boiler safety valve setting supplier
Choose these valves for small steam-heating boilers requiring pressure relief between 5 psi and 12 psi. They spring fully open at the set pressure and remain open until the system pressure is restored below the set pressure. All have a bronze body for durability and a long service life.

In order to ensure that the maximum allowable accumulation pressure of any system or apparatus protected by a safety valve is never exceeded, careful consideration of the safety valve’s position in the system has to be made. As there is such a wide range of applications, there is no absolute rule as to where the valve should be positioned and therefore, every application needs to be treated separately.
A common steam application for a safety valve is to protect process equipment supplied from a pressure reducing station. Two possible arrangements are shown in Figure 9.3.3.
The safety valve can be fitted within the pressure reducing station itself, that is, before the downstream stop valve, as in Figure 9.3.3 (a), or further downstream, nearer the apparatus as in Figure 9.3.3 (b). Fitting the safety valve before the downstream stop valve has the following advantages:
• The safety valve can be tested in-line by shutting down the downstream stop valve without the chance of downstream apparatus being over pressurised, should the safety valve fail under test.
• When setting the PRV under no-load conditions, the operation of the safety valve can be observed, as this condition is most likely to cause ‘simmer’. If this should occur, the PRV pressure can be adjusted to below the safety valve reseat pressure.
Indeed, a separate safety valve may have to be fitted on the inlet to each downstream piece of apparatus, when the PRV supplies several such pieces of apparatus.
• If supplying one piece of apparatus, which has a MAWP pressure less than the PRV supply pressure, the apparatus must be fitted with a safety valve, preferably close-coupled to its steam inlet connection.
• If a PRV is supplying more than one apparatus and the MAWP of any item is less than the PRV supply pressure, either the PRV station must be fitted with a safety valve set at the lowest possible MAWP of the connected apparatus, or each item of affected apparatus must be fitted with a safety valve.
• The safety valve must be located so that the pressure cannot accumulate in the apparatus viaanother route, for example, from a separate steam line or a bypass line.
It could be argued that every installation deserves special consideration when it comes to safety, but the following applications and situations are a little unusual and worth considering:
• Fire - Any pressure vessel should be protected from overpressure in the event of fire. Although a safety valve mounted for operational protection may also offer protection under fire conditions,such cases require special consideration, which is beyond the scope of this text.
• Exothermic applications - These must be fitted with a safety valve close-coupled to the apparatus steam inlet or the body direct. No alternative applies.
• Safety valves used as warning devices - Sometimes, safety valves are fitted to systems as warning devices. They are not required to relieve fault loads but to warn of pressures increasing above normal working pressures for operational reasons only. In these instances, safety valves are set at the warning pressure and only need to be of minimum size. If there is any danger of systems fitted with such a safety valve exceeding their maximum allowable working pressure, they must be protected by additional safety valves in the usual way.
In order to illustrate the importance of the positioning of a safety valve, consider an automatic pump trap (see Block 14) used to remove condensate from a heating vessel. The automatic pump trap (APT), incorporates a mechanical type pump, which uses the motive force of steam to pump the condensate through the return system. The position of the safety valve will depend on the MAWP of the APT and its required motive inlet pressure.
This arrangement is suitable if the pump-trap motive pressure is less than 1.6 bar g (safety valve set pressure of 2 bar g less 0.3 bar blowdown and a 0.1 bar shut-off margin). Since the MAWP of both the APT and the vessel are greater than the safety valve set pressure, a single safety valve would provide suitable protection for the system.
Here, two separate PRV stations are used each with its own safety valve. If the APT internals failed and steam at 4 bar g passed through the APT and into the vessel, safety valve ‘A’ would relieve this pressure and protect the vessel. Safety valve ‘B’ would not lift as the pressure in the APT is still acceptable and below its set pressure.
It should be noted that safety valve ‘A’ is positioned on the downstream side of the temperature control valve; this is done for both safety and operational reasons:
Operation - There is less chance of safety valve ‘A’ simmering during operation in this position,as the pressure is typically lower after the control valve than before it.
Also, note that if the MAWP of the pump-trap were greater than the pressure upstream of PRV ‘A’, it would be permissible to omit safety valve ‘B’ from the system, but safety valve ‘A’ must be sized to take into account the total fault flow through PRV ‘B’ as well as through PRV ‘A’.
A pharmaceutical factory has twelve jacketed pans on the same production floor, all rated with the same MAWP. Where would the safety valve be positioned?
One solution would be to install a safety valve on the inlet to each pan (Figure 9.3.6). In this instance, each safety valve would have to be sized to pass the entire load, in case the PRV failed open whilst the other eleven pans were shut down.
If additional apparatus with a lower MAWP than the pans (for example, a shell and tube heat exchanger) were to be included in the system, it would be necessary to fit an additional safety valve. This safety valve would be set to an appropriate lower set pressure and sized to pass the fault flow through the temperature control valve (see Figure 9.3.8).

Safety valves or pressure relief valves are pressure regulating devices that are responsible for expelling excess pressure from the system when the maximum pressure levels for which they have been designed are exceeded, usually due to a
Safety valves perform their function when the pressure of the system where the fluid is contained, becomes higher than the maximum set pressure of the valve previously adjusted. When the system pressure is higher than the valve’s set
pressure, this opens, releasing the excess pressure to the atmosphere or to containment tanks, depending on the toxicity of the fluid. After releasing the excess, the valve closes again and the system pressure returns to normal.
To ensure total safety of personnel and installation, make sure that the valves have passed all safety tests and meet the requirements of the system where they are to be installed. All our valves are supplied with certificates of materials, cas-
What is the difference between the instantaneous full opening safety valve AIT (PSV) and the normal opening relief valve AN or progressive opening relief valve AP (PRV)?
The Pressure Safety Valve (PSV) opens instantaneously and fully upon reaching the set pressure for which it is designed, expelling the excess pressure from the system immediately. They are optimised for use with steam or gases.
In contrast, the normally or progressively opening Pressure Relief Valve (PRV) opens gradually as the system pressure rises above the set pressure of the valve above its setting. They are optimised to work with liquids.
At VYC Industrial we are specialists in the design and manufacture of all types of safety valves. We have a wide range of safety valves to cover all the needs of the sector.
The Mod. 496 EN safety valve works as an automatic pressure releasing regulator activated by the static pressure existing at the entrance to the valve and is characterized by its ability to open instantly and totally.
The Mod. 495 EN pressure relief valve works as an automatic pressure releasing regulator activated by the static pressure existing at the entrance to the valve and is characterized by its ability to open instantly and totally.
The relief valve works as an automatic pressure releasing regulator activated by the static pressure existing at the entrance to the valve and is characterized by its ability to open instantly and totally.
The valve works as an automatic pressure releasing regulator activated by the static pressure existing at the entrance to the valve and is characterized by its ability to open instantly and totally.
The valve works as an automatic pressure releasing regulator activated by the static pressure existing at the entrance to the valve and is characterized by its ability to open instantly and totally.
The valve works as an automatic pressure releasing regulator activated by the static pressure existing at the entrance to the valve and is characterized by its ability to open instantly and totally.
The valve works as an automatic pressure releasing regulator activated by the static pressure existing at the entrance to the valve and is characterized by its ability to open instantly and totally.
The valve works as an automatic pressure releasing regulator activated by the static pressure existing at the entrance to the valve and is characterized by its ability to open instantly and totally.
The valve works as an automatic pressure releasing regulator activated by the static pressure existing at the entrance to the valve and is characterized by its ability to open, at the fi rst proportional to the pressure increase, and after instantly and totally.
The valve works as an automatic pressure releasing regulator activated by the static pressure existing at the entrance to the valve and is characterized by its ability to open, at the fi rst proportional to the pressure increase, and after instantly and totally.
The valve works as an automatic pressure releasing regulator activated by the static pressure existing at the entrance to the valve and is characterized by its ability to open, at the fi rst proportional to the pressure increase, and after instantly and totally.
The valve works as an automatic pressure releasing regulator activated by the static pressure existing at the entrance to the valve and is characterized by its ability to open proportional to the pressure increase.
The valve works as an automatic pressure releasing regulator activated by the static pressure existing at the entrance to the valve and is characterized by its ability to open proportional to the pressure increase.
The valve works as an automatic pressure releasing regulator activated by the static pressure existing at the entrance to the valve and is characterized by its ability to open instantly and totally.
The valve works as an automatic pressure releasing regulator activated by the static pressure existing at the entrance to the valve and is characterized by its ability to open instantly and totally.
The valve works as an automatic pressure releasing regulator activated by the static pressure existing at the entrance to the valve and is characterized by its ability to open instantly and totally.
The valve works as an automatic pressure releasing regulator activated by the static pressure existing at the entrance to the valve and is characterized by its ability to open instantly and totally.
The valve works as an automatic pressure releasing regulator activated by the static pressure existing at the entrance to the valve and is characterized by its ability to open instantly and totally.
They are used in places such as power, chemical and petrochemical plants to discharge safety valves, control valves, etc. in pressure lines and equipment that convey compressible substances such as steam, air, carbon dioxide, helium, methane, nitrogen, oxygen and other gases.
Test bench for regular inspections and setting and resetting safety valves. Ideal for distributors, maintenance companies or with in-house maintenance. It allows safety valves to be adjusted, tested and/or checked to the test pressure (setting) Pe wile cold (simulating service conditions), matching the opening pressure Ps and the closing pressure Pc, in accordance with the standard regulations.
Controlled safety pressure relief system CSPRS valves are mainly used where conventional direct-loaded spring action valves cannot guarantee the opening and closing margins that certain specifi c conditions of service demand.
The objective is to help the closure by means of pressure so that the valve remains completely watertight until reaching the set pressure and/or to activate the opening with pressure.
Increase the operating pressure of the system up to 99.9% of the set pressure.The control safety pressure relief system CSPRS device can be used with any safety valve available in the market and in particular, with models VYC Mod. 485, 486, 494, 495 and 496.

Boiler explosions have been responsible for widespread damage to companies throughout the years, and that’s why today’s boilers are equipped with safety valves and/or relief valves. Boiler safety valves are designed to prevent excess pressure, which is usually responsible for those devastating explosions. That said, to ensure that boiler safety valves are working properly and providing adequate protection, they must meet regulatory specifications and require ongoing maintenance and periodic testing. Without these precautions, malfunctioning safety valves may fail, resulting in potentially disastrous consequences.
Boiler safety valves are activated by upstream pressure. If the pressure exceeds a defined threshold, the valve activates and automatically releases pressure. Typically used for gas or vapor service, boiler safety valves pop fully open once a pressure threshold is reached and remain open until the boiler pressure reaches a pre-defined, safe lower pressure.
Boiler relief valves serve the same purpose – automatically lowering boiler pressure – but they function a bit differently than safety valves. A relief valve doesn’t open fully when pressure exceeds a defined threshold; instead, it opens gradually when the pressure threshold is exceeded and closes gradually until the lower, safe threshold is reached. Boiler relief valves are typically used for liquid service.
There are also devices known as “safety relief valves” which have the characteristics of both types discussed above. Safety relief valves can be used for either liquid or gas or vapor service.
Nameplates must be fastened securely and permanently to the safety valve and remain readable throughout the lifespan of the valve, so durability is key.
The National Board of Boiler and Pressure Vessel Inspectors offers guidance and recommendations on boiler and pressure vessel safety rules and regulations. However, most individual states set forth their own rules and regulations, and while they may be similar across states, it’s important to ensure that your boiler safety valves meet all state and local regulatory requirements.
The National Board published NB-131, Recommended Boiler and Pressure Vessel Safety Legislation, and NB-132, Recommended Administrative Boiler and Pressure Vessel Safety Rules and Regulationsin order to provide guidance and encourage the development of crucial safety laws in jurisdictions that currently have no laws in place for the “proper construction, installation, inspection, operation, maintenance, alterations, and repairs” necessary to protect workers and the public from dangerous boiler and pressure vessel explosions that may occur without these safeguards in place.
The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) governs the code that establishes guidelines and requirements for safety valves. Note that it’s up to plant personnel to familiarize themselves with the requirements and understand which parts of the code apply to specific parts of the plant’s steam systems.
High steam capacity requirements, physical or economic constraints may make the use of a single safety valve impossible. In these cases, using multiple safety valves on the same system is considered an acceptable practice, provided that proper sizing and installation requirements are met – including an appropriately sized vent pipe that accounts for the total steam venting capacity of all valves when open at the same time.
The lowest rating (MAWP or maximum allowable working pressure) should always be used among all safety devices within a system, including boilers, pressure vessels, and equipment piping systems, to determine the safety valve set pressure.
Avoid isolating safety valves from the system, such as by installing intervening shut-off valves located between the steam component or system and the inlet.
Contact the valve supplier immediately for any safety valve with a broken wire seal, as this indicates that the valve is unsafe for use. Safety valves are sealed and certified in order to prevent tampering that can prevent proper function.
Avoid attaching vent discharge piping directly to a safety valve, which may place unnecessary weight and additional stress on the valve, altering the set pressure.
Safety valves are an arrangement or mechanism to release a substance from the concerned system in the event of pressure or temperature exceeding a particular preset limit. The systems in the context may be boilers, steam boilers, pressure vessels or other related systems. As per the mechanical arrangement, this one get fitted into the bigger picture (part of the bigger arrangement) called as PSV or PRV that is pressure safety or pressure relief valves.
This type of safety mechanism was largely implemented to counter the problem of accidental explosion of steam boilers. Initiated in the working of a steam digester, there were many methodologies that were then accommodated during the phase of the industrial revolution. And since then this safety mechanism has come a long way and now accommodates various other aspects.
These aspects like applications, performance criteria, ranges, nation based standards (countries like United States, European Union, Japan, South Korea provide different standards) etc. manage to differentiate or categorize this safety valve segment. So, there can be many different ways in which these safety valves get differentiated but a common range of bifurcation is as follows:
The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) I tap is a type of safety valve which opens with respect to 3% and 4% of pressure (ASME code for pressure vessel applications) while ASME VIII valve opens at 10% over pressure and closes at 7%. Lift safety valves get further classified as low-lift and full lift. The flow control valves regulate the pressure or flow of a fluid whereas a balanced valve is used to minimize the effects induced by pressure on operating characteristics of the valve in context.
A power operated valve is a type of pressure relief valve is which an external power source is also used to relieve the pressure. A proportional-relief valve gets opened in a relatively stable manner as compared to increasing pressure. There are 2 types of direct-loaded safety valves, first being diaphragms and second: bellows. diaphragms are valves which spring for the protection of effects of the liquid membrane while bellows provide an arrangement where the parts of rotating elements and sources get protected from the effects of the liquid via bellows.
In a master valve, the operation and even the initiation is controlled by the fluid which gets discharged via a pilot valve. Now coming to the bigger picture, the pressure safety valves based segment gets classified as follows:
So all in all, pressure safety valves, pressure relief valves, relief valves, pilot-operated relief valves, low pressure safety valves, vacuum pressure safety valves etc. complete the range of safety measures in boilers and related devices.
Safety valves have different discharge capacities. These capacities are based on the geometrical area of the body seat upstream and downstream of the valve. Flow diameter is the minimum geometrical diameter upstream and downstream of the body seat.
The nominal size designation refers to the inlet orifice diameter. A safety Valve"s theoretical flowing capacity is the mass flow through an orifice with the same cross-sectional area as the valve"s flow area. This capacity does not account for the flow losses caused by the valve. The actual capacity is measured, and the certified flow capacity is the actual flow capacity reduced by 10%.
A safety valve"s discharge capacity is dependent on the set pressure and position in a system. Once the set pressure is calculated, the discharge capacity must be determined. Safety valves may be oversized or undersized depending on the flow throughput and/or the valve"s set pressure.
The actual discharge capacity of a safety valve depends on the type of discharge system used. In liquid service, safety valves are generally automatic and direct-pressure actuated.
A safety valve is used to protect against overpressure in a fluid system. Its design allows for a lift in the disc, indicating that the valve is about to open. When the inlet pressure rises above the set pressure, the guide moves to the open position, and media flows to the outlet via the pilot tube. Once the inlet pressure falls below the set pressure, the main valve closes and prevents overpressure. There are five criteria for selecting a safety valve.
The first and most basic requirement of a safety valve is its ability to safely control the flow of gas. Hence, the valve must be able to control the flow of gas and water. The valve should be able to withstand the high pressures of the system. This is because the gas or steam coming from the boiler will be condensed and fill the pipe. The steam will then wet the safety valve seat.
The other major requirement for safety valves is their ability to prevent pressure buildup. They prevent overpressure conditions by allowing liquid or gas to escape. Safety valves are used in many different applications. Gas and steam lines, for example, can prevent catastrophic damage to the plant. They are also known as safety relief valves. During an emergency, a safety valve will open automatically and discharge gas or liquid pressure from a pressurized system, preventing it from reaching dangerous levels.
The discharge capacity of a safety valve is based on its orifice area, set pressure, and position in the system. A safety valve"s discharge capacity should be calculated based on the maximum flow through its inlet and outlet orifice areas. Its nominal size is often determined by manufacturer specifications.
Its discharge capacity is the maximum flow through the valve that it can relieve, based on the maximum flow through each individual flow path or combined flow path. The discharge pressure of the safety valve should be more than the operating pressure of the system. As a thumb rule, the relief pressure should be 10% above the working pressure of the system.
It is important to choose the discharge capacity of a safety valve based on the inlet and output piping sizes. Ideally, the discharge capacity should be equal to or greater than the maximum output of the system. A safety valve should also be installed vertically and into a clean fitting. While installing a valve, it is important to use a proper wrench for installation. The discharge piping should slope downward to drain any condensate.
The discharge capacity of a safety valve is measured in a few different ways. The first is the test pressure. This gauge pressure is the pressure at which the valve opens, while the second is the pressure at which it re-closes. Both are measured in a test stand under controlled conditions. A safety valve with a test pressure of 10,000 psi is rated at 10,000 psi (as per ASME PTC25.3).
The discharge capacity of a safety valve should be large enough to dissipate a large volume of pressure. A small valve may be adequate for a smaller system, but a larger one could cause an explosion. In a large-scale manufacturing plant, safety valves are critical for the safety of personnel and equipment. Choosing the right valve size for a particular system is essential to its efficiency.
Before you use a safety valve, you need to know its discharge capacity. Here are some steps you need to follow to calculate the discharge capacity of a safety valve.
To check the discharge capacity of a safety valve, the safety valve should be installed in the appropriate location. Its inlet and outlet pipework should be thoroughly cleaned before installation. It is important to avoid excessive use of PTFE tape and to ensure that the installation is solid. The safety valve should not be exposed to vibration or undue stress. When mounting a safety valve, it should be installed vertically and with the test lever at the top. The inlet connection of the safety valve should be attached to the vessel or pipeline with the shortest length of pipe. It must not be interrupted by any isolation valve. The pressure loss at the inlet of a safety valve should not exceed 3% of the set pressure.
The sizing of a safety valve depends on the amount of fluid it is required to control. The rated discharge capacity is a function of the safety valve"s orifice area, set pressure, and position in the system. Using the manufacturer"s specifications for orifice area and nominal size of the valve, the capacity of a safety valve can be determined. The discharge flow can be calculated using the maximum flow through the valve or the combined flows of several paths. When sizing a safety valve, it"s necessary to consider both its theoretical and actual discharge capacity. Ideally, the discharge capacity will be equal to the minimum area.
To determine the correct set pressure for a safety valve, consider the following criteria. It must be less than the MAAP of the system. Set pressure of 5% greater than the MAAP will result in an overpressure of 10%. If the set pressure is higher than the MAAP, the safety valve will not close. The MAAP must never exceed the set pressure. A set pressure that is too high will result in a poor shutoff after discharge. Depending on the type of valve, a backpressure variation of 10% to 15% of the set pressure cannot be handled by a conventional valve.
Relief and safety Valves are used in high pressure systems to control the pressure and keep balance of the system. The different between safety valves and relief valves is that the safety valves fully open or close under a certain pressure while the relief valves can open in proportion to the pressure in front of them. The safety and pressure relief valves are used automatically. They both operate under similar conditions. When the pressure builds up in a system, it has to be managed by releasing the material to flow through. These valves have a threshold pressure at which they open. The consolidated safety and safety relief valves comprise of a bonnet vent and bellow with springs.
The springs are set up for the threshold pressure and when the pressure exceeds the threshold, the spring is pushed into the bonnet vent and the bellow opens the valve. The Safety Relief Valves can be open and shut valves. They either open or shut off at any given pressure. This is mostly for the safety of an application not to explode under high pressure. The Pressure Relief Valve on the other hand releases the material after the threshold pressure, but not fully. If the pressure is slightly higher the threshold, then the valve opens slightly. If the pressure is very high above the threshold, it opens wider. It also functions in the same manner when the pressure drops down. The valve closes in proportion to the pressure. The safety valve shuts down at once only when the pressure is below the threshold.
Ready Stock of ASTM A351 CF8M Spring Loaded Safety Valve in wide range of Sizes, Stainless Steel Air Compressor Pressure Relief Valve Manufacturers In India
Relief Valves are designed to control pressure in a system While Safety Valves are used for controlling the pressure in a system they release pressure immediately in the event of an emergency or system failure
The Setpoint of relief valve is usually set at 10 Percent above working pressure limit while safety valve is usually set at 3% above working pressure limit.
If you are operating systems that can only be off for short periods of time, it is sensible to keep a spare valve to swap over and then the removed valve can be inspected and recertified.
Years ago, it was not uncommon to read news about tragic boiler explosions, sometimes resulting in mass destruction. Today, boilers are equipped with important safety devises to help protect against these types of catastrophes. Let’s take a look at the most critical of these devices: the safety valve.
The safety valve is one of the most important safety devices in a steam system. Safety valves provide a measure of security for plant operators and equipment from over pressure conditions. The main function of a safety valve is to relieve pressure. It is located on the boiler steam drum, and will automatically open when the pressure of the inlet side of the valve increases past the preset pressure. All boilers are required by ASME code to have at least one safety valve, dependent upon the maximum flow capacity (MFC) of the boiler. The total capacity of the safety valve at the set point must exceed the steam control valve’s MFC if the steam valve were to fail to open. In most cases, two safety valves per boiler are required, and a third may be needed if they do not exceed the MFC.
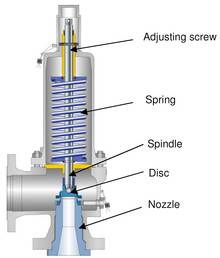
There are three main parts to the safety valve: nozzle, disc, and spring. Pressurized steam enters the valve through the nozzle and is then threaded to the boiler. The disc is the lid to the nozzle, which opens or closes depending on the pressure coming from the boiler. The spring is the pressure controller.
As a boiler starts to over pressure, the nozzle will start to receive a higher pressure coming from the inlet side of the valve, and will start to sound like it is simmering. When the pressure becomes higher than the predetermined pressure of the spring, the disc will start to lift and release the steam, creating a “pop” sound. After it has released and the steam and pressure drops below the set pressure of the valve, the spring will close the disc. Once the safety valve has popped, it is important to check the valve to make sure it is not damaged and is working properly.
A safety valve is usually referred to as the last line of safety defense. Without safety valves, the boiler can exceed it’s maximum allowable working pressure (MAWP) and not only damage equipment, but also injure or kill plant operators that are close by. Many variables can cause a safety valve on a boiler to lift, such as a compressed air or electrical power failure to control instrumentation, or an imbalance of feedwater rate caused by an inadvertently shut or open isolation valve.
Once a safety valve has lifted, it is important to do a complete boiler inspection and confirm that there are no other boiler servicing issues. A safety valve should only do its job once; safety valves should not lift continuously. Lastly, it is important to have the safety valves fully repaired, cleaned and recertified with a National Board valve repair (VR) stamp as required by local code or jurisdiction. Safety valves are a critical component in a steam system, and must be maintained.
All of Nationwide Boiler’s rental boilers include on to two safety valves depending on the size; one set at design pressure and the other set slightly higher than design. By request, we can reset the safeties to a lower pressure if the application requires it. In addition, the valves are thoroughly checked after every rental and before going out to a new customer, and they are replaced and re-certified as needed.

A little product education can make you look super smart to customers, which usually means more orders for everything you sell. Here’s a few things to keep in mind about safety valves, so your customers will think you’re a genius.
A safety valve is required on anything that has pressure on it. It can be a boiler (high- or low-pressure), a compressor, heat exchanger, economizer, any pressure vessel, deaerator tank, sterilizer, after a reducing valve, etc.
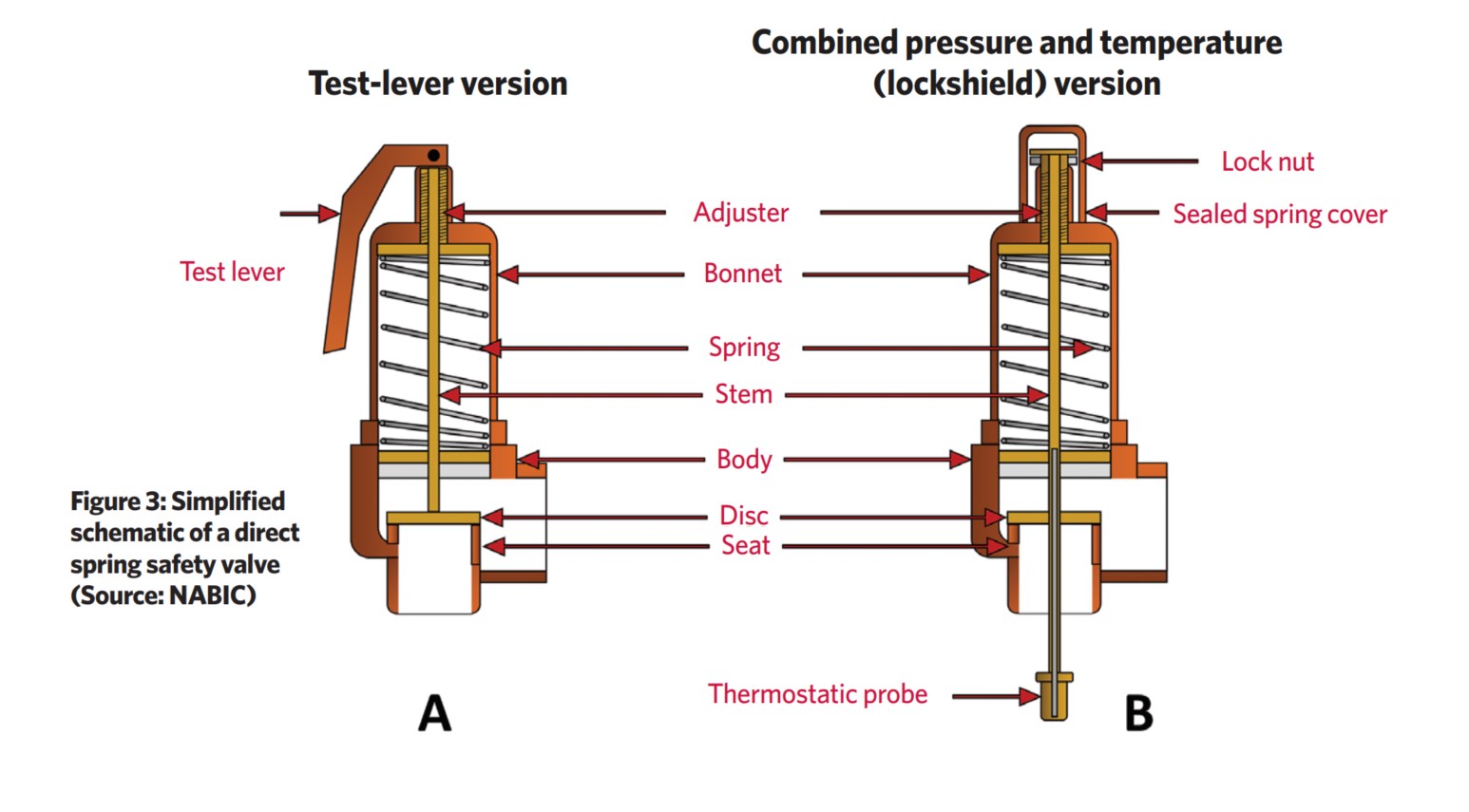
There are four main types of safety valves: conventional, bellows, pilot-operated, and temperature and pressure. For this column, we will deal with conventional valves.
A safety valve is a simple but delicate device. It’s just two pieces of metal squeezed together by a spring. It is passive because it just sits there waiting for system pressure to rise. If everything else in the system works correctly, then the safety valve will never go off.
A safety valve is NOT 100% tight up to the set pressure. This is VERY important. A safety valve functions a little like a tea kettle. As the temperature rises in the kettle, it starts to hiss and spit when the water is almost at a boil. A safety valve functions the same way but with pressure not temperature. The set pressure must be at least 10% above the operating pressure or 5 psig, whichever is greater. So, if a system is operating at 25 psig, then the minimum set pressure of the safety valve would be 30 psig.
Most valve manufacturers prefer a 10 psig differential just so the customer has fewer problems. If a valve is positioned after a reducing valve, find out the max pressure that the equipment downstream can handle. If it can handle 40 psig, then set the valve at 40. If the customer is operating at 100 psig, then 110 would be the minimum. If the max pressure in this case is 150, then set it at 150. The equipment is still protected and they won’t have as many problems with the safety valve.
Here’s another reason the safety valve is set higher than the operating pressure: When it relieves, it needs room to shut off. This is called BLOWDOWN. In a steam and air valve there is at least one if not two adjusting rings to help control blowdown. They are adjusted to shut the valve off when the pressure subsides to 6% below the set pressure. There are variations to 6% but for our purposes it is good enough. So, if you operate a boiler at 100 psig and you set the safety valve at 105, it will probably leak. But if it didn’t, the blowdown would be set at 99, and the valve would never shut off because the operating pressure would be greater than the blowdown.
All safety valves that are on steam or air are required by code to have a test lever. It can be a plain open lever or a completely enclosed packed lever.
Safety valves are sized by flow rate not by pipe size. If a customer wants a 12″ safety valve, ask them the flow rate and the pressure setting. It will probably turn out that they need an 8×10 instead of a 12×16. Safety valves are not like gate valves. If you have a 12″ line, you put in a 12″ gate valve. If safety valves are sized too large, they will not function correctly. They will chatter and beat themselves to death.
Safety valves need to be selected for the worst possible scenario. If you are sizing a pressure reducing station that has 150 psig steam being reduced to 10 psig, you need a safety valve that is rated for 150 psig even though it is set at 15. You can’t put a 15 psig low-pressure boiler valve after the reducing valve because the body of the valve must to be able to handle the 150 psig of steam in case the reducing valve fails.
The seating surface in a safety valve is surprisingly small. In a 3×4 valve, the seating surface is 1/8″ wide and 5″ around. All it takes is one pop with a piece of debris going through and it can leak. Here’s an example: Folgers had a plant in downtown Kansas City that had a 6×8 DISCONTINUED Consolidated 1411Q set at 15 psig. The valve was probably 70 years old. We repaired it, but it leaked when plant maintenance put it back on. It was after a reducing valve, and I asked him if he played with the reducing valve and brought the pressure up to pop the safety valve. He said no, but I didn’t believe him. I told him the valve didn’t leak when it left our shop and to send it back.
If there is a problem with a safety valve, 99% of the time it is not the safety valve or the company that set it. There may be other reasons that the pressure is rising in the system before the safety valve. Some ethanol plants have a problem on starting up their boilers. The valves are set at 150 and they operate at 120 but at startup the pressure gets away from them and there is a spike, which creates enough pressure to cause a leak until things get under control.
If your customer is complaining that the valve is leaking, ask questions before a replacement is sent out. What is the operating pressure below the safety valve? If it is too close to the set pressure then they have to lower their operating pressure or raise the set pressure on the safety valve.
Is the valve installed in a vertical position? If it is on a 45-degree angle, horizontal, or upside down then it needs to be corrected. I have heard of two valves that were upside down in my 47 years. One was on a steam tractor and the other one was on a high-pressure compressor station in the New Mexico desert. He bought a 1/4″ valve set at 5,000 psig. On the outlet side, he left the end cap in the outlet and put a pin hole in it so he could hear if it was leaking or not. He hit the switch and when it got up to 3,500 psig the end cap came flying out like a missile past his nose. I told him to turn that sucker in the right direction and he shouldn’t have any problems. I never heard from him so I guess it worked.
If the set pressure is correct, and the valve is vertical, ask if the outlet piping is supported by something other than the safety valve. If they don’t have pipe hangers or a wall or something to keep the stress off the safety valve, it will leak.
There was a plant in Springfield, Mo. that couldn’t start up because a 2″ valve was leaking on a tank. It was set at 750 psig, and the factory replaced it 5 times. We are not going to replace any valves until certain questions are answered. I was called to solve the problem. The operating pressure was 450 so that wasn’t the problem. It was in a vertical position so we moved on to the piping. You could tell the guy was on his cell phone when I asked if there was any piping on the outlet. He said while looking at the installation that he had a 2″ line coming out into a 2×3 connection going up a story into a 3×4 connection and going up another story. I asked him if there was any support for this mess, and he hung up the phone. He didn’t say thank you, goodbye, or send me a Christmas present.

Searching for tools to control the flow of your piping system? Explore one of the largest featured collections of products and discover a range of wholesale boiler safety valves on Alibaba.com. When you search for boiler safety valves and related items, you will be able to find many types of boiler safety valves varying in size, shape, use, and quality, all at prices in which are highly reasonable!
There are many uses of valves - mainly controlling the flow of fluids and pressure. Some examples include regulating water for irrigation, industrial uses for controlling processes, and residential piping systems. Magnetic valves like those using the solenoid, are often used in a range of industrial processes. Whereas backflow preventers are often used in residential and commercial buildings to ensure the safety and hygiene of the water supplies. Whether you are designing a regulation system for irrigation or merely looking for a new replacement, you will be able to find whatever type of boiler safety valves that you need. Our products vary from check valves to pressure reducing valves, ball valves, butterfly valves, thermostatic mixing valves, and a lot more.

Searching for tools to control the flow of your piping system? Explore one of the largest featured collections of products and discover a range of wholesale boiler safety valve on Alibaba.com. When you search for boiler safety valve and related items, you will be able to find many types of boiler safety valve varying in size, shape, use, and quality, all at prices in which are highly reasonable!
There are many uses of valves - mainly controlling the flow of fluids and pressure. Some examples include regulating water for irrigation, industrial uses for controlling processes, and residential piping systems. Magnetic valves like those using the solenoid, are often used in a range of industrial processes. Whereas backflow preventers are often used in residential and commercial buildings to ensure the safety and hygiene of the water supplies. Whether you are designing a regulation system for irrigation or merely looking for a new replacement, you will be able to find whatever type of boiler safety valve that you need. Our products vary from check valves to pressure reducing valves, ball valves, butterfly valves, thermostatic mixing valves, and a lot more.

Cast-iron boilers may be used in steam heating or hot water heating applications within the scope and service restrictions of ASME BPV Code Section IV. ASME BPV Code Section IV service restrictions limit steam boilers to pressures not exceeding 15 psi and hot water boilers to pressures not exceeding 160 psi and/or temperatures not exceeding 250°F.
One Piece – a single casting with no assembly joints. Another term used to describe this design is monobloc. This type of cast-iron boiler is usually small in size.
Sectional boilers are typically assembled with tapered connections called push nipples or elastomeric-type gaskets between the sections to seal the water-containing chambers. Another type of assembly uses external headers to connect the water containing chambers.
Cast-iron boilers can be found in almost any application where heating boilers are used. They are popular replacements for large welded steel boilers which may have been installed as the building was being constructed. Cast-iron sectional boilers can usually be installed in existing boiler rooms by moving the individual sections through doors or window openings. A very large boiler can be assembled in this manner without modifications to the building structure.
There will be two pieces of information missing from a cast-iron boiler nameplate: a National Board registration number and the year built. Cast-iron boilers are not registered with the National Board, and ASME BPV Code Section IV makes no provisions for a year of construction to appear on the nameplate. Since most inspection forms ask for a year of construction, the inspector will have to estimate. If the boiler is original to the building, the age of the building would directly correspond to the age of the boiler. If the boiler is a replacement, the inspector will have to question the owner to determine its age.
Cast-iron boilers may be used in steam heating or hot water heating applications within the scope and service restrictions of ASME BPV CodeSection IV. ASME BPV CodeSection IV service restrictions limit steam boilers to pressures not exceeding 15 psi and hot water boilers to pressures not exceeding 160 psi and/or temperatures not exceeding 250°F.
Steam boilers must have at least one safety valve with a set pressure not to exceed 15 psi. The safety valve inlet must not be smaller than NPS 1/2 nor larger than NPS 4-1/2.
Hot-water boilers must have at least one safety relief valve with a set pressure at or below the maximum allowable working pressure (MAWP) marked on the boiler. The safety relief valve inlet must not be smaller than NPS 3/4 nor larger than NPS 4-1/2. The minimum relieving capacity of safety or safety relief valves must equal or exceed the maximum output of the boiler. Cast-iron boilers constructed since 1943 will have information on the nameplate indicating the minimum required safety or safety relief valve capacity. Cast-iron boilers constructed prior to 1943 may not have that information. In those circumstances, the inspector must estimate the maximum output of the boiler. Gas or oil burners generally have a rating plate or label containing the Btu output of the burner. A generally applied guideline for older boilers is to use 80% of the maximum burner output as the maximum boiler output. Boilers fired with solid fuel such as coal or wood will be extremely difficult to estimate, since there is no way for the inspector to calculate the cast-iron boiler heating surface. In those cases, the inspector should request the boiler owner/user perform an accumulation test in accordance with HG-512(a), or a maximum burned fuel evaluation in accordance with HG-512(b) and Appendix B. These procedures should only be used if the safety or safety relief valve capacity is in doubt.
two pressure controls (if the boiler is automatically fired); one is considered the operating control and the other is considered the high-limit control (Note: some jurisdictions require the high-limit control be equipped with a manual reset switch) (HG-605);
an automatic low-water fuel cutoff – if the boiler is automatically fired (Note: some jurisdictions require an additional low-water fuel cutoff with a manual reset switch) (HG-606).
two temperature controls (if the boiler is automatically fired); one is considered the operating control and the other is considered the high-limit control (Note: some jurisdictions require the high limit control be equipped with a manual reset switch) (HG-613);
an automatic low-water fuel cutoff – if the boiler is automatically fired and has a heat input greater than 400,000 Btu/hr (Note: some jurisdictions require an additional low water fuel cutoff with a manual reset switch)(HG-614)
Clearances on the front, rear, sides, and top of all cast-iron boilers for operation, maintenance, and inspection shall meet jurisdictional requirements. If no jurisdictional requirements exist, then the boiler manufacturer"s requirements shall be met.
All cast-iron boilers should be installed on foundations or supports suitable for the weight of the boiler and its contents. The foundation or support must also be unaffected by the heat of the operating boiler.
Although most jurisdictions do not require inspection of the piping associated with an ASME BPV CodeSection IV boiler, there are some installation requirements in ASME BPV Code Section IV the inspector should review. Please see HG-703 and HG-705.
Steam boilers must have at least one safety valve with a set pressure not to exceed 15 psi. The safety valve inlet must not be smaller than NPS 1/2 nor larger than NPS 4-1/2.
Cast-iron boilers typically have a few inherent problems. The inspector should always look for water leaks at the connecting joints of sectional boilers. The inspector should request the removal of the sheet metal casing any time there is evidence of leakage and the leakage cannot be traced to an external source.
The most common problem associated with cast-iron boilers is cracking due to overheating or thermal shock. Overheating occurs when the boiler is allowed to operate with low-water conditions or poor circulation caused by sludge concentrated in the lower water passages of the boiler. Thermal shock can occur when a boiler is overheated and cold water is added in an attempt to raise the water level. Under those circumstances, cracking is usually the least that can happen. The worst that can happen is an explosion which shatters the cast-iron boiler into many pieces and cause destruction and injury.
Sectional cast-iron boilers use long rods, threaded on both ends, called draw bolts. It is not unusual for these draw bolts to appear loose when the boiler is cold. When the boiler is operating, the heat will cause the boiler to expand which tightens the draw bolts. A loose draw bolt on a hot boiler should be investigated by a competent cast-iron boiler service/repair company.
Cast-iron boilers typically have a few inherent problems. The inspector should always look for water leaks at the connecting joints of sectional boilers. The inspector should request the removal of the sheet metal casing any time there is evidence of leakage and the leakage cannot be traced to an external source.
Upon entering the boiler room, the inspector should perform a general assessment of the boiler, piping, controls, fuel system, and combustion air supply. The inspector should then:
compare the safety or safety relief valve nameplate data (set pressure and relieving capacity) with the boiler nameplate to ensure the safety or safety relief valve is adequate for this installation;
check the thermometer reading on hot water boilers (if there is a reason to question the accuracy of the thermometer, it should be replaced or recalibrated);
check the water gage glass to ensure it provides a clear indication of the water level in a steam boiler. (Please see the National Board Inspector Guide for Water Level Controls and Devices);
look for evidence of overheating (this may be difficult to detect on a cast-iron boiler; warped external sheet metal casings with scorched paint is usually a reliable indicator);
inspect the fuel-burning apparatus as required by the jurisdiction (for example, some jurisdictions mandate compliance with ASME Standard CSD-1, Controls & Safety Devices for Automatically Fired Boilers).
Internal inspections of cast-iron boilers can prove to be difficult or almost impossible. Threaded plugs on the cast iron boiler could be removed, but the inspector will see very little past the immediate vicinity of the opening on many cast iron boiler designs. In addition, the threaded plugs are sometimes heavily corroded which virtually "welds" them to the cast iron. Removal of threaded plugs in this condition may damage the cast iron irreparably. Some boilers may have valves installed in the lowest threaded openings of the boiler to facilitate draining and/or flushing of the boiler. If valves are present, the inspector can ask for them to be opened briefly to observe the condition of the water. If no water is present when the valves are opened, this could be an indication the lowest portion of the boiler is filled with sludge. The inspector is advised to follow the jurisdiction"s requirements for internal inspections of cast-iron boilers.
Threaded plugs in the piping connecting a water gage glass, water column, and low-water fuel cutoff to a steam boiler must be removed to allow inspection of the piping to ensure there is no blockage.
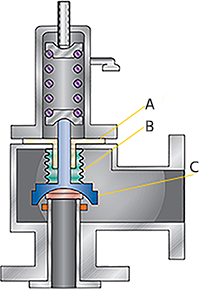
A safety valve is an important part of any engineering system or industrial installation working with media under high pressure, it is the safety of the operating personnel, the exclusion of equipment destruction and emergency situations.
Conveniently, the safety valve supplier can service, adjust or reset the pressure, and can repair and replace parts if necessary. LESER safety valves are known all over the world and are widely used in industry and heating. To provide customers with more options for service safety valves, OPEKS Energosystems, the official distributor of LESER, uses a proprietary set of LESER equipment and tools to set up and maintain valves at its own production facilities.
Setting the required response pressure of the safety valve consists of the following main steps:Fastening the safety valve using a standard mount in a tuning stand. Preparing to set up.
Valve assembly. Checking the tightness of the valve in the closed position, at a pressure less than the design one to prevent leakage of the working medium. Valve seat polishing, other work if necessary.
Setting up safety valves at the OPEKS production facility allows us to provide a shorter delivery time, shorten the period of service work, provide more opportunities and better service to our customers. Also, the company"s warehouse regularly maintains new valves for water, gases of different diameters with a response pressure, which is most often found in inquiries.
Cooperation with OPEKS Energosystems, which supplies and maintains LESER safety valves, as well as manufactures heat exchange equipment, modular units, steam condensate systems and other heat and power equipment, favorably stands out for its great opportunities for our Clients.




 8613371530291
8613371530291