application of safety valve supplier
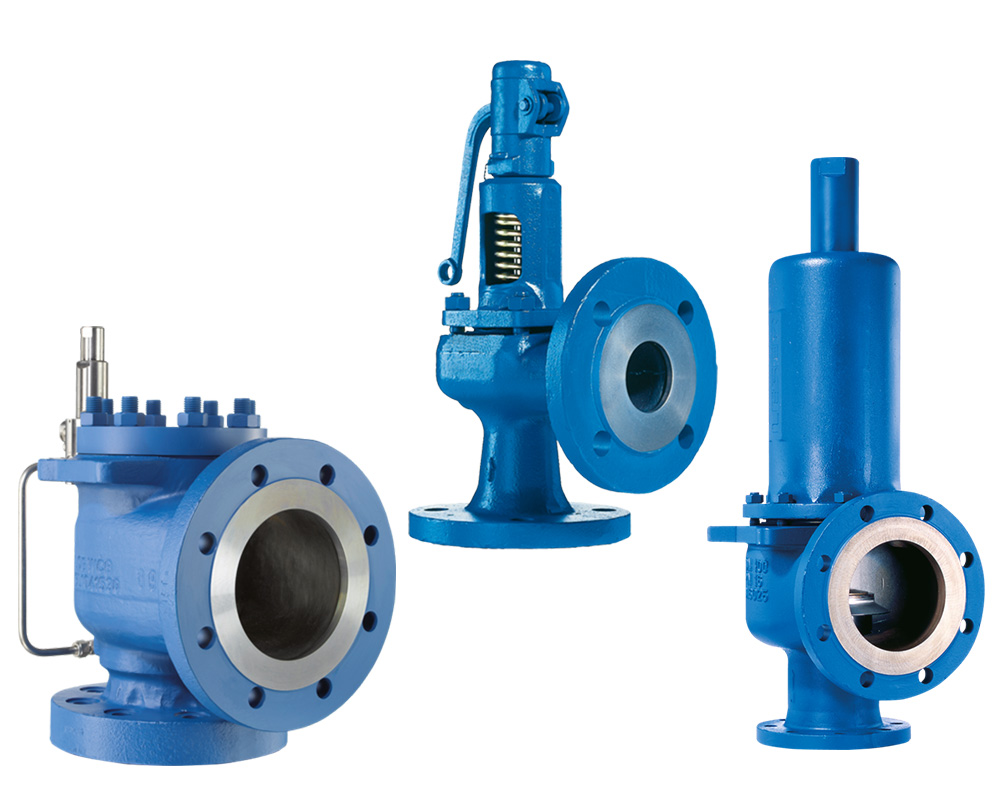

Industry leading pressure and safety relief valve designs with over 140 years of technical and application expertise providing custom engineered solutions for O&G, Refining, Chemical, Petrochemical, Process and Power applications. Our designs meet global and local codes and standards (API 526; ASME Section I, IV & VIII; EN ISO 4126; PED & more). Gain insight into the performance of your pressure relief valves with wireless monitoring.

Distributor of hydraulic press safety, quick opening safety, rotary and safety valves. Amerigear®, Boston Gear®, Carlisle®, DeMag®, Desch® and IMI Norgren®, pneumatic, double action, quick release and flow control valves also provided. Repair and preventative maintenance services are offered. Value added services such as custom barcoding, CAD capabilities, OEM assembly, plant surveys and third party logistics are also available. Serves the metal processing, metal service center, paper mill and paper converting, canning, grinding, commercial laundry, marine, oil and gas and material handling industries. Vendor managed inventory (VMI) programs available. Kanban delivery.

Emergency situations are not the only times relief valves are active; once installed they continuously regulate the flow of substance. They can also be pre-set to open when the pressure or temperature gets to a certain point that may be dangerous. Generally valves are placed on or near the pump head of the hose, pipe or tube. A wide variety of relief valve designs exist, although most resemble ball-check valves, swing check valves or diaphragm valves.
This last is particularly useful when controlling a flow of fluids that contains suspended solids. Most relief valves are spring operated, as are the majority of check valves. One specialized type of relief valve is known as a vacuum relief valve. As opposed to a normal relief valve, which relieves high pressure, a vacuum relief valve is used to relieve dangerously low pressures, or vacuums, by inserting air or an inert gas.
Like every other type of check valve, relief valves may be constructed from a variety of materials, including PVC, brass, ductile iron, copper, polyethylene, polypropylene, aluminum, steel, stainless steel and rubber. Which raw substance is used to produce each relief valve depends on the environment said relief valve will be in. The wrong product could result in erosion or contamination of the process stream. However, as long as research is done, finding the appropriate type of relief valve is possible. Every plumbing or fluid transfer application in the industrial, commercial and domestic arenas employ or will employ check valves. In fact, check valves of all kinds are an essential part of every day life. Because they need not be supervised to function and prevent product malfunction, check valves are not only desirable but often required by law to ensure the safety of water, gas and pressure applications.

Of all the challenges you face keeping your customers’ plants operating at full capacity, safety and relief valves shouldn’t be one of them. NASVI’s job is to give you the confidence that your valve supply chain is rock solid regardless the pressure it’s under.

The primary purpose of a safety valve is to protect life, property and the environment. Safety valves are designed to open and release excess pressure from vessels or equipment and then close again.
The function of safety valves differs depending on the load or main type of the valve. The main types of safety valves are spring-loaded, weight-loaded and controlled safety valves.
Regardless of the type or load, safety valves are set to a specific set pressure at which the medium is discharged in a controlled manner, thus preventing overpressure of the equipment. In dependence of several parameters such as the contained medium, the set pressure is individual for each safety application.

... -start valve with Series MX2 air treatment units without the need for additional connection interfaces. The soft-start valve is positioned upstream of the safety valves, ...
Two hands safety valve, which allows a safety use of two hands pneumatic controls (for example two push-button 3/2 N.C. to a certain distance) excluding false signals in case of push-button ...
The SI2 safety valve prevents the allowed operating pressure from being exceeded by more than 10%. If, after opening, the adjusted response pressure falls ...
... stainless steel full-lift clean service safety valve designed to AD Merkblatt A2 and TRD 421 standards and suitable for pure steam, vapour and inert gases.
Insert style flow control valves are comprised of a precision orifice in parallel with a check valve, combined into a single component. Each is designed for easy installation into metal housings using ...
Press-in style flow control valves are comprised of a precision flow orifice in parallel with a check valve, combined into a single component. Each part is designed for easy installation into plastic ...
If you have been searching for a safety release valve that you can use to reduce short-term pressure surges successfully and diminish the effects of gas leaks, this is the product for you. With a pe of ...
... have been type tested as well. These pressure regulators have safety valves which will slam shut in the event of emergencies, such as the gas reaching too high a pressure level. The valve ...
This product has hydraulically actuated class A gas safety valves to EN 161 used for automatic shut-off. It shuts off when unstimulated for gas and air, or even biologically produced methane. It has AISi ...
The S 104 Safety Shut Off valve is mainly used to avoid any damage to components as well as to avoid too high or too low pressure in the gas train. This could cause high financial losses and/or injured ...
The S50 Safety Shut Off valve is mainly used to avoid any damage to components as well as to avoid too high or too low pressure in the gas train. This could cause high financial losses and/or injured ...
The S100 Safety Shut Off valve is mainly used to avoid any damage to components as well as to avoid too high or too low pressure in the gas train. This could cause high financial losses and/or injured ...
... Pressure Safety Valve + Rupture Disk is protected and may be utilized autonomously as essential security gadgets or in conjunction. There are 3 possible combinations. The first combinations ...
Excavator pipe-rupture valves prevent uncontrolled cylinder movement in the event that a pipe or hose bursts. The ESV valve fulfills all of the requirements of the ISO 8643 and EN 474-5 standards for ...
Material: Body- CF8M; Valve Seat- CF8M Métal Seat, PTFE Soft Seat available Orifice Size: fc"(15mm), 3/4M(20mm), l"(25mm), l1/4,’(32mm)I ltë”(40mm), ...
The Safety valves from ATOS are designed to guarantee protection for application on various devices, especially those that monitor spool position. They are also recommended for hydraulic ...

As soon as mankind was able to boil water to create steam, the necessity of the safety device became evident. As long as 2000 years ago, the Chinese were using cauldrons with hinged lids to allow (relatively) safer production of steam. At the beginning of the 14th century, chemists used conical plugs and later, compressed springs to act as safety devices on pressurised vessels.
Early in the 19th century, boiler explosions on ships and locomotives frequently resulted from faulty safety devices, which led to the development of the first safety relief valves.
In 1848, Charles Retchie invented the accumulation chamber, which increases the compression surface within the safety valve allowing it to open rapidly within a narrow overpressure margin.
Today, most steam users are compelled by local health and safety regulations to ensure that their plant and processes incorporate safety devices and precautions, which ensure that dangerous conditions are prevented.
The principle type of device used to prevent overpressure in plant is the safety or safety relief valve. The safety valve operates by releasing a volume of fluid from within the plant when a predetermined maximum pressure is reached, thereby reducing the excess pressure in a safe manner. As the safety valve may be the only remaining device to prevent catastrophic failure under overpressure conditions, it is important that any such device is capable of operating at all times and under all possible conditions.
Safety valves should be installed wherever the maximum allowable working pressure (MAWP) of a system or pressure-containing vessel is likely to be exceeded. In steam systems, safety valves are typically used for boiler overpressure protection and other applications such as downstream of pressure reducing controls. Although their primary role is for safety, safety valves are also used in process operations to prevent product damage due to excess pressure. Pressure excess can be generated in a number of different situations, including:
The terms ‘safety valve’ and ‘safety relief valve’ are generic terms to describe many varieties of pressure relief devices that are designed to prevent excessive internal fluid pressure build-up. A wide range of different valves is available for many different applications and performance criteria.
In most national standards, specific definitions are given for the terms associated with safety and safety relief valves. There are several notable differences between the terminology used in the USA and Europe. One of the most important differences is that a valve referred to as a ‘safety valve’ in Europe is referred to as a ‘safety relief valve’ or ‘pressure relief valve’ in the USA. In addition, the term ‘safety valve’ in the USA generally refers specifically to the full-lift type of safety valve used in Europe.
Pressure relief valve- A spring-loaded pressure relief valve which is designed to open to relieve excess pressure and to reclose and prevent the further flow of fluid after normal conditions have been restored. It is characterised by a rapid-opening ‘pop’ action or by opening in a manner generally proportional to the increase in pressure over the opening pressure. It may be used for either compressible or incompressible fluids, depending on design, adjustment, or application.
Safety valves are primarily used with compressible gases and in particular for steam and air services. However, they can also be used for process type applications where they may be needed to protect the plant or to prevent spoilage of the product being processed.
Relief valve - A pressure relief device actuated by inlet static pressure having a gradual lift generally proportional to the increase in pressure over opening pressure.
Relief valves are commonly used in liquid systems, especially for lower capacities and thermal expansion duty. They can also be used on pumped systems as pressure overspill devices.
Safety relief valve - A pressure relief valve characterised by rapid opening or pop action, or by opening in proportion to the increase in pressure over the opening pressure, depending on the application, and which may be used either for liquid or compressible fluid.
In general, the safety relief valve will perform as a safety valve when used in a compressible gas system, but it will open in proportion to the overpressure when used in liquid systems, as would a relief valve.
Safety valve- A valve which automatically, without the assistance of any energy other than that of the fluid concerned, discharges a quantity of the fluid so as to prevent a predetermined safe pressure being exceeded, and which is designed to re-close and prevent further flow of fluid after normal pressure conditions of service have been restored.

Also known as pressure relief valves (PRV), pressure safety valves (PSV), and safety valves, these systems act as a safety measure. They relieve excess pressure from equipment failure, process upset, or fire by opening an auxiliary passage to divert the fluid (liquid, gas, steam or air) away from the pressure vessel. Once the pressure in the vessel is released and the danger is over the relief valve closes itself. Emergency situations are not the only times relief valves are active; once installed they continuously regulate the flow of substance. They can also be pre-set to open when the pressure or temperature gets to a certain point that may be dangerous.
Generally valves are placed on or near the pump head of the hose, pipe, or tube. A wide variety of relief valve designs exist, although most resemble ball-check valves, swing check valves or diaphragm valves. This last is particularly useful when controlling a flow of fluids that contains suspended solids. Most relief valves are spring operated, as are the majority of check valves. One specialized type of relief valve is known as a vacuum relief valve. As opposed to a normal relief valve, which relieves high pressure, a vacuum relief valve is used to relieve dangerously low pressures, or vacuums, by inserting air or an inert gas.
Which raw substance is used to produce each relief valve depends on the environment said relief valve will be in. The wrong product could result in erosion or contamination of the process stream. However, as long as research is done, finding the appropriate type of relief valve is possible. Every plumbing or fluid transfer application in the industrial, commercial, and domestic arenas employ or will employ check valves. In fact, check valves of all kinds are an essential part of every day life. Because they need not be supervised to function and prevent product malfunction, check valves are not only desirable but often required by law to ensure the safety of water, gas, and pressure applications.
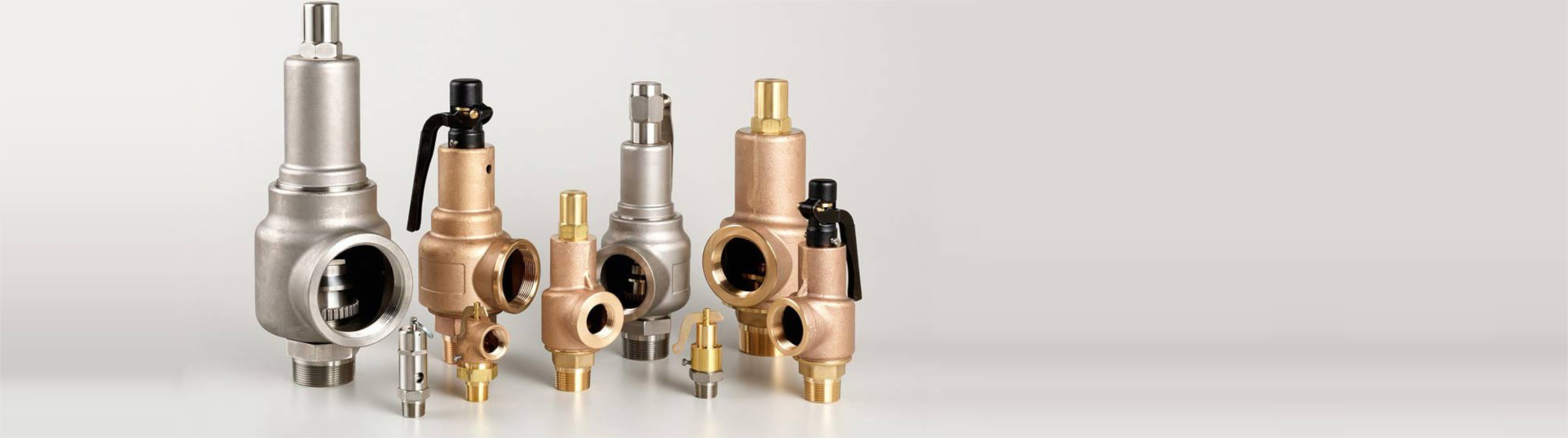

Curtiss-Wright"s selection of Pressure Relief Valves comes from its outstanding product brands Farris and Target Rock. We endeavor to support the whole life cycle of a facility and continuously provide custom products and technologies. Boasting a reputation for producing high quality, durable products, our collection of Pressure Relief Valves is guaranteed to provide effective and reliable pressure relief.
While some basic components and activations in relieving pressure may differ between the specific types of relief valves, each aims to be 100% effective in keeping your equipment running safely. Our current range includes numerous valve types, from flanged to spring-loaded, threaded to wireless, pilot operated, and much more.
A pressure relief valve is a type of safety valve designed to control the pressure in a vessel. It protects the system and keeps the people operating the device safely in an overpressure event or equipment failure.
A pressure relief valve is designed to withstand a maximum allowable working pressure (MAWP). Once an overpressure event occurs in the system, the pressure relief valve detects pressure beyond its design"s specified capability. The pressure relief valve would then discharge the pressurized fluid or gas to flow from an auxiliary passage out of the system.
Below is an example of one of our pilot operated pressure relief valves in action; the cutaway demonstrates when high pressure is released from the system.
Air pressure relief valves can be applied to a variety of environments and equipment. Pressure relief valves are a safety valve used to keep equipment and the operators safe too. They"re instrumental in applications where proper pressure levels are vital for correct and safe operation. Such as oil and gas, power generation like central heating systems, and multi-phase applications in refining and chemical processing.
At Curtiss-Wright, we provide a range of different pressure relief valves based on two primary operations – spring-loaded and pilot operated. Spring-loaded valves can either be conventional spring-loaded or balanced spring-loaded.
Spring-loaded valves are programmed to open and close via a spring mechanism. They open when the pressure reaches an unacceptable level to release the material inside the vessel. It closes automatically when the pressure is released, and it returns to an average operating level. Spring-loaded safety valves rely on the closing force applied by a spring onto the main seating area. They can also be controlled in numerous ways, such as a remote, control panel, and computer program.
Pilot-operated relief valves operate by combining the primary relieving device (main valve) with self-actuated auxiliary pressure relief valves, also known as the pilot control. This pilot control dictates the opening and closing of the main valve and responds to system pressure. System pressure is fed from the inlet into and through the pilot control and ultimately into the main valve"s dome. In normal operating conditions, system pressure will prevent the main valve from opening.
The valves allow media to flow from an auxiliary passage and out of the system once absolute pressure is reached, whether it is a maximum or minimum level.
When the pressure is below the maximum amount, the pressure differential is slightly positive on the piston"s dome size, which keeps the main valve in the closed position. When system pressure rises and reaches the set point, the pilot will cut off flow to the dome, causing depressurization in the piston"s dome side. The pressure differential has reversed, and the piston will rise, opening the main valve, relieving pressure.
When the process pressure decreases to a specific pressure, the pilot closes, the dome is repressurized, and the main valve closes. The main difference between spring-loaded PRVs and pilot-operated is that a pilot-operated safety valve uses pressure to keep the valve closed.
Pilot-operated relief valves are controlled by hand and are typically opened often through a wheel or similar component. The user opens the valve when the gauge signifies that the system pressure is at an unsafe level; once the valve has opened and the pressure has been released, the operator can shut it by hand again.
Increasing pressure helps to maintain the pilot"s seal. Once the setpoint has been reached, the valve opens. This reduces leakage and fugitive emissions.
At set pressure the valve snaps to full lift. This can be quite violent on large pipes with significant pressure. The pressure has to drop below the set pressure in order for the piston to reseat.
The pilot is designed to open gradually, so that less of the system fluid is lost during each relief event. The piston lifts in proportion to the overpressure.
At Curtiss-Wright we also provide solutions for pressure relief valve monitoring. Historically, pressure relief valves have been difficult or impossible to monitor. Our SmartPRV features a 2600 Series pressure relief valve accessorized with a wireless position monitor that alerts plant operators during an overpressure event, including the time and duration.
There are many causes of overpressure, but the most common ones are typically blocked discharge in the system, gas blowby, and fire. Even proper inspection and maintenance will not eliminate the occurrence of leakages. An air pressure relief valve is the only way to ensure a safe environment for the device, its surroundings, and operators.
A PRV and PSV are interchangeable, but there is a difference between the two valves. A pressure release valve gradually opens when experiencing pressure, whereas a pressure safety valve opens suddenly when the pressure hits a certain level of over pressurization. Safety valves can be used manually and are typically used for a permanent shutdown. Air pressure relief valves are used for operational requirements, and they gently release the pressure before it hits the maximum high-pressure point and circulates it back into the system.
Pressure relief valves should be subject to an annual test, one per year. The operator is responsible for carrying out the test, which should be done using an air compressor. It’s imperative to ensure pressure relief valves maintain their effectiveness over time and are checked for signs of corrosion and loss of functionality. Air pressure relief valves should also be checked before their installation, after each fire event, and regularly as decided by the operators.
Direct-acting solenoid valves have a direct connection with the opening and closing armature, whereas pilot-operated valves use of the process fluid to assist in piloting the operation of the valve.
A control valve works by varying the rate of fluid passing through the valve itself. As the valve stem moves, it alters the size of the passage and increases, decreases or holds steady the flow. The opening and closing of the valve is altered whenever the controlled process parameter does not reach the set point.
Control valves are usually at floor level or easily accessible via platforms. They are also located on the same equipment or pipeline as the measurement and downstream or flow measurements.
An industrial relief valve is designed to control or limit surges of pressure in a system, most often in fluid or compressed air system valves. It does so as a form of protection for the system and defending against instrument or equipment failure. They are usually present in clean water industries.
A PRV is often referred to as a pressure relief valve, which is also known as a PSV or pressure safety valve. They are used interchangeably throughout the industry depending on company standards.

This page lists the ApprovedPressure and Safety Relief ValveManufacturers (vendors), also provides inspection and test advice to thePressure and Safety Relief Valvepurchasers buying from vendors, suppliers and distributors.

The purpose of the valve is to, when energized, provide a flow path for a flow of hydraulic fluid from its source to the hydraulic system. When de-energized, the valve blocks flow from the hydraulic energy source and vents the hydraulic system to tank.
Q: What is Control Reliablitiy?A: Control Reliability essentially states that the safety system be designed, constructed and installed such that the failure of a single component within the device or system should not prevent normal machine stopping action from taking place, but shall prevent a successive machine cycle from being initiated until the failure is corrected. To achieve “Control Reliability”, a device should feature both redundancy and fault detection.
A: A safety valve, as it pertains to fluid power, is a component that, when properly applied, can allow access to an otherwise hazardous area. This is achieved by isolating the hydraulic source away from the system and venting any residual system pressure, downstream from the valve, to tank.
A: During normal operation, the valve operates like a traditional 3-way. If either of the redundant elements malfunction, the safety PLC or safety relay, monitoring the state of the redundant switches, will command the valve to its safe condition.
A: The three different configurations of Control Reliable Safety Valves are 2-way for blocking applications, 3-way for block and bleed applications, and LOTO or Lockout/Tagout.
A: A relief valve is a device that limits the maximum pressure in a system. It does help to keep a system and its surrounding environment safe from catastrophic failures due to over-pressurization but it is not a true safety product. The safety valves that we refer to are redundantly monitored devices that meet the rigorous requirements of safety standards organizations such as ANSI and ISO.
A: A blocking valve, as it pertains to fluid power, is a component that, when properly applied, can allow access to an otherwise hazardous area. This is achieved by isolating the hydraulic source away from the system.
A: During normal operation, the valve operates like a traditional 2-way. If either of the redundant elements malfunction, the safety PLC or safety relay monitoring the state of the redundant switches will command the valve to its safe condition.

Kunkle relief valves are available for ASME Section I, Section IV and Section VIII services with relief capacities certified by the National Board. In addition, Kunkle offers a range of non-code products and each valve, both code and non-code is set, tested, and retested to the customer’s specifications and then sealed at the factory to prevent tampering. Flotech is a Kunkle valve distributor.
Kunkle safety and relief valve products range in size from 1/4-inch NPT through 6-inch flange and are suitable for services ranging from cryogenic to 850°F at set pressures ranging from vacuum to 6,500 psig. They are available in a wide range of materials including Brass, Bronze, Carbon Steel, Stainless Steel, Cast Iron, and Aluminum.
Safety valves play an important role in keeping people and equipment safe. Building on the long legacy of the Consolidated Safety Valves, we work closely with customers and regulatory organizations to configure, engineer, and manufacture safety valves that can help maintain safer operating conditions in a full range of environments.
Our safety valves comply with the ASME Section I code for boiler applications. They are built with many features that meet ASME requirements for steam-compressible fluids. Baker Hughes’s Consolidated safety valves are known for exceptional quality, performance and dependability. It is important they are reliable even the in most demanding real-world applications. With a range of styles, models, options and configurations, our safety valves work in many different applications.
Not sure which valve you need for your application?Download ValSpeQ (Mooney regulators & Becker valves) or ValvStream™ (Masoneilan and Consolidated valves) to size, select and generate proposal documentation for your valves.
Consolidated Green Tag Centers (GTC) comprise one of the broadest OEM service networks in the industry. With more than 80 facilities located in more than 30 countries worldwide, the GTCNet™ network provides the aftermarket support you need. Our GTC customers receive responsive and effective service through OEM-certified repairs, innovative valve diagnostics from ValvKeep™- valve management and maintenance software, and the EVT-Pro, an electronic valve testing device. Each GTC location is staffed with highly qualified technicians, specifically trained and certified to deliver exceptional product support and technical expertise.
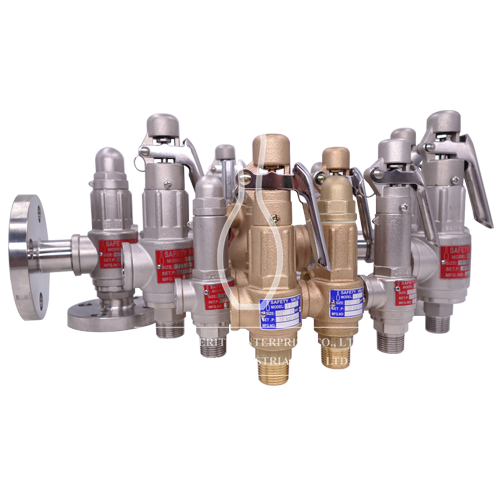
Three-way flow path design, one station installs two identical safety valve, one is on-line overpressure protection, while the other serves as maintenance spare. Low flow resistance ensures adequate discharge capacity of the safety valve. The operation of reversing system is safe, simple and fast. Rapid switching eliminates the need for device parking, provides continuous overpressure protection, and avoids costly cost losses from emergency parking repairs. Under each safety valve, a vent valve is installed to safely and effectively release the media before the safety valve is removed and into the discharge tube. The quick switching device is provided with a balance valve (high-pound ≥600lb) and thus operates lightly. The applicable temperature range is wide (low temperature to high temperature).

LESER safety valves are used by leading petrochemical, industrial gas, machine building, oil and gas production, chemical, food and pharmaceutical companies. LESER offers spring-loaded and pilot-operated safety valves for all industrial applications according to PED and ASME VIII as well as application-based solutions for special requirements. The LESER product range offers the right product for almost every application.
LESER safety valves are developed and manufactured in Germany. The LESER product range offers the right product for almost every application. Multiple options and special materials complete the range as a well as client-specific solutions.
Attractive Pricing - As the largest safety relief valve manufacturer in Europe (and #3 worldwide), LESER has the ability to produce high-quality products in a cost-efficient manner through large batch sizes and full automation of production; this allows LESER to pass on cost savings to the customer.
LESER Authorized Repair Centre (LARC) Network - More than 30 LARCs in North America provide the end-user with access to authorized, reliable, and convenient local support for the repair of their installed base.

Industrial equipment often uses either safety or relief valves to prevent damaging pressure levels from building up. Though they perform similar functions, there are some critical differences between safety and relief valves. Understanding these two valves’ differences is essential for proper pressure system operation. So here we discuss the pressure safety valve vs pressure relief valve.
A pressure relief valve is a device that releases pressure from a system. The relief valve is generally immune to the effects of back pressure and must be periodically stripped down. Pressure relief valves are one the essential parts of a pressure system to prevent system failures. They are set to open at a predetermined pressure level. Each pressure system has a setpoint that is a predetermined limit. The setpoint determines when the valve will open and prevents overpressure.
Pressure relief valves are typically used in gas or liquid systems where there is a need to prevent excessive pressure from building up. When the pressure in the system reaches a certain level, the valve will open and release the pressure. Pressure relief valves are an essential safety feature in many designs and can help to prevent damage to the system or components.
PRVs are generally considered to be safe and reliable devices. However, before installing a PRV in a system, some potential disadvantages should be considered. Here are five pros and cons of pressure relief valves:
Pros: Pressure relief valves are anessential safety feature in many systems. They protect against over-pressurization by relieving excess pressure from the system. This can help to prevent severe damage or even explosions.
Pressure relief valves can help to improve the efficiency of a system. The system can operate at lower overall pressure by relieving excess pressure and saving energy.
Pressure relief valves can be used as a safety device in systems that are susceptible to overpressurization. By relieving pressure before it builds up to a dangerous level, they can help to prevent accidents and injuries.
Cons: Pressure relief valves can be a potential source of leaks. If not properly maintained, the valve may not seat properly and can allow fluids or gasses to escape.
Pressure relief valves can sometimes cause problems if they do not open or close properly. This can lead to process disruptions and may cause safety issues.
A pressure safety valve is a device used to release pressure from a system that has exceeded its design limit. This safety valve is a fail-safe device. This type of valve is typically used in systems that contain fluids or gasses under high pressure. Pressure safety valves are designed to open and release pressure when the system has exceeded its maximum pressure limit. This helps to prevent the system from rupturing or exploding.
Pressure safety valves are an essential part of many different types of systems and can help keep both people and property safe. If anyone is ever in a situation where they need to release pressure from a system, it is essential to know how to use a pressure safety valve correctly.
A pressure safety valve (PSV) is a type used to relieve a system’s pressure. PSVs are commonly used in chemical and process industries, as well as in some kinds of pressure vessels. There are both advantages and disadvantages to using a PSV. Some of the pros of using a PSV include: PSVs can help to prevent overpressurization, which can be dangerous.
A safety valve is a pressure relief device used to prevent the over-pressurization of a system. On the other hand, a relief valve is a device used to relieve pressure from a system that is already overpressurized. Function Of Pressure Relief Valve Vs Safety Valve
The function of a pressure relief valve is to protect a system or component from excess pressure. A safety valve, on the other hand, is designed to protect from overpressurization. Both types of valves are used in various industries, but each has unique benefits and drawbacks.
Pressure relief valves are typically used in systems where a small amount of overpressure can cause damage. On the other hand, safety valves are designed for systems where overpressurization could be catastrophic. Both valves have advantages and disadvantages, so choosing the right type of valve for the specific application is essential.
Relief valves are usually set to open at a specific pressure and will close once the pressure has been relieved. Safety valves are similar in that they are also used to protect equipment from excessive pressure. However, safety valves are designed to stay open until they are manually closed. This is because safety valves are typically used in applications where it is not safe to have a closed valve, such as in a gas line. Operation Of Safety Relief Valve Vs Pressure Relief Valve
Two types of valves are commonly used in industrial settings: relief valves and safety valves. Both of these valves serve essential functions, but they operate in different ways.
Relief valves are designed to relieve pressure build-up in a system. They open when the system pressure reaches a certain point, which allows excess pressure to be released. On the other hand, safety valves are designed to prevent accidents by preventing system pressure from getting too high. They open when the system pressure reaches a certain point, which allows excess pressure to be released before an accident can occur.
So, which valve is better? That depends on the situation. A relief valve is the better option to protect the system from pressure build-up. If anyone need to protect the system from accidents, then a safety valve is the better option Setpoint Of Pressure Relief Valve Vs Safety Relief Valve
The relief valve is made to open when it reaches a specific pressure, commonly described as a “setpoint”. Setpoints shouldn’t be misinterpreted as the pressure set. A setpoint on a relief valve is set to the lowest possible pressure rating, which means it is set to the lowest system pressure before an overpressure situation is observed. The valve will open as the pressure increases to a point higher than the setpoint. The setting point is determined as pounds per square inch (PSIG) and should be within the maximum allowed operating pressure (MAWP) limits. In safety valves, the setpoint is typically placed at about 3 percent over the working pressure level, whereas relief valves are determined at 10 percent.
No, the safety valve and relief valve can not be used interchangeably. Though both valves are seal butterfly valve and used for safety purposes, they serve different functions. A safety valve relieves excess pressure that builds up in a system, while a relief valve regulates the pressure in a system.
Knowing the difference between these two types of valves is essential, as using the wrong valve for the intended purpose can potentially be dangerous. If unsure which type of valve to use, it is always best to consult with a professional.
A few key points help us understand the safety valve vs pressure relief valve. Safety valves are designed to relieve pressure in a system when it gets too high, while relief valves are designed to relieve pressure when it gets too low. Safety valves are usually set to open at a specific pressure, while relief valves are generally open at a particular vacuum. Safety valves are typically intended for one-time use, while relief valves can be used multiple times. Choose the trusted valve manufactureraccording to the specific business needs.




 8613371530291
8613371530291