overhead crane wire rope changing procedure quotation
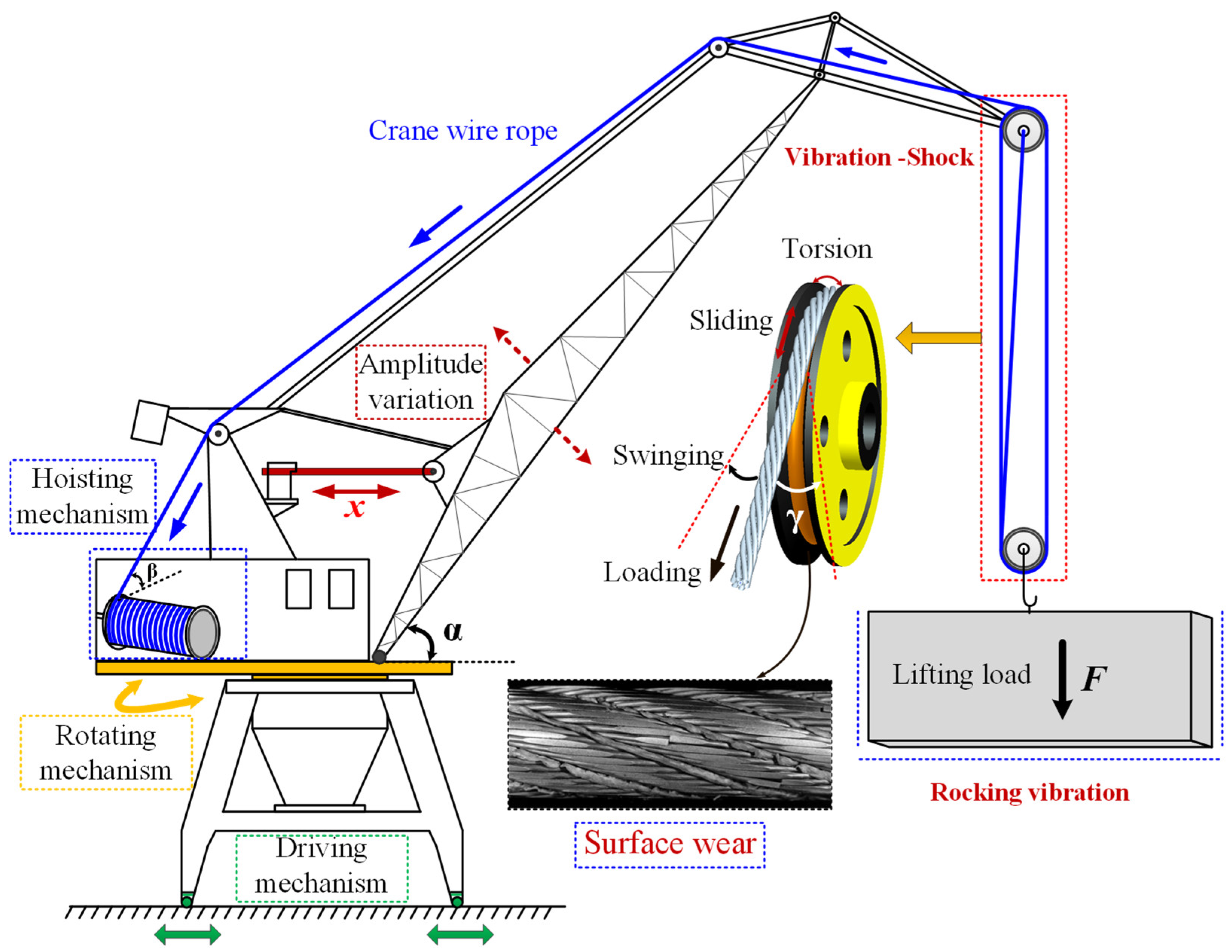
Radically redesigned with never-before-seen features – both inside and out – the S-series will set the standard in lifting for years to come. The newly designed structure includes next-generation features such as off-set reeving, stepless hoisting movement and synthetic rope. The tilted rope drum enables more direct rope angles to decrease the wear and tear of reeving components. And offset reeving means more balanced wheel loads for less stress on the crane structure.
The evolutionary synthetic rope is durable but light and doesn’t require lubrication. The rope also features a strong, symmetric structure for less rope defects and safer handling. Rope angle measurement allows for the use of Smart Features including Hook Centering, Snag Prevention and Follow Me.

吊,搬送する大型天井クレーン等の分野で利用される。Description: TECHNICAL FIELD The present invention relates to a method for replacing a wire rope of a crane, and more particularly, to efficiently use an old wire rope wound around a hoisting drum installed on a crane. The present invention relates to a method of replacing a new wire rope with an old wire rope which can be automatically wound on the ground. This is used in the field of large overhead cranes that suspend and transport heavy objects such as coiled steel plates and ingots.
えたフックブロック8を懸吊している。A wire rope wound around a hoisting drum such as a large overhead crane installed in a rolling mill of a steel mill is, for example,
いう)までも解く。In such an overhead crane, replacement work of the old wire rope 6 has been conventionally performed as follows. As shown in FIG. 9, first, the hoisting drum 5 is rotated in the hoisting direction (the direction opposite to the arrow 42), and the hoisting drum 5 is rotated.
The views of the old wire rope 6 are sequentially solved from the winding grooves 5c and 5d in the left-right inverted spiral shape engraved on the hook block 8, and the hook block 8 is lowered onto the support base 9 placed on the ground and firmly mounted.
Remove one end 6a (see FIG. 10) of the old wire rope 6 that is hung on the floor, tie the end 6a with a cremona rope (not shown), and lower it to the ground. Then, the Cremona rope is removed, and one end of the new wire rope 10 wound around the feeding means 11 arranged in advance on the ground and one end 6a of the old wire rope 6 are connected by a connecting fitting (not shown) or the like. . After that, the hoisting drum 5 is rotated in the hoisting direction 42, and the new wire rope 10 is started to be pulled up to the hoisting drum 5, while the old wire rope 6 is wound about three times around the winding groove 5d of the hoisting drum 5. Let This is to secure a frictional force such that the old wire rope 6 and the new wire rope 10 do not slip on the hoisting drum 5 when the hoisting drum 5 is subsequently rotated in the hoisting direction 42 and the old wire rope 6 is paid out. This is to keep it. After that, the other end 6b (the first end) of the old wire rope 6 hooked on the fixture 5b provided on the other end of the hoisting drum 5 (first
戻し、再度、上記と同じ作業を繰り返す。The other end of the old wire rope 6 is tied with a cremona rope or the like, and in this state, the hoisting drum 5 is further rotated in the hoisting direction 42, while the other end is guided so as not to bounce, while the club 4 is being guided. The old wire rope 6 is let out to the ground through the handrail 4a, and the worker waiting on the ground bundles the old wire rope 6 in a ring shape. During this operation, the old wire rope 6 wound around the winding drum 5 moves in the direction of the arrow 44 along the spiral winding groove 5d. When the wound portion of the old wire rope 6 reaches the central position approaching the winding groove 5c of the reverse spiral, there is no winding allowance for the old wire rope 6 to move, and at that time, the rotation of the hoisting drum 5 To stop. The old wire rope 6 in the wound state is loosened on the hoisting drum 5 by the operator"s manual work so as to float from the winding groove 5d, and the old wire rope 6 is left as it is at the left end of the winding groove 5d where the fixture 5b is located. Return to and repeat the same operation as above.
了される。When the connection between the new wire rope 10 and the old wire rope 6 reaches the upper position 43 of the hoist drum 5 by sequentially tracing the hook block 8 and the upper sheave 7 (see FIG. 10) by such work. The rotation of the hoisting drum 5 is stopped, the connecting portion is disconnected, and one end of the new wire rope 10 is hooked on the fixture 5b of the hoisting drum 5. The other end 6b of the old wire rope 6
Is tied with a cremona rope, and it is lowered to the ground, and the last part of the old wire rope 6 is also bundled into a ring on the ground. On the other hand, the other end of the new wire rope 10 is removed from the feeding means 11, the other end is tied with a cremona rope or the like and pulled up onto the club 4, and the other end is hooked on the fixture 5a of the hoisting drum 5. After the hoisting drum 5 is rotated in the hoisting direction 42 and the new wire rope 10 is additionally wound at both ends of the hoisting drum 5, the hoisting drum 5 is further rotated in the hoisting direction, whereby the new wire rope 10 Is wound around the hoisting drum 5, and the hook block 8 rises. In this way, the replacement work of the old wire rope 6 and the new wire rope 10 is completed.
非常に煩わしいものであった。In such a conventional replacement method, while rotating the hoisting drum 5 at the high position of the ceiling part, the old wire rope 6 is unwound to the ground, while the unwound old wire rope 6 is bundled by the operator on the ground. It was being done. For large overhead cranes, the diameter of the wire rope used for them is as large as 25 mm to 40 mm, and the work of bundling them is not very efficient because it requires a lot of manpower and is a very heavy work. In addition, it is necessary for the bundling operator and the crane operator to work while constantly signaling each other.
提案した。For this reason, the applicant of the present invention, after fixing the hook block to the ground, connects one end of the old wire rope to the new wire rope and connects the other end of the old wire rope to the winding means separately prepared. JP-A-63-17792 proposes a method for replacing the wire rope of a crane, in which the old wire rope is wound up only by the pulling force driven by the winding means without driving the hoisting drum. did.
善が強く望まれていた。In the above method, the pulling force of the winding means arranged on the ground acts on the entire wire rope, and by extension, the old wire rope in the portion stretched between the upper sheave and the hook block is also directly affected. It was necessary to fix the hook block particularly firmly. In addition, the strength of the winding means must be increased in order to obtain a sufficient tensile force, and the drive source requires considerably large power. This is even more so when the wire rope is thick and heavy, which causes problems such as an increase in the size of the device and an increase in cost, and a restriction on the work space. Further, since a large tension acts on the wire rope, the connection portion between the new wire rope and the old wire rope may be disconnected, and improvement of the work has been strongly desired.
ープ取替方法を提供することである。The present invention has been made in consideration of such circumstances, and an object of the present invention is not to require a compact and large space, to keep a large tension applied to the wire rope at all times, and to make the wire rope thick. It is an object of the present invention to provide a method for replacing a wire rope of a crane, in which the safety of the replacement work is highly secured and the wire rope can be efficiently replaced with a new wire rope.
けるワイヤロープの取替方法に適用される。INDUSTRIAL APPLICABILITY The present invention is applied to a method for replacing a wire rope in a crane equipped with a hoisting drum for winding a wire rope, which is installed on a truck traveling on a rail.
It is lowered to the ground by rotating in the winding direction (the direction opposite to the arrow 42), and is unwound from the hoisting drum 5 to the old winding of the old wire rope 6. The one end 6a of the old wire rope 6 is removed from one end of the hoisting drum 5, and the one end 6a of the old wire rope 6 is lowered to the ground and connected to one end of the new wire rope 10 wound around the feeding means 11. Next, the hoisting drum 5 is rotated in the hoisting direction 42, and the old wire rope 6 is wound around the hoisting drum 5 a predetermined number of times. Remove the other end 6b. Rotate the hoisting drum 5 further in the hoisting direction 42,
The new wire rope 10 is started to be pulled up to the hoisting drum 5, and the other end 6b of the old wire rope 6 is fed to the ground. The other end 6b of the old wire rope 6 is connected to the rotary table 17 arranged on the ground, and the winding direction of the winding drum 5 thereafter is increased.
The old wire rope 6 is fed to the ground by rotating the old wire rope 6 and the rotation speed of the rotary table 17 is adjusted so that the old wire rope 6 has a desired winding diameter without tension. That is, the ropes 6 are stacked in a ring shape and bundled.
うにしてもよい。Further, referring to FIG. 5, the iron cage 18 having a cylindrical iron cage 18a surrounded by the old wire ropes 6 which are stacked in a ring shape is detachably provided on the rotary table 17 and is fed to the ground. The old wire rope 6 may be bundled in a ring shape by the rotation of the rotary table 17 while preventing the winding wire of the old wire rope 6 from being disturbed by the cylindrical basket portion 18a.
While contacting the old wire rope 6 that has been fed to the ground through the upper opening of 8c, to the ring-shaped pipe material that is located at the boundary between the truncated cone-shaped groin portion 18b and the truncated cone-shaped small groin portion 18c. Alternatively, the old wire ropes 6 may be stacked and bundled in a ring shape by the rotation of the rotary table 17.
とした巻き取りを実現することができる。According to the present invention, one end of an old wire rope removed from a hoisting drum is connected to a new wire rope, and the old wire rope is wound around the hoisting drum a predetermined number of times, and then the hoisting drum is rotated in a hoisting direction. Since the other end of the old wire rope is drawn to the ground while being made to move, the old wire rope can be reliably drawn without slipping, and the new wire rope can be wound around the hoisting drum. Then, the old wire rope is extended to the other side by the rotation of the hoisting drum in the winding direction and the rotation speed of the rotary table is adjusted to connect the old wire rope to the movement of the rotary table arranged on the ground. Since the wire rope is wound, it is possible to efficiently stack the old wire ropes in a loop so that the old wire ropes have a desired winding diameter without exerting a large tension on the wire ropes. That is, if the rotation speed of the rotary table is increased, the winding can be made thinner, and if the winding is tightened too much, it can be slowed down and corrected, or a large bunch of wheels can be stacked. Orderly winding can be achieved with any diameter.
ないものとしておくことができる。If a carcass with a cylindrical cage that surrounds the old wire ropes that are bundled in a ring shape is detachably attached to the rotating table, the disorder of the winding appearance of the old wire ropes that have been fed to the ground will be cylindrical. Part is prevented by
The old wire rope can be smoothly looped and bundled by rotating the rotary table. For example, if the old wire rope suddenly jumps out, the cylindrical cage prevents it. Further, even if the ring-shaped bundle is greatly tilted, it is prevented from deviating from the turntable. Of course, the old wire ropes can be bundled compactly to facilitate the subsequent treatment, and the winding means can be made to require no space.
しておきたい場合に都合がよい。By forming a truncated cone-shaped basket on the upper part of the cylindrical basket, the old wire rope that is fed to the ground is brought into contact with the inner surface of the truncated cone and the rotary table rotates to form a ring shape. Can be stacked and bundled. For example, even if a situation occurs in which the old wire rope is excessively shaken by centrifugal force or the like due to the rotation of the turntable, the wound form after that is not greatly impaired. This is convenient when it is desired to keep the winding diameter large.
同心状の巻取り姿となるよう誘導することができる。A small frustoconical small squirrel cage is formed in the upper part of the frustoconical squirrel cage, and the old wire rope that is fed to the ground through the upper opening of the frustoconical small squirrel cage is cut into a truncated cone shape. The old wire ropes can be looped and bundled by rotating the rotary table by contacting them in a ring-shaped pipe shape located at the boundary between the pallet cage and the truncated cone small pallet cage. Not only does the frustoconical small squirrel cage guide the movement of the old wire rope to suppress unnecessary fluctuations, but the frustoconical small squirrel cage is narrower toward the top to allow the old wire rope to be thin. It is possible to prevent the body from jumping out of the body and guide it to have a concentric winding shape.
等の重量物を懸吊,搬送するものである。The wire rope replacement method shown in the present embodiment efficiently uses a thick and rigid old wire rope wound around the hoisting drum of a crane by using a vertically-shaped winding means that is compactly formed. It is a new wire rope that can be replaced and the old wire rope can be wound and bundled without requiring a large amount of power. The crane to which this wire rope replacement method is applied is, for example, a large overhead crane 1 as shown in FIG.
ーブ7を介してフックブロック8を懸吊している。As shown in FIG. 1, rails 3a, 3a are laid on a girder 3 of the overhead crane 1, and a club 4 as a truck moving on the rails 3a is rotated by a drive source (not shown). The hoisting drum 5 is stationary. The winding drum 5 is provided with spiral winding grooves 5c, 5d in the opposite direction on the left and right, and both ends 6a of the old wire rope 6 wound along the winding grooves 5c, 5d. As shown in FIG. 10, the wires 6b are hooked at both ends of the hoisting drum 5, and the wire ropes 6 thereof are hooked via the upper sheave 7 arranged at the lower part of the hoisting drum 5. Is suspended.
ブブロック(図示省略)に軸支されている。The hook block 8 pivotally supports four movable pulleys 8A, 8A, and a load hanging hook 8a (see FIG. 1) is hung at the bottom thereof. That is, the fixtures 5a and 5b for attaching the wire rope are provided at both ends of the hoisting drum 5, and the wire rope in which the hook block 8 is suspended via the upper sheave 7 on the fixtures 5a and 5b. One end 6a and the other end 6b of 6,
を巻き取る巻取手段12とにより構成される。As shown in FIG. 1, the wire rope replacement device has a support base 9 placed on the ground for mounting the hook block 8 and one end 6a of the old wire rope 6 removed from the hoisting drum 5. A feeding means for feeding the new wire rope 10 to be connected
9上でも充分な安定を得ることができる。The support base 9 is a base with four legs having a mounting surface on the top, and is simple enough for an operator to easily carry. As will be described later, since the old wire rope 6 to be replaced is unwound by the hoisting drum 5, a large external force does not act on the hook block 8 via the old wire rope 6 during the replacement work. It is possible to obtain sufficient stability even on a simple support base 9.
を、順次繰り出すことができるようになっている。The feeding means 11 has a rotatable disc (not shown) inside an annular base 14 having a plurality of shelves 13 arranged on the outer periphery thereof, and a core member protruding in the center of the disc. A new wire rope 10 is coiled around and mounted on a disk around 15
と共に駆動源19により回転されるようになっている。The winding means 12 is, as shown in FIGS. 4 and 5, a vertical guide shaft 16 for guiding the old wire rope 6 unwound from the winding drum 5 to be wound up.
In order to enclose the horizontal rotary table 17 that rotates with the guide shaft 16 to receive the old wire rope 6 in a ring shape, and the old wire rope 6 that is detachably provided on the rotary table 17 and is bundled in a ring shape. And a vertical frame 18 to be arranged, and the rotary table 17 is provided with a guide shaft 16
けている。The iron cage 18 is a ring-shaped pipe material 24 arranged laterally so as to surround the outer circumference of the old wire rope to be wound up.
Is provided with a cylindrical cross-shaped cage 18a, which is a combination of the pipe members 25 arranged in the vertical direction so as to intersect with each other, and on the upper part thereof, a two-pointed truncated conical cross-shaped cage for introducing and guiding an old wire rope. The portion 18b is provided with a truncated cone small cross-section basket 18c.
けられている。By the driving force of the vertical geared motor 19 described above, the guide shaft 16 integrated with the rotary table 17 and the cross cage 18 are rotated, and the old wire rope introduced from the upper opening of the truncated cone small cross cage 18c. 6 (see FIG. 1) can be bundled around the guide shaft 16 in a ring shape. The angle members 30 are radially arranged on the rotary table 17 so that a small space is formed under the bundled old wire ropes so that the bundled old wire ropes can be easily taken out. Also,
Has only to have an output enough to stack and bundle the fed old wire ropes 6, and the output is relatively small such as 3.7 kw. Cross cage 18 and rotary table
The rotation speed of the rotary table 17 can be adjusted according to the descending speed of the old wire rope 6 fed out from the table, so that the old wire rope 6 can be bundled without wasting space, and the old wire rope 6 can be bundled by changing the rotation speed. The ring diameter can be changed arbitrarily each time. Further, the operator can carry the operation box 33 with the frequency meter and operate it in any safe place.
に説明する。The replacement work of the old wire rope 6 and the new wire rope 10 by the wire rope replacement device thus configured will be described below.
置した支持台9上にフックブロック8を載置する。(A) First, as shown in FIG. 1, the old wire rope 6 is unwound by rotating the hoisting drum 5 in the lowering direction (the direction opposite to the arrow 42), and the hook block 8
端に、連結金具(図示せず)等で接続する。(C) The one end 6a of the old wire rope 6 is removed from the fixture 5a of the hoisting drum 5, and the one end 6a is tied with a cremona rope (not shown) or the like and manually lowered to the ground. And after removing the cremona rope, one end 6a
るためである。(D) Next, as shown in FIG. 2, the hoisting drum 5 is rotated in the hoisting direction 42, and the old wire rope 6 is wound around the winding groove 5d of the hoisting drum 5 a predetermined number of times, for example, about three times. After that, the other end 6b of the old wire rope 6 hooked on the fixture 5b of the hoisting drum 5 is removed. In addition, when the hoisting drum 5 is rotated, the above-described three times of winding do not cause the old wire rope 6 wound around the hoisting drum 5 to slip from the hoisting drum 5 and prevent the old wire rope 6 from winding. This is so that a desired frictional force can be exerted at the time of feeding and raising the new wire rope 10.
の下部に連繋,固定する。(E) The hoisting drum 5 is further rotated in the hoisting direction 42, and the new wire rope 10 is started to be pulled up to the hoisting drum 5, and the other end 6b of the old wire rope 6 is tied with the cremona rope. The handrail 4a of the club 4 shown in FIG. 1 is guided by a Cremona rope so that the end 6b does not bounce.
も、回転テーブル17から逸脱することが防止される。(F) If the winding means 12 is rotated by the drive source 19 while rotating the hoisting drum 5 in the hoisting direction 42, the old wire rope 6 is fed toward the ground by the rotational force of the hoisting drum 5. In this state, the old wire rope 6 can be wound inside the cage 18 by unwinding the old wire rope 6 to the ground and adjusting the rotation speed of the rotary table 17. That is, if the rotation is accelerated by the speed control of the rotary table 17, the winding can be thinned, and if the winding is tightened too much, the winding can be slowed to correct or a large ring is piled up. Orderly winding is realized. In this winding operation, the new wire rope 10 is unwound from the unwinding means 11 as much as the old wire rope 6 is wound up. As shown in the figure, if the guide shaft 16 is erected at the center of the rotary table 17, the winding state of the old wire rope 6 can be maintained at the center. Although the iron cage 18 may be omitted, if it is provided, the winding appearance of the old wire rope can be prevented from being disturbed. That is, even if the old wire rope 6 suddenly jumps out, the pipe material 25 of the cylindrical basket 18a blocks it.
溝5dに沿って固定具5b側へ逆戻りされる。(G) A winding groove in which the old wire rope 6 wound around the winding drum 5 is spirally engraved in the middle of this work.
The winding drum 5 is moved along the direction 5d in the direction of the arrow 44 to reach the end of the winding groove 5d at the substantially central position, so that the winding drum 5 is stopped from rotating. When the wire rope is thin and slightly light, the old wire rope 6 is loosened on the hoisting drum 5 by the operator"s manual work and floated from the winding groove 5d.
Return to the left end where the fixture 5b is located. If the wire rope is thick and heavy, the operator should remove part of the old wire rope 6 from the handrail 4a.
Loosen a little above. When the hoist drum 5 is further rotated in the same direction in a state where the old wire rope 6 is floated to the extent of causing slippage with the winding groove 5d, the old wire rope 6 is fixed along the winding groove 5d with the fixture 5b. It is returned to the side.
ねられる。(H) While repeating the above procedure, the operation of feeding the old wire rope 6 to the ground is performed by rotating the hoisting drum 5 in the winding direction, but the old wire rope 6 is not subjected to a strong tension, The old wire ropes 6 are looped and bundled on the turntable 17 so that the desired winding diameter is obtained.
Disconnect the connection. One end 6a of the old wire rope 6 is bound with a Cremona rope or the like, while one end of the new wire rope 10 is attached to the fixture 5b. One end 6a of the old wire rope 6 is gradually lowered to the ground by a worker on the club 4 using a cremona rope. At that time as well, the winding means 12 is rotated, and when all the old wire ropes 6 are bundled, the work of collecting the old wire ropes 6 is completed.
ックブロック8も上昇する。(J) Remove the fixed end of the new wire rope 10 from the feeding means 11, tie it with a cremona rope, and pull it all up on the club 4, and hook the other end on the fixture 5a of the hoisting drum 5. Rotate the hoisting drum 5 further and use the new wire rope 10
When the winding wire is wound around both ends of the hoisting drum 5 and further wound up, the new wire rope 10 is wound around the hoisting drum 5, and the hook block 8 also rises.
とは言うまでもない。In the winding operation performed in this manner, since the old wire rope 6 is unwound by the rotational force of the hoisting drum 5, a large tension based on the drive of the winding means 12 acts on the old wire rope 6 as in the conventional case. There is nothing to do. Therefore, disconnection of the connection between the old wire rope 6 and the new wire rope 10 is avoided. Further, since the force via the old wire rope 6 does not act on the hook block 8 as in the conventional case, the support base 9 can be relatively small, and the hook on the ground is not required. The block 8 can be easily supported. By the way, a cage
It goes without saying that if the 18 is removed from the rotary table 17, the wound old wire rope 6 can be easily taken out from the winding means 12.
生じても以後の巻取り姿を大きく損なうことはない。By the way, if the casket body 18 is provided with the truncated cone-shaped cage part 18b in the upper portion as shown in FIG. 5, the old wire rope 6 fed to the ground is brought into contact with the inner surface of the truncated cone-shaped casket part 18b. On the other hand, the rotary table 17 can be rotated and stacked in a ring shape. This is convenient when the winding diameter is often increased, as indicated by the dashed line. For example, even if a situation occurs in which the centrifugal force based on the rotation of the rotary table 17 acts excessively on the old wire rope 6 to cause it to be swung, it does not significantly impair the subsequent winding state.
滑な誘導が実現される。Further, when the truncated cone small cross basket 18c connected to the upper part of the truncated cone cross basket 18b is formed, the old wire which is fed to the ground through the upper opening of the truncated cone small cross basket 18c. While the rope 6 is in contact with the ring-shaped pipe material 24A located at the boundary between the frustoconical spatula portion 18b and the frustoconical spatula portion 18c, the old wire ropes 6 are bundled in a ring shape by the rotation of the rotary table 17. be able to. In this case, as shown by the chain double-dashed line, the inner ring surface of the pipe member 24A guides the movement of the old wire rope 6 and suppresses unnecessary wobbling of the old wire rope 6. Of course, the frustoconical small squirrel cage 18c becomes narrower as it goes upward, so that when the old wire rope is thin, it is prevented from jumping out of the squirrel cage 18 and a smooth concentric guidance is realized.
とすることができる。The winding means 12 does not require a particularly strong winding force as in the conventional case, and a rotating force for binding the old wire rope 6 fed out over the handrail 4a of the club 4 at its lower position to the rotary table 17. Just give it. Therefore, the vertical geared motor 19 serving as a drive source thereof can have a low output. Further, since the winding means 12 is hardly affected by the tension of the old wire rope 6, it is not necessary to fix it to the ground. Because of this, the old wire rope 6 can be made small together with the adoption of the cross cage 18, and the winding means 12 can be made more compact than the conventional one.
Even if the diameter of the old wire rope 6 is as thick as 40 mm and has high rigidity, the winding diameter in the carcass 18 can be reduced or increased, and the winding shape of the old wire rope 6 can be increased. The volume can be reduced.
パイプ材、42……巻き上げ方向。FIG. 1 is an overall configuration diagram of a wire rope replacement device used for carrying out the method of the present invention, FIG. 2 is a schematic diagram showing a tensioned state of the wire rope during replacement work, and FIG. FIG. 4 is a perspective view of the crane, FIG. 4 is a plan view of the winding means, and FIG.
6 is a perspective view of the operation box with a frequency meter, FIG. 7 is its internal circuit diagram, FIG. 8 is its external connection diagram, and FIG. 9 is a conventional wire rope. Replacement work diagram, No. 10
The figure is a schematic view showing a state in which the wire rope is stretched in a normal state of the crane. 1 ... Crane (overhead crane), 3a ... Rail, 4 ...
… Club (carriage), 5 …… Winding drum, 6 …… Old wire rope, 6a …… One end, 6b …… Other end, 8 …… Hook block, 10 …… New wire rope, 11 …… Feeding means, 17-Rotary table, 18-Case cage, 18a-Cylindrical cage section, 18b

An essential component of a crane quote usually begins with a description of what you’re lifting. It can help determine what type of system is recommended. Some industries have specific processes or requirements for lifting, which is why having this piece of information is indispensable to the crane dealer or manufacturer.
When deciding on the type of crane, building design can drive whether the crane needs a top or underrunning endtruck. If you’re replacing a crane, it’s easy to see which type you need. For new cranes, the primary factor in this decision will depend on the design of your building. Often, you’ll see top-running cranes on runways that are sitting on columns mounted to the walls of the building. Under-running cranes are used on cranes with runways suspended from the ceiling, for example, when a crane is placed in the middle of a building.
Knowing how much weight the crane will lift matters for many reasons. The biggest reason is safety. A crane lifting more than it is designed for is hazardous to your workers and increases the stress and maintenance to the crane and building superstructure. You want to ensure the crane will be able to lift enough weight for what you’re doing today and in the future. Listen to the dealer or manufacturer, as they will be your greatest resource and partner when purchasing a crane.
The CMAA (Crane Manufacturers Association of America) has alisting for crane duty classification. This classification defines how much the crane is used and allows the dealer or manufacturer to quote the best equipment for the job. Duty classes are labelled A through F and ranges from standby/infrequent service to continuous severe service. Generally, when no other duty requirement is indicated, class C is frequently quoted. This detail will be discussed further by the dealer or manufacturer as your quote is being developed.
During this visit you will be able to talk in more detail about the load. You can discuss the duty requirements in more detail, zeroing in further on what crane duty classification fits your requirements best, including details like the number of lifts per hour at full and varying capacities. You will talk about the hook coverage, assuring the hook will reach the entire floor area where loads are lifted. You may talk about the runway type and length to find the optimal lift speed, and wheel loading requirements so you can appropriately lift and move the load you want to pick up. Your dealer or manufacturer representative will also talk to you about what type of hoist will work best for your crane application. Generally, a chain hoist is appropriate for lifting loads up to two tons, while wire rope hoists are more robust and appropriate for loads over two tons.
Even if you are not a technical expert on cranes, providing yourself with some basic information when requesting a quote will make the process easier and allow you to have a more robust conversation when the real experts step in and help you finalize the quote.

Buying new crane ropes is a detailed and thorough process. While it may be time-consuming, wire rope replacement prioritizes safety for your workers, minimizes downtime on a jobsite, maximizes the lifespan of the crane and avoids the costly and time-consuming process of getting correct rope onsite and respooling your crane.
Sometimes, it can seem like the wire rope buying process is overly complicated. This is done on purpose to avoid as many issues as possible when the new rope is installed. The reason for that is so buyers avoid putting the wrong types of ropes on cranes and unnecessarily increasing the risk of injuries to workers or damage to loads being lifted. The processes are to make sure to prevent that added risk and put the correct rope on the correct machine, per Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) specifications.
Wire rope specialists ask these questions to understand your circumstances and what your needs are. With this information, they are better prepared to get the absolute correct rope.
Most of the time, the customer should have access to their crane’s operations manual that will show what rope diameter and length is specified. The customer may have to measure or come up with his own calculations on length. The crane manufacturer is going to make a specific drum for that specific type of wire rope.
The rope has to be specific to the lagging of the drum for that machine, which is why there are multiple variations for each size of wire rope because each kind is specific to the type of crane, and it shouldn’t be substituted. Mazzella will only install the rope that is the correct brand and tolerance on a particular crane.
Ordering the correct crane rope will prevent crane rope damage. The wrong rope could cause damage to the equipment, and at worst, boom failure. On the less severe side, you will have bad performance or it might not work at all. You could have twist and/or spooling issues. That could lead to the crane failing altogether, which creates downtime as you wait for the correct wire rope to be ordered/delivered and installed.
Many crane owners are working for somebody else when they’re doing jobs, so if the rope doesn’t work, they’re paying for work that is not getting done and falling behind schedule.
On the more severe side, you could total your crane and/or irreparably damage the load being lifted if you use the wrong wire rope. In the worst-case scenario, using the incorrect rope could result in severe injury and/or the loss of life.
Sometimes, customers assume that there’s a one-size-fits-all replacement, that if it’s a non-rotating rope, it should work on every application. There’s a lot of misinformation on what will work and what won’t work. With our experience and access to all brands of wire rope, Mazzella guarantees we can get you the right rope for your cranes. If Mazzella isn’t comfortable with the project, we won’t supply the wire rope.
If the wrong wire rope is ordered and delivered, it could be hours or days before the correct rope is on location. Especially with a lot of the larger cranes, manufacturers are shipping model-specific ropes all over the country, and depending on location and money, that could cause delays on your jobsite.
With our large inventory of rope, Mazzella can have a new spool of wire on a truck and out for delivery in a matter of hours. Avoid the pitfalls of ordering the wrong crane rope and you’ll have a new spool of wire rope on its way. Once the order process is done, what can your company do to prepare for delivery and installation?
It is a good idea to give management the proper notice of when the installer will be on-site, have the necessary technicians on-site to help the installer with the rope replacement and make sure the installer/technicians have a clear working space.
There’s a lot of downtime associated with making a mistake in the preparation process, so the more prepared you can be for the install, the better. You don’t want a situation where your crane is inactive because of an oversight or completely avoidable situation.
Also, Mazzella recommends you measure your sheaves with a sheave gauge. A sheave gauge will help you measure the wear of the root, the amount of wear on the groove wall and the diameter of the wire rope.
After ordering the correct rope and having the requisite space and approval for installation, how long will it take to remove and replace the old rope when the technician, assistants and supplies arrive onsite? For some small cranes, the timeframe could be as little as 45 minutes, but for larger cranes, removing the old rope and installing the new one could be a several-hour process.
There’s a lot of factors that go into a successful crane rope installation. The most important thing is the quicker your supplier responds to your order and gets a rope on location, the quicker that rope gets installed properly, saving time and money. Downtime is the key, and it could cost companies tens of thousands of dollars per day if their crane(s) are inoperable.
Once a new crane rope is installed, a break-in period or tension period is recommended to make sure everything is performing correctly, and help you avoid shock-loading the newly installed wire rope. The break-in period is recommended because installation and spooling equipment are not going to put adequate tension on the rope. A break-in period consists of putting a low percentage of the working load limit weight on the rope for several lift cycles, and running the blocks up to the boom length (working height) and back down. For the most specific guidelines on the breaking-in process for your new wire rope, refer to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
If a brand-new wire rope on a crane is not broken in properly before lifting a large load, it potentially could damage the rope and render useless the equipment that was just installed on your machine.
When Mazzella fulfills a crane ropes order, it is not just about the sale and the bottom line. While we’re in the business of selling crane ropes, we’re also in the business of building relationships and trust. We are committed to making sure you get the correct products for the right applications.
Crane rope issues don’t just happen 9-to-5 during the normal work week. They happen Friday nights, holidays, weekends and early mornings. They’re always on the clock, and it is just about being honest with the customer and letting them know, they type of rope that is required. That honesty and trust is of utmost importance for the safety of your workers and the proper maintenance of your cranes.
Mazzella has one of the largest crane ropes inventories in the United States. The company provides wire rope assemblies and manufactures bridge cables, crane cables, steel mill cables and thousands of OEM assemblies in sizes from ¼ to 3-inch diameter and 9 to 52 millimeter diameter, domestic and non-domestic and in stock and ready for same or next-day shipment.

The coil of rope should be placed on the ground and rolled out straight, ensuring that it does not become contaminated with dust, grit, moisture or other harmful material.
The rope should never be pulled away from a stationary coil as this will induce turn into the rope and form kinks. If the coil is too large to physically handle it may need to be placed on a turntable which will allow the rope to be paid out as the end of the rope is pulled away from the coil.
Where multi-layer coiling is involved the rope should be placed in equipment that has the capability of providing a back tension in the rope as it is being transferred from the supply reel to the drum. This is to ensure that the underlying laps of rope, particularly in the bottom layer, are wound tightly on the drum.
The supply reel should be positioned such that the fleet angle during installation is kept to a minimum. If a loop forms in the rope it should not be allowed to tighten to form a kink.
The reel stand should be mounted so as not to create a reverse bend during reeving, i.e. for a drum with an upper wind rope, take the rope off the top of the supply reel
Otherwise, winding can be performed by hanging the wire drum up in a crane hook, the hook must be lowered max., A sufficient weight (2.5% -5% of the wire MBL) must be hooked, and the steel wire could be wound close to the drum
Partnering with an overhead crane manufacturer is a big decision and one that should not be taken lightly. The design, manufacturing, and installation of an overhead crane system is an enormous investment, but a necessary one if you want to improve your company’s efficiency and workflows. The first step in that process is to gather and compare overhead crane quotes.
With more than 50 years of experience in the overhead crane industry, we have a highly-skilled team that can design and build custom overhead crane solutions. Our capabilities include light-duty cranes to large-capacity process cranes designed to operate in extreme environments.
We understand that you’ll want to take your time and do your research and due diligence before selecting an overhead crane company to partner with. We also know that each overhead crane project is unique and needs to be quoted accordingly.
For this reason, we wrote this article to help you better understand the overhead crane quotation process. We hope this will allow you to partner with an overhead crane company that you feel most comfortable working with!
If you’re looking to finance your overhead crane equipment, then your bank may require you to have at least three overhead crane manufacturers bid on the project. Even if you know you won’t be financing the equipment, you should do your due diligence and have a couple of different crane companies look at your facility, provide a scope of work, and provide their expert opinion on the right overhead crane for your business.
Gain perspective – Getting a couple of fresh sets of eyes on the project will help provide different options and opinions on the project. Each overhead crane builder may have a different idea or approach to go about solving your lifting and material handling challenges.
For example, one company may identify a potential problem or issue that another company overlooked. Or, if you have existing cranes in your facility, one company may want to completely replace them with new units, while another company may have a strategy for upgrading or modernizing your existing equipment at a significant cost-savings to your business.
Keep costs competitive – By having multiple manufacturers bid on your project, you will get a better sense of the true cost of buying and installing an overhead crane. Also, if a company knows that they aren’t the only ones bidding on the project, they will tend to provide a more comprehensive and competitive estimate and may be more willing to negotiate on the final purchase price to get your business.
It’s important to find the right company to partner with for your overhead crane project. There are a couple of different resources that you can use to research overhead crane manufacturers including referrals, industry events or trade shows, and utilizing the internet for research.
Ask for referrals – Utilize industry connections to find out if other companies you know or work with have an overhead crane on-site. Reach out to current customers, vendors, or suppliers and find out if they utilize overhead lifting devices. If so, find out who they worked with, if they were happy with the partnership, and ask them if they’d be willing to provide a contact or make an introduction on your behalf.
Attend industry trade shows or events– You may luck out and find out that an overhead crane company that specializes in lifting equipment is already scheduled to exhibit at an industry show you’ll be attending.
When a crane manufacturer comes on-site for a consultation, they’ll try to identify your specific lifting challenges, as well as evaluate your facility to get an understanding of the building’s floor space, support structures in place, and the size and capacity of the crane that they’ll be building.
Prior to their individual visits, it may help to put together some notes or a cheat sheet about your overhead lifting project. This will remind you to ask each company the same questions and also to provide them with the same specifications for your project so that each company builds their quote off of the same information.
Each of the following specifications will affect the cost of an overhead crane’s design and installation:Total number of cranes– How many cranes will need to be designed, built, and installed?
Capacity – The capacity is the maximum load which may be applied to the crane, the hoist, or below-the-hook lifting device, in a particular working configuration and under a particular condition of use. A crane’s capacity is a variable that takes many different factors into consideration and can best be calculated by the crane manufacturer. They can determine capacity based on their understanding of:The rigging or below-the-hook lifters that will be attached
Any other considerations for future usage or capabilitiesLift– Lift is how high into the air your material needs to be raised. When a team is calculating the lift capabilities of a crane, the following is taken into consideration:The height of any machinery or equipment on the floor that needs to be cleared
Elevation of an existing runwayNumber of lifts per hour – What is the duty cycle of this crane? Will it be making 2-5 lifts per hour at only 50% of its rated capacity? Or, will it be making 10-20 lifts per hours at, or near capacity, each time? Cranes in higher service classifications will require additional engineering and specialized components to solve complex lifting challenges.Hook approach– This is how close the crane hook can get to the end of a bridge or runway and considerations for the trolley hook approach, as well as the crane / runway hook approach. An under running crane will have a better trolley hook approach than a top running crane, so that may be a consideration if your crane needs to pick, or place, material near the walls or support structure within your facility.Power– Will the crane be powered by electricity, hand-powered, or air-powered (pneumatic)?
Operating environment– A severe, obstructed, or dangerous operating environment will affect the cost of an overhead crane.Environmental factors such as high heat, the presence of chemicals or fumes, steam, dust, or excess moisture can require special metal coatings to protect and enhance the operating life of the crane. It can also require special equipment or protection (PPE) for the installers during installation.
Obstructions can affect the cost of an overhead crane if the installers don’t have clear access to the area to remove an existing structure, or install a new one.Operating speed – The faster that the crane needs to operate, the more it will cost to design, source, and configure the individual crane components. A process crane making 10-20 lifts per hour will need a faster bridge, trolley, and hoist than a maintenance crane that requires more precision and slower speeds.Controls– Considerations will have to be made as to how the operator is loading or unloading material:A radio control gives the operator free range to move around to position and adjust the load prior to raising or releasing it.
Faster cranes and cranes that travel the length of the building, may require the operator to work from within an exposed or enclosed cab.Span– The horizontal distance center-to-center of the runway rails. Cranes with large spans will be more expensive than smaller-span cranes due to the need for engineered girders.
Runway location – Is there an existing runway in place? Is it sufficient to support the new crane structure? If a new runway system needs to be built, it will need to be determined if it will be mounted to new support columns, or if it can be tied back to the building.Consider any overhead or wall obstructions that may require additional design and engineering considerations. OSHA requires 3” clearance above the crane and 2” of clearance on the sides of the crane.
Once you’ve gone through the consultation process, a crane manufacturer will re-group with their team of estimators, engineers, and draftsmen and begin putting together a comprehensive proposal.
This process can take anywhere from 3-30 business days depending on the number of cranes being quoted, the complexity of the project, and the sourcing of crane components. Once they’ve completed this process, they’ll get back in touch with you to submit their official bid for the project.
Keep in mind that price should never be the only factor when selecting an overhead crane company to partner with. An overhead crane system is a complex and critical piece of equipment used to improve your business’ efficiency and production flows, and you should only partner with a company that you truly feel comfortable with.
We suggest evaluating the following things when comparing overhead crane quotes so that you have a comprehensive idea of what you’ll be spending on an overhead crane installation.
References– Have they provided, or can they provide, references for you to reach out to? Ask other companies that they’ve done business with if they were satisfied with the following:Overall relationship with the crane builder
Installing an overhead crane in your facility is a big monetary investment. However, it’s also an investment in your employees’ safety, as well as an investment in improving the efficiency of your production and workflow processes. Hopefully, you have a better understanding of what to look for when selecting an overhead crane manufacturer to partner with.
At Mazzella, we design and build world-class overhead crane systems. We have over 50 years of experience in the overhead crane industry and can build custom solutions ranging from light-duty economical cranes to large-capacity, high-duty cycle cranes.

Single girder overhead travelling crane on the rope guide, also known as rope row device, is a relatively simple damage to the attachment. However, many customers do not know how to replace the rope guide. This article briefly introduced the replacement guide rope device approach and process, for your reference.
Single girder overhead travelling crane replacement guide rope device is necessary with matching. Some manufacturers produce can not use the traditional rope guide. Please pay attention to communicate with us when you buy. When replacing the rope guide, should first cut off the power, remove the wire rope. After removing the hexagonal screw of the rope guide, you can take down the rope guide along the wire rope. During this period, it is necessary to pay attention to the wire rope into the rope groove before installing the rope guide, so that the wire rope does not enter the groove, there may again crush the rope guide.
First remove the fixed screws fixed in the rope guide; open the rope guide, the block in the rope guide on the side facing outward, the rope guide into the; wire rope head into the rope guide, adjust the rope guide, straighten out the winding order of the wire rope; wire rope head into the fixed pile, wedge it with iron wedge; fixed rope guide, install all the fixed screws of the rope guide; start, adjust the rope guide. This is to ensure that the upper and lower rope guide can accurately cut off the fire source, do not let the wire rope relax the good position; single girder overhead crane guide rope device device is simple, the device is strong.

A competent person must begin a visual inspection prior to each shift the equipment is used, which must be completed before or during that shift. The inspection must consist of observation of wire ropes (running and standing) that are likely to be in use during the shift for apparent deficiencies, including those listed in paragraph (a)(2) of this section. Untwisting (opening) of wire rope or booming down is not required as part of this inspection.
Significant distortion of the wire rope structure such as kinking, crushing, unstranding, birdcaging, signs of core failure or steel core protrusion between the outer strands.
In running wire ropes: Six randomly distributed broken wires in one rope lay or three broken wires in one strand in one rope lay, where a rope lay is the length along the rope in which one strand makes a complete revolution around the rope.
In rotation resistant ropes: Two randomly distributed broken wires in six rope diameters or four randomly distributed broken wires in 30 rope diameters.
In pendants or standing wire ropes: More than two broken wires in one rope lay located in rope beyond end connections and/or more than one broken wire in a rope lay located at an end connection.
If a deficiency in Category I (see paragraph (a)(2)(i) of this section) is identified, an immediate determination must be made by the competent person as to whether the deficiency constitutes a safety hazard. If the deficiency is determined to constitute a safety hazard, operations involving use of the wire rope in question must be prohibited until:
If the deficiency is localized, the problem is corrected by severing the wire rope in two; the undamaged portion may continue to be used. Joining lengths of wire rope by splicing is prohibited. If a rope is shortened under this paragraph, the employer must ensure that the drum will still have two wraps of wire when the load and/or boom is in its lowest position.
If a deficiency in Category II (see paragraph (a)(2)(ii) of this section) is identified, operations involving use of the wire rope in question must be prohibited until:
The employer complies with the wire rope manufacturer"s established criterion for removal from service or a different criterion that the wire rope manufacturer has approved in writing for that specific wire rope (see § 1926.1417),
If the deficiency is localized, the problem is corrected by severing the wire rope in two; the undamaged portion may continue to be used. Joining lengths of wire rope by splicing is prohibited. If a rope is shortened under this paragraph, the employer must ensure that the drum will still have two wraps of wire when the load and/or boom is in its lowest position.
If the deficiency (other than power line contact) is localized, the problem is corrected by severing the wire rope in two; the undamaged portion may continue to be used. Joining lengths of wire rope by splicing is prohibited. Repair of wire rope that contacted an energized power line is also prohibited. If a rope is shortened under this paragraph, the employer must ensure that the drum will still have two wraps of wire when the load and/or boom is in its lowest position.
Where a wire rope is required to be removed from service under this section, either the equipment (as a whole) or the hoist with that wire rope must be tagged-out, in accordance with § 1926.1417(f)(1), until the wire rope is repaired or replaced.
Wire ropes on equipment must not be used until an inspection under this paragraph demonstrates that no corrective action under paragraph (a)(4) of this section is required.
At least every 12 months, wire ropes in use on equipment must be inspected by a qualified person in accordance with paragraph (a) of this section (shift inspection).
The inspection must be complete and thorough, covering the surface of the entire length of the wire ropes, with particular attention given to all of the following:
Exception: In the event an inspection under paragraph (c)(2) of this section is not feasible due to existing set-up and configuration of the equipment (such as where an assist crane is needed) or due to site conditions (such as a dense urban setting), such inspections must be conducted as soon as it becomes feasible, but no longer than an additional 6 months for running ropes and, for standing ropes, at the time of disassembly.
If the deficiency is localized, the problem is corrected by severing the wire rope in two; the undamaged portion may continue to be used. Joining lengths of wire rope by splicing is prohibited. If a rope is shortened under this paragraph, the employer must ensure that the drum will still have two wraps of wire when the load and/or boom is in its lowest position.

The wire rope on a crane needs to be replaced when the inspection results indicate that its condition has diminished to the point where further use could be unsafe.
Even regular visual inspections of crane wire ropes do not ensure the avoidance of a disaster. Visual inspection covers only 20-25% of the rope’s metallic cross-section and is cursory and inaccurate.
Crane Wire Ropes Inspection Services with the use of the MRT Equipment manufactured by LRM-NDE Laboratory can detect, localize and evaluate the defects in all cross section area such as: broken wires, corrosion and wear. It allows to determine places where high temperature affects to the wire rope as well.
Regular Crane Wire Ropes Inspection according to with MRT procedure and international standards in cooperation with LRM-NDE Laboratory contributes to:
Crane Wire Ropes Inspection Services are carried out according to LRM-NDE procedure and ISO 4309:2017 Standard – Cranes — Wire ropes — Care and maintenance, inspection and discard.
Crane Wire Rope Inspection and Inspection of Stacker Reclaimer wire ropes are performed by a person competent in the operation of MRT equipment and interpretation of trace data.

Wire rope is constructed of multiple strands of wire that are twisted and braided together to form a spiral design or helix. Once the separate wires are shaped into a solid form, they become a single wire with greater strength because the individual wires equalize pressure and have greater flexibility than the individual strands.
To further enhance the strength of wire ropes, they are grouped and wound together to produce cables, which adds to their usefulness as a means of support, ability to lift, and give structural stability.
A key factor in wire rope is the lay of the strands, which can be regular or lang. With regular lay, or right and ordinary lay, the strands are wound from left to right with the wires laid in the opposite direction of the lay of the strands. With lang lay, the wires are wound in the same direction.
The structure and design of wire rope produces a final product that has superior strength, excellent strength flexibility, and the ability to handle constant bending stress as well as being weather resistant.
Wire rope is one of those products that has found a place in a wide variety of industries since it can be adapted and shaped to fit several applications. It can be found as a tow cable for boats and airplanes or in the movie industry as a harness for stunt artists. The varied uses of wire rope have made it an essential part of operations that require a rope with strength, endurance, and flexibility.
In the aerospace industry, wire ropes, or Bowden cables, connect pedals and levers in the airplane cockpit to send power to aircraft systems to control the airplane. The things that are controlled by wire ropes are propeller pitch, cowl flaps, and throttle. Wire ropes on aircraft are insulated to avoid vibrations.
Wire rope is extensively used in the auto industry for a wide variety of applications due to its versatility and strength. It is used for raising windows and opening and closing sunroofs. Other uses include steering wheels, cables, exhausts, springs, sunroofs, doors, and seat components. In the manufacturing process, wire rope is used to hoist vehicles, move large body parts, and on hoists and cranes.
The construction industry has a greatest reliance on wire rope because of the need to lift and lower heavy loads. Wire rope used in construction must have extremely high strength and exceptional performance for safety reasons and efficiency. Larger versions of wire rope are used for suspension bridges and supporting concrete columns.
The main use of wire rope in food processing is for lifting, moving loads, and other heavy tasks. Finished products or raw materials require being moved in storage units and processing centers. The strength and endurance of wire rope makes it possible to move these materials. Wire rope for food processing must be able to withstand regular chemical cleaning.
As with other industries, the oil and gas industry needs strong and reliable equipment for moving heavy equipment. In ocean drilling, machinery is dropped into the ocean using wire rope to securely hold devices to be dropped to extreme depths. Wire ropes are designed to withstand the extreme pressure and stress required. A further use of wire ropes for drilling operations is to maintain stability in the drilling lines. One of the unique features of oil rig wire rope is its length, which can exceed 10,000 feet.
A very common use for wire rope is mooring and towing of sea and freshwater boats and vessels. In the shipbuilding industry, wire rope is used to secure lifeboats as well as lower them into the water. On sailboats, wire rope is used to lift and lower sails. The benefit of using wire rope is its resistance to corrosion and rust caused by salt water and ocean mist.
The skiing industry, much like heavy equipment industries, uses wire rope to hold cars, lifts, or chairs to transport skiers up the mountain. This type of wire rope comes in several varieties depending on the size of the mountain. The benefits of wire rope for skiing is its dependability, guaranteed safety, and reliability. The main challenge of wire rope for use in sports is the weather conditions it must endure.
Since the beginnings of amusement parks, wire rope has been an essential part of attraction construction. It is used to bring roller coaster cars to the top of the ride, hold swings, and pull various vehicles through attractions. One of the main concerns of public amusement parks is safety since rides are filled with powerful machinery designed to operate continuously.
Making the dangerous and exciting shots in movies requires well planned safety precautions. One of the aspects of that planning is wire rope that is designed to protect performers when they are engaged in dangerous and life threatening shots. Dependable wire ropes are ideal since they




 8613371530291
8613371530291