boiler safety valve popping test manufacturer

When I teach my steam classes, I ask the attendees, "Do you test the pop safety valve?" Most do not. When I ask why, they tell me the same reason; the safety valve will leak. I joke during the classes that you do not want to test the pop safety valve on a Friday afternoon because it will almost certainly leak. I then ask, Do you check the low water cutoff? They look at me like I have a third eye and say they always check the low water cutoff. If you test the low water cutoff, you should test the pop safety valve. It is the last line of defense against a potential catastrophe. One of the things I do when performing a boiler service call is to explain the duty of the pop safety valve and ask the customer if they would like to have it tested. I explain that it could leak and if they refuse to test it, I will notate it on my service call in case something happens. In this way, my company is protected.
The best way to understand the pop safety valve is to read the instructions which came with the valve. I don"t have a life, and while you are watching the Masked Singer, I read O & M manuals. I know, I"m weird. I figure it"s my job to share things I find while reading these page-turners. The manufacturer hides all sorts of useful tidbits on the installation and maintenance of their valve. I have enclosed some information I gleaned while reading the instructions for a Conbraco/Apollo pop safety valve.
The valve must be mounted in a vertical, upright position directly to a clean, tapped opening in the top of the boiler. I see many safety valves installed horizontally and wonder if that voids the warranty. There should be no restrictions or valves in the piping to or from the safety valve. The installation instructions require the discharge piping to be schedule 40 pipe. They specifically say not to use schedule 80 pipe, which is 50% thicker than schedule 40 pipe. Many installers use copper tubing for the discharge, which does not meet the instructions. The other thing which confuses me the manufacturer instructs you not to use a pipe wrench to install the safety valve. I would wager 99% of all valves are installed using a pipe wrench. I wonder what kind of valve they want you to use.
I consult the pop safety manufacturer or the building insurance company to determine the frequency of tests. Apollo recommends quarterly testing using the Try Lever Test unless the valve is located in a severe service condition, and then it should be done more often. They further state the pop safety valve should have a Pressure Test annually before the heating season or at the end of any non-service period. This test will check your courage as you have to jump out the pressure controls and watch the operation of the boiler as the pressure builds. If the pop safety valve opens at the set pressure, the valve is working properly. This is not a test a novice should do alone.
Apollo suggests checking the pop safety valve at or near the maximum operating pressure by holding the test lever fully open for at least 5 seconds and letting it pop closed. On a low-pressure steam system, the pop safety valve is set for 15 psi. I like to run the boiler steam pressure up to 12 psi or higher to check the pop safety valve. After the test, I drop it to the operating pressure the owner requires. If the valve does not open, the boiler should be shut down until it is checked by a licensed contractor or qualified service person.
The pop safety manufacturer requires a minimum pressure differential of five psi between the pressure relief valve set pressure and the boiler operating pressure. It further states, Under no circumstances should the margin be less than five psig. On a low-pressure steam boiler, the pop safety valve will be set for 15 psi. That means the boiler steam pressure should be ten psi or lower. In breweries, it is common to see the boiler pressure set at 12-14 psi. This is less than the five psi differential and could create a dangerous condition.

Testing the safety relief valve is extremely important to the overall safety of your boiler system. In this post, we’ll be talking about what goes into testing a steam relief valve, but safety valve repairs should only be performed by a company holding a current Certificate of Authorization (VR) from the National Board of Pressure Vessel Inspectors.
Using certified and calibrated gauges is essential to accurate testing. WARE’s own Rick Walker recommends using two gauges, for maximum accuracy and in case one isn’t properly functioning.
Relief valves need to open and close at very specific pressures, and also need to open smoothly. A smooth opening contains a clean “pop” sound, and not a simmering or chattering sound. Responding to the appropriate pressures and opening and closing cleanly are both important signs a professional maintenance provider will look for in a safety valve.
Safety valves contain a compression screw, which puts pressure on a spring and causes the valve to function. The compression screw is where a maintenance provider will try to dial in your valve’s functionality and make set-pressure adjustments. It’s important to note if a valve is cold it might test higher, but as the valve gets hotter its metal will expand and its innerspring will slightly decompress.
Once the valve is warm and has stabilized, it’s best to give it more than one test (Rick does three) to make sure the valve is consistent and within ASME code.
ASME defines a safety valve as properly functioning at 150 psi if it tests within 3% of the set pressure. If your valve tests within 3% of the set pressure three times in a row on properly calibrated gauges, you’re likely good to go.
Remember, this procedure should only be done by professionals. If you’d like to schedule maintenance for your boiler, need assistance, or just want to learn more, contact us and check out our maintenance and service options at https://www.wareinc.com/boiler-services

For any facility that uses a pressure system or boiler, pressure relief valve testing is a must. While every facility has different testing requirements depending on industry and local code, the way you test pressure relief valves is much the same, regardless of how often you’re required to do it. If you’re gearing up for regular pressure relief valve testing, here are a few best practices to keep in mind as your testing schedule begins:
Pressure relief valve testing and inspection can include high noise levels and the discharge of high velocity and high-temperature fluids. Technicians should always take care to wear appropriate personal protective equipment, like eye and ear protection. When entering client facilities, it’s important that valve technicians also ask about and follow the facility’s unique PPE guidelines as well.
Pressure relief valve testing is most effective when completed on a regular schedule. Though every industry has a unique set of pressure relief valve testing requirements and guidelines, all facilities are best served with regular, comprehensive testing that includes both an operational test, and the verification of the valve’s nameplate set pressure.
If a pressure relief valve has never been tested before or has no record of prior testing, the National Board states that it must first be tested by lifting the test lever. If the valve doesn’t open and is stuck, it’s important that the equipment be immediately removed from service, until the valve can be replaced or repaired.
Pressure relief valves are necessary for the safe operation of any facility. If a valve is stuck, the equipment is considered hazardous, and testing must be completed under controlled conditions.
If the valve has been previously tested and has passed the operate-in-place test, it’s important to complete a test to verify nameplate set pressure. Every industry varies on the mandated frequency of these tests, but it is important to complete this type of pressure relief valve testing at least as regularly as your industry mandates, as it is the only way to verify that pressure relief valves are actuating at the appropriate setpoint.
Again, inline testing is a convenient and exceptionally accurate testing method here, as you do not have to halt operations to test valves inline. Bench testing is occasionally mandated, but because it requires full-facility downtime, it’s often best to opt for inline testing whenever possible.
An important best practice when testing pressure relief valves is to be aware of a valve’s pop-off pressure point. Pressure relief valve testing does work to verify the valve’s set point, but you never want to force the valve to pop open.
Instead, proper testing pushes the valve just to its simmer point, where the valve begins to lift, both so your technician gets an accurate read on the valve’s set point, and so no damage is done to the valve. Forcing the valve to pop-off with too much pressure can cause damage to the valve, and doesn’t always return an accurate setpoint, as the valve is overpressurized, rather than just tested to its specific simmer and setpoint.
Best practices for pressure relief valve testing indicate that technicians should test valves carefully, with a constant awareness of the valve’s pop-off pressure point, in order to avoid damage and to more accurately test the valve.
A key component of pressure relief valve testing is understanding when the valve needs maintenance. This is part of the reason we always recommend inline testing, where technicians are required to complete the testing. A valve technician understands the key signs of pressure relief valve failure and can replace or repair faulty valves onsite when testing valve inline.
Not every valve will pass pressure relief valve testing. It’s important that you understand when the replacement or repair of pressure relief valves is necessary, so you can keep your facility running safely and efficiently.
Does your company follow these best practices for pressure relief valve testing? Make the process easier and more efficient with AccuTEST’s advanced inline pressure relief valve testing system. See our system in action with a live webinar demo, or learn more about how inline pressure relief valve testing can increase your profitability.
There is a wide range of safety valves available to meet the many different applications and performance criteria demanded by different industries. Furthermore, national standards define many varying types of safety valve.
The ASME standard I and ASME standard VIII for boiler and pressure vessel applications and the ASME/ANSI PTC 25.3 standard for safety valves and relief valves provide the following definition. These standards set performance characteristics as well as defining the different types of safety valves that are used:
ASME I valve - A safety relief valve conforming to the requirements of Section I of the ASME pressure vessel code for boiler applications which will open within 3% overpressure and close within 4%. It will usually feature two blowdown rings, and is identified by a National Board ‘V’ stamp.
ASME VIII valve- A safety relief valve conforming to the requirements of Section VIII of the ASME pressure vessel code for pressure vessel applications which will open within 10% overpressure and close within 7%. Identified by a National Board ‘UV’ stamp.
Full bore safety valve - A safety valve having no protrusions in the bore, and wherein the valve lifts to an extent sufficient for the minimum area at any section, at or below the seat, to become the controlling orifice.
Conventional safety relief valve -The spring housing is vented to the discharge side, hence operational characteristics are directly affected by changes in the backpressure to the valve.
Balanced safety relief valve -A balanced valve incorporates a means of minimising the effect of backpressure on the operational characteristics of the valve.
Pilot operated pressure relief valve -The major relieving device is combined with, and is controlled by, a self-actuated auxiliary pressure relief device.
Power-actuated safety relief valve - A pressure relief valve in which the major pressure relieving device is combined with, and controlled by, a device requiring an external source of energy.
Standard safety valve - A valve which, following opening, reaches the degree of lift necessary for the mass flowrate to be discharged within a pressure rise of not more than 10%. (The valve is characterised by a pop type action and is sometimes known as high lift).
Full lift (Vollhub) safety valve -A safety valve which, after commencement of lift, opens rapidly within a 5% pressure rise up to the full lift as limited by the design. The amount of lift up to the rapid opening (proportional range) shall not be more than 20%.
Direct loaded safety valve -A safety valve in which the opening force underneath the valve disc is opposed by a closing force such as a spring or a weight.
Proportional safety valve - A safety valve which opens more or less steadily in relation to the increase in pressure. Sudden opening within a 10% lift range will not occur without pressure increase. Following opening within a pressure of not more than 10%, these safety valves achieve the lift necessary for the mass flow to be discharged.
Diaphragm safety valve -A direct loaded safety valve wherein linear moving and rotating elements and springs are protected against the effects of the fluid by a diaphragm
Bellows safety valve - A direct loaded safety valve wherein sliding and (partially or fully) rotating elements and springs are protected against the effects of the fluids by a bellows. The bellows may be of such a design that it compensates for influences of backpressure.
Controlled safety valve - Consists of a main valve and a control device. It also includes direct acting safety valves with supplementary loading in which, until the set pressure is reached, an additional force increases the closing force.
Safety valve - A safety valve which automatically, without the assistance of any energy other than that of the fluid concerned, discharges a quantity of the fluid so as to prevent a predetermined safe pressure being exceeded, and which is designed to re-close and prevent further flow of fluid after normal pressure conditions of service have been restored. Note; the valve can be characterised either by pop action (rapid opening) or by opening in proportion (not necessarily linear) to the increase in pressure over the set pressure.
Direct loaded safety valve -A safety valve in which the loading due to the fluid pressure underneath the valve disc is opposed only by a direct mechanical loading device such as a weight, lever and weight, or a spring.
Assisted safety valve -A safety valve which by means of a powered assistance mechanism, may additionally be lifted at a pressure lower than the set pressure and will, even in the event of a failure of the assistance mechanism, comply with all the requirements for safety valves given in the standard.
Supplementary loaded safety valve - A safety valve that has, until the pressure at the inlet to the safety valve reaches the set pressure, an additional force, which increases the sealing force.
Note; this additional force (supplementary load), which may be provided by means of an extraneous power source, is reliably released when the pressure at the inlet of the safety valve reaches the set pressure. The amount of supplementary loading is so arranged that if such supplementary loading is not released, the safety valve will attain its certified discharge capacity at a pressure not greater than 1.1 times the maximum allowable pressure of the equipment to be protected.
Pilot operated safety valve -A safety valve, the operation of which is initiated and controlled by the fluid discharged from a pilot valve, which is itself, a direct loaded safety valve subject to the requirement of the standard.
The common characteristic shared between the definitions of conventional safety valves in the different standards, is that their operational characteristics are affected by any backpressure in the discharge system. It is important to note that the total backpressure is generated from two components; superimposed backpressure and the built-up backpressure:
Subsequently, in a conventional safety valve, only the superimposed backpressure will affect the opening characteristic and set value, but the combined backpressure will alter the blowdown characteristic and re-seat value.
The ASME/ANSI standard makes the further classification that conventional valves have a spring housing that is vented to the discharge side of the valve. If the spring housing is vented to the atmosphere, any superimposed backpressure will still affect the operational characteristics. Thiscan be seen from Figure 9.2.1, which shows schematic diagrams of valves whose spring housings are vented to the discharge side of the valve and to the atmosphere.
By considering the forces acting on the disc (with area AD), it can be seen that the required opening force (equivalent to the product of inlet pressure (PV) and the nozzle area (AN)) is the sum of the spring force (FS) and the force due to the backpressure (PB) acting on the top and bottom of the disc. In the case of a spring housing vented to the discharge side of the valve (an ASME conventional safety relief valve, see Figure 9.2.1 (a)), the required opening force is:
In both cases, if a significant superimposed backpressure exists, its effects on the set pressure need to be considered when designing a safety valve system.
Once the valve starts to open, the effects of built-up backpressure also have to be taken into account. For a conventional safety valve with the spring housing vented to the discharge side of the valve, see Figure 9.2.1 (a), the effect of built-up backpressure can be determined by considering Equation 9.2.1 and by noting that once the valve starts to open, the inlet pressure is the sum of the set pressure, PS, and the overpressure, PO.
In both cases, if a significant superimposed backpressure exists, its effects on the set pressure need to be considered when designing a safety valve system.
Once the valve starts to open, the effects of built-up backpressure also have to be taken into account. For a conventional safety valve with the spring housing vented to the discharge side of the valve, see Figure 9.2.1 (a), the effect of built-up backpressure can be determined by considering Equation 9.2.1 and by noting that once the valve starts to open, the inlet pressure is the sum of the set pressure, PS, and the overpressure, PO.
Balanced safety valves are those that incorporate a means of eliminating the effects of backpressure. There are two basic designs that can be used to achieve this:
Although there are several variations of the piston valve, they generally consist of a piston type disc whose movement is constrained by a vented guide. The area of the top face of the piston, AP, and the nozzle seat area, AN, are designed to be equal. This means that the effective area of both the top and bottom surfaces of the disc exposed to the backpressure are equal, and therefore any additional forces are balanced. In addition, the spring bonnet is vented such that the top face of the piston is subjected to atmospheric pressure, as shown in Figure 9.2.2.
The bellows arrangement prevents backpressure acting on the upper side of the disc within the area of the bellows. The disc area extending beyond the bellows and the opposing disc area are equal, and so the forces acting on the disc are balanced, and the backpressure has little effect on the valve opening pressure.
Bellows failure is an important concern when using a bellows balanced safety valve, as this may affect the set pressure and capacity of the valve. It is important, therefore, that there is some mechanism for detecting any uncharacteristic fluid flow through the bellows vents. In addition, some bellows balanced safety valves include an auxiliary piston that is used to overcome the effects of backpressure in the case of bellows failure. This type of safety valve is usually only used on critical applications in the oil and petrochemical industries.
Since balanced pressure relief valves are typically more expensive than their unbalanced counterparts, they are commonly only used where high pressure manifolds are unavoidable, or in critical applications where a very precise set pressure or blowdown is required.
This type of safety valve uses the flowing medium itself, through a pilot valve, to apply the closing force on the safety valve disc. The pilot valve is itself a small safety valve.
The diaphragm type is typically only available for low pressure applications and it produces a proportional type action, characteristic of relief valves used in liquid systems. They are therefore of little use in steam systems, consequently, they will not be considered in this text.
The piston type valve consists of a main valve, which uses a piston shaped closing device (or obturator), and an external pilot valve. Figure 9.2.4 shows a diagram of a typical piston type, pilot operated safety valve.
The piston and seating arrangement incorporated in the main valve is designed so that the bottom area of the piston, exposed to the inlet fluid, is less than the area of the top of the piston. As both ends of the piston are exposed to the fluid at the same pressure, this means that under normal system operating conditions, the closing force, resulting from the larger top area, is greater than the inlet force. The resultant downward force therefore holds the piston firmly on its seat.
If the inlet pressure were to rise, the net closing force on the piston also increases, ensuring that a tight shut-off is continually maintained. However, when the inlet pressure reaches the set pressure, the pilot valve will pop open to release the fluid pressure above the piston. With much less fluid pressure acting on the upper surface of the piston, the inlet pressure generates a net upwards force and the piston will leave its seat. This causes the main valve to pop open, allowing the process fluid to be discharged.
When the inlet pressure has been sufficiently reduced, the pilot valve will reclose, preventing the further release of fluid from the top of the piston, thereby re-establishing the net downward force, and causing the piston to reseat.
Pilot operated safety valves offer good overpressure and blowdown performance (a blowdown of 2% is attainable). For this reason, they are used where a narrow margin is required between the set pressure and the system operating pressure. Pilot operated valves are also available in much larger sizes, making them the preferred type of safety valve for larger capacities.
One of the main concerns with pilot operated safety valves is that the small bore, pilot connecting pipes are susceptible to blockage by foreign matter, or due to the collection of condensate in these pipes. This can lead to the failure of the valve, either in the open or closed position, depending on where the blockage occurs.
The terms full lift, high lift and low lift refer to the amount of travel the disc undergoes as it moves from its closed position to the position required to produce the certified discharge capacity, and how this affects the discharge capacity of the valve.
A full lift safety valve is one in which the disc lifts sufficiently, so that the curtain area no longer influences the discharge area. The discharge area, and therefore the capacity of the valve are subsequently determined by the bore area. This occurs when the disc lifts a distance of at least a quarter of the bore diameter. A full lift conventional safety valve is often the best choice for general steam applications.
The disc of a high lift safety valve lifts a distance of at least 1/12th of the bore diameter. This means that the curtain area, and ultimately the position of the disc, determines the discharge area. The discharge capacities of high lift valves tend to be significantly lower than those of full lift valves, and for a given discharge capacity, it is usually possible to select a full lift valve that has a nominal size several times smaller than a corresponding high lift valve, which usually incurs cost advantages.Furthermore, high lift valves tend to be used on compressible fluids where their action is more proportional.
In low lift valves, the disc only lifts a distance of 1/24th of the bore diameter. The discharge area is determined entirely by the position of the disc, and since the disc only lifts a small amount, the capacities tend to be much lower than those of full or high lift valves.
Except when safety valves are discharging, the only parts that are wetted by the process fluid are the inlet tract (nozzle) and the disc. Since safety valves operate infrequently under normal conditions, all other components can be manufactured from standard materials for most applications. There are however several exceptions, in which case, special materials have to be used, these include:
Cast steel -Commonly used on higher pressure valves (up to 40 bar g). Process type valves are usually made from a cast steel body with an austenitic full nozzle type construction.
For all safety valves, it is important that moving parts, particularly the spindle and guides are made from materials that will not easily degrade or corrode. As seats and discs are constantly in contact with the process fluid, they must be able to resist the effects of erosion and corrosion.
The spring is a critical element of the safety valve and must provide reliable performance within the required parameters. Standard safety valves will typically use carbon steel for moderate temperatures. Tungsten steel is used for higher temperature, non-corrosive applications, and stainless steel is used for corrosive or clean steam duty. For sour gas and high temperature applications, often special materials such as monel, hastelloy and ‘inconel’ are used.
Standard safety valves are generally fitted with an easing lever, which enables the valve to be lifted manually in order to ensure that it is operational at pressures in excess of 75% of set pressure. This is usually done as part of routine safety checks, or during maintenance to prevent seizing. The fitting of a lever is usually a requirement of national standards and insurance companies for steam and hot water applications. For example, the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code states that pressure relief valves must be fitted with a lever if they are to be used on air, water over 60°C, and steam.
A test gag (Figure 9.2.7) may be used to prevent the valve from opening at the set pressure during hydraulic testing when commissioning a system. Once tested, the gag screw is removed and replaced with a short blanking plug before the valve is placed in service.
The amount of fluid depends on the particular design of safety valve. If emission of this fluid into the atmosphere is acceptable, the spring housing may be vented to the atmosphere – an open bonnet. This is usually advantageous when the safety valve is used on high temperature fluids or for boiler applications as, otherwise, high temperatures can relax the spring, altering the set pressure of the valve. However, using an open bonnet exposes the valve spring and internals to environmental conditions, which can lead to damage and corrosion of the spring.
When the fluid must be completely contained by the safety valve (and the discharge system), it is necessary to use a closed bonnet, which is not vented to the atmosphere. This type of spring enclosure is almost universally used for small screwed valves and, it is becoming increasingly common on many valve ranges since, particularly on steam, discharge of the fluid could be hazardous to personnel.
Some safety valves, most commonly those used for water applications, incorporate a flexible diaphragm or bellows to isolate the safety valve spring and upper chamber from the process fluid, (see Figure 9.2.9).
The Pressure Safety Valve Inspection article provides you information about inspection of pressure safety valve and pressure safety valve test in manufacturing shop as well as in operational plants.
Your pressure safety valve is a direct spring-loaded pressure-relief valve that is opened by the static pressure upstream of the valve and characterized by rapid opening or pop action.
Your construction code for pressure safety valve is API Standard 526 and covers the minimum requirements for design, materials, fabrication, inspection, testing, and commissioning.
These are:API Recommended Practice 520 for Sizing and SelectionAPI Recommended practice 521 Guideline for Pressure Relieving and Depressing SystemsAPI Recommended Practice 527 Seat Tightness of Pressure Relief Valves
For example in the state of Minnesota the ASME Code application and stamping for pressure vessel and boiler is mandatory which “U” and “S” symbols are designated for stamping on the nameplate.
For example if there is pressure vessel need to be installed in the state of Minnesota then the pressure vessel nameplate shall be U stamped and pressure vessel safety valve shall be UV stamped.
National Board Inspection Code (NBIC) have own certification scheme for pressure safety valves and using NB symbol. The NBIC code book for this certification is NB 18.
There are some other standards and codes which are used in pressure safety valve such as:ASME PTC 25 for pressure relief devices which majorly is used for assessment of testing facility and apparatus for safety valvesBS EN ISO 4126-1, 4126-2 and 4126-3 which is construction standard similar to API STD 526.
This API RP 527 might be used in conjunction of API RP 576 as testing procedure for seat tightness testing of pressure safety valve for periodical servicing and inspection.
These are only important points or summery of points for pressure safety valve in-service inspection and should not be assumed as pressure safety valve inspection procedure.
Pressure safety valve inspection procedure is comprehensive document which need to cover inspection methods to be employed, equipment and material to be used, qualification of inspection personnel involved and the sequence of the inspection activities as minimum.
You may use following content as summery of points for Pressure Safety Valve Inspection in operational plantDetermination pressure safety valve inspection interval based API STD 510 and API RP 576 requirementsInspection of inlet and outlet piping after pressure safety valve removal for any foulingInspection of pressure safety valve charge and discharge nozzles for possible deposit and corrosion productsTaking care for proper handling of pressure safety valves from unit to the valve shop. The detail of handling and transportation instruction is provided in API RP 576.Controlling of seals for being intact when the valves arrived to the valve shop.Making as received POP test and recording the relieving pressure.
If the POP pressure is higher than the set pressure the test need to be repeated and if in the second effort it was near to the set pressure it is because of deposit.If in the second effort it was not opened near to the set pressure either it was set wrongly or it was changed during the operationIf the pressure safety valve was not opened in 150% of set pressure it should be considered as stuck shut.If the pressure safety valve was opened below the set pressure the spring is weakenedMaking external visual inspection on pressure safety valve after POP test. The test need contain following item as minimum;the flanges for pitting and roughness
Making body wall thickness measurementDismantling of pressure safety valve if the result of as received POP test was not satisfactoryMaking detail and comprehensive visual and dimensional inspection on the dismantled valve parts (after cleaning)Making special attention to the dismantled valves seating surfaces inspection e.g. disk and seat for roughness, wear and damage which might cause valve leakage in serviceReplacing the damaged parts in dismantled valves based manufacture recommendation and API RP 576 requirementsMaking precise setting of the pressure safety valve after reassembly based manufacture recommendation or NB-18 requirements
Making at least two POP test after setting and making sure the deviation from set pressure is not more than 2 psi for valves with set pressure equal or less than 70 psi or 3% for valves with set pressure higher than 70 psiMaking valve tightness test for leakage purpose after approval of the setting pressure and POP tests. The test method and acceptance criteria must be according to the API RP 576.The API RP 527 also can be used for pressure safety valve tightness test.Recording and maintaining the inspection and testing results.

Safety is of the utmost importance when dealing with pressure relief valves. The valve is designed to limit system pressure, and it is critical that they remain in working order to prevent an explosion. Explosions have caused far too much damage in companies over the years, and though pressurized tanks and vessels are equipped with pressure relief vales to enhance safety, they can fail and result in disaster.
That’s also why knowing the correct way to test the valves is important. Ongoing maintenance and periodic testing of pressurized tanks and vessels and their pressure relief valves keeps them in working order and keep employees and their work environments safe. Pressure relief valves must be in good condition in order to automatically lower tank and vessel pressure; working valves open slowly when the pressure gets high enough to exceed the pressure threshold and then closes slowly until the unit reaches the low, safe threshold. To ensure the pressure relief valve is in good working condition, employees must follow best practices for testing them including:
If you consider testing pressure relief valves a maintenance task, you’ll be more likely to carry out regular testing and ensure the safety of your organization and the longevity of your
It’s important to note, however, that the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) and National Board Inspection Code (NBIC), as well as state and local jurisdictions, may set requirements for testing frequency. Companies are responsible for checking with these organizations to become familiar with the testing requirements. Consider the following NBIC recommendations on the frequency for testing relief valves:
High-pressure steam boilers greater than 15 psi and less than 400 psi – perform manual check every six months and pressure test annually to verify nameplate set pressure
High-pressure steam boilers 400 psi and greater – pressure test to verify nameplate set pressure every three years or as determined by operating experience as verified by testing history
High-temperature hot water boilers (greater than 160 psi and/or 250 degrees Fahrenheit) – pressure test annually to verify nameplate set pressure. For safety reasons, removal and testing on a test bench is recommended
When testing the pressure relief valve, raise and lower the test lever several times. The lever will come away from the brass stem and allow hot water to come out of the end of the drainpipe. The water should flow through the pipe, and then you should turn down the pressure to stop the leak, replace the lever, and then increase the pressure.
One of the most common problems you can address with regular testing is the buildup of mineral salt, rust, and corrosion. When buildup occurs, the valve will become non-operational; the result can be an explosion. Regular testing helps you discover these issues sooner so you can combat them and keep your boiler and valve functioning properly. If no water flows through the pipe, or if there is a trickle instead of a rush of water, look for debris that is preventing the valve from seating properly. You may be able to operate the test lever a few times to correct the issue. You will need to replace the valve if this test fails.
When testing relief valves, keep in mind that they have two basic functions. First, they will pop off when the pressure exceeds its safety threshold. The valve will pop off and open to exhaust the excess pressure until the tank’s pressure decreases to reach the set minimum pressure. After this blowdown process occurs, the valve should reset and automatically close. One important testing safety measure is to use a pressure indicator with a full-scale range higher than the pop-off pressure.
Thus, you need to be aware of the pop-off pressure point of whatever tank or vessel you test. You always should remain within the pressure limits of the test stand and ensure the test stand is assembled properly and proof pressure tested. Then, take steps to ensure the escaping pressure from the valve is directed away from the operator and that everyone involved in the test uses safety shields and wears safety eye protection.
After discharge – Because pressure relief valves are designed to open automatically to relieve pressure in your system and then close, they may be able to open and close multiple times during normal operation and testing. However, when a valve opens, debris may get into the valve seat and prevent the valve from closing properly. After discharge, check the valve for leakage. If the leakage exceeds the original settings, you need to repair the valve.
According to local jurisdictional requirements – Regulations are in place for various locations and industries that stipulate how long valves may operate before needing to be repair or replaced. State inspectors may require valves to be disassembled, inspected, repaired, and tested every five years, for instance. If you have smaller valves and applications, you can test the valve by lifting the test lever. However, you should do this approximately once a year. It’s important to note that ASME UG136A Section 3 requires valves to have a minimum of 75% operating pressure versus the set pressure of the valve for hand lifting to be performed for these types of tests.
Depending on their service and application– The service and application of a valve affect its lifespan. Valves used for clean service like steam typically last at least 20 years if they are not operated too close to the set point and are part of a preventive maintenance program. Conversely, valves used for services such as acid service, those that are operated too close to the set point, and those exposed to dirt or debris need to be replaced more often.
Pressure relief valves serve a critical role in protecting organizations and employees from explosions. Knowing how and when to test and repair or replace them is essential.

Boiler explosions have been responsible for widespread damage to companies throughout the years, and that’s why today’s boilers are equipped with safety valves and/or relief valves. Boiler safety valves are designed to prevent excess pressure, which is usually responsible for those devastating explosions. That said, to ensure that boiler safety valves are working properly and providing adequate protection, they must meet regulatory specifications and require ongoing maintenance and periodic testing. Without these precautions, malfunctioning safety valves may fail, resulting in potentially disastrous consequences.
Boiler safety valves are activated by upstream pressure. If the pressure exceeds a defined threshold, the valve activates and automatically releases pressure. Typically used for gas or vapor service, boiler safety valves pop fully open once a pressure threshold is reached and remain open until the boiler pressure reaches a pre-defined, safe lower pressure.
Boiler relief valves serve the same purpose – automatically lowering boiler pressure – but they function a bit differently than safety valves. A relief valve doesn’t open fully when pressure exceeds a defined threshold; instead, it opens gradually when the pressure threshold is exceeded and closes gradually until the lower, safe threshold is reached. Boiler relief valves are typically used for liquid service.
There are also devices known as “safety relief valves” which have the characteristics of both types discussed above. Safety relief valves can be used for either liquid or gas or vapor service.
Nameplates must be fastened securely and permanently to the safety valve and remain readable throughout the lifespan of the valve, so durability is key.
The National Board of Boiler and Pressure Vessel Inspectors offers guidance and recommendations on boiler and pressure vessel safety rules and regulations. However, most individual states set forth their own rules and regulations, and while they may be similar across states, it’s important to ensure that your boiler safety valves meet all state and local regulatory requirements.
The National Board published NB-131, Recommended Boiler and Pressure Vessel Safety Legislation, and NB-132, Recommended Administrative Boiler and Pressure Vessel Safety Rules and Regulationsin order to provide guidance and encourage the development of crucial safety laws in jurisdictions that currently have no laws in place for the “proper construction, installation, inspection, operation, maintenance, alterations, and repairs” necessary to protect workers and the public from dangerous boiler and pressure vessel explosions that may occur without these safeguards in place.
The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) governs the code that establishes guidelines and requirements for safety valves. Note that it’s up to plant personnel to familiarize themselves with the requirements and understand which parts of the code apply to specific parts of the plant’s steam systems.
High steam capacity requirements, physical or economic constraints may make the use of a single safety valve impossible. In these cases, using multiple safety valves on the same system is considered an acceptable practice, provided that proper sizing and installation requirements are met – including an appropriately sized vent pipe that accounts for the total steam venting capacity of all valves when open at the same time.
The lowest rating (MAWP or maximum allowable working pressure) should always be used among all safety devices within a system, including boilers, pressure vessels, and equipment piping systems, to determine the safety valve set pressure.
Avoid isolating safety valves from the system, such as by installing intervening shut-off valves located between the steam component or system and the inlet.
Contact the valve supplier immediately for any safety valve with a broken wire seal, as this indicates that the valve is unsafe for use. Safety valves are sealed and certified in order to prevent tampering that can prevent proper function.
Avoid attaching vent discharge piping directly to a safety valve, which may place unnecessary weight and additional stress on the valve, altering the set pressure.

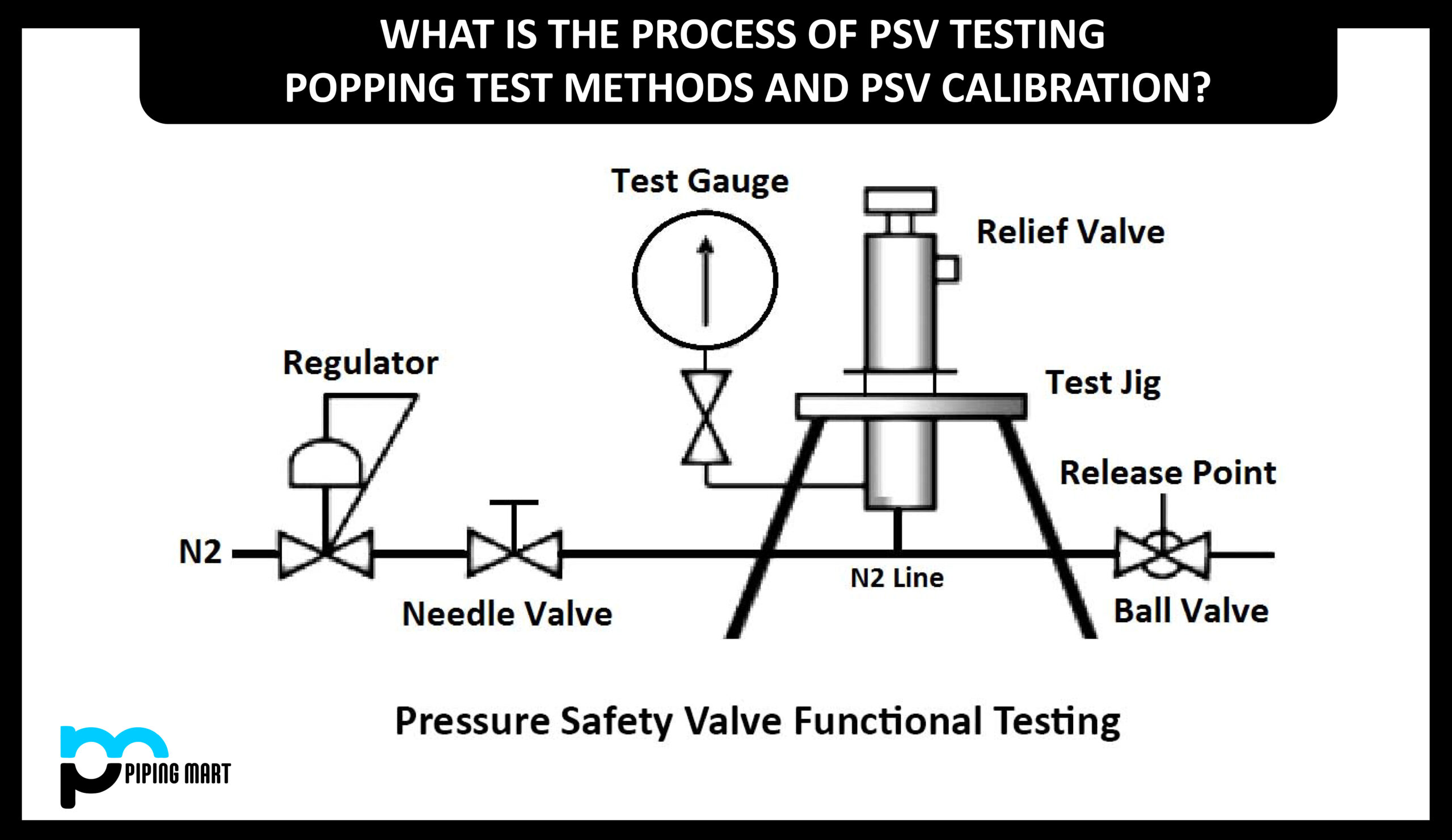
PSV or pressure safety valve is a device to protect the entire system. But to be confident and avoiding of leaving any chance of risk of PSV popping we need to test each and every Pressure safety valve with a specified PSV popping test procedure.
Testing of PSV and its procedure can be different but the findings of each method is to verify the exact working of the Pressure safety valve. In this article we will learn the following:
A pressure relief valve is a safety device that is designed to safeguard pressure-holding equipment during an event of overpressure of the equipment. An overpressure event means a condition that would cause pressure in a vessel that increases beyond the designed pressure or maximum allowable working pressure of that system.
The primary purpose of the pressure relief valve is to protect life and properties from overpressurization of equipment of the system by venting out fluid from overpressurized vessels.
Standard safety valve – A valve in which the opening reaches the degree of lift only necessary to be discharged within a pressure rise of not more than 10% (The valve is characterized by a pop type action and is sometimes known as high lift).
Full lift safety valve – A safety valve that opens rapidly within a 5% pressure rise up to the full lift as limited by the design. The amount of lift up to the rapid opening (proportional range) shall not be more than 20%.
Direct loaded safety valve – A safety valve in which the opening force underneath the valve disc is opposed by a closing force such as a spring or a weight.
Proportional safety valve – A safety valve that opens more or less steadily in relation to the increase in pressure. Sudden opening within a 10% lift range will not occur without a pressure increase. Following opening within a pressure of not more than 10%, these safety valves achieve the lift necessary for the mass flow to be discharged.
Diaphragm safety valve – A directly loaded safety valve in which linear moving and rotating elements and springs are protected against the effects of the fluid by a diaphragm.
Bellows safety valve – A direct loaded safety valve where sliding and (partially or fully) rotating elements and springs are protected against the effects of the fluids by a bellows. The bellows may be of such design that they compensate for the influences of backpressure.
Controlled safety valve– This type of pressure safety valve consists of the main valve and a control device. It also includes direct acting safety valves with supplementary loading in which, until the set pressure is reached, an additional force increases the closing force.
The PSV popping test or Pop test is a set pressure test of pressure safety valves. It is done with the help of compressed air which let flow it in the inlet of PSV until it opens. Then the authorized person for PSV calibration compares the opening force with the set pressure to see whether the valve works well or not.
When the inlet pressure of the pressure safety valve surpasses the threshold pressure, the “popping off” action is produced until the system pressure drops to the designated minimum pressure. The pressure safety valve then resets itself and closes down automatically.
Before testing, Set pressure needs to be determined by the pressure safety valve. A properly manufactured and serviced PSV has a set pressure engraved on the tag which is riveted on the body of the PSV.
Reduce the pressure gradually and record the reseating pressure, i.e. The pressure at which the valve will close. This happens instantly if the pressure source contains too low of a volume, thus making the seating pressure too difficult to record.
Even though the fundamental PRV testing technique is relatively simple, it produces results based on simple observations. Provision of signed certifications allows for little to no traceability other than the technician’s error.
Before putting a PSV into operation each pressure safety valve needs to be tested to protect equipment against overpressure. So it is important that every PSV has to be tested. There are 02 ways of testing of pressure safety valve:
Bench testing is the most popular type of method for testing pressure safety valves because it allows testing PSV in a controlled shop environment. Testing of valves that is already installed in the system requires the system to shut down.
Bench testing of PSV requires removing the pressure-relieving valve from its position and then carrying out a full functional test to check the behavior of the valve in case of overpressurizing.
Correspondingly, PSV testing cost less per testing of the valve in bench testing. But it can result in loss of production if the equipment is shut down or the removal of PSV requires for testing purposes.
When a PSV does not need the removal of the valve from installation or shut down the system is called “Inline or Online PSV testing”. A competent technician can test valves in the system using inline safety relief valve testing equipment to determine the actual setpoint.
In situ, PSV testing proves to be cost-effective as it does not require a plant shut down. But on the other hand, per PSV testing costs are much higher.
When PSV is already installed in the system or attached to the pressure holding equipment, it is costly to test pressure safety valves. In this case, PSVs are tested while in operational conditions. There are two ways of operational testing as follows:
The accumulation testing of PSV is a boiler safety test that determines whether the safety valves can release fluid quick enough to keep the pressure when by more than 10%. The main steam stop valve closes during this testing of the pressure safety valve.
The burner installed on it indicates that the steam pressure will not increase over 10% prior to the safety valve releasing excess steam pressure into the atmosphere.
Hydro testing, also called hydrostatic testing, is performed on pressure vessels to check for leaks. This testing completely fills a pressure vessel with water and pressures it. Once pressurized, leaks can be detected.
Every Pressure safety valve has a set pressure engraved on a plate which is riveted to its body. A set pressure needs to verify before making it functional for any system or pressure holding equipment. Some of the reasons why we need to perform a calibration test of PSV are as follows:
Sometimes, it has been observed that the closed position of the valve is not being activated for a required longer time. This affects the set pressure, so it is a good practice to test the valve.
Overpressure: This is pressure above-set pressure at the point where the valve will open fully. It has a tolerance of up to 10% above the set pressure.
A pressure safety valve or PSV is the last line of defense for all pressure holding systems and equipment that protect it from getting overpressurized. Working of Pressure is completely a mechanical system, hence this needs to be verified before installing it in operations.
It can be hazardous during the calibration or PSV popping test procedure. So, taking care of the operator and testing technician need to be done to make all the processes safe and harmless.
PSV popping test can be done either after installation or before installation. In both cases, the method of testing and its medium can be different to observe the result.

Problem about one safety valve was repeated the test 13th times to gets in the acceptable range. For my opinion, test result should not be accepted if the test has been repeated more that 4 times due to valve spring properties has been changed and AI recommend likes my opinion also. But I can not found test limits in code/ASME. Please advice.
Pressure relief devices are used to provide a means of venting excess pressure which could rupture a boiler or pressure vessel. A pressure relief device is the last line of defense for safety. If all other safety devices or operating controls fail, the pressure relief device must be capable of venting excess pressure.
There are many types of pressure relief devices available for use in the boiler and pressure vessel industry. This inspector guide will address the most common devices found on boilers and pressure vessels. Virtually all jurisdictions require a pressure relief device to be manufactured and certified in accordance with the ASME BPV Code in addition to being capacity-certified by the National Board.
Safety Valve – This device is typically used for steam or vapor service. It operates automatically with a full-opening pop action and recloses when the pressure drops to a value consistent with the blowdown requirements prescribed by the applicable governing code or standard.
Relief Valve – This device is typically used for liquid service. It operates automatically by opening farther as the pressure increases beyond the initial opening pressure and recloses when the pressure drops below the opening pressure.
Safety Relief Valve – This device includes the operating characteristics of both a safety valve and a relief valve and may be used in either application.
Temperature and Pressure Safety Relief Valve – This device is typically used on potable water heaters. In addition to its pressure-relief function, it also includes a temperature-sensing element which causes the device to open at a predetermined temperature regardless of pressure. The set temperature on these devices is usually 210°F.
Some devices, especially on larger boilers, may have a discharge pipe arrangement which incorporates provisions for expansion as the boiler heats up or cools down. These expansion provisions must allow the full range of movement required to prevent loads being applied to the device body.
Drain holes in the device body and discharge piping, when applicable, must be open to allow drainage of liquids from over the device disk on spring loaded valves. Any liquid allowed to remain on top of the device disk can adversely affect the operating characteristics of the device.
While inspecting a boiler or pressure vessel, the inspector will also be evaluating the pressure relief device(s) installed on, or associated with, the equipment. The inspector should:
Compare the device nameplate set pressure with the boiler or pressure vessel maximum allowable working pressure (MAWP) and ensure the device set pressure does not exceed the MAWP. A device with a set pressure less than MAWP is acceptable. If multiple devices are used, at least one must have a set pressure equal to or less than the MAWP. The ASME Code should be reviewed for other conditions relating to the use of multiple devices.
Instruct the owner or owner"s representative to lift the test lever, if so equipped, on spring-loaded devices. ASME BPV Code Section IV devices can have the test levers lifted without pressure in the boiler. All other devices must have at least 75% of the device set pressure under the device disk prior to lifting the test lever. If the device is found to be stuck in a closed position, the equipment should be immediately removed from service until such time the device can be replaced or repaired.
Lifting the test lever of a spring-loaded device may not be practical in all cases when inspecting pressure vessels. The contents of the vessel may be hazardous. In these cases, the vessel owner/user should have a testing procedure in place which will ensure documented inspection and testing of the device at regular intervals.
The small pressure relief devices found on many air compressor vessels have a ring inserted through a drilled hole on the end of the device stem. These are tested by pulling the stem straight out and then releasing. The discharge openings in this type of device are holes drilled around the periphery of the device. These holes often get filled with oily dust and grit which can cause eye damage when the device is tested. A rag, loosely wrapped around the device when testing, can help prevent personal injury from the dust and grit.

Many electronic, pneumatic and hydraulic systems exist today to control fluid system variables, such as pressure, temperature and flow. Each of these systems requires a power source of some type, such as electricity or compressed air in order to operate. A pressure Relief Valve must be capable of operating at all times, especially during a period of power failure when system controls are nonfunctional. The sole source of power for the pressure Relief Valve, therefore, is the process fluid.
Once a condition occurs that causes the pressure in a system or vessel to increase to a dangerous level, the pressure Relief Valve may be the only device remaining to prevent a catastrophic failure. Since reliability is directly related to the complexity of the device, it is important that the design of the pressure Relief Valve be as simple as possible.
The pressure Relief Valve must open at a predetermined set pressure, flow a rated capacity at a specified overpressure, and close when the system pressure has returned to a safe level. Pressure Relief Valves must be designed with materials compatible with many process fluids from simple air and water to the most corrosive media. They must also be designed to operate in a consistently smooth and stable manner on a variety of fluids and fluid phases.
The basic spring loaded pressure Relief Valve has been developed to meet the need for a simple, reliable, system actuated device to provide overpressure protection.
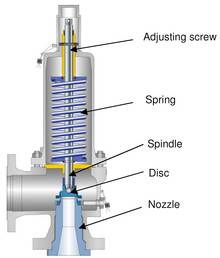
The Valve consists of a Valve inlet or nozzle mounted on the pressurized system, a disc held against the nozzle to prevent flow under normal system operating conditions, a spring to hold the disc closed, and a body/Bonnet to contain the operating elements. The spring load is adjustable to vary the pressure at which the Valve will open.
When a pressure Relief Valve begins to lift, the spring force increases. Thus system pressure must increase if lift is to continue. For this reason pressure Relief Valves are allowed an overpressure allowance to reach full lift. This allowable overpressure is generally 10% for Valves on unfired systems. This margin is relatively small and some means must be provided to assist in the lift effort.
Most pressure Relief Valves, therefore, have a secondary control chamber or huddling chamber to enhance lift. As the disc begins to lift, fluid enters the control chamber exposing a larger area of the disc to system pressure.
This causes an incremental change in force which overcompensates for the increase in spring force and causes the Valve to open at a rapid rate. At the same time, the direction of the fluid flow is reversed and the momentum effect resulting from the change in flow direction further enhances lift. These effects combine to allow the Valve to achieve maximum lift and maximum flow within the allowable overpressure limits. Because of the larger disc area exposed to system pressure after the Valve achieves lift, the Valve will not close until system pressure has been reduced to some level below the set pressure. The design of the control chamber determines where the closing point will occur.
A safety Valve is a pressure Relief Valve actuated by inlet static pressure and characterized by rapid opening or pop action. (It is normally used for steam and air services.)
A low-lift safety Valve is a safety Valve in which the disc lifts automatically such that the actual discharge area is determined by the position of the disc.
A full-lift safety Valve is a safety Valve in which the disc lifts automatically such that the actual discharge area is not determined by the position of the disc.
A Relief Valve is a pressure relief device actuated by inlet static pressure having a gradual lift generally proportional to the increase in pressure over opening pressure. It may be provided with an enclosed spring housing suitable for closed discharge system application and is primarily used for liquid service.
A safety Relief Valve is a pressure Relief Valve characterized by rapid opening or pop action, or by opening in proportion to the increase in pressure over the opening pressure, depending on the application and may be used either for liquid or compressible fluid.
A conventional safety Relief Valve is a pressure Relief Valve which has its spring housing vented to the discharge side of the Valve. The operational characteristics (opening pressure, closing pressure, and relieving capacity) are directly affected by changes of the back pressure on the Valve.
A balanced safety Relief Valve is a pressure Relief Valve which incorporates means of minimizing the effect of back pressure on the operational characteristics (opening pressure, closing pressure, and relieving capacity).
A pilotoperated pressure Relief Valve is a pressure Relief Valve in which the major relieving device is combined with and is controlled by a self-actuated auxiliary pressure Relief Valve.
A poweractuated pressure Relief Valve is a pressure Relief Valve in which the major relieving device is combined with and controlled by a device requiring an external source of energy.
A temperature-actuated pressure Relief Valve is a pressure Relief Valve which may be actuated by external or internal temperature or by pressure on the inlet side.
A vacuum Relief Valve is a pressure relief device designed to admit fluid to prevent an excessive internal vacuum; it is designed to reclose and prevent further flow of fluid after normal conditions have been restored.
Many Codes and Standards are published throughout the world which address the design and application of pressure Relief Valves. The most widely used and recognized of these is the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code, commonly called the ASME Code.
is the calculated mass flow from an orifice having a cross sectional area equal to the flow area of the safety Valve without regard to flow losses of the Valve.
the pressure at which a Valve is set on a test rig using a test fluid at ambient temperature. This test pressure includes corrections for service conditions e.g. backpressure or high temperatures.
is the value of increasing static inlet pressure of a pressure Relief Valve at which there is a measurable lift, or at which the discharge becomes continuous as determined by seeing, feeling or hearing.
Because cleanliness is essential to the satisfactory operation and tightness of a safety Valve, precautions should be taken during storage to keep out all foreign materials. Inlet and outlet protectors should remain in place until the Valve is ready to be installed in the system. Take care to keep the Valve inlet absolutely clean. It is recommended that the Valve be stored indoors in the original shipping container away from dirt and other forms of contamination.
Safety Valves mus




 8613371530291
8613371530291