boiler drum safety valve in stock
Boilers are designed for a certain maximum operating pressure. If this pressure is exceeded, there is danger of an explosion unless this pressure is relieved. This danger is so great that it necessitates equipping all boilers with safety valves to maintain the boiler pressure within design limits. safety valve setting is a statutory requirement. as discussed above, there are safety valves. one is installed at super heater out let and other two are placed at steam drum . super heater safety valve is set at lower pressure than drum safety valve.
to set these safety valves boiler is light up . the safety valve to be set is kept on service and other two are gagged. pressure on the boiler is raised slowly as per normal operation procedure of boiler . fuel feeding rate is kept at minimum. the safety valve is required to lift and reset at desired pressure at per boiler pressure rating. accordingly it is adjusted to get the lift and reset pressure.
like this all the three safety valves are set. all the gagging are removed. percussion is to be taken during initial build up. the drum pressure gauge should be perfect and calibrated. if the safety valve does not lift beyond the set pressure then the pressure of the boiler is to be reduced and setting to be done again.
IF YOU LIKE THIS POST “BOILER STEAM DRUM SAFETY VALVE”PLEASE LIKE , SHARE AND YOU COMMENTS IS VERY VALUABLE SO PLEASE GIVE YOUR SUGGESTIONS IN COMMENT BOX please read once time if any mistake you find in this artical please suggest me through comment box or if this website contains all original article which are written by me if any article on this site find copyrighted please inform me through at joginder005@gmail.com……..THANK’S
Hi all power engineers myself Joginder Chauhan. I am the founder of the website www.askpowerplant.com. I am also a power plant engineer and have more than 10-year experience in the field of power sectors during this time period I learned about different power technology like AFBC, CFBC, TRAVELLING GRATE, PULSATING GREAT, PF BOILER, WHRS, and many more things. my motive for this site sharing my power sector knowledge with each and everyone who belongs to this field, in this website I share information related to boiler operation, boiler maintenance, turbine operation & maintenance, boiler & turbine question answer, D.M plant, and all topic related to power plant sector please join this website for latest updation regarding power plant ………..thanks ( JOGINDER CHAUHAN )
Thermoglide design improves the gliding characteristics of internal parts thus enabling the valve to achieve its full lift and re-seat point within the fastest possible time

Years ago, it was not uncommon to read news about tragic boiler explosions, sometimes resulting in mass destruction. Today, boilers are equipped with important safety devises to help protect against these types of catastrophes. Let’s take a look at the most critical of these devices: the safety valve.
The safety valve is one of the most important safety devices in a steam system. Safety valves provide a measure of security for plant operators and equipment from over pressure conditions. The main function of a safety valve is to relieve pressure. It is located on the boiler steam drum, and will automatically open when the pressure of the inlet side of the valve increases past the preset pressure. All boilers are required by ASME code to have at least one safety valve, dependent upon the maximum flow capacity (MFC) of the boiler. The total capacity of the safety valve at the set point must exceed the steam control valve’s MFC if the steam valve were to fail to open. In most cases, two safety valves per boiler are required, and a third may be needed if they do not exceed the MFC.
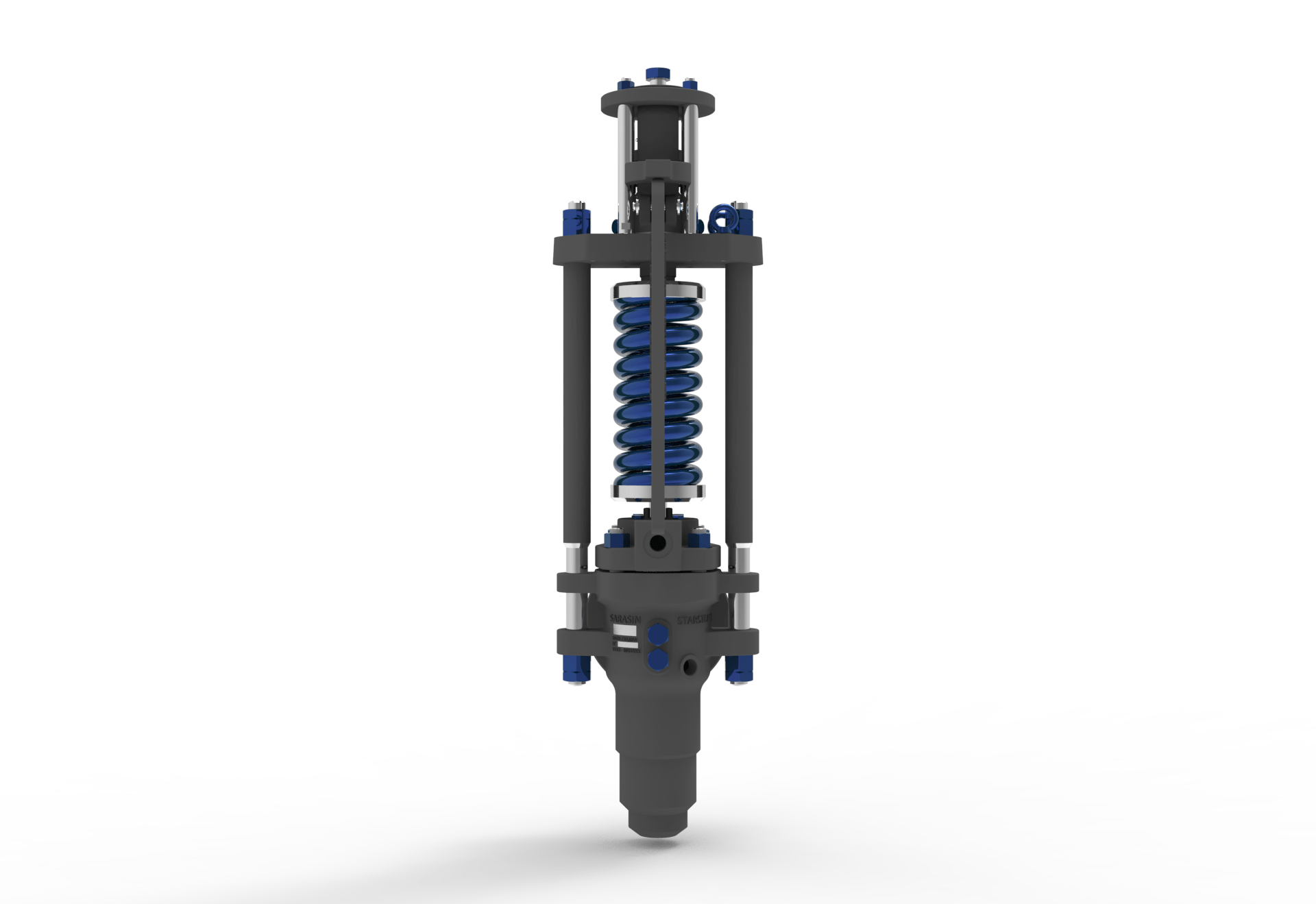
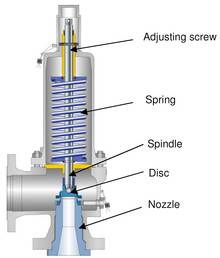
There are three main parts to the safety valve: nozzle, disc, and spring. Pressurized steam enters the valve through the nozzle and is then threaded to the boiler. The disc is the lid to the nozzle, which opens or closes depending on the pressure coming from the boiler. The spring is the pressure controller.
As a boiler starts to over pressure, the nozzle will start to receive a higher pressure coming from the inlet side of the valve, and will start to sound like it is simmering. When the pressure becomes higher than the predetermined pressure of the spring, the disc will start to lift and release the steam, creating a “pop” sound. After it has released and the steam and pressure drops below the set pressure of the valve, the spring will close the disc. Once the safety valve has popped, it is important to check the valve to make sure it is not damaged and is working properly.
A safety valve is usually referred to as the last line of safety defense. Without safety valves, the boiler can exceed it’s maximum allowable working pressure (MAWP) and not only damage equipment, but also injure or kill plant operators that are close by. Many variables can cause a safety valve on a boiler to lift, such as a compressed air or electrical power failure to control instrumentation, or an imbalance of feedwater rate caused by an inadvertently shut or open isolation valve.
Once a safety valve has lifted, it is important to do a complete boiler inspection and confirm that there are no other boiler servicing issues. A safety valve should only do its job once; safety valves should not lift continuously. Lastly, it is important to have the safety valves fully repaired, cleaned and recertified with a National Board valve repair (VR) stamp as required by local code or jurisdiction. Safety valves are a critical component in a steam system, and must be maintained.
All of Nationwide Boiler’s rental boilers include on to two safety valves depending on the size; one set at design pressure and the other set slightly higher than design. By request, we can reset the safeties to a lower pressure if the application requires it. In addition, the valves are thoroughly checked after every rental and before going out to a new customer, and they are replaced and re-certified as needed.

The Consolidated 1700 series Maxiflow safety valves are field-proven and are designed to provide optimum boiler overpressure protection. Increases plant efficiency by reducing steam losses via improved seat tightness and rapid opening to full lift with rapid closing as vessel pressure is reduced.
The Consolidated 1700 series Maxiflow safety valves are used extensively in sub-critical, drum type boilers and super-critical, once-through boilers. Inlet pressure ratings from ASME 600 class thru ASME 4500 class.
As soon as mankind was able to boil water to create steam, the necessity of the safety device became evident. As long as 2000 years ago, the Chinese were using cauldrons with hinged lids to allow (relatively) safer production of steam. At the beginning of the 14th century, chemists used conical plugs and later, compressed springs to act as safety devices on pressurised vessels.
Early in the 19th century, boiler explosions on ships and locomotives frequently resulted from faulty safety devices, which led to the development of the first safety relief valves.
In 1848, Charles Retchie invented the accumulation chamber, which increases the compression surface within the safety valve allowing it to open rapidly within a narrow overpressure margin.
Today, most steam users are compelled by local health and safety regulations to ensure that their plant and processes incorporate safety devices and precautions, which ensure that dangerous conditions are prevented.
The principle type of device used to prevent overpressure in plant is the safety or safety relief valve. The safety valve operates by releasing a volume of fluid from within the plant when a predetermined maximum pressure is reached, thereby reducing the excess pressure in a safe manner. As the safety valve may be the only remaining device to prevent catastrophic failure under overpressure conditions, it is important that any such device is capable of operating at all times and under all possible conditions.
Safety valves should be installed wherever the maximum allowable working pressure (MAWP) of a system or pressure-containing vessel is likely to be exceeded. In steam systems, safety valves are typically used for boiler overpressure protection and other applications such as downstream of pressure reducing controls. Although their primary role is for safety, safety valves are also used in process operations to prevent product damage due to excess pressure. Pressure excess can be generated in a number of different situations, including:
The terms ‘safety valve’ and ‘safety relief valve’ are generic terms to describe many varieties of pressure relief devices that are designed to prevent excessive internal fluid pressure build-up. A wide range of different valves is available for many different applications and performance criteria.
In most national standards, specific definitions are given for the terms associated with safety and safety relief valves. There are several notable differences between the terminology used in the USA and Europe. One of the most important differences is that a valve referred to as a ‘safety valve’ in Europe is referred to as a ‘safety relief valve’ or ‘pressure relief valve’ in the USA. In addition, the term ‘safety valve’ in the USA generally refers specifically to the full-lift type of safety valve used in Europe.
Pressure relief valve- A spring-loaded pressure relief valve which is designed to open to relieve excess pressure and to reclose and prevent the further flow of fluid after normal conditions have been restored. It is characterised by a rapid-opening ‘pop’ action or by opening in a manner generally proportional to the increase in pressure over the opening pressure. It may be used for either compressible or incompressible fluids, depending on design, adjustment, or application.
Safety valves are primarily used with compressible gases and in particular for steam and air services. However, they can also be used for process type applications where they may be needed to protect the plant or to prevent spoilage of the product being processed.
Relief valve - A pressure relief device actuated by inlet static pressure having a gradual lift generally proportional to the increase in pressure over opening pressure.
Relief valves are commonly used in liquid systems, especially for lower capacities and thermal expansion duty. They can also be used on pumped systems as pressure overspill devices.
Safety relief valve - A pressure relief valve characterised by rapid opening or pop action, or by opening in proportion to the increase in pressure over the opening pressure, depending on the application, and which may be used either for liquid or compressible fluid.
In general, the safety relief valve will perform as a safety valve when used in a compressible gas system, but it will open in proportion to the overpressure when used in liquid systems, as would a relief valve.
Safety valve- A valve which automatically, without the assistance of any energy other than that of the fluid concerned, discharges a quantity of the fluid so as to prevent a predetermined safe pressure being exceeded, and which is designed to re-close and prevent further flow of fluid after normal pressure conditions of service have been restored.
In order to ensure that the maximum allowable accumulation pressure of any system or apparatus protected by a safety valve is never exceeded, careful consideration of the safety valve’s position in the system has to be made. As there is such a wide range of applications, there is no absolute rule as to where the valve should be positioned and therefore, every application needs to be treated separately.
A common steam application for a safety valve is to protect process equipment supplied from a pressure reducing station. Two possible arrangements are shown in Figure 9.3.3.
The safety valve can be fitted within the pressure reducing station itself, that is, before the downstream stop valve, as in Figure 9.3.3 (a), or further downstream, nearer the apparatus as in Figure 9.3.3 (b). Fitting the safety valve before the downstream stop valve has the following advantages:
• The safety valve can be tested in-line by shutting down the downstream stop valve without the chance of downstream apparatus being over pressurised, should the safety valve fail under test.
• When setting the PRV under no-load conditions, the operation of the safety valve can be observed, as this condition is most likely to cause ‘simmer’. If this should occur, the PRV pressure can be adjusted to below the safety valve reseat pressure.
Indeed, a separate safety valve may have to be fitted on the inlet to each downstream piece of apparatus, when the PRV supplies several such pieces of apparatus.
• If supplying one piece of apparatus, which has a MAWP pressure less than the PRV supply pressure, the apparatus must be fitted with a safety valve, preferably close-coupled to its steam inlet connection.
• If a PRV is supplying more than one apparatus and the MAWP of any item is less than the PRV supply pressure, either the PRV station must be fitted with a safety valve set at the lowest possible MAWP of the connected apparatus, or each item of affected apparatus must be fitted with a safety valve.
• The safety valve must be located so that the pressure cannot accumulate in the apparatus viaanother route, for example, from a separate steam line or a bypass line.
It could be argued that every installation deserves special consideration when it comes to safety, but the following applications and situations are a little unusual and worth considering:
• Fire - Any pressure vessel should be protected from overpressure in the event of fire. Although a safety valve mounted for operational protection may also offer protection under fire conditions,such cases require special consideration, which is beyond the scope of this text.
• Exothermic applications - These must be fitted with a safety valve close-coupled to the apparatus steam inlet or the body direct. No alternative applies.
• Safety valves used as warning devices - Sometimes, safety valves are fitted to systems as warning devices. They are not required to relieve fault loads but to warn of pressures increasing above normal working pressures for operational reasons only. In these instances, safety valves are set at the warning pressure and only need to be of minimum size. If there is any danger of systems fitted with such a safety valve exceeding their maximum allowable working pressure, they must be protected by additional safety valves in the usual way.
In order to illustrate the importance of the positioning of a safety valve, consider an automatic pump trap (see Block 14) used to remove condensate from a heating vessel. The automatic pump trap (APT), incorporates a mechanical type pump, which uses the motive force of steam to pump the condensate through the return system. The position of the safety valve will depend on the MAWP of the APT and its required motive inlet pressure.
This arrangement is suitable if the pump-trap motive pressure is less than 1.6 bar g (safety valve set pressure of 2 bar g less 0.3 bar blowdown and a 0.1 bar shut-off margin). Since the MAWP of both the APT and the vessel are greater than the safety valve set pressure, a single safety valve would provide suitable protection for the system.
Here, two separate PRV stations are used each with its own safety valve. If the APT internals failed and steam at 4 bar g passed through the APT and into the vessel, safety valve ‘A’ would relieve this pressure and protect the vessel. Safety valve ‘B’ would not lift as the pressure in the APT is still acceptable and below its set pressure.
It should be noted that safety valve ‘A’ is positioned on the downstream side of the temperature control valve; this is done for both safety and operational reasons:
Operation - There is less chance of safety valve ‘A’ simmering during operation in this position,as the pressure is typically lower after the control valve than before it.
Also, note that if the MAWP of the pump-trap were greater than the pressure upstream of PRV ‘A’, it would be permissible to omit safety valve ‘B’ from the system, but safety valve ‘A’ must be sized to take into account the total fault flow through PRV ‘B’ as well as through PRV ‘A’.
A pharmaceutical factory has twelve jacketed pans on the same production floor, all rated with the same MAWP. Where would the safety valve be positioned?
One solution would be to install a safety valve on the inlet to each pan (Figure 9.3.6). In this instance, each safety valve would have to be sized to pass the entire load, in case the PRV failed open whilst the other eleven pans were shut down.
If additional apparatus with a lower MAWP than the pans (for example, a shell and tube heat exchanger) were to be included in the system, it would be necessary to fit an additional safety valve. This safety valve would be set to an appropriate lower set pressure and sized to pass the fault flow through the temperature control valve (see Figure 9.3.8).

We provide onsite safety relief valve diagnostic testing and repair services while helping you manage your overpressure protection assets for regulatory compliance.

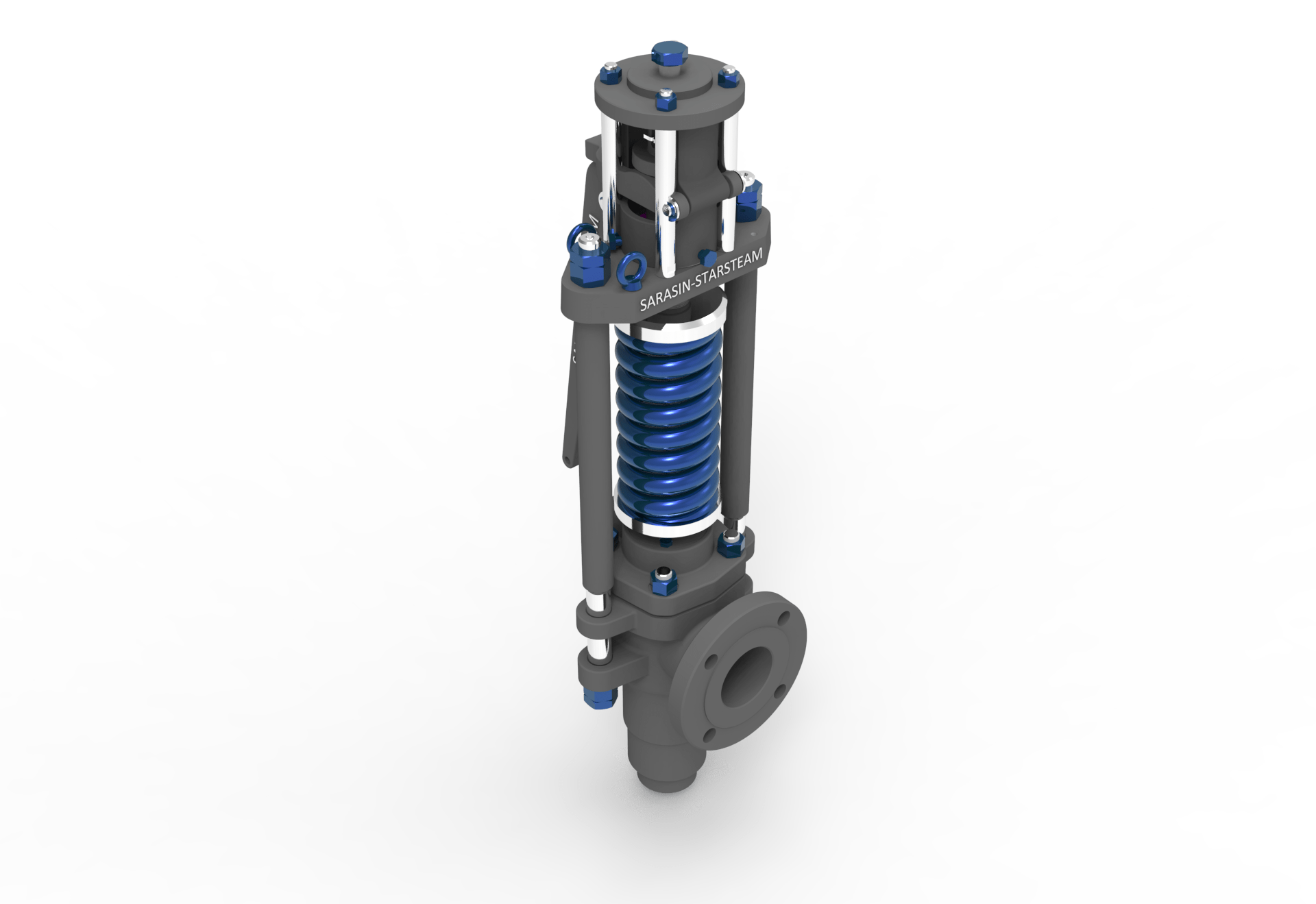
Steam Safety Valve is designed to meet the rigorous process conditions which are essential for steam boilers. This spring loaded safety valve is used in superheater and reheater applications and is specially engineered to provide fast response to overpressure and blowdown requirements. The Starsteam safety valves are designed to provide high integrity performance and repeatability particularly at high pressure and high temperatures in power plants as well as oil and gas applications. This safety valve features a Stardisc design which guarantees perfect tightness at high temperatures as well as repeated and accurate positioning on the nozzzle.

(1) Boiler safety valves and safety relief valves must be as indicated in PG-67 through PG-73 of section I of the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code (incorporated by reference; see 46 CFR 52.01-1) except as noted otherwise in this section.
(3) On river steam vessels whose boilers are connected in batteries without means of isolating one boiler from another, each battery of boilers shall be treated as a single boiler and equipped with not less than two safety valves of equal size.
(4) (Modifies PG-70.) The total rated relieving capacity of drum and superheater safety valves as certified by the valve manufacturer shall not be less than the maximum generating capacity of the boiler which shall be determined and certified by the boiler manufacturer. This capacity shall be in compliance with PG-70 of section I of the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code.
(5) In the event the maximum steam generating capacity of the boiler is increased by any means, the relieving capacity of the safety valves shall be checked by an inspector, and, if determined to be necessary, valves of increased relieving capacity shall be installed.
(6) (Modifies PG-67.) Drum safety valves shall be set to relieve at a pressure not in excess of that allowed by the Certificate of Inspection. Where for any reason this is lower than the pressure for which the boiler was originally designed and the revised safety valve capacity cannot be recomputed and certified by the valve manufacturer, one of the tests described in PG-70(3) of section I of the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code shall be conducted in the presence of the Inspector to insure that the relieving capacity is sufficient at the lower pressure.
(8) Lever or weighted safety valves now installed may be continued in use and may be repaired, but when renewals are necessary, lever or weighted safety valves shall not be used. All such replacements shall conform to the requirements of this section.
(1) (Modifies PG-68.) Superheater safety valves shall be as indicated in PG-68 of section I of the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code except as noted otherwise in this paragraph.
(2) The setting of the superheater safety valve shall not exceed the design pressure of the superheater outlet flange or the main steam piping beyond the superheater. To prevent damage to the superheater, the drum safety valve shall be set at a pressure not less than that of the superheater safety valve setting plus 5 pounds minimum plus approximately the normal load pressure drop through the superheater and associated piping, including the controlled desuperheater if fitted. See also § 52.01-95(b) (1).
(3) Drum pilot actuated superheater safety valves are permitted provided the setting of the pilot valve and superheater safety valve is such that the superheater safety valve will open before the drum safety valve.
(1) (Modifies PG-71.) Safety valves shall be installed as indicated in PG-71 of section I of the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code except as noted otherwise in this paragraph.
(2) The final setting of boiler safety valves shall be checked and adjusted under steam pressure and, if possible, while the boiler is on the line and the steam is at operating temperatures, in the presence of and to the satisfaction of a marine inspector who, upon acceptance, shall seal the valves. This regulation applies to both drum and superheater safety valves of all boilers.
(3) The safety valve body drains required by PG-71 of section I of the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code shall be run as directly as possible from the body of each boiler safety valve, or the drain from each boiler safety valve may be led to an independent header common only to boiler safety valve drains. No valves of any type shall be installed in the leakoff from drains or drain headers and they shall be led to suitable locations to avoid hazard to personnel.
(1) (Modifies PG-72.) The operation of safety valves shall be as indicated in PG-72 of section I of the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code except as noted in paragraph (d)(2) of this section.
(2) (Modifies PG-73.) The lifting device required by PG-73.1.3 of section I of the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code shall be fitted with suitable relieving gear so arranged that the controls may be operated from the fireroom or engineroom floor.

Experitec is an authorized Anderson Greenwood™ and Crosby™ assembler and a National Board-Certified VR, Test Only, and ASME UV stamp holder. As such, we carry an extensive inventory of Anderson Greenwood and Crosby parts and assemblies right on the shelf. In addition, we have the ability to source pressure relief valves from a variety of manufacturers. This combination allows Experitec to repair all your pressure relief valves. Our vision is to serve our customers like no others. We can and will cater to your specific needs. Remember, don’t let the lack of a qualified PRV repair compromise the safety of your plant and your people.
The SMS-7100 direct spring operated pressure relief valves has been designed to protect against excess pressure steam boilers and to provide superior performance.
Flanged, Butt weld spring loaded, direct acting, full nozzle safety relief valves for steam service (ASME Sect.I). Media: steam (suitable also for gas).




 8613371530291
8613371530291