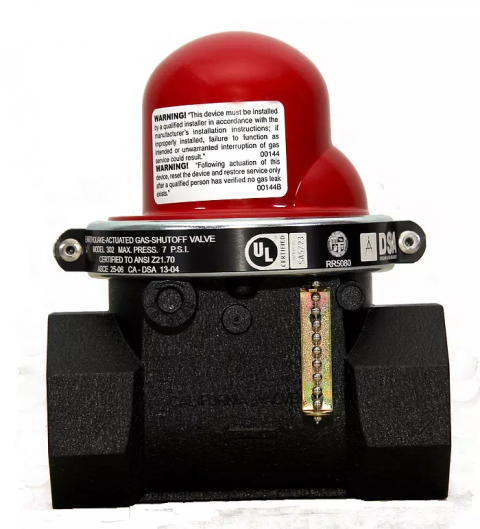
An earthquake-actuated gas shutoff valve (also known as an earthquake valve or a seismic valve) is a simple mechanical device installed just downstream of the meter on the pipe between the meter and the house (Figures 1 and 2). If the valve is subjected to significant movement, a ball or “float” in the valve drops into place to block the flow of gas through the pipe and into the building. If an earthquake does impact the home, gas flow will be stopped by the valve so gas will not continue to flow into the home, where it could potentially leak from any ruptures in the line downstream of the meter and possibly catch fire or explode. Earth movement equivalent to an earthquake registering approximately 5.4 or greater on the Richter scale will activate the locking mechanism. (The Richter scale ranges from 1.5-barely detectable to 9.5-catastrophic; a 5.4 quake could cause considerable damage.) Many utilities require the installer to attach a stabilizing bracket to the piping near the valve to minimize the likelihood that an accidental bump will activate the valve.
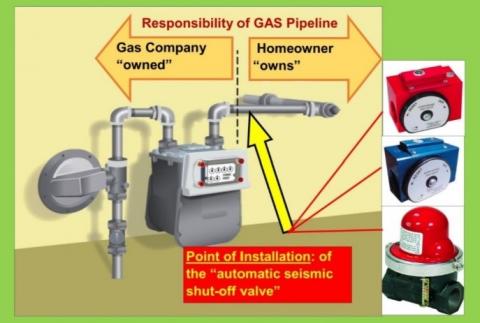
Seismic valves can be required by insurance companies or local departments of building and safety in areas prone to seismic activity. Some city, state, and/or county regulations require the installation of seismic valves; some leave this up to the owner’s discretion. Seismic valves are typically located on the homeowner’s side of the meter, on the pipeline leading from the meter into the house, which is usually located in an easily accessed location outside, above ground on the side or front of the house. The seismic valve is located downstream of the utility manual gas shut-off valve, pressure regulator, meter, and the service tee (see Figures 1 and 2).
Seismic valves are purchased by the homeowner and installed by either the homeowner or a licensed plumber or contractor who has been certified to do so. Most utilities do not install seismic valves (for example, SoCalGas 2021). Some utilities offer assistance in purchasing the valves. For example, the City of Berkeley, California, offers free seismic valves to homeowners who complete a training program (City of Berkeley 2018). The City of Malibu, California, requires a plumbing permit to install valves but waives fees for the permit process (City of Malibu). Utilities do not typically allow attachments or connections of any kind on the utility’s piping and equipment before the point where the service tee connects to the gas houseline piping. After installation, the valve must not obstruct any gas operations or utility services in or around their piping, gas service shut-off valves, gas meters, or gas pressure regulating equipment (PG&E 2021).
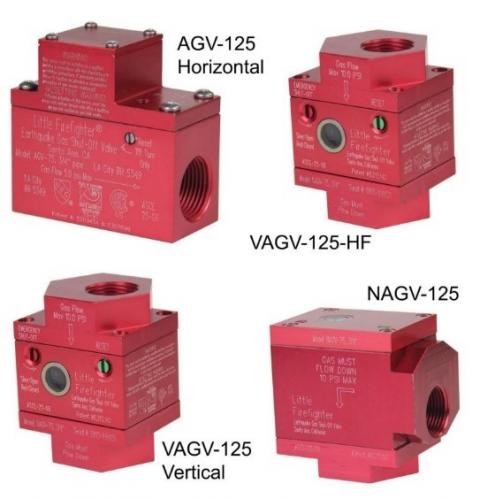
Seismic valve products should meet the requirements of ASCE 25-97 and ANSI Z21.70-1981 Standards for Seismic Gas Valves. Some locales require that installers use a state-approved model for excess flow gas shut-off valves and earthquake-actuated gas shut-off valves. Seismic valves installed in California should be certified by the California State Architect"s Office as meeting California Standard No. 12-23-1 for Earthquake-Actuated Automatic Gas Shutoff Systems. The State of California’s Division of the State Architect (DSA) oversees the certification of both types of gas shutoff valves as required by the Health and Safety Code and lists approved models on the website of the DSA Gas Shut-off Valves Certification Program. Products used in Los Angeles need to be approved by the City of Los Angeles. Examples of seismic valves approved for use in California are shown in Figures 3 and 4.
Seismic valves will operate to shut off the gas when they sense enough earth movement, whether a line rupture occurs or not. If the gas is shut off by a seismic valve, some utilities specify that the homeowner is not to turn the gas back on themselves but should notify the utility to have a utility representative perform a safety check, restore gas service, and relight appliance pilot lights. For this reason, some utilities do not encourage the installation of seismic shutoff valves for residential service due to the time required to go around and reset all of the valves following an earthquake. Some jurisdictions require excess flow valves instead. Check the applicable jurisdiction for specific requirements in your area (FEMA E-74, 2011).
The valve is manually reset once a safety inspection has been done to verify there are no leaks in the building. Some jurisdictions allow homeowners to reset their own automatic shutoff valves. This is one reason some homeowners prefer to have an earthquake-actuated shutoff valve even if not required to do so by the local building department or their homeowner’s insurance company. In the event of an earthquake, an earthquake-actuated valve will shut off gas flow as soon as significant earth movement is detected without waiting to sense a gas leak. If, after the quake, no leaks are detected, the homeowner may be able to reset the valve or hire a plumber to reset the valve and re-establish gas service. Many homes have both types of valves.
Excess flow valves automatically stop the flow of gas on the service line between the main gas line at the street and the customer"s meter (on the "utility side" of the meter) if excess flow or loss of pressure is detected, indicating a rupture of the gas line (American Gas Association 2011), whether the rupture is caused by an earthquake, or some other natural cause such as a sinkhole or a washout, or damage from digging or drilling equipment, or motor vehicle impact to the meter, or line breakage in the home.
In 2006, Congress mandated the use of excess flow valves on all new or replaced gas distribution lines serving single-family residences (49 CFR 192.383(a)). By the end of 2014, an estimated 9 million excess flow valves were in service and over 800,000 new valves were being installed every year (P&GJ 2016). In a Final Rule published in the Federal Register on October 14, 2016, the Pipeline and Hazardous Materials Safety Administration (PHMSA) made changes to 49 CFR Part 192 to expand the requirement to include multifamily residences and small commercial buildings, and required gas utilities to notify customers who had existing homes without excess flow valves of their right to request installation of one. For new homes, the cost of installation is included in the charge for the new line.
Dates at which utilities began installing excess flow valves for new homes vary by utility, although many pre-date the 2006 Congressional mandate. For example, all homes with gas service built in Oregon after 1993 have an excess flow valve installed by the utility at construction. With an existing home, if you are unsure if an excess flow valve is already installed, contact the gas utility. In existing homes without an excess flow valve, the customer can request that the utility install one, at the homeowner’s expense (Colorado Springs Utilities). The utility or their service contractor will install the excess flow valve on the underground service line pipe running from the street to the meter. Costs vary depending on location and difficulty of the installation, with reported costs ranging from $400 to $7,000. For example, the City of Ellensburg, Washington, estimates $500 to $1000 (City of Ellensburg). TECO Peoples Gas in Florida estimates $1,200 to $1,800 (TECO Peoples Gas). PG&E estimates $2,500 to $6,000 or more, based on the specific site (PG&E 2017).
In an emergency, some utilities tell their homeowners that the gas can be turned off at the main gas service shutoff valve, with the following guidelines (for example, PG&E 2021, SoCalGas 2021).
Do not shut off the gas unless you smell gas, hear gas escaping, see a broken gas line, suspect a gas leak, or are advised to do so by the gas utility. If you shut off the gas, there may be a considerable delay before the utility can turn your service back on.
Locate the main gas shutoff valve. It is typically next to the gas meter. It may be on the side of front of the house, or in a cabinet meter outside of the house, under the house, or underground.
Give the valve a quarter turn in either direction. The valve is closed when the tang (the part of the valve you put the wrench on) is crosswise (perpendicular) to the pipe. See Figures 5 and 6.
Note, some jurisdictions and gas utility companies stipulate that manual gas shut-off can only be performed by the utility or its certified contractors (California Public Utilities Commission General Order 112-E).
Manually turn off the gas shutoff valve at each appliance. For safety, a shut-off valve should be installed at every natural gas appliance. If a leak happens at a specific appliance, the valve allows you to turn off the natural gas at the appliance rather than shutting off the natural gas service line to the whole house. Some valves require a wrench. See Figure 7.
Consult your local utility for guidance. Some utilities advise homeowners not to shut off the gas unless they smell gas, hear gas escaping, see a broken gas line, or suspect a gas leak because, if they do shut off the gas, there may be a considerable delay before the utility can turn the service back on (for example, PG&E).

While it"s possible to manually shut off your natural gas, the following specialized valves are available that can automatically shut off your service in case of an emergency:
Earthquake natural gas shut-off valve (also known as a seismic natural gas shut-off valve) automatically shuts off your natural gas service when an earthquake of a sufficient magnitude occurs at your home.
An excess-flow valve (EFV) automatically closes and restricts the flow of natural gas in the event an underground pipe is damaged or if there is a significant increase in the flow of natural gas to the meter.
If you want to have an earthquake natural gas shut-off installed, or are required to have one by your insurance company or the local Department of Building and Safety, the valve must be installed on your house line.
If installation requires natural gas service closure, you"ll need to contact us to shut off the service and restore service when installation is completed. Natural gas service shut off and restoration of service orders can be scheduled by contacting us at 1-800-427-2200.
Under the regulations of the California Public Utilities Commission (CPUC), General Order 112-E, only SoCalGas® or its certified contractors are authorized to operate the natural gas service shut-off valve.
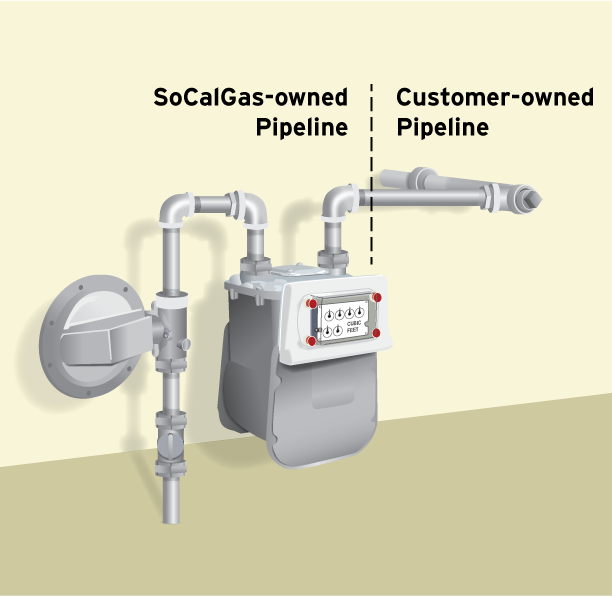
When you hire a qualified professional to install your earthquake valve, you"ll need to make sure that the valve is installed on your house line, not on SoCalGas" facilities. SoCalGas" facilities include all of the pipe fittings installed and maintained by SoCalGas, up to and including the last elbow or tee connecting to your house line. See the diagram below for to see where your house line starts.
All unauthorized valve installations found on SoCalGas" facilities will be removed. In addition, earthquake valves are not permitted in utility curb meter vaults.
If an earthquake or other significant event causes your earthquake shut-off or excess-flow valve to close, you can follow the manufacturer"s instructions for resetting the valve so that natural gas flows again. However, we recommend that you contact a qualified professional or SoCalGas to reset the valve, and to perform a safety check of your natural gas appliances before they are placed back in operation to verify that no natural gas leaks exist, and to re-light your pilot lights.
Remember that following a major emergency it may take many days or even weeks before someone can come to your location. (SoCalGas charges a fee to reset valves and re-light pilot lights when your earthquake shut-off valve has closed due to a non-earthquake occurrence.)
Price: The cost of the valve is going to vary based on the type and size of the valve, as well as the installation requirements and the company installing it.
Choosing a valve: In order to choose the right valve size and manufacturer, contact your local Department of Building and Safety to find out their earthquake valve requirements.
Where to buy a valve: You can purchase an earthquake valve at supply retailers, licensed plumbing contractors, or directly from the valve manufacturer.
Using a contractor: You can hire a qualified professional to install the earthquake or excess-flow valve on your house line. SoCalGas will not install a valve for you.
Effective February 10, 2002, California Public Utility Commission (CPUC) Decision 01-11-068 prohibits installation of an earthquake valve on SoCalGas" facilities. In addition, SoCalGas no longer installs earthquake shut-off valves for its customers, and does not allow any customer owned equipment, including excess-flow valves, be installed on SoCalGas" facilities.
If you have an earthquake valve that was installed by SoCalGas or one of its authorized contractors on or before the February 10, 2002 cutoff date, that is located on SoCalGas" facilities, with proper documentation your installation may be allowed to remain in place. Authorized contractors are those who participated in SoCalGas" earthquake program and were trained by SoCalGas to work on their facilities.
Additional information regarding earthquake valves and natural gas service restoration after a valve activates can be found in Tariff Book, Rule 10, Section G, "Earthquake Valve Service."
An Excess Flow Valve, or EFV, is a safety device installed on natural gas distribution pipelines to automatically close and restrict the flow of natural gas in the event an underground pipe is damaged or if there is a significant increase in the flow of natural gas to the meter. These conditions are typically caused by digging or construction but can also be caused by damage to your natural gas meter by a vehicle impact.
EFV can reduce the risk of explosions, fires, and personal injury because they close or restrict any unplanned or excessive natural gas flow. Installation of an EFV will not protect a customer from household appliance malfunctions, small punctures in underground pipelines, and pipeline damage from earthquakes or flooding. It is
important to understand that an EFV does not shut off the flow of natural gas completely. Some leakage may still occur resulting in a hazardous condition.
An EFV is installed on the service pipeline that runs underground between the natural gas main (usually located in or near the street, alley or easement) and the SoCalGas® meter on the customer’s property).
The best way to prevent damage to a natural gas pipeline due to digging is to call 811, the Underground Service Alert program, at least two working days before digging. Underground Service Alert will coordinate with SoCalGas to mark the locations of buried utility-owned lines - absolutely FREE.
If you are interested in having an EFV installed on the service pipeline serving you[1], please call SoCalGas at 1-800-427-2200. SoCalGas will first check to see if your service already has an EFV installed and, if not, an estimate to install the EFV will be provided. The cost to install an EFV can vary widely depending on site specific conditions and can range from $2,500 to $5,000 or more.
If you decide to have an EFV installed, we will coordinate with you to schedule the installation (note that it is possible that natural gas service will be interrupted to install the EFV). The construction crew will dig around the natural gas line in order to install the EFV and when the job is complete natural gas service will be restored (if it was shut off). If paving or concrete needs repair that work will be scheduled at a later date.

Earthquake-actuated gas shutoff valves designed to automatically shut off the gas at the location of the valve in the event of a seismic disturbance and certified by the State Architect as conforming to California Code of Regulations, Title 24, Part 12, Chapter 12-16-1, shall be provided for buildings when such installation is required by local ordinance. Earthquake-actuated gas shutoff valves which have not been certified by the State Architect shall be prohibited in buildings open to the public under mandatory installation by local ordinance. Installation of the valves shall be in accordance with local ordinance, and in the absence of such per the manufacturer"s installation instructions.

Surface-controlled subsurface safety valves (SCSSVs) are critical components of well completions, preventing uncontrolled flow in the case of catastrophic damage to wellhead equipment. Fail-safe closure must be certain to ensure proper security of the well. However, this is not the only function in which it must be reliable—the valve must remain open to produce the well. Schlumberger surface controlled subsurface safety valves exceed all ISO 10432 and API Spec 14A requirements for pressure integrity, leakage acceptance criteria, and slam closure.
Through decades of innovation and experience, Schlumberger safety valve flapper systems are proven robust and reliable. The multizone dynamic seal technology for hydraulic actuation of subsurface safety valves is a further improvement in reliability performance when compared with traditional seal systems in the industry.
The multizone seal technology is currently available in the GeoGuard high-performance deepwater safety valves, which is validated to API Spec 14A V1 and V1-H.

There are many sites that recommend an earthquake safety valve to be installed on a gas line but they also sell service of installing so seems like they are just selling their service. Considering that there are moving parts in an earthquake valve what is the expected life of an earthquake safety valve and how frequently it should be tested?
Looks like gas co does not recommend them because not everyone knows how to reset the valve and relight their water heaters so it is a logistical issue when an earthquake hits for the gas company to restore everyone"s gas.
Please take a moment to understand the simplicity of our valves’ operation. It has been our experience, that the simpler the operation, the more accurate the function is when needed. Each valve is tested and certified before leaving our factory ensuring it meets Los Angeles Counties’ strict approvals.
Earthquakes can occur in Indiana at any time. Citizens should plan and practice what to do in the event of an earthquake in order to properly respond before, during, and after the shaking begins.
Conduct calm family discussions about earthquakes. Decide upon an outdoor meeting location for your family to reunite after a quake and conduct in-home practice drills. Teach your
Conduct a thorough investigation of your home, checking for any defective wiring, leaky gas connections, and deep cracks in the ceiling or foundation that could pose a danger
Install flexible, corrugated pipe fittings to avoid gas and water leaks. Flexible fittings are more resistant to breakage. If recommended by your gas service provider, have an
During an earthquake:Drop, Cover, and Hold on! Drop to the floor, get under a sturdy table, and hold on until the shaking stops. If your entire body does not fit underneath the furniture, position your
If you smell gas or hear a hissing sound, open a window and quickly leave the building. Shut off the main gas valve only if you suspect a gas leak. Return home only when it is declared
If you are driving, watch out for road hazards, including fallen trees, power lines, and damaged bridges and roads. If a power line fell onto your car during the earthquake, stay inside
Use the telephone only for emergencies. 911 systems will be overloaded after an earthquake. Keep the phone lines clear for emergency calls to get through.
Inspect your home for signs of structural damage, particularly to the foundation and chimney. Damage to these areas can pose serious safety hazards in the months after an earthquake. Do




 8613371530291
8613371530291