pilot safety valve free sample

The Groth 1400 Series Pilot-Operated Relief Valves are used to replace weight-loaded or spring loaded valves in many applications to increase efficiency and reduce evaporation losses. Several advantages are obtained over the traditional valves. For example, the process pressures may be closer to the set pressure than would be considered prudent and safe with the traditional valve. Additionally, greater conservation is obtained due to minimum product loss which in turn provides increased profits.
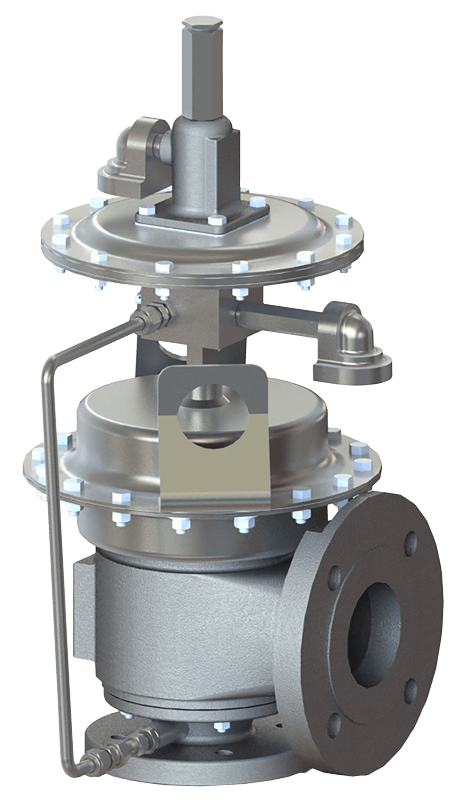
The primary purpose of a safety valve is to protect life, property and the environment. Safety valves are designed to open and release excess pressure from vessels or equipment and then close again.
The function of safety valves differs depending on the load or main type of the valve. The main types of safety valves are spring-loaded, weight-loaded and controlled safety valves.
Regardless of the type or load, safety valves are set to a specific set pressure at which the medium is discharged in a controlled manner, thus preventing overpressure of the equipment. In dependence of several parameters such as the contained medium, the set pressure is individual for each safety application.

A little product education can make you look super smart to customers, which usually means more orders for everything you sell. Here’s a few things to keep in mind about safety valves, so your customers will think you’re a genius.
A safety valve is required on anything that has pressure on it. It can be a boiler (high- or low-pressure), a compressor, heat exchanger, economizer, any pressure vessel, deaerator tank, sterilizer, after a reducing valve, etc.
There are four main types of safety valves: conventional, bellows, pilot-operated, and temperature and pressure. For this column, we will deal with conventional valves.
A safety valve is a simple but delicate device. It’s just two pieces of metal squeezed together by a spring. It is passive because it just sits there waiting for system pressure to rise. If everything else in the system works correctly, then the safety valve will never go off.
A safety valve is NOT 100% tight up to the set pressure. This is VERY important. A safety valve functions a little like a tea kettle. As the temperature rises in the kettle, it starts to hiss and spit when the water is almost at a boil. A safety valve functions the same way but with pressure not temperature. The set pressure must be at least 10% above the operating pressure or 5 psig, whichever is greater. So, if a system is operating at 25 psig, then the minimum set pressure of the safety valve would be 30 psig.
Most valve manufacturers prefer a 10 psig differential just so the customer has fewer problems. If a valve is positioned after a reducing valve, find out the max pressure that the equipment downstream can handle. If it can handle 40 psig, then set the valve at 40. If the customer is operating at 100 psig, then 110 would be the minimum. If the max pressure in this case is 150, then set it at 150. The equipment is still protected and they won’t have as many problems with the safety valve.
Here’s another reason the safety valve is set higher than the operating pressure: When it relieves, it needs room to shut off. This is called BLOWDOWN. In a steam and air valve there is at least one if not two adjusting rings to help control blowdown. They are adjusted to shut the valve off when the pressure subsides to 6% below the set pressure. There are variations to 6% but for our purposes it is good enough. So, if you operate a boiler at 100 psig and you set the safety valve at 105, it will probably leak. But if it didn’t, the blowdown would be set at 99, and the valve would never shut off because the operating pressure would be greater than the blowdown.
All safety valves that are on steam or air are required by code to have a test lever. It can be a plain open lever or a completely enclosed packed lever.
Safety valves are sized by flow rate not by pipe size. If a customer wants a 12″ safety valve, ask them the flow rate and the pressure setting. It will probably turn out that they need an 8×10 instead of a 12×16. Safety valves are not like gate valves. If you have a 12″ line, you put in a 12″ gate valve. If safety valves are sized too large, they will not function correctly. They will chatter and beat themselves to death.
Safety valves need to be selected for the worst possible scenario. If you are sizing a pressure reducing station that has 150 psig steam being reduced to 10 psig, you need a safety valve that is rated for 150 psig even though it is set at 15. You can’t put a 15 psig low-pressure boiler valve after the reducing valve because the body of the valve must to be able to handle the 150 psig of steam in case the reducing valve fails.
The seating surface in a safety valve is surprisingly small. In a 3×4 valve, the seating surface is 1/8″ wide and 5″ around. All it takes is one pop with a piece of debris going through and it can leak. Here’s an example: Folgers had a plant in downtown Kansas City that had a 6×8 DISCONTINUED Consolidated 1411Q set at 15 psig. The valve was probably 70 years old. We repaired it, but it leaked when plant maintenance put it back on. It was after a reducing valve, and I asked him if he played with the reducing valve and brought the pressure up to pop the safety valve. He said no, but I didn’t believe him. I told him the valve didn’t leak when it left our shop and to send it back.
If there is a problem with a safety valve, 99% of the time it is not the safety valve or the company that set it. There may be other reasons that the pressure is rising in the system before the safety valve. Some ethanol plants have a problem on starting up their boilers. The valves are set at 150 and they operate at 120 but at startup the pressure gets away from them and there is a spike, which creates enough pressure to cause a leak until things get under control.
If your customer is complaining that the valve is leaking, ask questions before a replacement is sent out. What is the operating pressure below the safety valve? If it is too close to the set pressure then they have to lower their operating pressure or raise the set pressure on the safety valve.
Is the valve installed in a vertical position? If it is on a 45-degree angle, horizontal, or upside down then it needs to be corrected. I have heard of two valves that were upside down in my 47 years. One was on a steam tractor and the other one was on a high-pressure compressor station in the New Mexico desert. He bought a 1/4″ valve set at 5,000 psig. On the outlet side, he left the end cap in the outlet and put a pin hole in it so he could hear if it was leaking or not. He hit the switch and when it got up to 3,500 psig the end cap came flying out like a missile past his nose. I told him to turn that sucker in the right direction and he shouldn’t have any problems. I never heard from him so I guess it worked.
If the set pressure is correct, and the valve is vertical, ask if the outlet piping is supported by something other than the safety valve. If they don’t have pipe hangers or a wall or something to keep the stress off the safety valve, it will leak.
There was a plant in Springfield, Mo. that couldn’t start up because a 2″ valve was leaking on a tank. It was set at 750 psig, and the factory replaced it 5 times. We are not going to replace any valves until certain questions are answered. I was called to solve the problem. The operating pressure was 450 so that wasn’t the problem. It was in a vertical position so we moved on to the piping. You could tell the guy was on his cell phone when I asked if there was any piping on the outlet. He said while looking at the installation that he had a 2″ line coming out into a 2×3 connection going up a story into a 3×4 connection and going up another story. I asked him if there was any support for this mess, and he hung up the phone. He didn’t say thank you, goodbye, or send me a Christmas present.
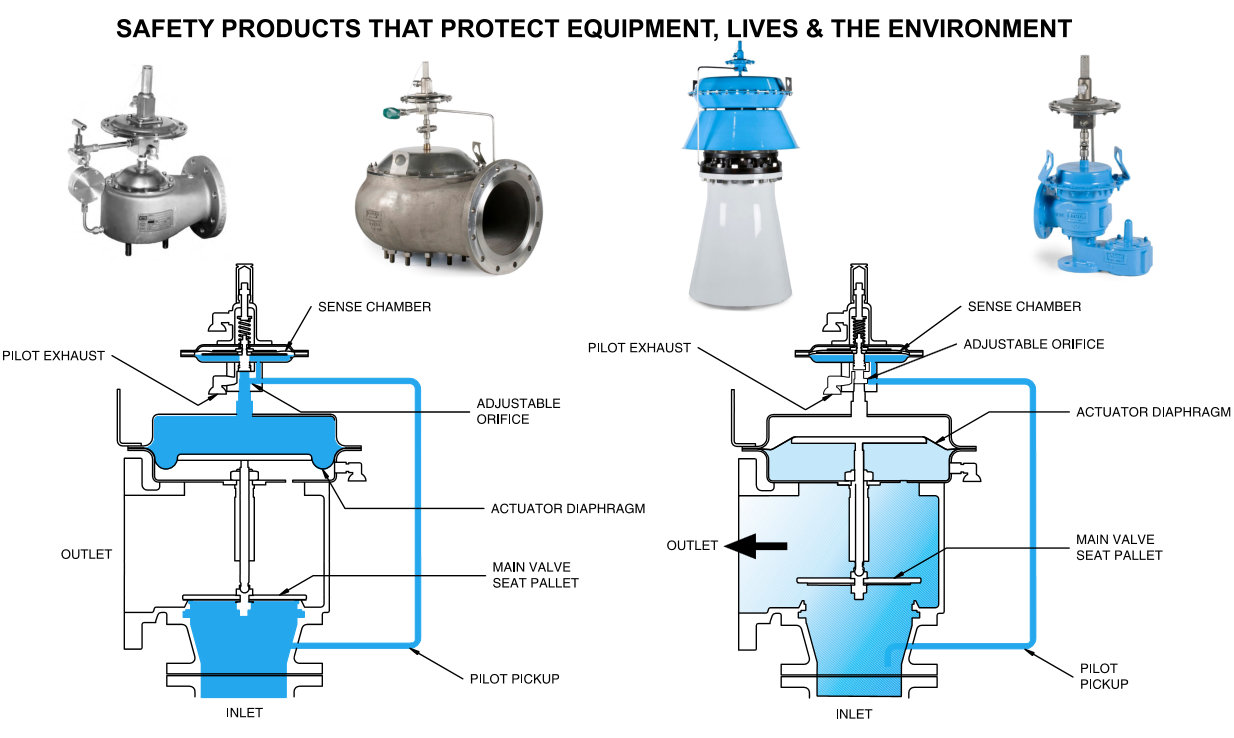
The primary purpose of a pressure relief valve is to protect life, property and the environment. Pressure relief valves are designed to open and release excess pressure from vessels or equipment and then close again.
The function of pressure relief valves differs depending on the main type or loading principle of the valve. The main types of pressure relief valves are spring-loaded, weight-loaded and controlled pressure relief valves.
Regardless of the type or load, pressure relief valves are set to a specific set pressure at which the medium is discharged in a controlled manner, thus preventing overpressure of the equipment. In dependence of several parameters such as the contained medium, the set pressure is individual for each safety application.
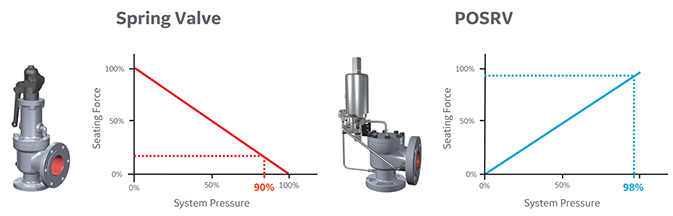
During the forecast period, the global safety valve market size is estimated to reach USD 13.2 Billion by 2030 and is expected to exhibit a significant growth rate of 9.20% CAGR.
Safety Valves are precautionary valves that automatically actuate when the preset safety valve pressure and temperature are exceeded. These safety valves can be used to protect the critical equipment from damage by controlling excess pressure without any electrical support. For protecting equipment from unsafe pressure these mainly operate at a predetermined pressure. Additionally, these valves protect the employees around the plants and the environment around them. Safety valves are used in various applications like pharmaceutical, construction, oil & gas industries which foster the growth of the market.
During the lockdown, the global safety valve market is negatively impacted. Not only the safety valve market but the whole world was also affected drastically by this pandemic. To control the prevalence of the coronavirus, the government has imposed stringent regulations like lockdowns, maintaining social distance, covering the face with masks, manufacturing industries shut down, and transportation bans.
Even though at the primary stage of the pandemic, the safety valve market has fallen. Developing the innovations in the safety valve system and growing awareness regarding the benefits of the safety valve market by the key players are increasing the growth of this market.
Growing demand for safety valves in the oil & gas industry, the rise in nuclear energy generation, the growing importance of safety valves in industrial processes are the major driving factors of this market. The continuous need for safety valve replacement and the use of 3D printers in manufacturing lines are boosting the growth of the market. The safety valve market is highly dependent on investments in manufacturing facilities.
Some of the numerous factors that drive the safety valve market are rising demand for water & power, pollution control regulations, and rapid growth of process industries are supposed to escalate the growth of the safety valve industry during the assessment period. Growth in the construction of nuclear power plants is fueling the growth of the market. The increase of accidental incidences and soaring demand for safety valves in several industrial sectors are increasing the growth of the global market.
The constant growth of oil & gas exploration in few parts across the globe is restraining the market. The fabrication of safety valves are very expensive which is hindering the market growth
To increase the growth of the safety valve market industry integration of safety valves into the Internet of Things (IoT) environment is creating the opportunity. The innovations in the safety valve systems are anticipated to increase the strong growth of the market.
To provide a strategic profile of the prominent key players in the market, analyze their core competencies, forecast statistics, and draw a global safety valve market growth landscape.
The global safety valve market based on material is sub-segmented into steel, alloy, cast iron, cryogenic, and others. As the steel safety valves are durable and don’t leak in hot or cold temperatures, the steel segment is expected to dominate the global market.
It is segmented into less than 1”, 1” to 10”, and 11” to 20”, and 20” & above. Among these, during the review period, the 1” to 10” segment is projected to grow at the significant CAGR for the safety valves market for the benefits behind this size range like controlling the flow and pressure of liquids, gases, and slurries within different end-use industries.
The global safety valve market industry is divided into oil & gas, energy & power, food & beverage, chemicals, water & wastewater treatment, and others. In the global safety market, the oil & gas segment is expected to hold the largest share, because the oil & gas industries are the most significant revenue-generating industries which need almost all types of valves like gate, globe, ball, check and butterfly. Some of the products include a safety valve air compressor, safety valve boiler, and safety valve heater.
Asia-Pacific, Europe, North America, the Middle East & Africa, and South America are the main geographies included in this market. Due to the rapid urbanization and growing industrialization Asia-Pacific holds the largest safety valve market share.
The global safety valve market region-wise is divided into Asia-Pacific, Europe, North America, and the Middle East & Africa. Out of these regions, Asia-Pacific holds the largest market share for its growing infrastructural developments, rise of investments in various industries like oil & gas, construction industry, and drastic urbanization. Growing demand from mining, chemical, and municipal industries is expected to propel market growth in this region.
Safety valves are used in the application of the construction industry to control liquid flow in firefighting systems, water supply systems, and piping systems. The rising construction industry propels the market growth in this region. North America is accounting as the second-largest market for its growing investments in the construction industry.
Naples, Italy, Baker Hughes launched a new steam test facility in November 2018, ASME Section I safety valves that serve better to the European aftermarket with a rapid response for steam applications. The future development of the current aftermarket is launched as the new aftermarket plant which is expanded by the product scope and capacity of the plant. To fulfill the range of Masoneilan control valves and consolidated safety valves ranging up to 2000 psi test pressure.
In October 2018, Emerson Electric Co. to help the LNG marine transportation consumers developed low-pressure pilot operated pressure relief valves (POPRVs) by reducing their size which helps to reduce the investments by 25% and protects the end-users from overpressure by offering them extra profit margin.
In May 2019, the Mexican government announced that it is going to construct a new refinery set in the Tobasco coast, Mexico in June 2019. Hence safety valves are used in refineries to control the pressure of liquids and gases in plants.
This global safety valve market research includes the Market Overview, COVID-19 analysis, Market Dynamics, Study Objectives, Segment Overview, Regional Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Recent developments, Segmentation Table, and FAQs. The market scenario includes the safety valve market drivers, restraints, challenges, and opportunities. The safety valve forecast segments are material, size, end-use, and region.

In order to ensure that the maximum allowable accumulation pressure of any system or apparatus protected by a safety valve is never exceeded, careful consideration of the safety valve’s position in the system has to be made. As there is such a wide range of applications, there is no absolute rule as to where the valve should be positioned and therefore, every application needs to be treated separately.
A common steam application for a safety valve is to protect process equipment supplied from a pressure reducing station. Two possible arrangements are shown in Figure 9.3.3.
The safety valve can be fitted within the pressure reducing station itself, that is, before the downstream stop valve, as in Figure 9.3.3 (a), or further downstream, nearer the apparatus as in Figure 9.3.3 (b). Fitting the safety valve before the downstream stop valve has the following advantages:
• The safety valve can be tested in-line by shutting down the downstream stop valve without the chance of downstream apparatus being over pressurised, should the safety valve fail under test.
• When setting the PRV under no-load conditions, the operation of the safety valve can be observed, as this condition is most likely to cause ‘simmer’. If this should occur, the PRV pressure can be adjusted to below the safety valve reseat pressure.
Indeed, a separate safety valve may have to be fitted on the inlet to each downstream piece of apparatus, when the PRV supplies several such pieces of apparatus.
• If supplying one piece of apparatus, which has a MAWP pressure less than the PRV supply pressure, the apparatus must be fitted with a safety valve, preferably close-coupled to its steam inlet connection.
• If a PRV is supplying more than one apparatus and the MAWP of any item is less than the PRV supply pressure, either the PRV station must be fitted with a safety valve set at the lowest possible MAWP of the connected apparatus, or each item of affected apparatus must be fitted with a safety valve.
• The safety valve must be located so that the pressure cannot accumulate in the apparatus viaanother route, for example, from a separate steam line or a bypass line.
It could be argued that every installation deserves special consideration when it comes to safety, but the following applications and situations are a little unusual and worth considering:
• Fire - Any pressure vessel should be protected from overpressure in the event of fire. Although a safety valve mounted for operational protection may also offer protection under fire conditions,such cases require special consideration, which is beyond the scope of this text.
• Exothermic applications - These must be fitted with a safety valve close-coupled to the apparatus steam inlet or the body direct. No alternative applies.
• Safety valves used as warning devices - Sometimes, safety valves are fitted to systems as warning devices. They are not required to relieve fault loads but to warn of pressures increasing above normal working pressures for operational reasons only. In these instances, safety valves are set at the warning pressure and only need to be of minimum size. If there is any danger of systems fitted with such a safety valve exceeding their maximum allowable working pressure, they must be protected by additional safety valves in the usual way.
In order to illustrate the importance of the positioning of a safety valve, consider an automatic pump trap (see Block 14) used to remove condensate from a heating vessel. The automatic pump trap (APT), incorporates a mechanical type pump, which uses the motive force of steam to pump the condensate through the return system. The position of the safety valve will depend on the MAWP of the APT and its required motive inlet pressure.
This arrangement is suitable if the pump-trap motive pressure is less than 1.6 bar g (safety valve set pressure of 2 bar g less 0.3 bar blowdown and a 0.1 bar shut-off margin). Since the MAWP of both the APT and the vessel are greater than the safety valve set pressure, a single safety valve would provide suitable protection for the system.
Here, two separate PRV stations are used each with its own safety valve. If the APT internals failed and steam at 4 bar g passed through the APT and into the vessel, safety valve ‘A’ would relieve this pressure and protect the vessel. Safety valve ‘B’ would not lift as the pressure in the APT is still acceptable and below its set pressure.
It should be noted that safety valve ‘A’ is positioned on the downstream side of the temperature control valve; this is done for both safety and operational reasons:
Operation - There is less chance of safety valve ‘A’ simmering during operation in this position,as the pressure is typically lower after the control valve than before it.
Also, note that if the MAWP of the pump-trap were greater than the pressure upstream of PRV ‘A’, it would be permissible to omit safety valve ‘B’ from the system, but safety valve ‘A’ must be sized to take into account the total fault flow through PRV ‘B’ as well as through PRV ‘A’.
A pharmaceutical factory has twelve jacketed pans on the same production floor, all rated with the same MAWP. Where would the safety valve be positioned?
One solution would be to install a safety valve on the inlet to each pan (Figure 9.3.6). In this instance, each safety valve would have to be sized to pass the entire load, in case the PRV failed open whilst the other eleven pans were shut down.
If additional apparatus with a lower MAWP than the pans (for example, a shell and tube heat exchanger) were to be included in the system, it would be necessary to fit an additional safety valve. This safety valve would be set to an appropriate lower set pressure and sized to pass the fault flow through the temperature control valve (see Figure 9.3.8).




 8613371530291
8613371530291