flow safety valve manufacturer

Flow Safe is a manufacturer of spring-operated and pilot-operated high-performance pressure relief devices. The Flow Safe product line is specifically designed for applications in Natural Gas Distribution, Pipeline, Aerospace, Marine, Industrial Gasses and other liquid and gas process applications.
Due to the continued escalation of raw materials as well as additional COVID-related costs, Flow Safe is announcing a list price increase effective Aug. 2, 2021. The increase will be between 8% and 10% depending on the product line.

The Flow Safe sales/support team has more combined years of application engineering experience with high performing safety relief valves than any other competitor on the globe. We are pioneers in providing quality pressure relief device repair, holding one of the first National Board VR stamps issued, VR#34.
Our goal is to continue the expansion of our customer service, particularly in our Houston, Texas facility, and to expand our products in the established market segments recognized in our core business plan. Flow Safe excels in over pressure protection and will continue to work hard to hold our position of number one in the world of manufacturing, engineering and service of high performing pressure relief devices.

Emergency situations are not the only times relief valves are active; once installed they continuously regulate the flow of substance. They can also be pre-set to open when the pressure or temperature gets to a certain point that may be dangerous. Generally valves are placed on or near the pump head of the hose, pipe or tube. A wide variety of relief valve designs exist, although most resemble ball-check valves, swing check valves or diaphragm valves.
This last is particularly useful when controlling a flow of fluids that contains suspended solids. Most relief valves are spring operated, as are the majority of check valves. One specialized type of relief valve is known as a vacuum relief valve. As opposed to a normal relief valve, which relieves high pressure, a vacuum relief valve is used to relieve dangerously low pressures, or vacuums, by inserting air or an inert gas.
Like every other type of check valve, relief valves may be constructed from a variety of materials, including PVC, brass, ductile iron, copper, polyethylene, polypropylene, aluminum, steel, stainless steel and rubber. Which raw substance is used to produce each relief valve depends on the environment said relief valve will be in. The wrong product could result in erosion or contamination of the process stream. However, as long as research is done, finding the appropriate type of relief valve is possible. Every plumbing or fluid transfer application in the industrial, commercial and domestic arenas employ or will employ check valves. In fact, check valves of all kinds are an essential part of every day life. Because they need not be supervised to function and prevent product malfunction, check valves are not only desirable but often required by law to ensure the safety of water, gas and pressure applications.

Industry leading pressure and safety relief valve designs with over 140 years of technical and application expertise providing custom engineered solutions for O&G, Refining, Chemical, Petrochemical, Process and Power applications. Our designs meet global and local codes and standards (API 526; ASME Section I, IV & VIII; EN ISO 4126; PED & more). Gain insight into the performance of your pressure relief valves with wireless monitoring.

Distributor of hydraulic press safety, quick opening safety, rotary and safety valves. Amerigear®, Boston Gear®, Carlisle®, DeMag®, Desch® and IMI Norgren®, pneumatic, double action, quick release and flow control valves also provided. Repair and preventative maintenance services are offered. Value added services such as custom barcoding, CAD capabilities, OEM assembly, plant surveys and third party logistics are also available. Serves the metal processing, metal service center, paper mill and paper converting, canning, grinding, commercial laundry, marine, oil and gas and material handling industries. Vendor managed inventory (VMI) programs available. Kanban delivery.
Taylor Valve Technology® is a manufacturer leader in high-quality industrial valves. We deliver safety relief, high-pressure relief, and back pressure relief valves. Our wide array of choke and control valves and pilot-operated valve products are second to none. Products are designed for demanding industrial needs, meeting quality API and ASME Code requirements. High-demand oil & gas industry, chemical plants, power generators, and the processing industry depend on our valves for consistency and durability. Get effective flow control of liquid, steam, and gas. Valves ship from the Taylor Valve Technology, Inc. United States facility. Delivering worldwide, you can depend on quick turnaround times.

... -start valve with Series MX2 air treatment units without the need for additional connection interfaces. The soft-start valve is positioned upstream of the safety valves, ...
Two hands safety valve, which allows a safety use of two hands pneumatic controls (for example two push-button 3/2 N.C. to a certain distance) excluding false signals in case of push-button ...
The SI2 safety valve prevents the allowed operating pressure from being exceeded by more than 10%. If, after opening, the adjusted response pressure falls ...
... stainless steel full-lift clean service safety valve designed to AD Merkblatt A2 and TRD 421 standards and suitable for pure steam, vapour and inert gases.
Insert style flow control valves are comprised of a precision orifice in parallel with a check valve, combined into a single component. Each is designed for easy installation into metal housings using ...
Press-in style flow control valves are comprised of a precision flow orifice in parallel with a check valve, combined into a single component. Each part is designed for easy installation into plastic ...
If you have been searching for a safety release valve that you can use to reduce short-term pressure surges successfully and diminish the effects of gas leaks, this is the product for you. With a pe of ...
... have been type tested as well. These pressure regulators have safety valves which will slam shut in the event of emergencies, such as the gas reaching too high a pressure level. The valve ...
This product has hydraulically actuated class A gas safety valves to EN 161 used for automatic shut-off. It shuts off when unstimulated for gas and air, or even biologically produced methane. It has AISi ...
The S 104 Safety Shut Off valve is mainly used to avoid any damage to components as well as to avoid too high or too low pressure in the gas train. This could cause high financial losses and/or injured ...
The S50 Safety Shut Off valve is mainly used to avoid any damage to components as well as to avoid too high or too low pressure in the gas train. This could cause high financial losses and/or injured ...
The S100 Safety Shut Off valve is mainly used to avoid any damage to components as well as to avoid too high or too low pressure in the gas train. This could cause high financial losses and/or injured ...
... Pressure Safety Valve + Rupture Disk is protected and may be utilized autonomously as essential security gadgets or in conjunction. There are 3 possible combinations. The first combinations ...
Excavator pipe-rupture valves prevent uncontrolled cylinder movement in the event that a pipe or hose bursts. The ESV valve fulfills all of the requirements of the ISO 8643 and EN 474-5 standards for ...
Material: Body- CF8M; Valve Seat- CF8M Métal Seat, PTFE Soft Seat available Orifice Size: fc"(15mm), 3/4M(20mm), l"(25mm), l1/4,’(32mm)I ltë”(40mm), ...
The Safety valves from ATOS are designed to guarantee protection for application on various devices, especially those that monitor spool position. They are also recommended for hydraulic ...

Pressure relief valves are a critical component of fuel, hydraulic, and pneumatic systems in many industries. These valves can serve one of three functions—safety relief, pressure regulation, or protection against thermal expansion. The Lee Company offers a wide range of pressure relief valve configurations designed to ensure that we can offer the right solution for a specific application, helping to guarantee the safety and reliability of your product.
Compact gas and thermal safety relief valves of brass and stainless steel construction. Soft seats available in either plastic or elastomer materials. Valves are ideal for instrumentation panels, line blocks on cryogenic storage tanks, thermal relief or "Whistler valve" applications. Made in accordance with ASME Section VIII or "CE" mark. Adjustable blowdown design allows operation close to normal operating conditions.

There is a wide range of safety valves available to meet the many different applications and performance criteria demanded by different industries. Furthermore, national standards define many varying types of safety valve.
The ASME standard I and ASME standard VIII for boiler and pressure vessel applications and the ASME/ANSI PTC 25.3 standard for safety valves and relief valves provide the following definition. These standards set performance characteristics as well as defining the different types of safety valves that are used:
ASME I valve - A safety relief valve conforming to the requirements of Section I of the ASME pressure vessel code for boiler applications which will open within 3% overpressure and close within 4%. It will usually feature two blowdown rings, and is identified by a National Board ‘V’ stamp.
ASME VIII valve- A safety relief valve conforming to the requirements of Section VIII of the ASME pressure vessel code for pressure vessel applications which will open within 10% overpressure and close within 7%. Identified by a National Board ‘UV’ stamp.
Full bore safety valve - A safety valve having no protrusions in the bore, and wherein the valve lifts to an extent sufficient for the minimum area at any section, at or below the seat, to become the controlling orifice.
Conventional safety relief valve -The spring housing is vented to the discharge side, hence operational characteristics are directly affected by changes in the backpressure to the valve.
Balanced safety relief valve -A balanced valve incorporates a means of minimising the effect of backpressure on the operational characteristics of the valve.
Pilot operated pressure relief valve -The major relieving device is combined with, and is controlled by, a self-actuated auxiliary pressure relief device.
Power-actuated safety relief valve - A pressure relief valve in which the major pressure relieving device is combined with, and controlled by, a device requiring an external source of energy.
Standard safety valve - A valve which, following opening, reaches the degree of lift necessary for the mass flowrate to be discharged within a pressure rise of not more than 10%. (The valve is characterised by a pop type action and is sometimes known as high lift).
Full lift (Vollhub) safety valve -A safety valve which, after commencement of lift, opens rapidly within a 5% pressure rise up to the full lift as limited by the design. The amount of lift up to the rapid opening (proportional range) shall not be more than 20%.
Direct loaded safety valve -A safety valve in which the opening force underneath the valve disc is opposed by a closing force such as a spring or a weight.
Proportional safety valve - A safety valve which opens more or less steadily in relation to the increase in pressure. Sudden opening within a 10% lift range will not occur without pressure increase. Following opening within a pressure of not more than 10%, these safety valves achieve the lift necessary for the mass flow to be discharged.
Diaphragm safety valve -A direct loaded safety valve wherein linear moving and rotating elements and springs are protected against the effects of the fluid by a diaphragm
Bellows safety valve - A direct loaded safety valve wherein sliding and (partially or fully) rotating elements and springs are protected against the effects of the fluids by a bellows. The bellows may be of such a design that it compensates for influences of backpressure.
Controlled safety valve - Consists of a main valve and a control device. It also includes direct acting safety valves with supplementary loading in which, until the set pressure is reached, an additional force increases the closing force.
Safety valve - A safety valve which automatically, without the assistance of any energy other than that of the fluid concerned, discharges a quantity of the fluid so as to prevent a predetermined safe pressure being exceeded, and which is designed to re-close and prevent further flow of fluid after normal pressure conditions of service have been restored. Note; the valve can be characterised either by pop action (rapid opening) or by opening in proportion (not necessarily linear) to the increase in pressure over the set pressure.
Direct loaded safety valve -A safety valve in which the loading due to the fluid pressure underneath the valve disc is opposed only by a direct mechanical loading device such as a weight, lever and weight, or a spring.
Assisted safety valve -A safety valve which by means of a powered assistance mechanism, may additionally be lifted at a pressure lower than the set pressure and will, even in the event of a failure of the assistance mechanism, comply with all the requirements for safety valves given in the standard.
Supplementary loaded safety valve - A safety valve that has, until the pressure at the inlet to the safety valve reaches the set pressure, an additional force, which increases the sealing force.
Note; this additional force (supplementary load), which may be provided by means of an extraneous power source, is reliably released when the pressure at the inlet of the safety valve reaches the set pressure. The amount of supplementary loading is so arranged that if such supplementary loading is not released, the safety valve will attain its certified discharge capacity at a pressure not greater than 1.1 times the maximum allowable pressure of the equipment to be protected.
Pilot operated safety valve -A safety valve, the operation of which is initiated and controlled by the fluid discharged from a pilot valve, which is itself, a direct loaded safety valve subject to the requirement of the standard.
The common characteristic shared between the definitions of conventional safety valves in the different standards, is that their operational characteristics are affected by any backpressure in the discharge system. It is important to note that the total backpressure is generated from two components; superimposed backpressure and the built-up backpressure:
Subsequently, in a conventional safety valve, only the superimposed backpressure will affect the opening characteristic and set value, but the combined backpressure will alter the blowdown characteristic and re-seat value.
The ASME/ANSI standard makes the further classification that conventional valves have a spring housing that is vented to the discharge side of the valve. If the spring housing is vented to the atmosphere, any superimposed backpressure will still affect the operational characteristics. Thiscan be seen from Figure 9.2.1, which shows schematic diagrams of valves whose spring housings are vented to the discharge side of the valve and to the atmosphere.
By considering the forces acting on the disc (with area AD), it can be seen that the required opening force (equivalent to the product of inlet pressure (PV) and the nozzle area (AN)) is the sum of the spring force (FS) and the force due to the backpressure (PB) acting on the top and bottom of the disc. In the case of a spring housing vented to the discharge side of the valve (an ASME conventional safety relief valve, see Figure 9.2.1 (a)), the required opening force is:
In both cases, if a significant superimposed backpressure exists, its effects on the set pressure need to be considered when designing a safety valve system.
Once the valve starts to open, the effects of built-up backpressure also have to be taken into account. For a conventional safety valve with the spring housing vented to the discharge side of the valve, see Figure 9.2.1 (a), the effect of built-up backpressure can be determined by considering Equation 9.2.1 and by noting that once the valve starts to open, the inlet pressure is the sum of the set pressure, PS, and the overpressure, PO.
In both cases, if a significant superimposed backpressure exists, its effects on the set pressure need to be considered when designing a safety valve system.
Once the valve starts to open, the effects of built-up backpressure also have to be taken into account. For a conventional safety valve with the spring housing vented to the discharge side of the valve, see Figure 9.2.1 (a), the effect of built-up backpressure can be determined by considering Equation 9.2.1 and by noting that once the valve starts to open, the inlet pressure is the sum of the set pressure, PS, and the overpressure, PO.
Balanced safety valves are those that incorporate a means of eliminating the effects of backpressure. There are two basic designs that can be used to achieve this:
Although there are several variations of the piston valve, they generally consist of a piston type disc whose movement is constrained by a vented guide. The area of the top face of the piston, AP, and the nozzle seat area, AN, are designed to be equal. This means that the effective area of both the top and bottom surfaces of the disc exposed to the backpressure are equal, and therefore any additional forces are balanced. In addition, the spring bonnet is vented such that the top face of the piston is subjected to atmospheric pressure, as shown in Figure 9.2.2.
The bellows arrangement prevents backpressure acting on the upper side of the disc within the area of the bellows. The disc area extending beyond the bellows and the opposing disc area are equal, and so the forces acting on the disc are balanced, and the backpressure has little effect on the valve opening pressure.
Bellows failure is an important concern when using a bellows balanced safety valve, as this may affect the set pressure and capacity of the valve. It is important, therefore, that there is some mechanism for detecting any uncharacteristic fluid flow through the bellows vents. In addition, some bellows balanced safety valves include an auxiliary piston that is used to overcome the effects of backpressure in the case of bellows failure. This type of safety valve is usually only used on critical applications in the oil and petrochemical industries.
Since balanced pressure relief valves are typically more expensive than their unbalanced counterparts, they are commonly only used where high pressure manifolds are unavoidable, or in critical applications where a very precise set pressure or blowdown is required.
This type of safety valve uses the flowing medium itself, through a pilot valve, to apply the closing force on the safety valve disc. The pilot valve is itself a small safety valve.
The diaphragm type is typically only available for low pressure applications and it produces a proportional type action, characteristic of relief valves used in liquid systems. They are therefore of little use in steam systems, consequently, they will not be considered in this text.
The piston type valve consists of a main valve, which uses a piston shaped closing device (or obturator), and an external pilot valve. Figure 9.2.4 shows a diagram of a typical piston type, pilot operated safety valve.
The piston and seating arrangement incorporated in the main valve is designed so that the bottom area of the piston, exposed to the inlet fluid, is less than the area of the top of the piston. As both ends of the piston are exposed to the fluid at the same pressure, this means that under normal system operating conditions, the closing force, resulting from the larger top area, is greater than the inlet force. The resultant downward force therefore holds the piston firmly on its seat.
If the inlet pressure were to rise, the net closing force on the piston also increases, ensuring that a tight shut-off is continually maintained. However, when the inlet pressure reaches the set pressure, the pilot valve will pop open to release the fluid pressure above the piston. With much less fluid pressure acting on the upper surface of the piston, the inlet pressure generates a net upwards force and the piston will leave its seat. This causes the main valve to pop open, allowing the process fluid to be discharged.
When the inlet pressure has been sufficiently reduced, the pilot valve will reclose, preventing the further release of fluid from the top of the piston, thereby re-establishing the net downward force, and causing the piston to reseat.
Pilot operated safety valves offer good overpressure and blowdown performance (a blowdown of 2% is attainable). For this reason, they are used where a narrow margin is required between the set pressure and the system operating pressure. Pilot operated valves are also available in much larger sizes, making them the preferred type of safety valve for larger capacities.
One of the main concerns with pilot operated safety valves is that the small bore, pilot connecting pipes are susceptible to blockage by foreign matter, or due to the collection of condensate in these pipes. This can lead to the failure of the valve, either in the open or closed position, depending on where the blockage occurs.
The terms full lift, high lift and low lift refer to the amount of travel the disc undergoes as it moves from its closed position to the position required to produce the certified discharge capacity, and how this affects the discharge capacity of the valve.
A full lift safety valve is one in which the disc lifts sufficiently, so that the curtain area no longer influences the discharge area. The discharge area, and therefore the capacity of the valve are subsequently determined by the bore area. This occurs when the disc lifts a distance of at least a quarter of the bore diameter. A full lift conventional safety valve is often the best choice for general steam applications.
The disc of a high lift safety valve lifts a distance of at least 1/12th of the bore diameter. This means that the curtain area, and ultimately the position of the disc, determines the discharge area. The discharge capacities of high lift valves tend to be significantly lower than those of full lift valves, and for a given discharge capacity, it is usually possible to select a full lift valve that has a nominal size several times smaller than a corresponding high lift valve, which usually incurs cost advantages.Furthermore, high lift valves tend to be used on compressible fluids where their action is more proportional.
In low lift valves, the disc only lifts a distance of 1/24th of the bore diameter. The discharge area is determined entirely by the position of the disc, and since the disc only lifts a small amount, the capacities tend to be much lower than those of full or high lift valves.
Except when safety valves are discharging, the only parts that are wetted by the process fluid are the inlet tract (nozzle) and the disc. Since safety valves operate infrequently under normal conditions, all other components can be manufactured from standard materials for most applications. There are however several exceptions, in which case, special materials have to be used, these include:
Cast steel -Commonly used on higher pressure valves (up to 40 bar g). Process type valves are usually made from a cast steel body with an austenitic full nozzle type construction.
For all safety valves, it is important that moving parts, particularly the spindle and guides are made from materials that will not easily degrade or corrode. As seats and discs are constantly in contact with the process fluid, they must be able to resist the effects of erosion and corrosion.
The spring is a critical element of the safety valve and must provide reliable performance within the required parameters. Standard safety valves will typically use carbon steel for moderate temperatures. Tungsten steel is used for higher temperature, non-corrosive applications, and stainless steel is used for corrosive or clean steam duty. For sour gas and high temperature applications, often special materials such as monel, hastelloy and ‘inconel’ are used.
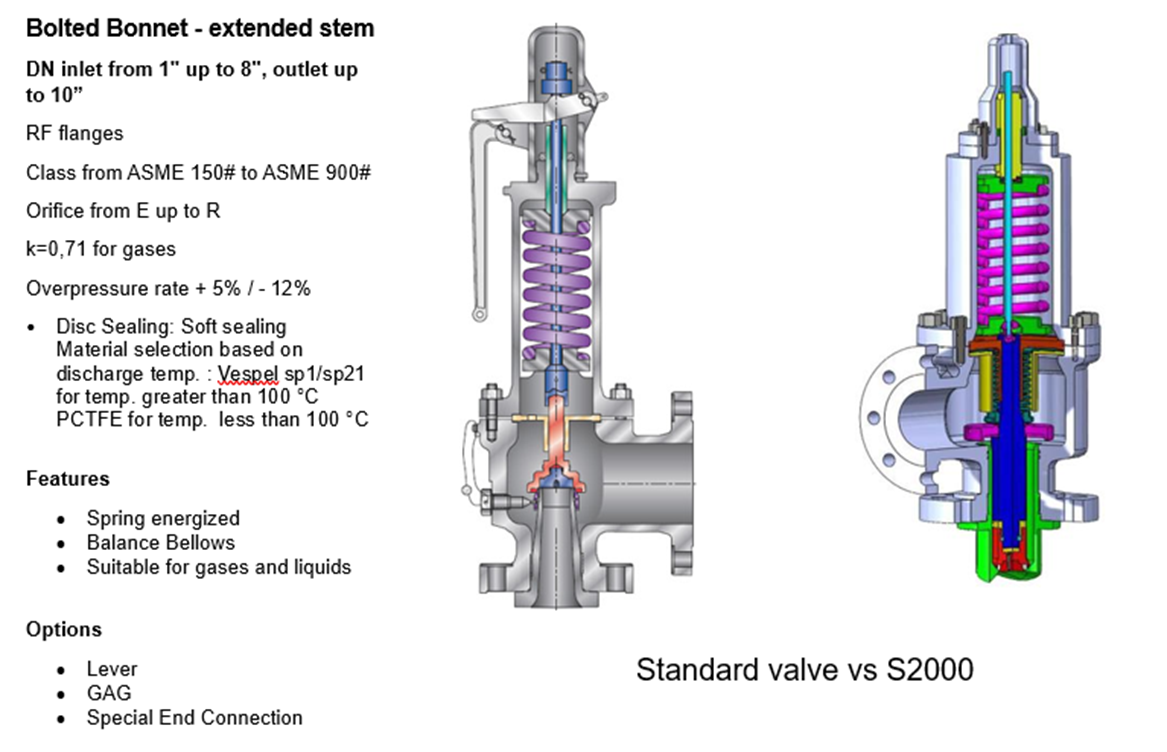
Standard safety valves are generally fitted with an easing lever, which enables the valve to be lifted manually in order to ensure that it is operational at pressures in excess of 75% of set pressure. This is usually done as part of routine safety checks, or during maintenance to prevent seizing. The fitting of a lever is usually a requirement of national standards and insurance companies for steam and hot water applications. For example, the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code states that pressure relief valves must be fitted with a lever if they are to be used on air, water over 60°C, and steam.
A test gag (Figure 9.2.7) may be used to prevent the valve from opening at the set pressure during hydraulic testing when commissioning a system. Once tested, the gag screw is removed and replaced with a short blanking plug before the valve is placed in service.
The amount of fluid depends on the particular design of safety valve. If emission of this fluid into the atmosphere is acceptable, the spring housing may be vented to the atmosphere – an open bonnet. This is usually advantageous when the safety valve is used on high temperature fluids or for boiler applications as, otherwise, high temperatures can relax the spring, altering the set pressure of the valve. However, using an open bonnet exposes the valve spring and internals to environmental conditions, which can lead to damage and corrosion of the spring.
When the fluid must be completely contained by the safety valve (and the discharge system), it is necessary to use a closed bonnet, which is not vented to the atmosphere. This type of spring enclosure is almost universally used for small screwed valves and, it is becoming increasingly common on many valve ranges since, particularly on steam, discharge of the fluid could be hazardous to personnel.
Some safety valves, most commonly those used for water applications, incorporate a flexible diaphragm or bellows to isolate the safety valve spring and upper chamber from the process fluid, (see Figure 9.2.9).

A safety valve must always be sized and able to vent any source of steam so that the pressure within the protected apparatus cannot exceed the maximum allowable accumulated pressure (MAAP). This not only means that the valve has to be positioned correctly, but that it is also correctly set. The safety valve must then also be sized correctly, enabling it to pass the required amount of steam at the required pressure under all possible fault conditions.
Once the type of safety valve has been established, along with its set pressure and its position in the system, it is necessary to calculate the required discharge capacity of the valve. Once this is known, the required orifice area and nominal size can be determined using the manufacturer’s specifications.
In order to establish the maximum capacity required, the potential flow through all the relevant branches, upstream of the valve, need to be considered.
In applications where there is more than one possible flow path, the sizing of the safety valve becomes more complicated, as there may be a number of alternative methods of determining its size. Where more than one potential flow path exists, the following alternatives should be considered:
This choice is determined by the risk of two or more devices failing simultaneously. If there is the slightest chance that this may occur, the valve must be sized to allow the combined flows of the failed devices to be discharged. However, where the risk is negligible, cost advantages may dictate that the valve should only be sized on the highest fault flow. The choice of method ultimately lies with the company responsible for insuring the plant.
For example, consider the pressure vessel and automatic pump-trap (APT) system as shown in Figure 9.4.1. The unlikely situation is that both the APT and pressure reducing valve (PRV ‘A’) could fail simultaneously. The discharge capacity of safety valve ‘A’ would either be the fault load of the largest PRV, or alternatively, the combined fault load of both the APT and PRV ‘A’.
This document recommends that where multiple flow paths exist, any relevant safety valve should, at all times, be sized on the possibility that relevant upstream pressure control valves may fail simultaneously.
The supply pressure of this system (Figure 9.4.2) is limited by an upstream safety valve with a set pressure of 11.6 bar g. The fault flow through the PRV can be determined using the steam mass flow equation (Equation 3.21.2):
Once the fault load has been determined, it is usually sufficient to size the safety valve using the manufacturer’s capacity charts. A typical example of a capacity chart is shown in Figure 9.4.3. By knowing the required set pressure and discharge capacity, it is possible to select a suitable nominal size. In this example, the set pressure is 4 bar g and the fault flow is 953 kg/h. A DN32/50 safety valve is required with a capacity of 1 284 kg/h.
Where sizing charts are not available or do not cater for particular fluids or conditions, such as backpressure, high viscosity or two-phase flow, it may be necessary to calculate the minimum required orifice area. Methods for doing this are outlined in the appropriate governing standards, such as:
The methods outlined in these standards are based on the coefficient of discharge, which is the ratio of the measured capacity to the theoretical capacity of a nozzle with an equivalent flow area.
Coefficients of discharge are specific to any particular safety valve range and will be approved by the manufacturer. If the valve is independently approved, it is given a ‘certified coefficient of discharge’.
This figure is often derated by further multiplying it by a safety factor 0.9, to give a derated coefficient of discharge. Derated coefficient of discharge is termed Kdr= Kd x 0.9
Critical and sub-critical flow - the flow of gas or vapour through an orifice, such as the flow area of a safety valve, increases as the downstream pressure is decreased. This holds true until the critical pressure is reached, and critical flow is achieved. At this point, any further decrease in the downstream pressure will not result in any further increase in flow.
A relationship (called the critical pressure ratio) exists between the critical pressure and the actual relieving pressure, and, for gases flowing through safety valves, is shown by Equation 9.4.2.
Overpressure - Before sizing, the design overpressure of the valve must be established. It is not permitted to calculate the capacity of the valve at a lower overpressure than that at which the coefficient of discharge was established. It is however, permitted to use a higher overpressure (see Table 9.2.1, Module 9.2, for typical overpressure values). For DIN type full lift (Vollhub) valves, the design lift must be achieved at 5% overpressure, but for sizing purposes, an overpressure value of 10% may be used.
For liquid applications, the overpressure is 10% according to AD-Merkblatt A2, DIN 3320, TRD 421 and ASME, but for non-certified ASME valves, it is quite common for a figure of 25% to be used.
Backpressure - The sizing calculations in the AD-Merkblatt A2, DIN 3320 and TRD 421 standards account for backpressure in the outflow function,(Ψ), which includes a backpressure correction.
Two-phase flow - When sizing safety valves for boiling liquids (e.g. hot water) consideration must be given to vaporisation (flashing) during discharge. It is assumed that the medium is in liquid state when the safety valve is closed and that, when the safety valve opens, part of the liquid vaporises due to the drop in pressure through the safety valve. The resulting flow is referred to as two-phase flow.
The required flow area has to be calculated for the liquid and vapour components of the discharged fluid. The sum of these two areas is then used to select the appropriate orifice size from the chosen valve range. (see Example 9.4.3)
Many standards do not actually specify sizing formula for two-phase flow and recommend that the manufacturer be contacted directly for advice in these instances.

The L22E Emergency Relief Vents are designed to provide superior sealing and industry leading high flow rates. When properly sized, the high flow capacity will prevent the tank from damage in an emergency case.
Model L1220A is used for pressure and vacuum relief where vapors must be piped away. Escaping vapors are piped away through a flanged outlet connection. This helps to provide increased fire protection and safety.
Model L2300A is designed for emergency relief capacity above that supplied by a standard operating valve used on tanks, piping, and low pressure vessels. Emergency relief valves provide relief from excessive internal pressures which may cause tank damage.
Model L1200A is designed to protect your tank from damage created by overpressure or excessive vacuum. Costly product evaporation losses due to normal tank “breathing†are greatly reduced. Because the Model L1200A retains toxic vapors, atmospheric contamination is minimized. This helps to provide increased fire protection and safety.
Balanced style SRV’s for liquid service. Balanced against the effects of backpressure without bellows. Made in accordance with ASME Section VIII or “CE” mark. Initial modulation at low flow with fixed blowdown. Available in carbon or stainless steel materials as standard. Special alloy construction available upon request. Plastic seated with a variety of elastomer seal materials and connection styles available.
pump system. Constant pressure on the discharge side of the chemical feed (metering) pump prevents siphoning, ensuring proper operation of the pump and an accurate chemical dosage rate. KENCO KPRV Pressure Relief Valves are similar in design to KBPV Valves but are three-way valves
that allow unrestricted flow through two ports and a third relief port designed to be connected back to tank. This configuration provides protection from over pressurization of the chemical feed systems lines and components by relieving the system pressure back to tank through the third port when the system pressure exceeds the KPRV’s set pressure.
that allow unrestricted flow through two ports and a third relief port designed to be connected back to tank. This configuration provides protection from over pressurization of the chemical feed systems lines and components by relieving the system pressure back to tank through the third port when the system pressure exceeds the KPRV’s set pressure.
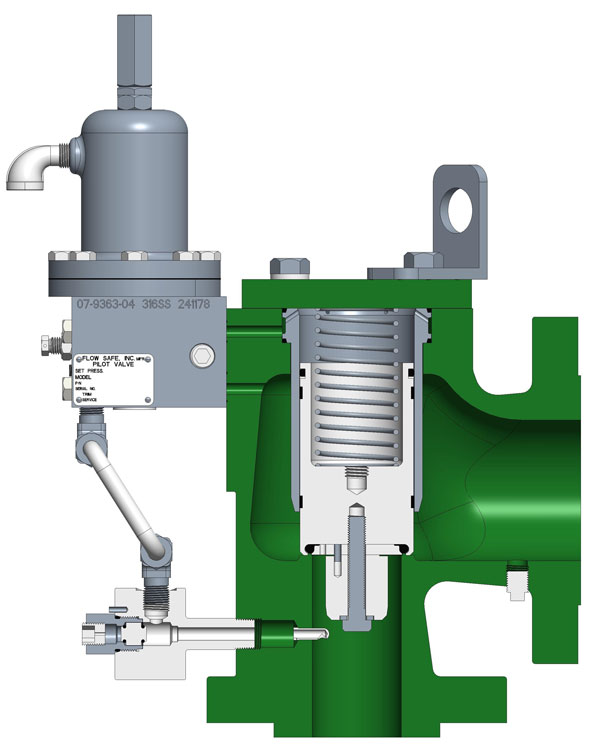
The F7000/F8000 series POSRV’s features the first direct mount pilot valve with integral porting. Design provides for easy conversion of orifice sizes through addition of annular flow plug (F8000 series), interchangeable pilot mounting (F100/F200/F300/F500), and field adjustability. Other features include a low profiles, inline repair, and minimal connections.
The F7000/F8000 series POSRV’s features the first direct mount pilot valve with integral porting. Design provides for easy conversion of orifice sizes through addition of annular flow plug (F8000 series), interchangeable pilot mounting (F100/F200/F300/F500), and field adjustability. Other features include a low profiles, inline repair, and minimal connections.
The F7000/F8000 series POSRV’s features the first direct mount pilot valve with integral porting. Design provides for easy conversion of orifice sizes through addition of annular flow plug (F8000 series), interchangeable pilot mounting (F100/F200/F300/F500), and field adjustability. Other features include a low profiles, inline repair, and minimal connections.
Pilot operated pressure relief valves with aluminum or carbon steel construction, and modulating-action pilots. A variety of soft seat materials are available. Ideal for natural gas regulator and meter protection, and positive displacement blower protection. This product provides high capacity flow rates and are inline repairable. Made for DOT / gas transmission applications (non-ASME Code). FLOWSAFE customers buy smaller valves, save money!




 8613371530291
8613371530291