boiler safety valve setting price
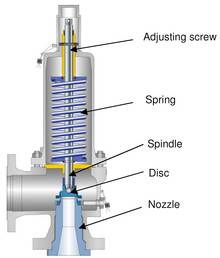
Searching for tools to control the flow of your piping system? Explore one of the largest featured collections of products and discover a range of wholesale boiler safety valves on Alibaba.com. When you search for boiler safety valves and related items, you will be able to find many types of boiler safety valves varying in size, shape, use, and quality, all at prices in which are highly reasonable!
There are many uses of valves - mainly controlling the flow of fluids and pressure. Some examples include regulating water for irrigation, industrial uses for controlling processes, and residential piping systems. Magnetic valves like those using the solenoid, are often used in a range of industrial processes. Whereas backflow preventers are often used in residential and commercial buildings to ensure the safety and hygiene of the water supplies. Whether you are designing a regulation system for irrigation or merely looking for a new replacement, you will be able to find whatever type of boiler safety valves that you need. Our products vary from check valves to pressure reducing valves, ball valves, butterfly valves, thermostatic mixing valves, and a lot more.

Electric steam boil is safer than the latter type because they are low-pressure and less to maintain. If high pressure boil is not safe, it is known to have a low boiling point and is the safer option to any water boil than the latter type. High pressure boil safety at the same time and are the safe as well as the latter type.

In order to ensure that the maximum allowable accumulation pressure of any system or apparatus protected by a safety valve is never exceeded, careful consideration of the safety valve’s position in the system has to be made. As there is such a wide range of applications, there is no absolute rule as to where the valve should be positioned and therefore, every application needs to be treated separately.
A common steam application for a safety valve is to protect process equipment supplied from a pressure reducing station. Two possible arrangements are shown in Figure 9.3.3.
The safety valve can be fitted within the pressure reducing station itself, that is, before the downstream stop valve, as in Figure 9.3.3 (a), or further downstream, nearer the apparatus as in Figure 9.3.3 (b). Fitting the safety valve before the downstream stop valve has the following advantages:
• The safety valve can be tested in-line by shutting down the downstream stop valve without the chance of downstream apparatus being over pressurised, should the safety valve fail under test.
• When setting the PRV under no-load conditions, the operation of the safety valve can be observed, as this condition is most likely to cause ‘simmer’. If this should occur, the PRV pressure can be adjusted to below the safety valve reseat pressure.
Indeed, a separate safety valve may have to be fitted on the inlet to each downstream piece of apparatus, when the PRV supplies several such pieces of apparatus.
• If supplying one piece of apparatus, which has a MAWP pressure less than the PRV supply pressure, the apparatus must be fitted with a safety valve, preferably close-coupled to its steam inlet connection.
• If a PRV is supplying more than one apparatus and the MAWP of any item is less than the PRV supply pressure, either the PRV station must be fitted with a safety valve set at the lowest possible MAWP of the connected apparatus, or each item of affected apparatus must be fitted with a safety valve.
• The safety valve must be located so that the pressure cannot accumulate in the apparatus viaanother route, for example, from a separate steam line or a bypass line.
It could be argued that every installation deserves special consideration when it comes to safety, but the following applications and situations are a little unusual and worth considering:
• Fire - Any pressure vessel should be protected from overpressure in the event of fire. Although a safety valve mounted for operational protection may also offer protection under fire conditions,such cases require special consideration, which is beyond the scope of this text.
• Exothermic applications - These must be fitted with a safety valve close-coupled to the apparatus steam inlet or the body direct. No alternative applies.
• Safety valves used as warning devices - Sometimes, safety valves are fitted to systems as warning devices. They are not required to relieve fault loads but to warn of pressures increasing above normal working pressures for operational reasons only. In these instances, safety valves are set at the warning pressure and only need to be of minimum size. If there is any danger of systems fitted with such a safety valve exceeding their maximum allowable working pressure, they must be protected by additional safety valves in the usual way.
In order to illustrate the importance of the positioning of a safety valve, consider an automatic pump trap (see Block 14) used to remove condensate from a heating vessel. The automatic pump trap (APT), incorporates a mechanical type pump, which uses the motive force of steam to pump the condensate through the return system. The position of the safety valve will depend on the MAWP of the APT and its required motive inlet pressure.
This arrangement is suitable if the pump-trap motive pressure is less than 1.6 bar g (safety valve set pressure of 2 bar g less 0.3 bar blowdown and a 0.1 bar shut-off margin). Since the MAWP of both the APT and the vessel are greater than the safety valve set pressure, a single safety valve would provide suitable protection for the system.
Here, two separate PRV stations are used each with its own safety valve. If the APT internals failed and steam at 4 bar g passed through the APT and into the vessel, safety valve ‘A’ would relieve this pressure and protect the vessel. Safety valve ‘B’ would not lift as the pressure in the APT is still acceptable and below its set pressure.
It should be noted that safety valve ‘A’ is positioned on the downstream side of the temperature control valve; this is done for both safety and operational reasons:
Operation - There is less chance of safety valve ‘A’ simmering during operation in this position,as the pressure is typically lower after the control valve than before it.
Also, note that if the MAWP of the pump-trap were greater than the pressure upstream of PRV ‘A’, it would be permissible to omit safety valve ‘B’ from the system, but safety valve ‘A’ must be sized to take into account the total fault flow through PRV ‘B’ as well as through PRV ‘A’.
A pharmaceutical factory has twelve jacketed pans on the same production floor, all rated with the same MAWP. Where would the safety valve be positioned?
One solution would be to install a safety valve on the inlet to each pan (Figure 9.3.6). In this instance, each safety valve would have to be sized to pass the entire load, in case the PRV failed open whilst the other eleven pans were shut down.
If additional apparatus with a lower MAWP than the pans (for example, a shell and tube heat exchanger) were to be included in the system, it would be necessary to fit an additional safety valve. This safety valve would be set to an appropriate lower set pressure and sized to pass the fault flow through the temperature control valve (see Figure 9.3.8).
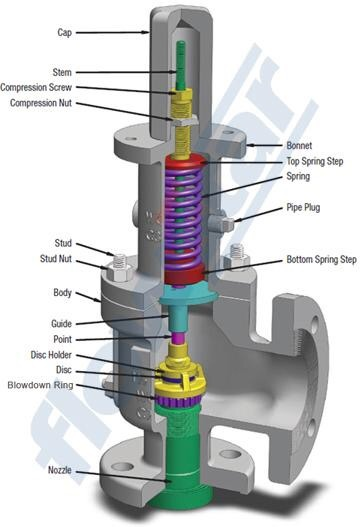
Throughout the years, HZVALVE has developed its Quality System which is an integral part of our manufacturing policy. Our primary goal is to provide products that meet and exceed market standards. In this sense, HZVALVE is an ISO-9001 Audited and Certified Company that has achieved major certifications worldwide. Our system consists of a rigorous quality control as well as the selection of raw materials from approved vendors. Control over our manufacturing process is vital. Serial numbers allow HZVALVE to monitor and trace fabrication processes along with the materials of components.
HZVALVE owned independent quality department with over 25 experienced inspectors. Our target is to cover all vital point including material, procession, assembling, testing and package for overall quality controlling and supervision. We keep the understanding that the high quality products create more value to customers.
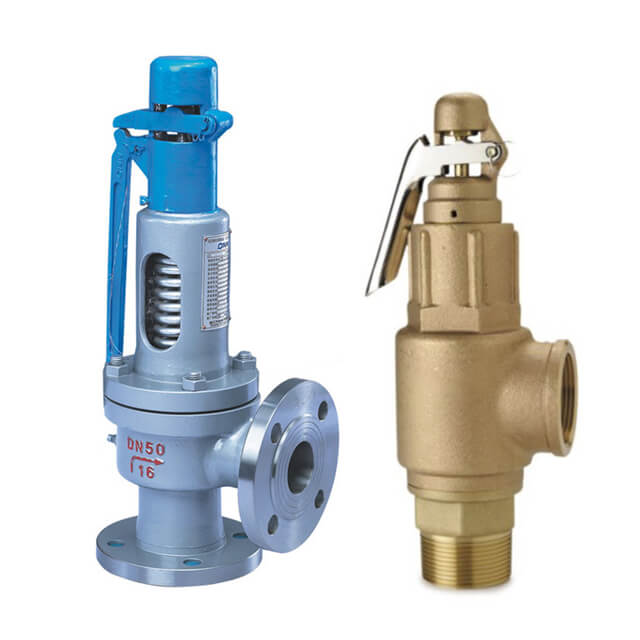

The safety valve is designed for TV systems. There is a cover on the valve that protects the valve from unwanted readjustment and manipulation. The valve body is made of brass and the seals together with the diaphragm are both made of EPDM.

Boilers are high pressure and temperature systems used for generating steam to drive steam turbines for electricity generation If due to any reason of operation or malfunction in equipment or controls the operating pressure in the system goes above the safe limit of the material of construction it can cause catastrophe To prevent such catastrophes safety valves are provided in the boiler at various locations

A rope appx. 6-7 meters with a hook one end should be attached to the valve lifting lever before starting the pressure rise. It will help in operating the lever to avoid chattering & over pressure
Safety valves blow down should be set more than required, as blow down percentage decreases as the steam temperature increases. An approximate rule is to add 0.5% of set pressure to the blow down for each 56.5 °C rise in SH steam temperature.
If a Super heater safety valve lifts at 189.5 kg/cm2 & reseats at 180 kg/cm2 at the temperature of 400 deg c, then calculate the blowdown calculation at 540 deg c

Chatter is devastating to the internals of a Boiler Safety Valve. However, there is an even more important reason to avoid chatter at all cost. Chatter prevents the Safety Valve from reaching or sustaining full lift. This results in the Boiler is not being protected from a catastrophic overpressure event. Chatter may be the result of several issues. The least likely is an inaccurately adjusted Safety Valve. More than likely, chatter is an issue of piping or installation. Inlet or outlet piping may be the culprit. Reduced Piping, too much length or too many bends (or some combination of those three) on the Inlet or the Outlet may result in Chatter. On some occasions, the Safety Valve is improperly sized resulting in chatter due to insufficient flow through the Safety Valve when it is called on to operate. In other words, the Safety Valve is oversized and there is enough pressure to cause the Safety Valve to lift, but not enough flow to keep it open. Bigger is not always better. All the issues referred to above result in pressure drop at the PRV Inlet, which causes chatter.
The only mentions of pressure drop in ASME Sec I, Power Boiler Code, are in PG-68.1 for Superheater Safety Valve Set Pressure calculation and in PG-68.4 for Reheater Outlet Safety Valve Set Pressure calculation. PG-72.1 is a requirement designed to ensure the Safety Valve does not chatter. Notice PG-72 has a title that refers to “Operation of Pressure Relief Valves.” It is referring to the Blowdown Ring Settings, not the inlet Pressure Drop due to piping losses.
In a related code, ASME Sec VIII-1, UG-135, INSTALLATION, in UG-135(b)(1) states, “The opening through all pipe, fittings, and nonreclosing pressure relief devices (if installed) between a pressure vessel and its pressure relief valve shall have at least the area of the pressure relief valve inlet . The characteristics of this upstream system shall be such that the pressure drop will not reduce the relieving capacity below that required or adversely affect the proper operation of the pressure relief valve.”
ASME Sec VIII-1, Non-Mandatory Appendix M, M-6 (a) states, “M-6 INLET PRESSURE DROP FOR HIGH LIFT, TOP-GUIDED SAFETY, SAFETY RELIEF, AND PILOT-OPERATED PRESSURE RELIEF VALVES IN COMPRESSIBLE FLUID SERVICE (a) The nominal pipe size of all piping, valves and fittings, and vessel components between a pressure vessel and its safety, safety relief, or pilot-operated pressure relief valves shall be at least as large as the nominal size of the device inlet, and the flow characteristics of the upstream system shall be such that the cumulative total of all nonrecoverable inlet losses shall not exceed 3% of the valve set pressure. The inlet pressure losses will be based on the valve nameplate capacity corrected for the characteristics of the flowing fluid.
Following the requirements for Safety Valve installation in ASME Code, Sec I, Power Boilers, will resolve the chatter issue without calculating pressure losses in piping. Refer to ASME Sec I, PG-71, “Mounting of Pressure Relief Valves.” The restrictions on size and length of piping should be sufficient to prevent chatter due to piping losses.
Regarding the least likely cause of chatter, i.e. Safety Valve adjustment, if the Upper Adjusting Ring (Guide Ring) is too high, the Safety Valve will pop, but will not remain open. It will reclose and immediately pop again resulting in chatter. This is due to the Upper Ring providing an "outer wall" to the Huddling Chamber to keep the Steam underneath the Disc long enough to achieve full lift. Setting the Upper Ring too high removes the "outer wall" of the Huddling Chamber resulting in chatter. Setting the Safety Valve in accordance with PG-73.5.2 (a), which states, “Pressure relief valves for steam service shall be tested with steam. The blowdown control elements of the pressure relief valve shall be set to the manufacturer"s specifications,” should eliminate the possibility of chatter due to an adjusting ring setting. It should be noted that the typical, ASME Sec VIII, Pressure Relief Valve, is a single ring design, Safety-Relief Valve. The Adjusting Ring Setting of the Single Ring Design, Safety-Relief Valve will not result in Chatter.

It is found on the majority of espresso machine boilers, but there are exceptions, such as Pavoni, Rancilio and few others. As it is a non-returnable item, please measure yours before ordering.

Safety valves or pressure relief valves are pressure regulating devices that are responsible for expelling excess pressure from the system when the maximum pressure levels for which they have been designed are exceeded, usually due to a
Safety valves perform their function when the pressure of the system where the fluid is contained, becomes higher than the maximum set pressure of the valve previously adjusted. When the system pressure is higher than the valve’s set
pressure, this opens, releasing the excess pressure to the atmosphere or to containment tanks, depending on the toxicity of the fluid. After releasing the excess, the valve closes again and the system pressure returns to normal.
To ensure total safety of personnel and installation, make sure that the valves have passed all safety tests and meet the requirements of the system where they are to be installed. All our valves are supplied with certificates of materials, cas-
What is the difference between the instantaneous full opening safety valve AIT (PSV) and the normal opening relief valve AN or progressive opening relief valve AP (PRV)?
The Pressure Safety Valve (PSV) opens instantaneously and fully upon reaching the set pressure for which it is designed, expelling the excess pressure from the system immediately. They are optimised for use with steam or gases.
In contrast, the normally or progressively opening Pressure Relief Valve (PRV) opens gradually as the system pressure rises above the set pressure of the valve above its setting. They are optimised to work with liquids.
At VYC Industrial we are specialists in the design and manufacture of all types of safety valves. We have a wide range of safety valves to cover all the needs of the sector.
The Mod. 496 EN safety valve works as an automatic pressure releasing regulator activated by the static pressure existing at the entrance to the valve and is characterized by its ability to open instantly and totally.
The Mod. 495 EN pressure relief valve works as an automatic pressure releasing regulator activated by the static pressure existing at the entrance to the valve and is characterized by its ability to open instantly and totally.
The relief valve works as an automatic pressure releasing regulator activated by the static pressure existing at the entrance to the valve and is characterized by its ability to open instantly and totally.
The valve works as an automatic pressure releasing regulator activated by the static pressure existing at the entrance to the valve and is characterized by its ability to open instantly and totally.
The valve works as an automatic pressure releasing regulator activated by the static pressure existing at the entrance to the valve and is characterized by its ability to open instantly and totally.
The valve works as an automatic pressure releasing regulator activated by the static pressure existing at the entrance to the valve and is characterized by its ability to open instantly and totally.
The valve works as an automatic pressure releasing regulator activated by the static pressure existing at the entrance to the valve and is characterized by its ability to open instantly and totally.
The valve works as an automatic pressure releasing regulator activated by the static pressure existing at the entrance to the valve and is characterized by its ability to open instantly and totally.
The valve works as an automatic pressure releasing regulator activated by the static pressure existing at the entrance to the valve and is characterized by its ability to open, at the fi rst proportional to the pressure increase, and after instantly and totally.
The valve works as an automatic pressure releasing regulator activated by the static pressure existing at the entrance to the valve and is characterized by its ability to open, at the fi rst proportional to the pressure increase, and after instantly and totally.
The valve works as an automatic pressure releasing regulator activated by the static pressure existing at the entrance to the valve and is characterized by its ability to open, at the fi rst proportional to the pressure increase, and after instantly and totally.
The valve works as an automatic pressure releasing regulator activated by the static pressure existing at the entrance to the valve and is characterized by its ability to open proportional to the pressure increase.
The valve works as an automatic pressure releasing regulator activated by the static pressure existing at the entrance to the valve and is characterized by its ability to open proportional to the pressure increase.
The valve works as an automatic pressure releasing regulator activated by the static pressure existing at the entrance to the valve and is characterized by its ability to open instantly and totally.
The valve works as an automatic pressure releasing regulator activated by the static pressure existing at the entrance to the valve and is characterized by its ability to open instantly and totally.
The valve works as an automatic pressure releasing regulator activated by the static pressure existing at the entrance to the valve and is characterized by its ability to open instantly and totally.
The valve works as an automatic pressure releasing regulator activated by the static pressure existing at the entrance to the valve and is characterized by its ability to open instantly and totally.
The valve works as an automatic pressure releasing regulator activated by the static pressure existing at the entrance to the valve and is characterized by its ability to open instantly and totally.
They are used in places such as power, chemical and petrochemical plants to discharge safety valves, control valves, etc. in pressure lines and equipment that convey compressible substances such as steam, air, carbon dioxide, helium, methane, nitrogen, oxygen and other gases.
Test bench for regular inspections and setting and resetting safety valves. Ideal for distributors, maintenance companies or with in-house maintenance. It allows safety valves to be adjusted, tested and/or checked to the test pressure (setting) Pe wile cold (simulating service conditions), matching the opening pressure Ps and the closing pressure Pc, in accordance with the standard regulations.
Controlled safety pressure relief system CSPRS valves are mainly used where conventional direct-loaded spring action valves cannot guarantee the opening and closing margins that certain specifi c conditions of service demand.
The objective is to help the closure by means of pressure so that the valve remains completely watertight until reaching the set pressure and/or to activate the opening with pressure.
Increase the operating pressure of the system up to 99.9% of the set pressure.The control safety pressure relief system CSPRS device can be used with any safety valve available in the market and in particular, with models VYC Mod. 485, 486, 494, 495 and 496.




 8613371530291
8613371530291