steel wire rope end terminations factory

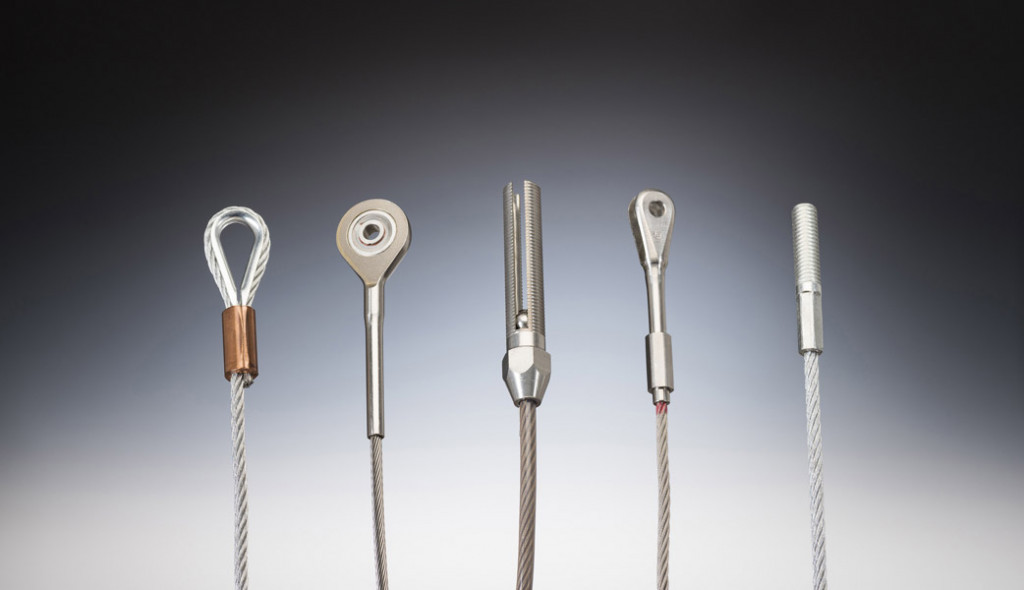
As a rigger or end-user of wire rope, it’s important to understand the types of terminations, or treatments, that can be used at the ends of a length of wire rope. These terminations are usually made by forming an eye or attaching a fitting, and are designed to be a permanent end termination on the wire rope where it connects to the load.
Wire rope is an extremely versatile mechanical device that can be used to help support and move an object or load. In the lifting and rigging industries, wire rope is attached to a crane or hoist and fitted with swivels, shackles or hooks to attach to a load and move it in a controlled matter. It can also be used to lift and lower elevators, or as a means of support for suspension bridges or towers.
In this article, we’ll explain what some of the following terms mean and how the can be used to terminate the end of a wire rope cable:Wire rope sockets—spelter sockets, swaged sockets, and wedge sockets
When you understand the construction and specifications of the wire rope you need, as well as the right type of end termination you need, you’ll be able to select the best performing and longest-lasting wire rope for the job at hand.
There are essentially two techniques that can be used to create a termination on a length of wire rope or cable:You can form an eye, or loop, in the wire rope
Eyes, or loops, can be created at one end of a length of wire rope by using a mechanical splice with a swaged sleeve, a hand-tucked splice, or wire rope clips.
A swaged socket is applied to the end of a wire rope cable and is then forced into place using special dies and a hydraulic machine called a swager. When properly applied with the correct sized fitting, swaged sockets have an efficiency rating of 100% of the breaking strength of the rope.
A poured socket, commonly referred to as a spelter socket, attaches a termination fitting onto the end of a wire rope cable by pouring molten zinc or resin into a socket that then hardens and holds the fitting onto the end of the cable.
Due to the rigidity of this type of termination, the wires of the rope are subject to fatigue where the wires enter the socket, if the poured socket is subject to constant vibration.
Wedge sockets secure the rope to the end attachment by passing it around a grooved, wedge-shaped piece of steel and pulling it down under load into the bowl of the fixture.
Wedge sockets are popular because they can be installed in field and adjusted in field – providing 80% efficiency of rope breaking strength. Wedge sockets are popular in applications where the wire rope may be subjected to abuse and abrasion—particularly in construction and mining applications.
Wire rope clips can be used to form a load bearing eye at the end of a cable or wire rope, or to connect two cables together with a lap splice. Wire rope clips are popular because they can be installed in the field and provide 80% efficiency of the rope breaking strength.
However, the use of wire rope clips is heavily regulated by ASME B30.26 Rigging Hardware. When using wire rope clips, the end user must account for the following:When using U-bolt wire rope clips, the saddle shall be placed on the live end of the wire rope, with the U-bolt on the dead-end side—NEVER SADDLE A DEAD HORSE!
After installation, the connection shall be loaded to at least the expected working load. After unloading, the wire rope clips shall be re-tightened to the torque specifications of the manufacturer or a Qualified Person.
This type of wire rope clip is essentially a U-bolt, two nuts, and a metal base (saddle) that can be made from forged steel or cast iron. Careful consideration and attention must be given to the way U-bolt type wire rope clips are installed.
The base of the wire rope clip is made from forged steel. Forged clips are heated and hammered into the desired shape—resulting in a consistent grain structure in the steel. Forged wire rope clips are used for critical, heavy-duty, overhead loads such as winch lines, crane hoist lines, support lines, guy lines, towing lines, tie downs, scaffolds, etc.
Malleable wire rope clips are used for making eye termination assemblies only with right regular lay wire rope and only for light duty uses with small applied loads, such as hand rails, fencing, guard rails, etc. The base of the wire rope clips is made from malleable cast iron, which may fracture under heavy use and does not have the desirable metal properties of steel, or the beneficial grain structure that a forged base has.
Double saddle wire rope clips consist of two saddles, each with a leg, and two nuts—one used on the top and one on the bottom. Double saddle wire rope clips can be used in either direction, so they take the guesswork out during installation when applying to the live end and the dead end of a piece of wire rope.
An eye splice may be used to terminate the loose end of a wire rope when forming a loop. The strands of the end of a wire rope are unwound and then the wire is bent around, and the unwrapped strands are then weaved back into the wire rope to form an eye.
A Flemish eye splice is created when the wire rope is opened, and the strands are laid out into two parts. The two strands are looped in opposite directions and then laid back together—forming an eye, or loop, at one end of the wire rope cable. The strands are then rolled back around the rope body and a metal sleeve fitting is slipped over the splice and swaged using hydraulic machinery. This splicing method provides the most efficient use of rope capacity and is highly economical.
A hand tucked splice is formed when the shorter “dead” end is tucked into the longer “live” end of the wire rope—forming an eye. These types of splices allow for easy inspection of the wire rope wires and strands.
When the end of a rope is turned back and formed into an eye, a thimble is often used to keep the shape of the eye, prevent the rope from being crushed, and keep the rope from being bent at a diameter smaller than the rope manufacturer’s recommendations.
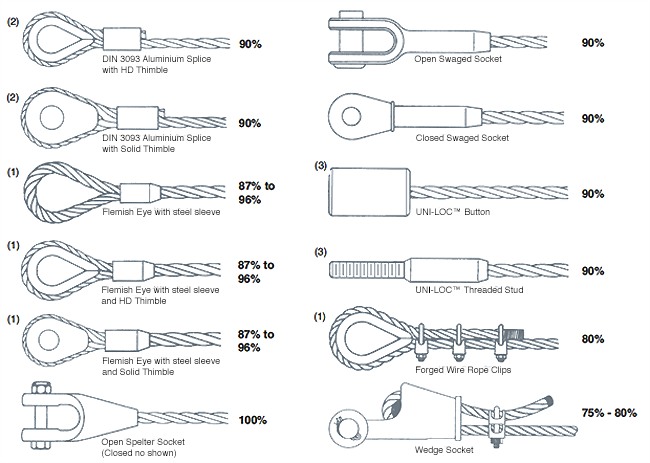
The table below will explain the efficiencies of the different types of wire rope end terminations for both independent wire rope core (IWRC) and fiber core (FC) wire rope configurations. Rope efficiency is described as the ratio of a wire rope’s actual breaking strength and the aggregate strength of all individual wires tested separately—usually expressed as a percentage.IWRCFC
*Spelter sockets in smaller rope sizes (usually less than 7/16”) may not always develop 100% efficiency and are not recommended by some rope manufacturers.
When you need to order a replacement wire rope, understanding the right type of end termination will help to make sure you get a direct replacement rope so you can get your project back on track. We hope this article gives you a better understanding of terms related to sockets, wire rope clips, and eye splices and that you understand what type of end termination may be best for your application.
At Mazzella, we offer all different kinds of wire rope from all of the leading manufacturers. We sell the highest-quality domestic and non-domestic rigging products because product quality and operating safety go hand-in-hand. We have one of the largest and most complete inventories of both domestic and non-domestic rigging and lifting products to suit your lifting needs.
All efficiency ratings are based on the difference between the actual breaking strength of a rope and the attained breaking strength with that specific fittings. The only fitting which will attain a 100% efficiency are spelter sockets; provided they are properly attached.

• Based on the catalog breaking strength of wire rope, Crosby wire rope clip have an efficiency rating of 80% for 3-4mm to 22mm sizes, and 90% for sizes 24-26mm through 90mm.
• Meets or exceed all requirements of ASME B30.26 including identification, ductility, design factor, proof load and temperature requirements. Importantly, these wire rope clips meet other critical performance requirements including fatigue life, impact properties and material traceability, not addressed by ASME B30.26.
Spelter socket terminations have an efficiency rating of 100%, based on the catalog strength of wire rope. Ratings are based on the recommend use with 6×7, 6×19, or 6×36, IPS or XIP (EIP), XXIP (EEIP), RRL, FC, or IWRC wire rope. Strand constructed with minimal number of wires (e.g. 1×7) requires special consideration that socket basket be five (5) times the strand diameter or fifty (50) times the wire diameter, whichever is the greater.
Wedge socket terminations have an efficiency rating of 80% based on the catalog strength of XXIP wire rope.Meets or exceed all requirements of ASME B30.26 including identification, ductility, design factor, proof load and temperature requirements. Importantly, these sockets meet other critical performance requirements including fatigue life, impact properties and material traceability, not addressed by ASME B30.26.Type approval and certification in accordance with ABS 2006 steel Vessel Rules 1-1-17.7, and ABS Guide fo r Certification of Cranes.Basket is cast steel and individually magnetic particle inspected.Pin diameter and jaw opening allows wedge and socket to be used in conjunction with closed swage and spelter sockets.Secures the tail or “dead end” of the wire rope to the wedge, thus eliminates the loss or “punch out” of the wedge.
Eliminates the need for an extra piece of rope, and is easily installed.The TERMINATORᵀᴹ wedge eliminates the potential breaking off of the tail due to fatigue.The tail, which is secured by the base of the clip and the wedge, is left undeformed and available for reuse.
Utilizes standard Crosby Red-U-Bolt® wire rope clip.The 9-10mm through 28mm standard S-421 wedge socket can be retrofitted with the new style TERMINATORᵀᴹ wedge.Available with Bolt, Nut, and Cotter Pin. US patent 5,553,360, Canada patent 2,217,004 and foreign equivalents.Meets the performance requirements of EN 13411-6: 2003.
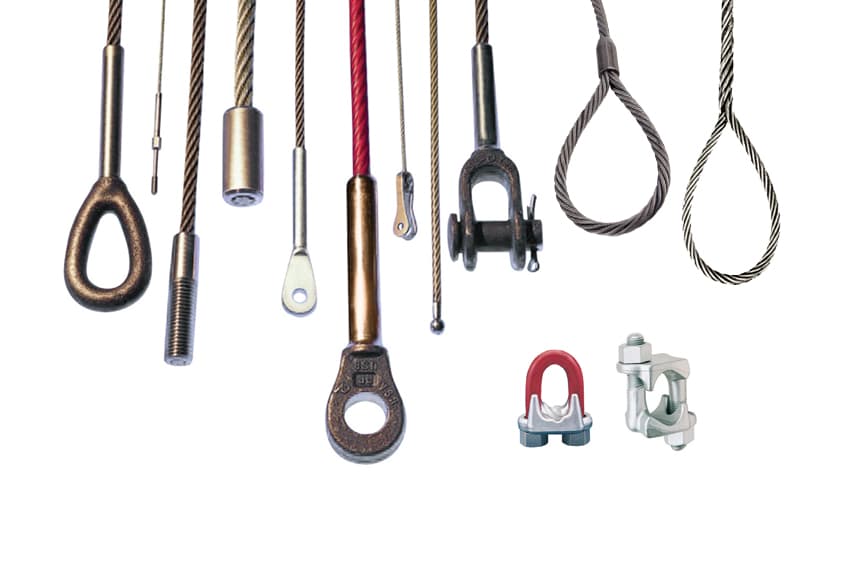
Large structures and equipment needing stabilization and support require specially-fabricated wire rope products. These assemblies usually fit swaged or poured terminations to wire rope. Assemblies like these used on boom cranes are referred to as either pennant or boom lines. Similarly-made products are also frequently used in structures such as large awnings and support cables for bridges.
The proper application of these types of assemblies requires careful consideration of capacity, length, plane, and type of termination. The capacity of the socketed assembly will be determined by the diameter and grade of wire rope. Trinity Sling offers a wide variety of wire ropes suitable for socketed and threaded wire rope terminations. The length of a socketed or threaded wire rope assembly requires exacting measurements. These usually are ordered in pairs and require length matching. Due to the differences in stretch inherent in different batches of wire rope, it is not recommended that new socketed slings be matched to used assemblies. The lengths will be mismatched under load.
At Trinity Sling we have years of experience with the various types of socket terminations. The terminations most commonly come with one of three types of connections; open socket (female), closed socket (male), and threaded ends. An open socket looks like a fork with a pin that can be inserted to close and secure the end fitting to the opening of the fork. A closed socket has an eye. The eye of the closed socket is designed to accept the pin of the open socket so they can be linked together. Threaded wire rope end fittings can be made with any type of thread pitch or thread length required for the application.
With open and closed socket wire rope terminations the plane of the attachment to the wire rope is also important. The plane of the assembly is determined by the degree relative to each end to which the terminations are attached. Consult the diagram from the Wire Rope Sling User’s Manual for reference to same and opposite planes.
Whether a job requires poured sockets or swaged sockets, well-built assemblies will carry up to 98% of the rated break strength of the rope. Poured sockets are usually set with an epoxy covering the broomed wires inside the socket, while swaged end fittings are attached by forming the shank of the end fitting over the wire rope with a press. Poured socket wire rope end fittings feature flexibility of assembly.
With a properly-trained person and the right equipment, poured sockets can be made in the field. Field installation should not be used in critical or overhead lifting or supporting applications, however, as those applications cannot be proof tested in the field.
As for all products fabricated by Trinity Sling we use only the highest quality materials and industry-recommended manufacturing techniques for our end fittings. Trinity Sling’s high capacity test bed is available for proof loading and recertification of all type of pennant lines and socketed end fittings. Trinity Sling can also offer tagging and asset tracking of each assembly with the InfoChip tagging and tracking system.
With the assistance of our trained sales personnel Trinity Sling can help design and fabricate specialty swaged end fittings to meet your specific needs. Such specialty end fittings are often used in military applications or in specialty manufactured goods. Trinity offers a wide variety of custom and standard fittings to accommodate most any rigging situation. Rigging experts with decades of experience in the industry are available Monday through Friday from 8-5 CST to answer questions, provide quotes, or satisfy hard-to-fill spec requirements for jobs across the U.S. and Canada, often from existing inventory. Call 1-877-589-2404 for more information or to place an order.

In addition to the standard range, SWR supply high quality wire rope fittings for various uses including architectural, marine, yacht rigging and structural applications. SWR"s fittings are sourced from approved factories worldwide and fully supported by test certificates where applicable.

Lexco® Cable provides a full line of fork ends and jaw ends for use in a wide range of applications, from military and marine to industrial and architectural and more.
The term “fork/jaw ends” describes clevisesthat swage directly to the cable. In some respects, a fork/jaw end can be thought of as a two-in-one fitting, because a more rudimentary approach to fork/jaw end functionality is a cable loop with a shackle secured to it. This two-part configuration works perfectly well in many instances where a flexible cable construction can be used. However, in other situations, a rigid cable is advantageous. Typically, this is the case when minimizing stretch and modulus of elasticity are predicated on providing structural support. Where a cable is too rigid to form a thimble loop, the need for an inline fitting, such as a fork/jaw, is born.
Our fork and jaw end fittings must be machine swaged for proper hold strength. Lexco takes pride in our assembly work and will quote any assembly you need per your specification or design print.
MIL SPEC and Naval spec fork and jaw end fittings do not include clevis pins (must be ordered separately). All other fork ends and jaw ends include clevis pins.
Note:The hold strength of a fork end or jaw end is affected by the construction of the cable to which it is attached. A fork/jaw end installed on a 1x19 cable may yield a different holding strength than an identical fork/jaw end installed on a 7x7 cable, for example."
When referring to “fork ends” and “open swage sockets,” it is inferred that the clevis end of the fitting is fixed to the swage area. In other words, both portions of the fitting are one continuous piece.
Lexco® Cable supplies both commercial grade and MIL SPEC (MS20667) fork ends. Typically machined from 304 stainless steel, they are available in various sizes to accommodate cable from 1/16” to 1” in diameter.
Commercial and military grade fork ends must be machine swaged for proper hold strength. Please contacta Lexco® sales representative to receive an assembly quote.
Note:A fork end’s hold strength is affected by the construction of the cable to which it is attached. For example, a fork end installed on a 7x7 cable may yield a different holding strength than an identical fork end installed on a 1x19 cable.

This document specifies the minimum requirements for the molten metal and resin socketing of steel wire ropes within the scopes of EN 12385-4:2002+A1:2008; EN 12385-5:2021; EN 12385-6:2004;
The document is applicable only to those requirements that ensure that the socketing is strong enough to withstand a force of at least 100 % of the minimum breaking force of the rope (i.e. socket termination efficiency factor KT = 1,0).
NOTE Rope terminations made by socketing in accordance with this document can be used for determining the breaking force of wire ropes in accordance with EN 12385-1:2002+A1:2008, Annex A.
This document deals with all significant hazards, hazardous situations and events relevant to metal and resin socket terminations, when they are used as intended and under conditions of misuse which are reasonably foreseeable (see Clause 4).Standard
$ 7.31ISO 16841:2014 identifies the different types of pulling eyes prepared at, or attached to, a steel wire rope end for connection to another rope when installing a new rope or re-reeving an existing rope on a machine. It also specifies the minimum requirements for pulling eyes, including their geometry, strength, maximum line pull to which the pulling eye is intended to be subjected and information for use to be provided by the manufacturer.
$ 6.50This European Standard specifies the minimum requirements for swage terminals and the securing of such terminals by a swaging process to carbon steel rope conforming to EN 12385-4 and EN 12385-5, spiral strand rope conforming to EN 12385-10 and stainless steel stranded rope.
This European Standard is not applicable to spiral rope incorporating full lock wires - see EN 12385-10 -, nor ropes with coverings and /or fillings (see 3.6.3 of EN 12385-2:2002+A1:2008).
This European Standard is applicable to swaged terminations that have a terminal efficiency factor, KT, of at least 0,9 and are used as part of a wire rope accessory such as a sling, or wire rope assembly that performs a raising, lowering, hauling or supporting function on lifting machinery.
This European Standard deals with all significant hazards, hazardous situations and events relevant to swaged terminations, when used as intended and under conditions of misuse which are reasonably foreseeable (see Clause 4).
$ 5.96This European Standard specifies the construction requirements, calculation of WLL, testing and certification of steel wire rope grommets, cable-laid grommets and cable-laid slings using strand and wire rope conforming to EN 12385-4.
$ 8.13This European Standard specifies the construction requirements, calculation of WLL, verification, certification and marking of steel wire rope slings for general lifting service. It covers single-, two-, three- and four-leg slings, with ferrule-secured or spliced eye terminations and spliced or ferrule-secured endless slings made from 8 mm to 60 mm diameter 6 strand ordinary lay steel wire rope with fibre or steel core and 8 strand ordinary lay steel wire rope with a steel core conforming to EN 12385-4.
$ 7.31This European Standard specifies the minimum requirements for non welded general purpose steel thimbles produced from plate having dimensions in accordance with Figure 1. The thimbles are intended to be used in slings made with six or eight strand steel wire ropes from 8 mm to 60 mm diameter complying with EN 12385-4.
This European Standard deals with all significant hazards, hazardous situations and events relevant to asymmetric wedge sockets for terminations for steel wire ropes, when used as intended and under conditions of misuse which are reasonably foreseeable by the manufacturer.
$ 7.31This standard specifies minimum requirements for the splicing of eye terminations for six or eight strand steel wire ropes of up to 60 mm diameter complying with prEN 12385-4 used for slings to ensure that the spliced eye is strong enough to withstand a force of at least 80 % of the minimum breaking load of the rope.
$ 5.15This European Standard has been prepared to provide a means of conforming with the essential safety requirements of the Machinery Directive and associated EFTA Regulations.
This European Standard applies to the ferrule-securing of eye terminations formed either by a Flemish eye or turn-back eye and covers ferrules made of non alloy carbon steel and aluminium.
This European Standard applies to slings and assemblies using steel wire ropes for general lifting applications up to and including 60mm diameter conforming to EN 12385-4, lift ropes conforming to EN 12385-5 and spiral strand ropes conforming to EN 12385-10.
This European standard deals with all significant hazards, hazardous situations and events relevant to this particular steel wire rope termination when used as intended and under conditions of use which are foreseeable by the manufacturer.
This standard applies to terminations of steel wire ropes with ferrules and ferrule-securing which are manufactured after the date of this publication.
NOTE One design of ferrule-secured turn-back eye termination using an oval aluminium ferule which satisfies the requirements of this European Standard is given for information in annex A.Standard
$ 8.13This Part specifies the general requirements for the manufacture and testing of steel wire rope, whose particular requirements are specified in the other Parts.
This document is applicable to ferrule-secured terminations with solid thimbles in combination with ferrules (see EN 13411-3), that have an efficiency factor KT of at least 0,9, and to spliced terminations with solid thimbles (see EN 13411-2), that have an efficiency factor KT of at least 0,8, which are used as accessories for steel wire ropes, such as slings or wire rope assemblies, having a lifting, lowering or load-bearing effect in hoisting equipment.
$ 6.50This document specifies the minimum requirements for symmetrical wedge socket terminations for stranded steel wire ropes conforming to EN 12385-5 for lifts.
This document deals with all significant hazards, hazardous situations and events relevant to symmetric wedge sockets for terminations for steel wire ropes, when used as intended and under conditions of misuse which are reasonably foreseeable by the manufacturer.
$ 7.31This document specifies the particular materials, manufacturing and testing requirements for stranded ropes for suspension, compensating and governor duties for traction drive and hydraulic lifts moving between guides and similar applications.
This document does not establish requirements for information for use other than those given in Clause 7 of Part 1. Neither does it cover the requirements for ropes fitted with terminations.
$ 0.00This document specifies the type of information for use and maintenance of steel wire ropes to be provided by the rope manufacturer or to be included in the manufacturer’s handbook that accompanies a machine, piece of equipment or installation of which the steel wire rope forms a part.
For steel wire ropes conforming to Parts 8 and 9 used on cableway installations designed to carry persons, additional information for use and maintenance is given in EN 12927.
$ 8.13This document specifies the particular materials, manufacturing and testing requirements for stranded ropes for suspension, compensating and governor duties for traction drive and hydraulic lifts moving between guides and similar applications.
This document does not establish requirements for information for use other than those given in Clause 7 of Part 1. Neither does it cover the requirements for ropes fitted with terminations.
$ 7.31This European Standard specifies the additional materials, manufacturing and testing requirements to those given in Part 1 for stranded ropes (with round and/or shaped strands) and flat ropes for use as hoist ropes, stage ropes and balance ropes in mine-shafts.
$ 7.31This European Standard specifies the additional materials, manufacturing and testing requirements to those given in Part 1 for stranded steel wire "hauling" and "carrying-hauling" ropes for cableway installations designed to carry persons.
$ 6.50This European Standard specifies the additional materials, manufacturing and testing requirements for full-locked coil hoist and half-locked and full-locked coil guide ropes for mine shafts to those given in Part 1.
For information only, typical breaking forces for both full-locked coil hoist ropes and half-locked and full-locked coil guide ropes, based on one particular combination of wire tensile strength grades in each case, are given in annex B (hoist ropes) and annex C (guide ropes) for some of the more common sizes of rope.Standard
$ 5.96This European Standard specifies the additional materials, manufacturing and testing requirements to those given in Part 1 for locked coil carrying ropes for cableway installations designed to carry persons.Standard
This document applies to the ferrule-securing of eye terminations formed either by a Flemish eye or turn-back eye and covers ferrules made of non alloy carbon steel and aluminium.
This document applies to slings and assemblies using steel wire ropes for general lifting applications up to and including 60 mm diameter conforming to EN 12385-4, lift ropes conforming to EN 12385-5 and spiral strand ropes conforming to EN 12385-10.
This document deals with all significant hazards, hazardous situations, and events relevant to this particular steel wire rope termination when used as intended and under conditions of use which are foreseeable by the manufacturer.
This document applies to terminations of steel wire ropes with ferrules and ferrule-securing which are manufactured after the date of this publication.
NOTE One design of ferrule-secured turn-back eye termination using an oval aluminium ferule which satisfies the requirements of this document when securing ropes having rope grades up to and including 1960 is given for information in Annex A.Draft
$ 8.13This European Standard specifies the minimum requirements for the molten metal and resin socketing of steel wire ropes conforming to EN 12385 parts 4 to 10.
The standard covers only those requirements that ensure that the socketing is strong enough to withstand a force of at least 100 % of the minimum breaking force of the rope.
NOTE Rope terminations made by socketing in accordance with this European Standard can be used for determining the breaking force of wire ropes in accordance with annex A of EN 12385-1:2002.
$ 6.50This European Standard specifies the construction requirements, calculation of WLL, testing and certification of steel wire rope grommets, cable-laid grommets and cable-laid slings using strand and wire rope conforming to EN 12385-4.
$ 7.31This European Standard specifies the construction requirements, calculation of WLL, verification, certification and marking of steel wire rope slings for general lifting service. It covers single-, two-, three- and four-leg slings, with ferrule-secured or spliced eye terminations and spliced or ferrule-secured endless slings made from 8 mm to 60 mm diameter 6 strand ordinary lay steel wire rope with fibre or steel core and 8 strand ordinary lay steel wire rope with a steel core conforming to EN 12385-4.
$ 7.31This European Standard specifies the minimum requirements for symmetrical wedge socket terminations for stranded steel wire ropes conforming to EN 12385-5 for lifts.
This European Standard deals with all significant hazards, hazardous situations and events relevant to symmetric wedge sockets for terminations for steel wire ropes, when used as intended and under conditions of misuse which are reasonable foreseeable by the manufacturer.
$ 7.31This European Standard specifies the minimum requirements for symmetrical wedge socket terminations for stranded steel wire ropes conforming to EN 12385-5 for lifts.
This European Standard deals with all significant hazards, hazardous situations and events relevant to symmetric wedge sockets for terminations for steel wire ropes, when used as intended and under conditions of misuse which are reasonable foreseeable by the manufacturer.
This European Sstandard deals with all significant hazards, hazardous situations and events relevant to asymmetric wedge sockets for terminations for steel wire ropes, when used as intended and under conditions of misuse which are reasonable foreseeable by the manufacturer.
This European Standard applies to the ferrule-securing of eye terminations formed either by a Flemish eye or turn-back eye and covers ferrules made of non alloy carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminium and copper.
This European Standard applies to slings and assemblies using steel wire ropes for general lifting applications up to and including 60mm diameter conforming to EN 12385-4, lift ropes conforming to EN 12385-5 and spiral strand ropes conforming to EN 12385-10.
This European standard deals with all significant hazards, hazardous situations and events relevant to this particular steel wire rope termination when used as intended and under conditions of use which are foreseeable by the manufacturer.
This standard applies to terminations of steel wire ropes with ferrules and ferrule-securing which are manufactured after the date of this publication.
NOTE One design of ferrule-secured turn-back eye termination using an oval aluminium ferule which satisfies the requirements of this European Standard is given for information in annex A.Standard
$ 8.13This European Standard specifies the minimum requirements for the safe behaviour of terminations associated with U-bolt wire rope grips manufactured from ferrous materials for use as intended by the manufacturer of the U bolt grip.
Suitable uses include suspending static loads and single use lifting operations which have been assesseed by a competent person taking into account appropriate safety factors, frequency and duration of use.
This standard does not cover U-bolt wire rope grips as the primary securing devices on mine hoists, crane hoists or eye terminations for slings for general lifting service.
$ 6.50This European Standard specifies the minimum requirements for the molten metal and resin socketing of steel wire ropes conforming to prEN 12385 parts 4 to 10.
The standard covers only those requirements that ensure that the socketing is strong enough to withstand a force of at least 100 % of the minimum breaking force of the rope.
NOTE Rope terminations made by socketing in accordance with this European Standard can be used for determining the breaking force of wire ropes in accordance with annex A of prEN 12385-1:2001.
$ 6.50This European Standard specifies the minimum requirements for non welded general purpose steel thimbles produced from plate having dimensions in accordance with Figure 1. The thimbles are intended to be used in slings made with six or eight strand steel wire ropes from 8 mm to 60 mm diameter complying with prEN 12385-4:2001.
$ 5.15This standard specifies minimum requirements for spliced eye terminations for six or eight stranded steel wire ropes used for slings. Type tests covering the type acceptance of splicing methods are also specified. The hazards covered by this standard are identified in clause 4.Standard
$ 5.00This part of this European Standard specifies the general requirements related to safety for the manufacture and testing of steel wire ropes. It shall be used in conjunction with the appropriate part of this standard which specifies the additional or deviating requirements related to the specific rope application.
The hazards covered by this part are identified in clause 4. Any additional hazards related to the specific rope application are identified in the appropriate part of this standard.
$ 7.31This Part of this European Standard specifies the type of information for use and maintenance of steel wire ropes to be provided by the rope manufacturer or to be included in the manufacturer"s handbook that accompanies a machine, piece of equipment or installation of which the steel wire rope forms a part.
For steel wire ropes conforming to Parts 8 and 9 used on cableway installations designed to carry persons, additional information for use and maintenance is given in prEN 12927-7.
$ 7.31This Part of this European Standard specifies the additional materials, manufacturing and testing requirements to those given in Part 1 for full locked coil and spiral strand ropes incorporating zinc or zinc alloy coated wires for general structural applications.
For information only, typical breaking forces for both full-locked coil rope and spiral strand rope are given in annexes B and C for some of the more common sizes.Standard
$ 7.31This Part of EN 12385 defines terms, specifies designations and classifies steel wire ropes and is for use in conjunction with all other Parts of this standard.It applies to ropes which have been manufactured after the date of issue of the standard.Standard
$ 10.83This part of this European Standard specifies the additional materials, manufacturing and testing requirements for stranded ropes for general lifting applications to those given in part 1.
This Part of this European Standard does not establish requirements for information for use other than those given in clause 7 of part 1. Neither does it cover the requirements for ropes fitted with terminations.
$ 8.13This part of this European Standard specifies the additional materials, manufacturing and testing requirements for stranded ropes for suspension, compensating and governor duties for traction drive and hydraulic lifts moving between guides to those given in part 1.
This Part of this European Standard does not establish requirements for information for use other than those given in clause 7 of part 1. Neither does it cover the requirements for ropes fitted with terminations.




 8613371530291
8613371530291