first step act and safety valve quotation

This website is using a security service to protect itself from online attacks. The action you just performed triggered the security solution. There are several actions that could trigger this block including submitting a certain word or phrase, a SQL command or malformed data.

The Act requires the submission of several reports to review the BOP"s implementation of the law and assess the effects of the new risk and needs assessment system.
Conducting research and data analysis on: evidence-based recidivism reduction programs relating to the use of prisoner risk and needs assessment tools;
Advising on the most effective and efficient uses of such programs; and which evidence-based recidivism reduction programs are the most effective at reducing recidivism, and the type, amount, and intensity of programming that most effectively reduces the risk of recidivism;

The Federal Safety Valve law permits a sentence in a drug conviction to go below the mandatory drug crime minimums for certain individuals that have a limited prior criminal history. This is a great benefit for those who want a second chance at life without sitting around incarcerated for many years. Prior to the First Step Act, if the defendant had more than one criminal history point, then they were ineligible for safety valve. The First Step Act changed this, now allowing for up to four prior criminal history points in certain circumstances.
The First Step Act now gives safety valve eligibility if: (1) the defendant does not have more than four prior criminal history points, excluding any points incurred from one point offenses; (2) a prior three point offense; and (3) a prior two point violent offense. This change drastically increased the amount of people who can minimize their mandatory sentence liability.
Understanding how safety valve works in light of the First Step Act is extremely important in how to incorporate these new laws into your case strategy. For example, given the increase in eligible defendants, it might be wise to do a plea if you have a favorable judge who will likely sentence to lesser time. Knowing these minute issues is very important and talking to a lawyer who is an experienced federal criminal defense attorney in southeast Michigan is what you should do. We are experienced federal criminal defense attorneys and would love to help you out. Contact us today.

The safety valve is a provision in the Sentencing Reform Act and the United States Federal Sentencing Guidelines that authorizes a sentence below the statutory minimum for certain nonviolent, non-managerial drug offenders with little or no criminal history.FIRST STEP Act was signed into law in December 2018, which expanded the safety valve to include offenders with up to four criminal history points, excluding 1-point offenses, such as minor misdemeanors.

Over the years I have been retained by a few criminal defense clients after they had bad experience with a prior lawyer. The reasons for switching defense attorneys in midstream vary: sometimes it is concern over the lawyer’s competence, or concern that their case is not getting the attention it deserves, or even that they just don’t see eye to eye with their lawyer. One of the most common, and disturbing reasons though is that the client feels that their prior attorney ripped them off. These complaints generally involve “flat-fee” retainer agreements in which a lawyer and a client agree upon a fixed sum of money for the entire defense representation no matter whether it goes to trial or ends in a plea deal. I see cases all the time where a lawyer accepts a major felony case for a ridiculously low flat-fee just to land the client. Then, when it becomes obvious the case will require a lot of work, the attorney hits the client up for more money. I have even seen cases where the attorney threatens to withdraw from the case if the client does not come up with the additional funds. I call these “pump and dumps:” The lawyer pumps the client for a quick cash infusion and if the client balks, the lawyer tries to dump the client or the retainer agreement. When this happens, the client rightfully becomes upset and the situation quickly becomes untenable. What should a client do? They have (or should have) a written and enforceable fee agreement with the attorney. Then again, who wants a lawyer defending them from serious criminal charges when they claim they are being paid for their work? Defending clients charged with serious or complex felony cases in state and federal courts takes a great amount of work on the part of the criminal defense attorney, the client, and the defense team. These cases are expensive. To get an idea of how expensive, ask the attorney what their normal hourly fee is. The ask them how many hours they would expect to work in a case such as yours. What if it is a plea? What if it is a trial? If the lawyer’s retainer agreement sounds too good to be true, it probably is. The best thing a person can do when selecting a criminal defense attorney is to deal very clearly with this issue up-front. Hourly fee agreements will avoid the problem altogether. The attorney is paid only for the work performed. When negotiating an hourly fee agreement with a criminal defense attorney, be sure to ask the attorney to give a good faith estimate of the number of hours she or he thinks the case will consume depending on various outcomes like a plea agreement or a trial. If you are negotiating a flat-flee agreement make sure that both parties understand that regardless of how many hours the attorney must spend on the case, the fee agreement spells out the total amount to be paid in attorney fees. To protect both parties, flat fee agreements can be modified to suit the needs of each case. For example: The amount of the fee could be staggered to depend on at what stage of the proceedings the case is resolved: Pre-Indictment, with a plea agreement, after a trial etc. Regardless of the attorney and the fee structure you choose. I always recommend the potential client talk to as many knowledgeable and experienced criminal defense attorneys as the situation allows before settling on their pick. This will give the prospective client some idea of comparable fee agreements and rates. It will also allow both parties to get to know each other a little bit before signing up to work so closely together over so serious a matter. Switching attorneys in the middle of the case is sometimes unavoidable, but it is a situation best-avoided if possible.

Over the years I have been retained by a few criminal defense clients after they had bad experience with a prior lawyer. The reasons for switching defense attorneys in midstream vary: sometimes it is concern over the lawyer’s competence, or concern that their case is not getting the attention it deserves, or even that they just don’t see eye to eye with their lawyer. One of the most common, and disturbing reasons though is that the client feels that their prior attorney ripped them off. These complaints generally involve “flat-fee” retainer agreements in which a lawyer and a client agree upon a fixed sum of money for the entire defense representation no matter whether it goes to trial or ends in a plea deal. I see cases all the time where a lawyer accepts a major felony case for a ridiculously low flat-fee just to land the client. Then, when it becomes obvious the case will require a lot of work, the attorney hits the client up for more money. I have even seen cases where the attorney threatens to withdraw from the case if the client does not come up with the additional funds. I call these “pump and dumps:” The lawyer pumps the client for a quick cash infusion and if the client balks, the lawyer tries to dump the client or the retainer agreement. When this happens, the client rightfully becomes upset and the situation quickly becomes untenable. What should a client do? They have (or should have) a written and enforceable fee agreement with the attorney. Then again, who wants a lawyer defending them from serious criminal charges when they claim they are being paid for their work? Defending clients charged with serious or complex felony cases in state and federal courts takes a great amount of work on the part of the criminal defense attorney, the client, and the defense team. These cases are expensive. To get an idea of how expensive, ask the attorney what their normal hourly fee is. The ask them how many hours they would expect to work in a case such as yours. What if it is a plea? What if it is a trial? If the lawyer’s retainer agreement sounds too good to be true, it probably is. The best thing a person can do when selecting a criminal defense attorney is to deal very clearly with this issue up-front. Hourly fee agreements will avoid the problem altogether. The attorney is paid only for the work performed. When negotiating an hourly fee agreement with a criminal defense attorney, be sure to ask the attorney to give a good faith estimate of the number of hours she or he thinks the case will consume depending on various outcomes like a plea agreement or a trial. If you are negotiating a flat-flee agreement make sure that both parties understand that regardless of how many hours the attorney must spend on the case, the fee agreement spells out the total amount to be paid in attorney fees. To protect both parties, flat fee agreements can be modified to suit the needs of each case. For example: The amount of the fee could be staggered to depend on at what stage of the proceedings the case is resolved: Pre-Indictment, with a plea agreement, after a trial etc. Regardless of the attorney and the fee structure you choose. I always recommend the potential client talk to as many knowledgeable and experienced criminal defense attorneys as the situation allows before settling on their pick. This will give the prospective client some idea of comparable fee agreements and rates. It will also allow both parties to get to know each other a little bit before signing up to work so closely together over so serious a matter. Switching attorneys in the middle of the case is sometimes unavoidable, but it is a situation best-avoided if possible.

Under federal law, judges are generally prohibited from changing a sentence once it has been imposed. Compassionate release, to put it simply, provides a “safety valve” against this general principle, allowing federal judges to reduce a prisoner’s sentence when it is warranted by “extraordinary and compelling reasons.” For the past thirty years, statutory and bureaucratic roadblocks made compassionate release an unlikely avenue for prisoners to receive sentence reductions. With the passage of the First Step Act of 2018, the U.S. Congress made the first significant changes to the compassionate release statute in decades, permitting defendants for the first time to bring such motions directly to their sentencing courts. An overwhelming majority of circuit courts have concluded that the First Step Act’s changes to the compassionate release statute mean that district judges are not free to consider any extraordinary and compelling reason that a defendant might raise. Nevertheless, appellate courts remain divided over what exactly constitutes an extraordinary and compelling reason for a sentence reduction. This Note examines the historical development of, and rationales for, compassionate release and the reasons why appellate courts have struggled to define and apply the “extraordinary and compelling reasons” standard consistently. After recognizing that Congress’s goals in creating the compassionate release mechanism were to promote consistency while keeping the sentencing power in the judiciary, this Note proposes a two-part solution to balance these goals. This Note’s proposed framework ensures that judicial discretion continues to serve a critical role in compassionate release decisions and seeks to resolve the current disagreements among appellate courts.
For some, the open ocean is prison. The Maritime Drug Law Enforcement Act (MDLEA) prohibits individuals from knowingly or intentionally distributing a controlled substance or possessing it with the intent to distribute. Empowered by the MDLEA, the United States Coast Guard arrests and detains foreign nationals hundreds of miles outside of U.S. territorial waters. After months shackled to Coast Guard ships, these individuals face the harsh reality of American mandatory minimum drug sentencing, judged by the kilograms of drugs on their vessels. But the MDLEA conflates kilograms with culpability. More often than not, those sentenced are fishermen-turned-smugglers due to financial desperation or coercionnot the kingpins the statute aspired to target.
In the First Step Act of 2018, Congress attempted to grant sentencing reprieve to these defendants by extending the safety valve provision to the MDLEA. When it works, the safety valve provision enables judges to sentence below mandatory minimum penalties. Unfortunately, the unique qualities of international drug couriers preclude them from receiving such relief. Until the legislature and presiding judges recognize this, MDLEA defendants will continue to receive irrationally long prison sentences. This Note argues that including the MDLEA as an offense under the safety valve provision fails to mitigate the MDLEA’s harsh mandatory minimum sentences.
This Note begins in Part I by discussing the MDLEA’s history as well as how the Coast Guard arrests these defendants. It then explains how the statutory mandatory minimum sentence interacts with the Sentencing Guidelines and highlights the flaws of this system. Part II addresses the safety valve provision as well as the previous circuit split regarding its applicability to the MDLEA. Part III introduces the First Step Act of 2018 and describes how it resolved that split. Part III then evaluates the effectiveness of the First Step Act’s change and provides a recent case example. Finally, Part IV concentrates on how defendants sentenced under the MDLEA are uniquely incapable of sentencing reprieve. It explores general improvements for the safety valve as well as specific changes for the MDLEA. This Note ultimately argues that Congress must amend the MDLEA’s sentencing regime.

In federal cases, Congress not only defines what is a crime that can cost the accused both freedom and property, but it also passes statutes that control how federal judges are allowed to sentence those who have been convicted of federal drug crimes. For instance, federal judges must follow the United States Sentencing Guidelines when sentencing someone upon conviction of a federal crime. For more on sentencing guidelines and how they work, read our discussion in Federal Sentencing Guidelines: Conspiracy To Distribute Controlled Substance Cases.
Sometimes, Congress sets a bottom line on the number of years someone must spend behind bars upon conviction for a specific federal crime. The federal judge in these situations has no discretion: he or she must follow the Congressional mandate.
These are called “mandatory minimums” in sentencing. They are commonly applied in federal drug cases in here Texas and elsewhere across the country. For more detail, read Mandatory Minimum Penalties in Federal Sentencing.
Of course, there are a tremendous number of federal laws that define federal drug crimes. For purposes of illustration, consider those federal drug crimes that come with either (1) a sentence of 10 years to life imprisonment or (2) those that come with a sentence of 5 to 40 years behind bars, both defined as the mandatory sentences to be given upon conviction for these defined federal drug crimes.
For reference, these refer to the statutory language of 21 U.S.C. §841(b)(1)(A) and 21 U.S.C. §841(b)(1)(B), which instruct the federal judge on how he or she shall sentence anyone convicted of the manufacture, distribution, or dispensing of a controlled substance (i.e., an illegal drug) or possession with intent to either of these things.
Key here: the judge is given the mandatory minimum number of years that the accused must spend behind bars by Congress via the federal statutory language. A federal judge cannot go below ten (10) years for a federal drug crime based upon 21 U.S.C. §841(b)(1)(A). He or she cannot go below five (5) years for a federal drug crime conviction based upon 21 U.S.C. §841(b)(1)(B).
How do you know if you are charged with one of these federal drug crimes that come with a mandatory minimum sentence of either 5-to-40 years (a “b1B” case) or 10-to-life (a “b1A” case)? Read the language of your Indictment. It will specify the statute’s citation. If you do not have a copy of your Indictment, please feel free to contact my office and we can provide you a copy.
Can’t there be any way to get around that set-in-stone bottom line? Yes. There is also a statutory exception which allows the federal judge to dip below that mandatory minimum number of years in some situations. It is called the “Safety Valve” defense.
Congress has passed another law that provides for an exception to the instructions given to federal judges on the mandatory minimum sentences that must be given according to Congressional mandate.
The law, 18 U.S.C. § 3553(f), provides for an exception that allows the federal judge some leeway in drug crime convictions where he or she would otherwise be required to follow the mandatory minimum sentencing statute. This is the Safety Value statute. It states as follows:
(f)Limitation on Applicability of Statutory Minimums in Certain Cases.—Notwithstanding anyother provision of law, in the case of an offense under section 401, 404, or 406 of theControlled Substances Act(21 U.S.C. 841, 844, 846), section 1010 or 1013 of theControlled Substances Import and Export Act(21 U.S.C. 960, 963), or section 70503 or 70506 of title 46, the court shall impose a sentence pursuant to guidelines promulgated by the United States Sentencing Commission undersection 994 of title 28without regard to any statutory minimum sentence, if the court finds at sentencing, after the Government has been afforded the opportunity to make a recommendation, that—
(4)the defendant was not an organizer, leader, manager, or supervisor of others in the offense, as determined under the sentencing guidelines and was not engaged in a continuing criminal enterprise, as defined in section 408 of theControlled Substances Act; and
(5)not later than the time of the sentencing hearing, the defendant has truthfully provided to the Government all information and evidence the defendant has concerning the offense or offenses that were part of the same course of conduct or of a common scheme or plan, but the fact that the defendant has no relevant or useful other information to provide or that the Government is already aware of the information shall not preclude a determination by the court that the defendant has complied with this requirement.
The only way to allow for this exception to be applied in a federal sentencing hearing is for the defense to argue its application and to provide authenticated and admissible support for use of the Safety Valve.
How does the defense do this? It takes much more than referencing the exception to the general rule itself. The defense will have to demonstrate the convicted defendant meets the Safety Valve’s five (5) requirements.
Federal sentencing has its own reference manual that is used throughout the United States, called the United States Sentencing Guidelines (“USSG”). We have gone into detail about the USSG and its applications in earlier discussions; to learn more, read:
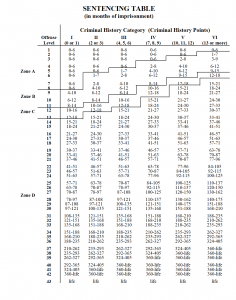
Essentially, the accused can be charged with a three-point offense; a two-point offense; or a one-point offense. The number of points will depend on things like if it is a violent crime; violent crimes get more points than non-violent ones. The higher the overall number of points, and the ultimate total score, then the longer the sentence to be given under the USSG.
For a successful safety valve defense, the defense has to show that the total Criminal History Points are four (4) or less. If you have a maximum of four Criminal History points, you have met the first criteria for the safety valve.
Note: prior to the passage of the First Step Act, things were much harsher. If the defense had even two Criminal History Points, then the accused was ineligible for the safety valve. The First Step Act increased the number of points, or score, from one to four as the maximum allowed for application of the safety valve. For more on the First Step Act, see The First Step Act and Texas Criminal Defense in 2019: Part 1 of 2 and The First Step Act and Texas Criminal Defense in 2019: Part 2 of 2.
Looking at the Safety Valve statute ( 18 U.S.C. § 3553(f)), the second step in achieving application of the safety valve defense involves the circumstances of the underlying criminal activity and whether or not it involved violence of threats or violence, or if the defendant possessed a firearm at the time.
It has been my experience that it is pretty common for there to be a firearm of some sort involved in a federal drug crime prosecution. Here, the impact of Texas being a part of the Fifth Judicial District for the United States Court of Appeals (“Fifth Circuit”) is important.
This is because this overseeing federal appeals court has looked at 18 U.S.C. § 3553(f) and its definition of possession of a firearm, and come to a different conclusion that the definition given in the USSG.
In the USSG, two points are given (“enhanced”) for possessing a firearm in furtherance of a federal drug trafficking offense. See, USSG §2D1.10, entitled Endangering Human Life While Illegally Manufacturing a Controlled Substance; Attempt or Conspiracy.
Meanwhile, the Fifth Circuit has ruled that under the Safety Valve Statute, the standard for the government is much higher. According to their ruling, in order to be disqualified from application of the safety valve because of possession of a firearm, the defendant has to have been actually in possession of the firearm or in construction possession of it. See, US v. Wilson, 105 F.3d 219 (5th Cir. 1997).
Consider how this works in a federal drug crime conspiracy case. Under the USSG, a defendant can receive two (2) points (“enhancement”) for possession of a firearm even if they never had their hands on the gun. As long as a co-conspirator (co-defendant) did have possession of it, and that possession was foreseeable by the defendant, then the Sentencing Guidelines allow for a harsher sentence (more points).
The position of the Fifth Circuit looks upon this situation and determines that it is one thing for the defendant to have possession of the firearm, and another for there to be stretching things to cover constructive possession when he or she never really had the gun.
This is the example of the importance of effective criminal defense representation, where research reveals that it is easier to achieve a safety valve defense with a reference to case law. The Fifth Circuit allows a situation where someone can get two (2) points under the USSG (“enhancement”) and still be eligible for the safety valve defense.
The commentary to § 5C1.2(2) provides that “[c]onsistent with [U.S.S.G.] § 1B1.3 (Relevant Conduct),” the use of the term “defendant” in § 5C1.2(2) “limits the accountability of the defendant to his own conduct and conduct that he aided or abetted, counseled, commanded, induced, procured, or willfully caused.” See U.S.S.G. § 5C1.2, comment. (n.4). This language mirrors § 1B1.3(a)(1)(A). Of import is the fact that this language omits the text of § 1B1.3(a)(1)(B) which provides that “relevant conduct” encompasses acts and omissions undertaken in a “jointly undertaken criminal activity,” e.g. a conspiracy.
Being bound by this commentary, we conclude that in determining a defendant’s eligibility for the safety valve, § 5C1.2(2) allows for consideration of only the defendant’s conduct, not the conduct of his co-conspirators. As it was Wilson’s co-conspirator, and not Wilson himself, who possessed the gun in the conspiracy,the district court erred in concluding that Wilson was ineligible to receive the benefit of § 5C1.2. Because application of § 5C1.2 is mandatory, see U.S.S.G. § 5C1.2 (providing that the court “shall” impose a sentencing without regard to the statutory minimum sentence if the defendant satisfies the provision’s criteria), we vacate Wilson’s sentence and remand for resentencing.
The defense must also be able to prove that the defendant’s role in the underlying criminal offense did not result in the death or bodily injury of someone else to achieve the safety valve defense under 18 U.S.C. § 3553(f).
In drug cases, this can mean more than some type of violent scenario. The mere type of drug or controlled substance involved can impact the success of this defense. Sometimes, the drugs themselves are the type that can cause severe harm or death. Several controlled substances can be lethal. In a federal drug case, there is a special definition for death resulting from the distribution of a controlled substance.
If the defense can prove with authenticated and admissible evidence that the defendant did not distribute a drug or controlled substance that ended up with someone’s death, or severe bodily injury, then the safety valve defense will be available to them.
Role adjustments happen when someone is alleged to be involved in a conspiracy, and they act in some type of position of responsibility. They can be a leader, or organizer, or somebody who supervises other people in the operations, all as defined in the USSG.
If the defendant was deemed to meet one of these definitions, and had some kind of role involving responsibility or power in the illegal drug operations, then the USSG will add points (“enhance”) as a “role adjustment.”
If you are to achieve the safety valve defense, you cannot receive any “role adjustment” under the Sentencing Guidelines. This must be established to the court by your defense attorney at the sentencing.
Finally, under 18 U.S.C. § 3553(f) the defense must show that the defendant has given a full and complete statement to the authorities. Specifically, the statute requires a showing that:
The defendant has truthfully provided to the Government all information and evidence the defendant has concerning the offense or offenses that were part of the same course of conduct or of a common scheme or plan, but the fact that the defendant has no relevant or useful other information to provide or that the Government is already aware of the information shall not preclude a determination by the court that the defendant has complied with this requirement.
I realize that for many people, this language brings with it the assumption that the defendant has to be a snitch in order to meet this requirement for the safety valve defense. This is not true.
With an experienced criminal defense lawyer, what it does mean is that the defendant has a meeting with the authorities with the goal of meeting the Safety Valve Statute requirements and no more.
The attorney can limit the scope of the meeting. He or she can make sure that law enforcement follows the rules for the meeting. The meeting is necessary for the defendant to achieve a safety valve defense, so there is no way to avoid a safety valve interview.
To get the sentence that is below the mandatory minimum sentence, the meeting is a must. However, it is not a free-for-all for the government where the defendant is ratting on other people.
I arranged for my client to have his safety valve meeting as well as establishing the other criteria needed for application of the Safety Valve statute. I was present at the meeting. There was no cooperation regarding the other defendants, and he did nothing more than the minimum to qualify for the defense. He was no snitch.
As a result, the safety valve was applied by the federal judge and my client achieved a safety valve application where he was sentenced to 8 years for distribution of meth: well below the 10 years of the mandatory minimums and the USSG calculation in his case of around 14 years.
Sadly, the same day that my client was sentenced, so were several of the co-conspirator defendants. I was aware that they were also eligible for the safety valve defense. However, the federal agent at the sentencing hearings that day told me that their lawyers never contact the government for a safety valve meeting.
They were never debriefed, so they could not meet the requirements for application of the safety value statute. The judge had no choice –they each had to be sentenced to the mandatory minimum sentences under the law.

For years, Congress had attempted to pass criminal justice reform legislation, such as the Sentencing Reform and Corrections Act (SRCA) introduced in 2015 by Senators Chuck Grassley (R-Iowa) and Dick Durbin (D-Ill.). But the SRCA failed to pass in 2016 despite overwhelming bipartisan support, thanks to opposition from Sen. Tom Cotton (R-Ark.) and then-Senator Jeff Sessions (R-Ala.).
That all changed last December when the Senate finally passed, and President Trump signed, the FIRST STEP Act — a modest bill that, despite some initial setbacks, includes key parts of the SRCA. That makes it the first major reduction to federal drug sentences.
The Brennan Center has been advocating for federal sentencing reform for years: Attorneys at the Center’s Justice Program were heavily involved in the fight to pass the SRCA and its predecessor, the Smarter Sentencing Act of 2013.
But when Donald Trump was elected president in 2016, many worried that sentencing reform would prove impossible for the next four years. Trump’s position on criminal justice reform was unclear at best and regressive at worse. His early moves appeared to confirm these suspicions: While still President-Elect, Trump nominated Jeff Sessions, a vocal critic of any reduction to the U.S. prison population, to be the nation’s chief law enforcement officer. Nonetheless, Grassley and Durbin reintroduced the SRCA again in October 2017 and navigated it through committee in early 2018. The bill looked poised to stall once again due to vocal opposition from Sessions.
But the momentum started to pick up in early 2018, when the White House brokered the Prison Reform and Redemption Act, a bipartisan bill aimed at improving conditions in federal prisons. This bill, which was renamed the FIRST STEP Act after some modest improvements were added, still lacked any meaningful sentencing reform component, meaning it would have done little to reduce the prison population. For the White House, that was part of the appeal: Republican leaders believed that SRCA’s sentencing reform provisions made it a nonstarter among conservatives. But because of that, the Brennan Center and a coalition of more than 100 civil rights groups opposed the bill, arguing that the votes were there for sentencing reform — if only Republican leaders would put a bill on the floor. Nonetheless, the FIRST STEP Act passed the House of Representatives by a wide margin of 360 to 59.
That’s where the process stood until late last year. A breakthrough occurred in November, when lawmakers and advocates reached a compromise on the FIRST STEP Act, amending it to incorporate four provisions from the SRCA. The measure garnered the support of the president and both Republicans and Democrats in Congress. Critically, the compromise was blessed by Grassley and Durbin, signaling that the new bill adequately met the goals of their own prior bill.
The FIRST STEP Act initially stalled in the Senate amid opposition from a right-wing minority faction led again by Cotton. And, critically, time was running out in the legislative session, making Republican leaders balk at spending precious floor time on the bill. But another series of compromises quieted opposition from Sen. Ted Cruz (R-Texas) and garnered support for the bill from Sen. John Cornyn (R-Texas), the majority whip, clearing the path for an easy floor vote. After that change and continued pressure from Trump, Grassley, the Koch Brothers, and constituents in Kentucky, Senate Majority Leader Mitch McConnell announced in mid-December that he would bring up the bill for a vote before the end of the year, during the lame-duck Congress.
Longtime opponents of reform like Cotton still had a chance to block the bill: They could run out the clock. But a series of procedural shortcuts allowed McConnell to bring the bill to the floor by essentially slotting the text of the bill into another piece of legislation that was already eligible for Senate consideration. And so another hurdle was cleared.
But one more remained. During the amendment process for the FIRST STEP Act, Cotton and Sen. John Kennedy (R-La.) pushed for a series of “poison pill” amendments that would have unacceptably weakened the bill and split the bipartisan coalition supporting it, just at the moment of passage. But those amendments ultimately failed to materialize in the final bill, which cleared the Senate by an overwhelming 87–12 margin. Not a single Democrat voted against the bill, and Republican opponents of reform were relegated to a small minority. Next, then-House Speaker Paul Ryan (R-Wis.) cleared the way for quick consideration of the bill in the House of Representatives — and sent it to President Trump’s desk just before Christmas. The president signed the bill on December 21.
The FIRST STEP Act is consequential because it includes provisions for meaningful sentencing reform, which would reduce the number and amount of people in prison and is part of the starting point of any serious legislation for criminal justice reform. Sentencing laws played a central role in the rise of mass incarceration in recent decades. The federal prison population, in particular, has risen by more than 700 percent since 1980, and federal prison spending has increased by nearly 600 percent. That growth has disproportionally affected Black, Latino, and Native Americans.
Federal mandatory minimum sentences were a catalyst for the recent surge of unnecessarily harsh prison sentences. More than two-thirds of federal prisoners serving a life sentence or a virtual life sentence have been convicted of non-violent crimes.
But research continues to show that long prison sentences are often ineffective. One Brennan Center study found that overly harsh sentences have done little to reduce crime. In fact, in some cases, longer prison stays can actually increase the likelihood of people returning to criminal activity. These sentences disproportionately impact people of color and low-income communities.
The FIRST STEP Act shortens mandatory minimum sentences for nonviolent drug offenses. It also eases a federal “three strikes” rule — which currently imposes a life sentence for three or more convictions — and issues a 25-year sentence instead. Most consequentially, it expands the “drug safety-valve,” which would give judges more discretion to deviate from mandatory minimums when sentencing for nonviolent drug offenses.
In an overdue change, the bill also makes the Fair Sentencing Act retroactive. Passed in 2010, the Fair Sentencing Act has helped reduce the sentencing disparity between crack and powder cocaine offenses — a disparity that has hurt racial minorities. The FIRST STEP Act will now apply the Fair Sentencing Act to 3,000 people who were convicted of crack offenses before the law went into effect.
Beyond sentencing reform, the FIRST STEP Act includes provisions that will improve conditions for current prisoners and address several laws that increased racial disparities in the federal prison system. The bill will require federal prisons to offer programs to reduce recidivism; ban the shackling of pregnant women; and expand the cap on “good time credit” — or small sentence reductions based on good behavior — from around 47 to 54 days per year. That “good time” amendment will benefit as many 85 percent of federal prisoners.
The FIRST STEP Act is a critical win in the fight to reduce mass incarceration. While the bill is hardly a panacea, it’s the largest step the federal government has taken to reduce the number of people in federal custody. (The federal government remains the nation’s leading incarcerator, and more people are under the custody of the federal Bureau of Prisons than any single state system.)
The FIRST STEP Act’s overwhelming passage demonstrates that the bipartisan movement to reduce mass incarceration remains strong. And the bill, which retains major parts of SRCA’s sentencing reform provisions, is now known as “Trump’s criminal justice bill.” This means that conservatives seeking to curry favor with the president can openly follow his example or push for even bolder reforms. Finally, this dynamic creates a unique opening for Democrats vying for the White House in 2020 to offer even better solutions to end mass incarceration.
The FIRST STEP Act marks progress for criminal justice reform, but it has some notable shortcomings. It will leave significant mandatory minimum sentences in place. In addition, two of the bill’s key sentencing provisions are not retroactive, which minimizes their overall impact.
“It’s imperative that this first step not be the only step,” said Inimai Chettiar, director of the Brennan Center’s Justice Program. “Now we must focus our efforts on bigger and bolder widespread reforms that will make our system more fair and more humane. We know better, and we must do better.”
The Brennan Center has outlined many additional steps that both federal and state lawmakers can take toward ending mass incarceration in the United States.
One step is to eliminate incarceration for lower-level crimes, such as minor marijuana trafficking and immigration crimes. The default sentences for those crimes should be alternatives to incarceration, such as treatment, community service, or probation. Second, lawmakers should also pass legislation that would make default prison sentences — which are often excessively long — proportional to the specific crimes committed. If Congress and every state enacted this pair of reforms, the national prison population would be safely reduced by 40 percent. Third, Congress can use the power of the purse to encourage these changes. Washington spends a significant amount of money supporting state criminal justice systems: Those dollars could be used to reward policies that reduce rather than entrench mass incarceration.
Ultimately, the FIRST STEP Act is one step in the right direction for reducing mass incarceration in the United States. It has elevated criminal justice reform as a rare space for bipartisan consensus and cooperation in a fractured national political environment. With an awareness of that consensus, we should push for the bigger next steps that will move us toward ending mass incarceration.

This website is using a security service to protect itself from online attacks. The action you just performed triggered the security solution. There are several actions that could trigger this block including submitting a certain word or phrase, a SQL command or malformed data.




 8613371530291
8613371530291