difference between safety valve and relief valve marine made in china

Industrial equipment often uses either safety or relief valves to prevent damaging pressure levels from building up. Though they perform similar functions, there are some critical differences between safety and relief valves. Understanding these two valves’ differences is essential for proper pressure system operation. So here we discuss the pressure safety valve vs pressure relief valve.
A pressure relief valve is a device that releases pressure from a system. The relief valve is generally immune to the effects of back pressure and must be periodically stripped down. Pressure relief valves are one the essential parts of a pressure system to prevent system failures. They are set to open at a predetermined pressure level. Each pressure system has a setpoint that is a predetermined limit. The setpoint determines when the valve will open and prevents overpressure.
Pressure relief valves are typically used in gas or liquid systems where there is a need to prevent excessive pressure from building up. When the pressure in the system reaches a certain level, the valve will open and release the pressure. Pressure relief valves are an essential safety feature in many designs and can help to prevent damage to the system or components.
PRVs are generally considered to be safe and reliable devices. However, before installing a PRV in a system, some potential disadvantages should be considered. Here are five pros and cons of pressure relief valves:
Pros: Pressure relief valves are anessential safety feature in many systems. They protect against over-pressurization by relieving excess pressure from the system. This can help to prevent severe damage or even explosions.
Pressure relief valves can help to improve the efficiency of a system. The system can operate at lower overall pressure by relieving excess pressure and saving energy.
Pressure relief valves can be used as a safety device in systems that are susceptible to overpressurization. By relieving pressure before it builds up to a dangerous level, they can help to prevent accidents and injuries.
Cons: Pressure relief valves can be a potential source of leaks. If not properly maintained, the valve may not seat properly and can allow fluids or gasses to escape.
Pressure relief valves can sometimes cause problems if they do not open or close properly. This can lead to process disruptions and may cause safety issues.
A pressure safety valve is a device used to release pressure from a system that has exceeded its design limit. This safety valve is a fail-safe device. This type of valve is typically used in systems that contain fluids or gasses under high pressure. Pressure safety valves are designed to open and release pressure when the system has exceeded its maximum pressure limit. This helps to prevent the system from rupturing or exploding.
Pressure safety valves are an essential part of many different types of systems and can help keep both people and property safe. If anyone is ever in a situation where they need to release pressure from a system, it is essential to know how to use a pressure safety valve correctly.
A pressure safety valve (PSV) is a type used to relieve a system’s pressure. PSVs are commonly used in chemical and process industries, as well as in some kinds of pressure vessels. There are both advantages and disadvantages to using a PSV. Some of the pros of using a PSV include: PSVs can help to prevent overpressurization, which can be dangerous.
A safety valve is a pressure relief device used to prevent the over-pressurization of a system. On the other hand, a relief valve is a device used to relieve pressure from a system that is already overpressurized. Function Of Pressure Relief Valve Vs Safety Valve
The function of a pressure relief valve is to protect a system or component from excess pressure. A safety valve, on the other hand, is designed to protect from overpressurization. Both types of valves are used in various industries, but each has unique benefits and drawbacks.
Pressure relief valves are typically used in systems where a small amount of overpressure can cause damage. On the other hand, safety valves are designed for systems where overpressurization could be catastrophic. Both valves have advantages and disadvantages, so choosing the right type of valve for the specific application is essential.
Relief valves are usually set to open at a specific pressure and will close once the pressure has been relieved. Safety valves are similar in that they are also used to protect equipment from excessive pressure. However, safety valves are designed to stay open until they are manually closed. This is because safety valves are typically used in applications where it is not safe to have a closed valve, such as in a gas line. Operation Of Safety Relief Valve Vs Pressure Relief Valve
Two types of valves are commonly used in industrial settings: relief valves and safety valves. Both of these valves serve essential functions, but they operate in different ways.
Relief valves are designed to relieve pressure build-up in a system. They open when the system pressure reaches a certain point, which allows excess pressure to be released. On the other hand, safety valves are designed to prevent accidents by preventing system pressure from getting too high. They open when the system pressure reaches a certain point, which allows excess pressure to be released before an accident can occur.
So, which valve is better? That depends on the situation. A relief valve is the better option to protect the system from pressure build-up. If anyone need to protect the system from accidents, then a safety valve is the better option Setpoint Of Pressure Relief Valve Vs Safety Relief Valve
The relief valve is made to open when it reaches a specific pressure, commonly described as a “setpoint”. Setpoints shouldn’t be misinterpreted as the pressure set. A setpoint on a relief valve is set to the lowest possible pressure rating, which means it is set to the lowest system pressure before an overpressure situation is observed. The valve will open as the pressure increases to a point higher than the setpoint. The setting point is determined as pounds per square inch (PSIG) and should be within the maximum allowed operating pressure (MAWP) limits. In safety valves, the setpoint is typically placed at about 3 percent over the working pressure level, whereas relief valves are determined at 10 percent.
No, the safety valve and relief valve can not be used interchangeably. Though both valves are seal butterfly valve and used for safety purposes, they serve different functions. A safety valve relieves excess pressure that builds up in a system, while a relief valve regulates the pressure in a system.
Knowing the difference between these two types of valves is essential, as using the wrong valve for the intended purpose can potentially be dangerous. If unsure which type of valve to use, it is always best to consult with a professional.
A few key points help us understand the safety valve vs pressure relief valve. Safety valves are designed to relieve pressure in a system when it gets too high, while relief valves are designed to relieve pressure when it gets too low. Safety valves are usually set to open at a specific pressure, while relief valves are generally open at a particular vacuum. Safety valves are typically intended for one-time use, while relief valves can be used multiple times. Choose the trusted valve manufactureraccording to the specific business needs.
As you already know, there are a multitude of pressure relief valves out there. In the industry, we tend to use terms like safety valve and relief valve interchangeably. And for the most part, this makes sense. Most pressure relief valves are designed to do the same thing — release pressure in a system.
But is there a difference between some of these commonly used terms, and if so, what does it mean for you? Here’s a quick breakdown of two popular terms: safety valve vs. relief valve.
While both terms refer to valves used to release pressure from a pressurized system, their technical definitions are a bit different. In general, the term relief valve refers to a valve within a pressurized system that is used to control pressure for the optimal functionality of the system. Relief valves are designed to help your facility avoid system failures, and protect equipment from overpressurized conditions.
The term safety valve, on the other hand, refers to pressure valves that are designed to protect people, property, and processes. In other words, the term safety valve refers to a failsafe, last resort valve that will release pressure to prevent a catastrophe, usually in the event that all other relief valves have failed to adequately control pressure within a system.
The general purpose of both safety valves and relief valves are the same. Both are pressure relief valves, and they are designed to let off pressure in any situation where a system becomes overpressurized. That said, relief valves and safety valves do function slightly differently:
Relief Valves are designed to control pressure in a system, most often in fluid or compressed air systems. These valves open in proportion to the increase in system pressure. This means they don’t fly all the way open when the system is slightly overpressure. Instead, they open gradually, allowing the system to return to the preset pressure level. When that level is reached, the valve shuts again.
Safety Valves are used for one reason — safety. Instead of controlling the pressure in a system, they’re designed to immediately release pressure in the event of an emergency or system failure. Unlike relief valves, safety valves open immediately and completely to avoid a disaster, rather than to control the pressure of a system.
While both safety valves and relief valves work to release excess pressure, the way they go about it is a little different. Check out this table, courtesy of Difference Between, for a little more information about the differences between the two valves:
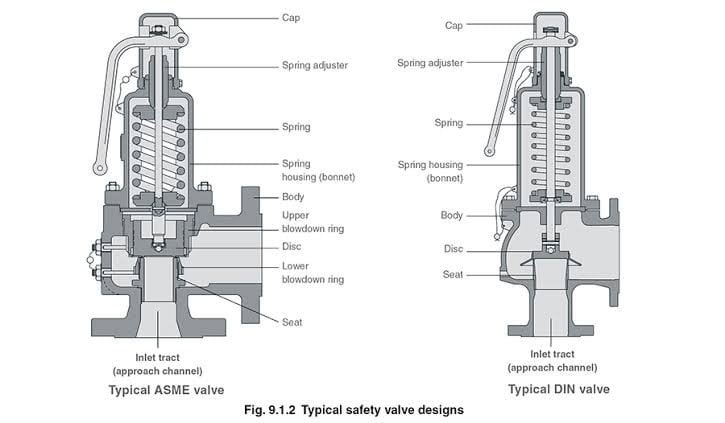
Whenever we talk about the pressure in the process industries we come across two types of safety equipments and that is the safety v/v and the relief v/v.
Most of us think that both are same thing but that’s not the case. Though their functions are same yet there are certain differences among them. Both of them are used in the industry to prevent the accumulation of excess pressure, but there are operational differences between them.
Relief valves which are also known as Pressure relief valves are one of the protective devices which are used to protect a pressurize working system and equipments from getting damaged due to an over-pressure or excessive pressure conditions.
In every pressurized working system there is a set pressure under which the system works properly and efficiently, this set pressure is known as set point and when the pressure is above set point the relief valve opens and the excess pressure is released.
It is made very sensitive such that even for a slight increment in the pressure lifts the safety valve and gets closed quickly as soon as the pressure is released to maintain the desired pressure in the vessel.
1. A relief valve is a device used to limit the pressure in the system within certain specified limit or a set level.A safety valve is a device designed to actuate automatically when the pressure becomes excess.
2. The opening of a relief Valve is directly proportional to the increase in the vessel pressure.2. A safety valve opens almost immediately and fully in order to prevent over pressure condition.
3. A relief valve opens when the pressure reached the specific limit and it is usually operated by an operator.3. The purpose of the safety valve is mainly to safeguard people, property and the environment. It operates without any human intervention.
4. The set point of a relief valve is usually set at 10% above working pressure.4. The set point of safety valve is usually set at 3 % above working pressure.
5. Relief valves are categorized into pop-type, direct-operated, pilot-operated, and internal relief valves.5. Safety valves are divided into wide variety of types based on their applications and performance in different areas of use.
From the definition of both the valves we can conclude that the relief v/v which is also known as the pressure relief v/v is a safety device which is used to maintain a proper preset pressure in the vessel or the system within a prescribed limit condition to prevent a situation of over pressure.
On the other hand, the safety valve is a protective device which is used in a system to control the pressure inside the system under a predetermined limit.
The pressure relief valves are generally used in the hydraulic systems to control the pressure within specified limit and when the pressure increases than the preset value.
It lifts up and provide an escape of the excess pressure through an alternate channel or bypass provided in the system back to the source from where the input is coming or may be a different chamber provided to accept the excess of the liquid.
On contrary in case of safety valve, the main function of the safety valve is to provide safety to the property, life, and the environment which can get damaged due to failure of the system because of the excess pressure.
The pressure relief valves are generally used in the hydraulic systems to control the pressure within specified limit and when the pressure increases than the preset value, it lifts up and provide an escape of the excess pressure through an alternate channel or bypass provided in the system back to the source from where the input is coming or may be a different chamber provided to accept the excess of the liquid.
On contrary in case of safety valve, the main function of the safety valve is to provide safety to the property, life, and the environment which can get damaged due to failure of the system because of the excess pressure.
We used the set point in case of the relief valve, the “Set Point” basically refers to a point set to the lowest maximum pressure rating which means that the pressure is set below the maximum operative pressure which is allowed for a system to operate without being get into the state of overpressure.
In Simple words we can say that the relief valve pressure is set to maintain and control the pressure inside the system, the set pressure is dependent on the working pressure of the system.
On the other hand , the pressure of safety valve is set on the basis of various factors of consideration like the material used, the environment in which it has to be used, the type of work it has to perform.
The boilers material used for 6 Bar will have the materials which can withstand upto 12 Bar (it depends on the manufacturer) So the Safety valve will be set to 7-8 bar so as to prevent the boiler failure.
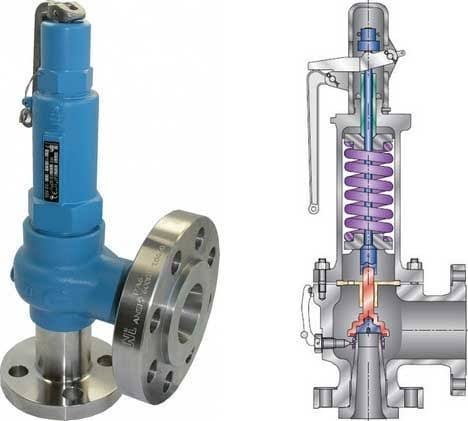

As soon as mankind was able to boil water to create steam, the necessity of the safety device became evident. As long as 2000 years ago, the Chinese were using cauldrons with hinged lids to allow (relatively) safer production of steam. At the beginning of the 14th century, chemists used conical plugs and later, compressed springs to act as safety devices on pressurised vessels.
Early in the 19th century, boiler explosions on ships and locomotives frequently resulted from faulty safety devices, which led to the development of the first safety relief valves.
In 1848, Charles Retchie invented the accumulation chamber, which increases the compression surface within the safety valve allowing it to open rapidly within a narrow overpressure margin.
Today, most steam users are compelled by local health and safety regulations to ensure that their plant and processes incorporate safety devices and precautions, which ensure that dangerous conditions are prevented.
The principle type of device used to prevent overpressure in plant is the safety or safety relief valve. The safety valve operates by releasing a volume of fluid from within the plant when a predetermined maximum pressure is reached, thereby reducing the excess pressure in a safe manner. As the safety valve may be the only remaining device to prevent catastrophic failure under overpressure conditions, it is important that any such device is capable of operating at all times and under all possible conditions.
Safety valves should be installed wherever the maximum allowable working pressure (MAWP) of a system or pressure-containing vessel is likely to be exceeded. In steam systems, safety valves are typically used for boiler overpressure protection and other applications such as downstream of pressure reducing controls. Although their primary role is for safety, safety valves are also used in process operations to prevent product damage due to excess pressure. Pressure excess can be generated in a number of different situations, including:
The terms ‘safety valve’ and ‘safety relief valve’ are generic terms to describe many varieties of pressure relief devices that are designed to prevent excessive internal fluid pressure build-up. A wide range of different valves is available for many different applications and performance criteria.
In most national standards, specific definitions are given for the terms associated with safety and safety relief valves. There are several notable differences between the terminology used in the USA and Europe. One of the most important differences is that a valve referred to as a ‘safety valve’ in Europe is referred to as a ‘safety relief valve’ or ‘pressure relief valve’ in the USA. In addition, the term ‘safety valve’ in the USA generally refers specifically to the full-lift type of safety valve used in Europe.
Pressure relief valve- A spring-loaded pressure relief valve which is designed to open to relieve excess pressure and to reclose and prevent the further flow of fluid after normal conditions have been restored. It is characterised by a rapid-opening ‘pop’ action or by opening in a manner generally proportional to the increase in pressure over the opening pressure. It may be used for either compressible or incompressible fluids, depending on design, adjustment, or application.
Safety valves are primarily used with compressible gases and in particular for steam and air services. However, they can also be used for process type applications where they may be needed to protect the plant or to prevent spoilage of the product being processed.
Relief valve - A pressure relief device actuated by inlet static pressure having a gradual lift generally proportional to the increase in pressure over opening pressure.
Relief valves are commonly used in liquid systems, especially for lower capacities and thermal expansion duty. They can also be used on pumped systems as pressure overspill devices.
Safety relief valve - A pressure relief valve characterised by rapid opening or pop action, or by opening in proportion to the increase in pressure over the opening pressure, depending on the application, and which may be used either for liquid or compressible fluid.
In general, the safety relief valve will perform as a safety valve when used in a compressible gas system, but it will open in proportion to the overpressure when used in liquid systems, as would a relief valve.
Safety valve- A valve which automatically, without the assistance of any energy other than that of the fluid concerned, discharges a quantity of the fluid so as to prevent a predetermined safe pressure being exceeded, and which is designed to re-close and prevent further flow of fluid after normal pressure conditions of service have been restored.

Safety valve is a special valve that the opening and closing parts are normally closed under the action of external force. When the medium pressure in the equipment or pipeline increases beyond the specified value, the medium pressure in the pipeline or equipment is prevented from exceeding the specified value by discharging the medium outside the system. Safety valve belongs to automatic valve category, which is mainly used in boiler, pressure vessel and pipeline. The control pressure does not exceed the specified value, which plays an important role in protecting personal safety and equipment operation. Note the safety valve can only be used after pressure test.
In most cases, the safety valve is the last safety defense line. If the above safety measures fail, the safety valve will take off and release pressure to prevent the pressure in the pressure equipment from exceeding the design allowable value. Safety valve is a kind of intrinsic safety protection measure. It takes off automatically by spring force and medium force, without any manual participation and external force participation, so as to prevent the safety accident caused by human misoperation. The function of the safety valve is realized through the following action process: when the system reaches the maximum allowable pressure, the safety valve can be opened accurately, and can discharge stably with the increase of the system pressure, and can discharge the rated amount of working medium under the rated discharge pressure. When the system pressure drops to a certain value, it should be closed in time, and keep the necessary sealing under the closed state Sex.
According to the different overall structure and loading mechanism, the common types of safety valve are spring loaded safety valve, balance bellows safety valve and pilot safety valve.
Spring loaded safety valve is a common safety valve, which overcomes the force produced by the medium pressure under the valve disc by the closing force of the spring. If the medium is harmless to people and the environment, such as non-toxic, non flammable and low-cost, such as air, it can be directly discharged into the atmosphere, in this case, the ordinary safety valve is used.
Balanced bellow safety valve, the effective area of the bellow is equal to the area of the sealing surface of the valve seat, which is used to counteract the effect of back pressure on the set pressure. It is suitable for the working conditions of high temperature and pressure, high back pressure or the medium can not be directly discharged into the atmosphere.
The pilot type safety valve is usually composed of a main valve with a movable unbalanced disc and an external pilot valve (piston). It drives or controls the opening and closing of the main valve by means of the medium discharged from the pilot valve. Compared with the balanced bellows type safety valve, its back pressure compensation coefficient is higher, which reduces the influence of back pressure on the action characteristics to a minimum and the discharge volume is large. For example, in the process of overpressure, the discharge of medium in the reactor is very large. If the balance bellows type safety valve is used, 16 sets are needed at most. If the pilot type safety valve is selected, 8 sets are enough, or even less. It will bring many advantages to users, such as less installation, less maintenance, less work and convenient maintenance. Of course, the technical complexity of the pilot safety valve is high, which puts forward higher requirements for the technical level of operators.
In the load spring safety valve, the valve closing pressure or spring force is applied by the coil spring under the pressure of the adjusting screw. The spring force is transferred to the disc through the stem. As long as the spring force is greater than the force generated at the inlet of the safety valve, the valve disc will seal the nozzle. The following figure shows the expanded nozzle and disc area of the relief valve at the pressure acting on the disc.
According to the preset conditions, the safety valve will open at the preset pressure. The spring force FS is applied in the closing direction, and the force FP generated by the pressure at the inlet of the safety valve is applied in the opening direction. When the pressure FS and medium force FP reach a balance, there is no force to place the valve disc on the valve seat; at this time, the safety valve will start to leak, and the sound of medium discharge can be seen or heard (the sound of medium just discharged).
Before the safety valve is obviously opened, the pressure at the valve inlet must be increased above the set pressure. Due to the flow restriction between the disc and the adjusting ring, the pressure gradually increases in this so-called mixing chamber. This pressure now acts on the expanded disc area, further increasing the pressure FP, which overcomes the additional force required to enter a compression spring. The valve will open quickly with a “bang” and in most cases it will be fully open. Overpressure refers to the pressure increase beyond the necessary set pressure of the safety valve to achieve full opening and full displacement of the valve. This overpressure is usually expressed as a percentage of the set pressure. The value is usually 10%, between 3% and 21% according to relevant specifications and applications.
In most applications, the proper size of safety valve will reduce the pressure when the vessel is discharged. The pressure of the vessel will drop at any subsequent point in time, but not later than the end of the pre-set condition. A decrease in pressure in the vessel will reduce the pressure FP. However, at set pressure, flow still acts on the expanded disc area, which opens the valve. Further pressure reduction is required before the spring force FS exceeds FP again and the relief valve begins to close again. Moreover, under the so-called reseating pressure, the disc will contact the nozzle again and the safety valve will close again. Return pressure difference refers to the difference between the set pressure of the safety valve and the return pressure, which is calculated as a percentage of the set pressure. According to the definition of relevant codes and standards, the reseating differential pressure is generally – 7% to – 10%, and it is – 4% to – 20% according to relevant codes and services (steam, gas or liquid).
API 526 safety valve series has a down regulating ring, and its set pressure is defined as the set pressure of the valve when the pressure reaches the initial discharge sound.
It is important to understand that the operating pressure of the protected equipment should be less than the reseating pressure of the safety valve. Most manufacturers and relevant codes and standards recommend that the difference between the reseating pressure and the operating pressure of 3% – 5% can achieve reasonable adjustment of the valve seat, and can again achieve good tightness of the valve seat.
Because the area of the pressure chamber is larger than the area of the main valve seat, the closing pressure is larger than the opening pressure. This allows the main valve to close tightly.
When the pressure reaches the set pressure, the pilot relief valve is activated. The medium will no longer lead to the pressure chamber (see Figure). This prevents further pressure rise in the pressure chamber.
At the same time, the pressure of the pressure chamber is discharged. Results the closing pressure of the main valve disappeared, which provided the precondition for the system overpressure to push the main valve to open.
The main valve is open. According to the design of pilot safety valve, there are two opening modes of safety valve, one is quick and thorough (quick opening action), the other is gradual and local (regulating action).
When the pressure in the pressure chamber increases, the main valve can be closed again through quick and thorough (quick opening action) or gradual local (regulating action).
Safety valve, also known as overflow valve, is a special valve that the opening and closing parts are normally closed under the action of external force. When the medium pressure in the equipment or pipeline increases beyond the specified value, the medium pressure in the pipeline or equipment is prevented from exceeding the specified value by discharging the medium outside the system. Safety valve belongs to automatic valve category, which is mainly used in boiler, pressure vessel and pipeline. The control pressure does not exceed the specified value, which plays an important role in protecting personal safety and equipment operation. Note the safety valve can only be used after pressure test.
The figure shows several typical structures of the safety valve. Fig. A is a piston type safety valve with a flat valve core. The air source pressure acts on piston A. when the pressure exceeds the safety value determined by the spring force, piston a is jacked open and part of the compressed air is discharged into the atmosphere from the valve port; when the air source pressure is lower than the safety value, the spring drives the piston to move down and close the valve port.
Figure B and figure C are ball valve type and diaphragm type safety valves respectively, with the same working principle as piston type. These three kinds of safety valves are all spring-loaded to provide control force. Adjusting the spring preload can change the safety value, so they are called direct acting safety valves.
Fig. D is a pilot type safety valve. The small direct acting valve provides control pressure to act on the diaphragm. The hard core on the diaphragm is the valve core, which is pressed on the valve seat. When the air source pressure a is greater than the safety pressure, the valve core is opened, and the compressed air is discharged into the atmosphere from the left output hole. The pressure characteristics of the diaphragm safety valve and the pilot safety valve are good and the action is sensitive, but the maximum opening force is relatively small, that is, the flow characteristics are poor. In practical application, the type of safety valve should be selected according to the actual needs, and its diameter should be selected according to the maximum exhaust volume.
① before leaving the factory, the opening pressure of the safety valve shall be adjusted one by one to the setting value required by the user. If the user puts forward the working pressure level of the spring, it shall be adjusted according to the lower limit value of the pressure level.
② before installing the safety valve on the protected equipment or before installation, the user must readjust it on the installation site to ensure that the set pressure value of the safety valve meets the requirements.
④ before rotating the adjusting screw, the inlet pressure of the valve shall be reduced below 90% of the opening pressure to prevent the valve disc from being driven to rotate when rotating the adjusting screw, so as to damage the sealing surface.
⑤ in order to ensure the accuracy of the opening pressure value, the medium conditions during adjustment, such as medium type and temperature, shall be close to the actual operation conditions as much as possible. With the change of medium type, especially when the accumulation state of medium is different (for example, from liquid phase to gas phase), the opening pressure often changes. When the working temperature increases, the opening pressure generally decreases. Therefore, when it is adjusted at room temperature and used at high temperature, the set pressure at room temperature shall be slightly higher than the required opening pressure. The degree to which it is related to the valve structure and material selection shall be based on the manufacturer’s instructions.
⑥ when the conventional safety valve is used to fix additional back pressure, the setting value should be less than the required back pressure when the opening pressure is adjusted after testing.
① to adjust the discharge pressure and reseating pressure of the valve, the action test of the valve reaching the full opening height must be carried out. Therefore, it can only be carried out on the large capacity test device or after the safety valve is installed on the protected equipment. The adjustment method depends on the valve structure.
② for the structure with recoil plate and valve seat adjusting ring, the valve seat adjusting ring is used for adjustment. Screw out the fixing screw of the adjusting ring, extend a thin iron bar or other tools from the exposed screw hole, and then move the teeth on the adjusting ring to make the adjusting ring rotate left and right. When the adjusting ring rotates counterclockwise to the left, its position increases, and the discharge pressure and the reseating pressure decrease. On the contrary, when the adjusting ring is rotated clockwise, its position will decrease, and the discharge pressure and reseating pressure will increase. For each adjustment, the adjustment: the rotation range of the ring should not be too large (generally, the number of teeth can be turned). After each adjustment, screw on the fixing screw so that its end is located in the groove between the two teeth of the adjusting ring, which can not only prevent the adjusting ring from turning, but also do not generate radial pressure on the adjusting ring. For the sake of safety, the inlet pressure of the safety valve shall be properly reduced (generally lower than 90% of the opening pressure) before the adjusting ring is moved to prevent the valve from suddenly opening during the adjustment, causing accidents.
③ for the structure with up and down regulating rings (one regulating ring on the guide sleeve and one regulating ring on the valve seat), the adjustment is more complicated. The valve seat adjusting ring is used to change the size of the channel between the disc and the adjusting ring, so as to change the accumulation of pressure in the chamber between the disc and the adjusting ring when the valve is initially opened. When the valve seat adjusting ring is raised, the degree of pressure accumulation increases, so that the valve proportional opening stage is reduced and the sudden rapid opening is achieved quickly. Therefore, raising the valve seat adjusting ring can reduce the discharge pressure. It should be noted that the seat adjusting ring can not be raised too close to the disc. In this way, the leakage at the sealing surface may cause the valve to open prematurely and suddenly, but because the medium pressure at this time is not enough to keep the valve disc in the open position, the valve disc will close immediately, so the valve will jump frequently. Valve seat adjustment: the ring is mainly used to reduce the valve proportion, the opening stage and adjust the discharge pressure, but also has an impact on the reseating pressure.
The upper pitch ring is used to change the angle of the flow medium after reflection at the lower side of the valve disc, so as to change the magnitude of the fluid force, so as to adjust the reseating pressure. When the upper pitch ring is raised, the turning angle decreases, and the fluid force decreases accordingly, so that the reseating pressure increases. On the contrary, when the upper adjusting ring is lowered, the reseating pressure is reduced. Of course, when the upper regulating ring changes the reseating pressure, it also affects the discharge pressure. That is to say, raising the upper regulating ring will increase the discharge pressure, and lowering the upper regulating ring will reduce the discharge pressure, but the effect is not as obvious as the reseating pressure.
After the adjustment of the safety valve, it shall be sealed with lead to prevent any change of the adjusted condition. When repairing the safety valve, the position of adjusting screw and adjusting ring shall be recorded before disassembling the valve, so as to facilitate the adjustment after finishing. Lead sealing shall be applied again after readjustment.
Safety valve is widely used in: steam boiler, liquefied petroleum gas tank car or liquefied petroleum gas railway tank car, oil production well, high pressure bypass of steam power generation equipment, pressure pipeline, pressure vessel, etc.
The safety valve is suitable for clean, particle free, low viscosity fluid. Where it is necessary to install a safety relief device but not suitable for installing a safety valve, a bursting disc shall be installed or the safety valve shall be used in series with the bursting disc.
1. Independent pressure system (with shut-off valve separated from other systems). The system refers to all gas phase, all liquid phase or gas phase connection;
After discharge, the valve disc does not return to its seat: This is mainly caused by the bent stem of spring, incorrect installation position of valve disc or being stuck. It should be reassembled.
Leakage: under the normal working pressure of the equipment, leakage between the valve disc and the sealing surface of the valve seat exceeds the allowable level. The reason is: there is dirt between the valve disc and the sealing surface of the valve seat. The lifting wrench can be used to open the valve several times to wash away the dirt; the sealing surface is damaged. According to the degree of damage, it shall be repaired by grinding or grinding after turning; the valve rod shall be bent, tilted or the lever and fulcrum shall be skewed to make the valve core and disc misplaced. It shall be reassembled or replaced; the spring elasticity shall be reduced or lost. The spring shall be replaced and the opening pressure shall be readjusted.
The safety valve does not open when it reaches the specified pressure: the reason for this situation is the inaccurate constant pressure. The compression amount of the spring or the position of the heavy hammer shall be readjusted; the disc and the valve seat shall be stuck. The safety valve shall be subject to manual air release or water discharge test regularly; the lever of the lever type safety valve is stuck or the heavy hammer is moved. The position of the hammer should be readjusted and the lever should move freely. [span]
The pressure continues to rise after exhaust: This is mainly because the displacement of the selected safety valve is less than the safe discharge capacity of the equipment, so the appropriate safety valve should be re selected; the valve rod center line is not correct or the spring is rusted, so that the valve disc cannot be opened to the proper height, so the valve rod should be re assembled or the spring should be replaced; if the section of the exhaust pipe is not enough, the exhaust pipe conforming to the safe discharge area should be adopted.
Safety valve disc frequency jump or vibration: mainly due to the spring stiffness is too large. The spring with proper rigidity should be used; the adjustment ring is not adjusted properly, so that the reseating pressure is too high. The position of the adjusting ring should be readjusted; the resistance of the discharge pipe is too large, resulting in excessive discharge back pressure. The discharge pipe resistance shall be reduced.
The safety valve is opened when the specified pressure is not reached: the main reason is that the constant pressure is not correct; the aging spring force decreases. The adjusting screw shall be tightened properly or the spring shall be replaced.
According to the diversity and complexity of coal chemical system pressure and medium, the influence of temperature, pressure, medium and other factors in the equipment shall be considered when selecting the safety valve, and the appropriate safety valve model shall be configured according to the flow diameter and diameter of the safety valve according to the design requirements. When determining the safety valve, its nominal pressure must be greater than the set pressure. When the valve reaches full opening, the pressure cannot exceed the nominal pressure of the safety valve. The smaller the working pressure range of the spring is, the better the working performance of the safety valve will be.
(1) If the non-toxic and pollution-free medium is allowed to leak to the atmosphere, open full open safety valve with valve cap shall be selected; if regular opening test is required for safety valve, safety valve with lifting wrench shall be selected. When the medium pressure reaches more than 75% of the set pressure, lifting wrench shall be used to check the flexibility of valve opening.
(2) Closed safety valve must be used for toxic or flammable medium, and good sealing shall be provided at the valve cover and protective cover gasket to ensure that the discharged medium does not leak out. After the safety valve takes off, the medium shall be discharged according to the specified outlet, and air tightness test shall be conducted at the same time.
(3) In the case of high back pressure, the back pressure balanced safety valve or pilot safety valve shall be selected. If necessary, two safety valves for mutual standby shall be installed. The mechanical interlock device shall be used for the inlet and outlet shut-off valve to meet the medium discharge required by the equipment during maintenance.
(4) The bellows safety valve shall be selected for the medium with high toxicity, strong corrosion and extreme danger. The bellows safety valve uses bellows to isolate the spring and guide mechanism from the medium, eliminate the impact of back pressure fluctuation on the valve performance, and protect the spring and other internal parts from medium corrosion.
① when the operating temperature of the closed safety valve exceeds 250 ℃ and the operating temperature of the open safety valve exceeds 350 ℃, the safety valve with radiator shall be selected;
② when the gas medium pressure in the equipment is greater than 3.0 MP, and when the temperature exceeds 235 ℃, the safety valve with radiator shall be used.
Safety valve is an important accessory of pressure limiting and pressure relief for special equipment (boiler, pressure vessel, pressure pipeline, etc.). Therefore, pay attention to the following points when setting the safety valve:
(2) when the safety valve is used for discharging flammable liquid, the outlet of the safety valve shall be connected with the emergency storage tank. When the discharged material is high temperature combustible, the receiving container shall be equipped with corresponding protective facilities.
(3) the general safety valve can be vented locally, and the vent port shall be more than 1 meter (m) higher than the operator, and shall not face the open fire location, spark emission location and high-temperature equipment within 15 meters (m). The vent of safety valve of indoor equipment and container shall lead out from the roof and be more than 2m (m) higher than the roof.
(4) when there is a block valve at the inlet of the safety valve, the block valve shall be in the normally open state and shall be lead sealed to avoid mistakes.
(1) the cross-sectional area of the through-hole of the connecting pipe and pipe fitting between the safety valve and the boiler or pressure vessel shall not be less than the inlet cross-sectional area of the safety valve; if several safety valves share one inlet pipe, the flow cross-sectional area of the inlet pipe shall not be less than the sum of the inlet cross-sectional area of the safety valve.
(2) generally, stop valve shall not be installed between safety valve and boiler drum or header, or take out pipe of steam. It is generally not suitable to install stop valve or other outlet pipe between safety valve and pressure vessel; for pressure vessel containing highly toxic, highly and moderately hazardous, inflammable, corrosive, viscous medium or precious medium, stop valve can be installed between safety valve and pressure vessel only with the approval of the technical director in charge of pressure vessel of the user and the formulation of reliable preventive measures 。 During normal operation of the pressure vessel, the stop valve must be kept fully open, sealed or locked with lead. The structure and diameter of the stop valve shall not hinder the safety relief of the safety valve.
(3) the spring-loaded safety valve with threaded connection shall be connected with the short pipe with thread, and the short pipe shall be welded with the simplified body and header.
(4) the safety valve must be equipped with discharge pipe. The drain pipe shall avoid twists and turns as much as possible to minimize resistance. The discharge pipe shall be directly connected to a safe place and have sufficient circulation cross-sectional area to ensure smooth exhaust. For the safety valve that can interact with each other to produce chemical reaction, it is not allowed to share a discharge pipe; when the safety valve is installed on the equipment with corrosive and combustible gas, anti-corrosion or anti fire and explosion measures shall also be taken during discharge; when the equipment with safety valve is toxic medium, and the vapor density of the medium is greater than the air density, the medium and steam discharged from the safety valve shall be introduced to Closed system, and recovered from closed system to use in production.
(6) the safety valve installed in the open air shall be provided with reliable measures to prevent the discharge of the safety valve from being affected by the freezing of the water contained in the valve medium when the temperature is lower than 0oC.
(7) when the medium crystallization temperature of the safety valve is higher than the minimum ambient temperature, the safety valve must be equipped with insulation jacket, and installed with insulation purging steam to prevent the medium crystallization from blocking the safety valve and affecting the normal operation performance of the safety valve. The inlet and outlet pipes of the safety valve must also be designed with steam insulation jacketed pipe or added with insulation steam tracing pipe to prevent medium crystallization from blocking the pipe.
Due to different production requirements, equipment properties and process requirements, safety valve standards adopted are also different. Common international standards include ASME, API, ISO, JIS, DIN, BS, ghost, etc. common domestic standards include GB, JB and TSG There are some differences in the regulations of safety valve in each standard.
When marking the working temperature andWorking pressureWhen working pressure must be marked with P and attached to the lower right corner of the P word.mediumThe maximum temperature is the integer obtained from the maximum temperature of 10 except the medium. For example, the working temperature is 540 C and the working pressure is 10MPa.valveIts code name is P54100.
1. The safety valve shall be equipped with a device to prevent the hammer from moving by itself and a guide frame to limit the lever from deviating. The spring safety valve shall be equipped with a device to lift the handle and prevent the adjustment screw from being unscrewed at will.
2. It shall be installed vertically at the highest position of the boiler manufacturer and header. Between the safety valve and the drum or header, there shall be no outlet pipe and valve for taking steam.
3. The cross-sectional area of the connecting pipe between the safety valve and the boiler shall not be less than the cross-sectional area of the inlet of the safety valve. If several safety valves are installed together on a short pipe directly connected to the drum, the passage cross-sectional area of the short pipe shall not be less than 1.25 times of the exhaust area of all safety valves.
4. For the boiler with rated steam pressure less than or equal to 3.82MPa, the safety valve throat diameter shall not be less than 25mm; for the boiler with rated steam pressure greater than 3.82MPa, the safety valve throat diameter shall not be less than 20mm.
5. Generally, the safety valve shall be equipped with exhaust pipe, which shall be directly connected to the safety place and have sufficient cross-sectional area to ensure smooth exhaust. The bottom of the vent pipe of the safety valve shall be equipped with a drain pipe connected to the safety place. It is not allowed to install a valve on the vent pipe and drain pipe.
6. The safety valve of pressure vessel should be directly installed on the highest position of pressure vessel. The safety valve of liquefied gas storage tank must be installed at the gas phase position. Generally, short pipe can be used to connect with the vessel, so the diameter of the short pipe of the safety valve shall not be less than the valve diameter of the safety valve.
7. Generally, no valve shall be installed between the safety valve and the container. For the container with inflammable, explosive or viscous medium, in order to facilitate the cleaning or replacement of the safety valve, a stop valve can be installed. The stop valve must be fully opened and lead sealed during normal operation to avoid disorderly movement.
8. For boilers with rated evaporation capacity greater than 0.5t/h, at least two safety valves shall be installed; for boilers with rated evaporation capacity less than or equal to 0.5t/h, at least one safety valve shall be installed. Safety valves must be installed at the outlet of separable economizer and steam superheater.
9. For the pressure vessel with inflammable, explosive or toxic medium, the medium discharged by the safety valve must have safety device and recovery system. The installation of the lever type safety valve must be kept in a vertical position, and the spring safety valve should also be installed vertically to avoid affecting its action. During installation, attention shall also be paid to fit, coaxiality of parts and uniform stress of each bolt.
10. The outlet of the safety valve shall be free of resistance to avoid back pressure. If a discharge pipe is installed, its inner diameter shall be larger than the outlet diameter of the safety valve. The discharge port of the safety valve shall pay attention to antifreeze. For containers containing inflammable, toxic and highly toxic media, the discharge pipe shall be directly connected to the outdoor safe place or have facilities for proper treatment. No valve is allowed to be installed in the discharge pipe.
11. The newly installed safety valve shall be attached with the product certificate. Before installation, it shall be recalibrated, lead sealed and safety valve calibration shall be issued.
12. No valve shall be installed between pressure equipment and safety valve. For containers containing inflammable, explosive, toxic or viscous media, in order to facilitate replacement and cleaning, stop valve can be installed. Its structure and size shall not hinder the normal operation of safety valve. In normal operation, the stop valve must be fully opened and sealed with lead.
When the operation of coal chemical system is not stable, the medium in the equipment is affected by the change of system pressure and temperature, the particles and impurities in the medium will rush into the valve body, and some solid impurities fall on the sealing surface, causing the gap between the valve core and the valve seat to cause leakage, forming pressure marks on the sealing surface, and forming pits and grooves caused by the corrosion of the medium between the sealing surfaces, resulting in the continuous leakage of the medium Or adhesion can not meet the production requirements, then the safety valve should be repaired.
The repair of safety valve is mainly the repair of the sealing surface of safety valve. Most of the safety valves on the chemical equipment are left with pungent chemicals after use. Attention shall be paid to the protection during disassembly. The valve body and spring of some safety valves are adhered with solidification medium. After disassembly, high temperature steam or other non corrosive cleaning agent shall be used to remove residues. The sealing surface of non-metallic material is generally replaced or turned after being damaged. The metal sealing surface is grinded when the damage is not serious. When lapping, the valve seat and the valve core must be separately lapping with a flat grinding tool. When the sealing surface is seriously damaged or has obvious pressing damage and other defects, use abrasive paste with particle size of 300-400 for initial grinding, then use abrasive paste with particle size of 600-800 for fine grinding, and finally use abrasive paste with particle size of 1000-1200 for polishing and fine grinding. Each time when changing the abrasive paste, it must be cleaned with acetone. When polishing and fine grinding, apply a small amount of abrasive paste to grind gently until it is bright. After grinding, put the valve core And the grinding paste on the sealing surface shall be cleaned up, and after several times of grinding, the sealing requirements shall be met.
Online calibration and calibration bench calibration are the two most commonly used calibration methods, and appropriate calibration methods are selected according to the operating conditions of equipment, medium type, operating pressure and other factors in coal chemical plant. The advantage of on-line calibration is that it is carried out when the equipment is running, the safety valve does not need to be disassembled from the equipment, and the calibration speed is fast, which is convenient for the calibration of welded safety valve. At the same time, the reseating pressure can be measured, and the calibration result is closer to the actual working condition; the disadvantage is that the calibration is dangerous, so the tightness test cannot be carried out. The calibration of the calibration bench is to open the safety valve through nitrogen, water and other media and record the opening pressure. The advantage is to solve the setting and leakage detection of the safety valve with normal temperature medium and working temperature below 250 ℃, save the adjustment time of the newly installed safety valve, reduce the energy consumption and reduce the work risk. The disadvantage is that there is an error between the operating temperature and the normal temperature (the spring becomes soft under high temperature), so it can only be opened The setting of starting pressure and sealing test can not verify the reseating pressure. During the calibration, it should be noted that the calibration bench should be used for the safety valve that cannot consider back pressure safety valve, high temperature or low temperature medium. The adjustment of calibration spring of high pressure safety valve can only be fine adjusted, and the air flow and water flow for calibration must be filtered.
During the calibration of safety valve, attention shall be paid to the adjustment of reseating pressure, which refers to the static pressure at the inlet of safety valve when the valve disc contacts the valve seat again with the decrease of system pressure, the valve opening height is zero, and the medium stops flowing out continuously. If the reseating pressure is too low and the medium outflow is large, the loss of medium and energy will be caused. If it is too high to discharge the system medium, the valve will have frequency jump. Therefore, in the case of rich experience, the reseating pressure will be adjusted as high as possible to reduce the loss of medium and energy. The adjustment method is to adjust the clearance through the adjusting ring. The smaller the clearance is, the greater the resistance when ejecting, the greater the force to hold the valve core to drop, the more difficult it is to reseat; the larger the clearance is, the easier it is to fall back, and the higher the reseating pressure is. Since the normal temperature calibration bench is unable to carry out the opening height and emission test, the regulating ring shall be kept in the factory state when the calibration bench is used to calibrate the safety valve.
(YaangPipe Industry is a leading manufacturer and supplier of nickel alloy and stainless steel products, including Super Duplex Stainless Steel Flanges, Stainless Steel Flanges, Stainless Steel Pipe Fittings, Stainless Steel Pipe. Yaang products are widely used in Shipbuilding, Nuclear power, Marine engineering, Petroleum, Chemical, Mining, Sewage treatment, Natural gas and Pressure vessels and other industries.)

5/1/2022 · That stated, relief valves and safety valves do function slightly differently: Relief Valves are made to control pressure inside a system, most frequently in fluid or compressed air systems. These valves open compared to the rise in system pressure. What this means is it normally won’t fly completely open once the product is slightly overpressure.
PRV: Pressure Relief Valve. A PRV is a type of safety valve. The valve opens gradually during normal operation to maintain an optimal pressure level inside the vessel. PSV: Pressure Safety Valve. If the PRV fails to maintain optimal pressure, the PSV kicks in. This valve opens quickly to avoid overpressurization when a set pressure is reached
In the most basic terms, the difference is that pressure control valves are the first line of defence and is therefore used for primary safety, while pressure relief valves are used as a last resort backup since they are used to maintain a pre-set downstream pressure.
1/2/ · 01/28/ 1:21 AM. The relief valve is supposed to regulate the pressure (the opening or the orifice is dependant upon the inlet pressure). The Pressure cooker top weighted nozzle is the relief valve. The safety valve opens to full flow when the pressure crosses the limit.
Relief valves are typically used for incompressible fluids such as water or oil. Safety valves are typically used for compressible fluids such as steam or other gases. Safety Valve Safety valves can often be distinguished by the presence of an external lever at the top of the valve body, which is used as an operational check.
Unlike relief valves, safety valves open immediately and completely to prevent a tragedy, instead of to manage pressure of the system. While both safety valves and relief valves try to release
Industry leading pressure and safety relief valve designs with over 140 years of technical and application expertise providing custom engineered solutions for O&G, Refining, Chemical, Petrochemical, Process and Power applications. Our designs meet global and local codes and standards (API 526; ASME Section I, IV & VIII; EN ISO 4126; PED & more
17/6/2005 · Similar idea to MintJulep, a Relief valve is an operational valve that is designed to open/close at lower pressure/vaccume, a Safety valve is to protect the equipment in exceptional circumstance. Mark Hutton 3 quark (Mechanical) 25 May 05 02:15 hmmm there are also expressions like Safety Relief Valves and Safety and Relief Valves.
17/6/ · What is a safety relief valve? The safety relief valve is a part that assists in the release of atmospheric pressure; or, in other words, it relieves the pressure outside a system. Thus, when the time comes, it will open fully and release the pressure, preventing an explosion. What is a pressure relief valve?
In addition, some of the benefits of using safety relief valve combined with bursting disc are: When in use, the rupture disc provides a superior process seal, therefore reducing fugitive emissions. Valves re-close after an over-pressure event, thus saving process media and allowing operation to continue until the bursting disc can be replaced.
The basic difference between a safety & relief valve: A relief valve relieves the pressure by relieving the fluid back into the system, to the low pressure side - eg. the relief valves of a positive displacement pump. A safety valve , on the other hand, relieves the pressure into the atmosphere i.e. out of the system. OR
A safety valve relieves excess pressure that builds up in a system, while a relief valve regulates the pressure in a system. Knowing the difference between these two types of valves is essential, as using the wrong valve for the intended purpose can potentially be dangerous.
11/7/ · Formally, a safety valve operates automatically, using the force of the gas or liquid to operate the action of the valve. However, some sources claim that a proper safety valve not only contains the automatic operation but a manual override as well, causing them to be slightly different than a standard relief valve.
SOme section 1 valves have dual outlets to reduce reaction loads on the piping. Section VIII valves are for unfired pressure vessels. The spring is usually enclosed, but open springs and/or alloy are optional. Rated capacity is at 10% overpressure,16% permissible with multiple valves and 21% permissible for Fire rating.
The safety valve belongs to the pressure release device, which can only operate when the working pressure exceeds the allowable range to protect the system. The relief valve can make the high-pressure medium quickly to meet the pressure requirements of the system and its working process is continuous.
1PC Body Threaded Ball Valve Overview Thread Ball Valve is a form of quarter-turn valve which uses a hollow, perforated and pivoting ball to control fluids flow through it. It is open when the ball"s hole is in line with the flow and closed when it is pivoted 90-degrees by the valve handle.
Safety valve This device is typically used for steam or vapor service. It operates automatically with a full-opening pop action and recloses when the pressure drops to a value consistent with the blowdown requirements prescribed by the applicable governing code or standard. Relief valve This device is used for liquid service.
13/1/ · • Safety valve — This device is typically used for steam or vapor service. It operates automatically with a full-opening pop action and recloses when the pressure drops to a value consistent with the blowdown requirements prescribed by the applicable governing code or standard. • Relief valve — This device is used for liquid service.
28/1/ · For example, a relief valve can prevent that a pump is running against a closed valve. Often, systems actively continue their operation with the relief valve slightly open. Safety valves on the
When opposed to relief valves, safety valves can open quite quickly. A safety valve opens from a predetermined pressure; the valve opens slowly at first, then fully to eliminate the undesirable pressure from the system as rapidly as feasible. A pressure relief valve with a quick opening or pop action that is triggered by intake static pressure.
10/6/ · In a simple terms, a relief valve is a device designed to control the pressure in a vessel or system to a specific set level. where as, A safety valve, is a device used to let go excess pressure from a vessel or equipment when the pressure crosses a certain predetermined limit.
13/9/ · WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN A SAFETY VALVE AND RELIEF VALVE? RELIEF VALVE IS PROVIDED TO LIFT AT TIME OF OVER PRESSURIZING OF THE SYSTEM AND IT WILL LIFT WHEN A SYSTEM PRESSURE EXCEED 10%




 8613371530291
8613371530291