steel wire rope terminations factory

As a rigger or end-user of wire rope, it’s important to understand the types of terminations, or treatments, that can be used at the ends of a length of wire rope. These terminations are usually made by forming an eye or attaching a fitting, and are designed to be a permanent end termination on the wire rope where it connects to the load.
Wire rope is an extremely versatile mechanical device that can be used to help support and move an object or load. In the lifting and rigging industries, wire rope is attached to a crane or hoist and fitted with swivels, shackles or hooks to attach to a load and move it in a controlled matter. It can also be used to lift and lower elevators, or as a means of support for suspension bridges or towers.
In this article, we’ll explain what some of the following terms mean and how the can be used to terminate the end of a wire rope cable:Wire rope sockets—spelter sockets, swaged sockets, and wedge sockets
When you understand the construction and specifications of the wire rope you need, as well as the right type of end termination you need, you’ll be able to select the best performing and longest-lasting wire rope for the job at hand.
There are essentially two techniques that can be used to create a termination on a length of wire rope or cable:You can form an eye, or loop, in the wire rope
Eyes, or loops, can be created at one end of a length of wire rope by using a mechanical splice with a swaged sleeve, a hand-tucked splice, or wire rope clips.
A swaged socket is applied to the end of a wire rope cable and is then forced into place using special dies and a hydraulic machine called a swager. When properly applied with the correct sized fitting, swaged sockets have an efficiency rating of 100% of the breaking strength of the rope.
A poured socket, commonly referred to as a spelter socket, attaches a termination fitting onto the end of a wire rope cable by pouring molten zinc or resin into a socket that then hardens and holds the fitting onto the end of the cable.
Due to the rigidity of this type of termination, the wires of the rope are subject to fatigue where the wires enter the socket, if the poured socket is subject to constant vibration.
Wedge sockets secure the rope to the end attachment by passing it around a grooved, wedge-shaped piece of steel and pulling it down under load into the bowl of the fixture.
Wedge sockets are popular because they can be installed in field and adjusted in field – providing 80% efficiency of rope breaking strength. Wedge sockets are popular in applications where the wire rope may be subjected to abuse and abrasion—particularly in construction and mining applications.
Wire rope clips can be used to form a load bearing eye at the end of a cable or wire rope, or to connect two cables together with a lap splice. Wire rope clips are popular because they can be installed in the field and provide 80% efficiency of the rope breaking strength.
However, the use of wire rope clips is heavily regulated by ASME B30.26 Rigging Hardware. When using wire rope clips, the end user must account for the following:When using U-bolt wire rope clips, the saddle shall be placed on the live end of the wire rope, with the U-bolt on the dead-end side—NEVER SADDLE A DEAD HORSE!
After installation, the connection shall be loaded to at least the expected working load. After unloading, the wire rope clips shall be re-tightened to the torque specifications of the manufacturer or a Qualified Person.
This type of wire rope clip is essentially a U-bolt, two nuts, and a metal base (saddle) that can be made from forged steel or cast iron. Careful consideration and attention must be given to the way U-bolt type wire rope clips are installed.
The base of the wire rope clip is made from forged steel. Forged clips are heated and hammered into the desired shape—resulting in a consistent grain structure in the steel. Forged wire rope clips are used for critical, heavy-duty, overhead loads such as winch lines, crane hoist lines, support lines, guy lines, towing lines, tie downs, scaffolds, etc.
Malleable wire rope clips are used for making eye termination assemblies only with right regular lay wire rope and only for light duty uses with small applied loads, such as hand rails, fencing, guard rails, etc. The base of the wire rope clips is made from malleable cast iron, which may fracture under heavy use and does not have the desirable metal properties of steel, or the beneficial grain structure that a forged base has.
Double saddle wire rope clips consist of two saddles, each with a leg, and two nuts—one used on the top and one on the bottom. Double saddle wire rope clips can be used in either direction, so they take the guesswork out during installation when applying to the live end and the dead end of a piece of wire rope.
An eye splice may be used to terminate the loose end of a wire rope when forming a loop. The strands of the end of a wire rope are unwound and then the wire is bent around, and the unwrapped strands are then weaved back into the wire rope to form an eye.
A Flemish eye splice is created when the wire rope is opened, and the strands are laid out into two parts. The two strands are looped in opposite directions and then laid back together—forming an eye, or loop, at one end of the wire rope cable. The strands are then rolled back around the rope body and a metal sleeve fitting is slipped over the splice and swaged using hydraulic machinery. This splicing method provides the most efficient use of rope capacity and is highly economical.
A hand tucked splice is formed when the shorter “dead” end is tucked into the longer “live” end of the wire rope—forming an eye. These types of splices allow for easy inspection of the wire rope wires and strands.
When the end of a rope is turned back and formed into an eye, a thimble is often used to keep the shape of the eye, prevent the rope from being crushed, and keep the rope from being bent at a diameter smaller than the rope manufacturer’s recommendations.
The table below will explain the efficiencies of the different types of wire rope end terminations for both independent wire rope core (IWRC) and fiber core (FC) wire rope configurations. Rope efficiency is described as the ratio of a wire rope’s actual breaking strength and the aggregate strength of all individual wires tested separately—usually expressed as a percentage.IWRCFC
*Spelter sockets in smaller rope sizes (usually less than 7/16”) may not always develop 100% efficiency and are not recommended by some rope manufacturers.
When you need to order a replacement wire rope, understanding the right type of end termination will help to make sure you get a direct replacement rope so you can get your project back on track. We hope this article gives you a better understanding of terms related to sockets, wire rope clips, and eye splices and that you understand what type of end termination may be best for your application.
At Mazzella, we offer all different kinds of wire rope from all of the leading manufacturers. We sell the highest-quality domestic and non-domestic rigging products because product quality and operating safety go hand-in-hand. We have one of the largest and most complete inventories of both domestic and non-domestic rigging and lifting products to suit your lifting needs.

• Based on the catalog breaking strength of wire rope, Crosby wire rope clip have an efficiency rating of 80% for 3-4mm to 22mm sizes, and 90% for sizes 24-26mm through 90mm.
• Meets or exceed all requirements of ASME B30.26 including identification, ductility, design factor, proof load and temperature requirements. Importantly, these wire rope clips meet other critical performance requirements including fatigue life, impact properties and material traceability, not addressed by ASME B30.26.
Spelter socket terminations have an efficiency rating of 100%, based on the catalog strength of wire rope. Ratings are based on the recommend use with 6×7, 6×19, or 6×36, IPS or XIP (EIP), XXIP (EEIP), RRL, FC, or IWRC wire rope. Strand constructed with minimal number of wires (e.g. 1×7) requires special consideration that socket basket be five (5) times the strand diameter or fifty (50) times the wire diameter, whichever is the greater.
Wedge socket terminations have an efficiency rating of 80% based on the catalog strength of XXIP wire rope.Meets or exceed all requirements of ASME B30.26 including identification, ductility, design factor, proof load and temperature requirements. Importantly, these sockets meet other critical performance requirements including fatigue life, impact properties and material traceability, not addressed by ASME B30.26.Type approval and certification in accordance with ABS 2006 steel Vessel Rules 1-1-17.7, and ABS Guide fo r Certification of Cranes.Basket is cast steel and individually magnetic particle inspected.Pin diameter and jaw opening allows wedge and socket to be used in conjunction with closed swage and spelter sockets.Secures the tail or “dead end” of the wire rope to the wedge, thus eliminates the loss or “punch out” of the wedge.
Eliminates the need for an extra piece of rope, and is easily installed.The TERMINATORᵀᴹ wedge eliminates the potential breaking off of the tail due to fatigue.The tail, which is secured by the base of the clip and the wedge, is left undeformed and available for reuse.
Utilizes standard Crosby Red-U-Bolt® wire rope clip.The 9-10mm through 28mm standard S-421 wedge socket can be retrofitted with the new style TERMINATORᵀᴹ wedge.Available with Bolt, Nut, and Cotter Pin. US patent 5,553,360, Canada patent 2,217,004 and foreign equivalents.Meets the performance requirements of EN 13411-6: 2003.
All efficiency ratings are based on the difference between the actual breaking strength of a rope and the attained breaking strength with that specific fittings. The only fitting which will attain a 100% efficiency are spelter sockets; provided they are properly attached.

In addition to the standard range, SWR supply high quality wire rope fittings for various uses including architectural, marine, yacht rigging and structural applications. SWR"s fittings are sourced from approved factories worldwide and fully supported by test certificates where applicable.

Wire assemblies are also useful in motion control and mechanical automation applications for not only lifting but pulling and support as well. Wire rope assemblies allow for the incorporation of wire cables into machinery or other equipment for use improving connectivity and versatility and to prevent damage, such as fraying, to the rope mechanisms.
The capacity of a given system is determined by the type and placement of wire rope fittings in the assembly. Common fittings include clamps, clips, sleeves, links, hooks, forks, eyes, studs, and pins. The utility and added security afforded by wire rope assemblies allows their use in both commercial and residential arenas in addition to their traditional applications in the industrial sector.
As cables for heavy-duty hoisting vary considerably from those used to support a home shelving unit, it is vital that the intended use be considered when selecting the proper assembly. Wire rope manufacturers often provide a range of wire fitting options in order to accommodate the many different uses for the cables.
While specific fittings and terminations are achieved through various metal stamping, die cutting, or swaging techniques, the process of wire rope making is fairly uniform, though specifics will vary.
Wire ropes comprise the base or body of every assembly, these are the lengths of stranded wire cable that run between two fittings or pieces of equipment. Each rope consists of three main elements. Cold drawn metallic filaments are twisted or braided into strands which are in turn helically wrapped around a core, which may be metal or fiber based. The number of strands per cable and filaments per strand are used to identify wire ropes as are the lay or style in which each component was assembled.
Fittings and wires are commonly made of the same materials; most popular are durable metals. Steel and stainless steel, titanium, nickel alloys, and other metals are selected based on specific properties such as resistance to wear and corrosion, tensile strength, and weight to strength ratios.
Further considerations for wire rope assemblies include diameter, length, flexibility, difficulty of flattening, temperature resistance, and average lifespan.

Wire rope manufacturers produce their products in order to provide a high load capacity, versatile alternative to weaker ropes like manila rope or hemp rope. Wire rope products are used for a wide variety of motion transmission applications, among them: lifting, baling, tie down, hoisting, hauling, towing, mooring, anchoring, rigging, cargo control, guidance and counterbalance. They can also be used as railing, fencing and guardrailing.
Wire rope is a must-have for many heavy duty industrial applications. From mining to forestry to marine and beyond, there’s wire rope for almost every job. Some of the many industries in which wire rope is popular include: construction, agriculture, marine, industrial manufacturing, fitness, sports and recreation (plastic coated cables for outdoor playground equipment and sports equipment), electronics, theater (black powder coated cables for stage rigging), mining, gas and oil, transportation, security, healthcare and consumer goods.
Wire rope as we know it was invented just under 200 years ago, between 1831 and 1834. At that time, the goal was to create a rope strong enough to support work in the mines of the Harz Mountains. Invented by Wilhelm Albert, a German mining engineer, this wire rope consisted on four three-stranded wires. It was much stronger than older rope varieties, such as manila rope, hemp rope and metal chain rope.
While studying at Freiburg School of Mines, a man named L.D.B. Gordon visited the mines in the Harz Mountains, where he met Albert. After he left, Gordon wrote to his friend Robert Stirling Newall, urging him to create a machine for manufacturing wire ropes. Newall, of Dundee, Scotland, did just that, designing a wire rope machine that made wire ropes with four strands, consisting of four wires each. After Gordon returned to Dundee, he and Newall, along with Charles Liddell, formed R.S. Newall and Company. In 1840, Newall received a patent for “certain improvements in wire rope and the machinery for making such rope.”
In 1841, an American manufacturer named John A. Roebling began producing wire rope for suspension bridges. Soon after, another set of Americans, Josiah White and Erskine Hazard, started incorporating wire rope into coal mining and railroad projects, forming Lehigh Coal & Navigation Company (LC&N Co.). In 1848, wire rope from their wire rope factory in Mauch Chunk, Pennsylvania provided the lift cables needed to complete the Ashley Planes Project. This project sought to improve the performance and appearance of the freight railroad that ran through Ashley, Pennsylvania, by adding lift cables. This increased tourism and increased the railroad’s coal capacity. Before, cars took almost four hours to return; after, they took less than 20 minutes.
Wire rope likewise changed the landscape (again) in Germany, in 1874, when an engineering firm called Adolf Bleichert & Co. used wire rope to build Bi-cable aerial tramways. These allowed them to mine the Ruhr Valley. Several years later, they also used wire rope to build tramways for the German Imperial Army and the Wehrmacht. These tramways were wildly successful, opening up roads in Germany and all over Europe and the USA.
Since the 1800s, manufacturers and engineers have found ways to improve wire rope, through stronger materials and material treatments, such as galvanization, and different rope configurations. Today, wire rope makes possible many heavy industrial processes. It has become a necessity of the modern world.
Strands are made by tightly twisting or braiding individual wire together. One strand could have anywhere between two and several dozen wire filaments depending on the necessary strength, flexibility, and weight capacity.
One of the most dynamic elements of wire cables is the inner core. The strands are wrapped around the core, and it can be made of different metals, fibers, or even impregnated fiber materials. For heavy applications, cores are often made of a different strand of wire called an independent wire rope core (IWRC). An IWRC has a considerable amount of flexibility and it is still very strong. In fact, at least 7.5% of the strength increase in a wire rope can be attributed to an IWRC.
While they sometimes use other metals, like aluminum, nickel, copper, titanium, and even bronze for some applications, manufacturers primarily produce wire rope from steel. This is because steel is very strong and stretchable. Among the most common types they use are: galvanized wire, bright wire, stainless steel and cold drawn steel.
Of the wire rope steels, cold drawn carbon steel wire is most popular, although stainless steel wire rope is sometimes employed as well. Stainless steel rope is most popular for its anti-corrosive properties. Bright wire rope, a type of ungalvanized steel wire rope, is also popular. For added strength and durability, galvanized steel wire rope/galvanized steel cables are a very popular choice. Galvanized aircraft cable, for example, is always a must in aerospace.
When choosing or designing a custom wire rope for your application, suppliers consider factors such as: the environment in which the rope will function, required rust resistance, required flexibility, temperature resistance, required breaking strength and wire rope diameter. To accommodate your needs, manufacturers can do special things like: make your rope rotation resistant, color code your rope, or add a corrosion resistant coating. For instance, sometimes they specially treat and coat a cable with plastic or some other compound for added protection. This is particularly important to prevent fraying if the wire rope is often in motion on a pulley.
Manufacturers and distributors identify the differences in wire cable by listing the number of strands and the amount of wires per strand so that anyone that orders understand the strength of the cable. Sometimes they are also categorized by their length or pitch. Common examples of this include: 6 x 19, 6 x 25, 19 x 7, 7 x 19, 7 x 7, 6 x 26 and 6 x 36.
More complex wire rope identification codes connote information like core type, weight limit and more. Any additional hardware like connectors, fasteners, pulleys and fittings are usually listed in the same area to show varying strengths and degrees of fray prevention.
Cable wire rope is a heavy-duty wire rope. To give it its high strength, manufacturers construct it using several individual filaments that are twisted in strands and helically wrapped around the core. A very common example of cable wire rope is steel cable.
Spiral rope is made up an assemblage of wires with round or curved strands. The assemblage features at least one outer layer cord pointed in the opposite direction of the wire. The big advantage of spiral ropes is the fact that they block moisture, water and pollutants from entering the interior of the rope.
Similarly, stranded rope steel wire is made up of an assemblage of spirally wound strands. Unlike spiral rope, though, its wire patterns have crisscrossing layers. These layers create an exceptionally strong rope. Stranded rope may have one of three core material types: wire rope, wire strand or fiber.
Wire rope chain, like all chains, is made up of a series of links. Because it is not solid, wire rope chain is quite flexible. At the same time, it is prone to mechanical failure.
Wire rope slings are made from improved plow wire steel, a strong steel wire that offers superior return loop slings and better security. The plow wire steel also shields rope at its connection points, which extends its working life. Wire rope slings, in general, provide their applications with increased safety, capacity and performance. Wire rope sling is a rope category that encompasses a wide range of sub-products, such as permaloc rope sling, permaloc bridle slings and endless slings. These and other wire rope slings may be accompanied by a wide variety of sling terminations, such as thimbles, chokers and hooks.
Wire rope offers its user many advantages. First, design of even distribution of weight among strands makes it ideal for lifting extremely heavy loads. Second, wire rope is extremely durable and, when matched properly to the application, can withstand great stress and elements like corrosion and abrasion. In addition, it is very versatile. Its many iterations and the ways in which the rope can treated means that users can get rope custom fit for virtually any application.
Depending on the type of wire rope with which you are working and your application, you may want to invest in different accessories. Among these accessories are: wire rope clips, steel carabiners, fittings, fasteners and connections.
To ensure that your wire rope quality remains high, you must regularly inspect them for wear and degradation. The right wire rope should be selected for a particular use. Watch out for performance-impacting damage like: rust, fraying and kinks. To make sure that they stay in tip-top shape, you should also clean and lubricate them as needed. Check for this need as a part of your regular inspection.
Rope care is about more than inspection. It’s also about making an effort to use and store them properly every time you use them. For example, never exceed your rope’s rated load and breaking strength. Doing so will not only cause the weakening of your cable, but it may even cause immediate breakage. In addition, always store your wire rope cable in a dry and warm area, away from those elements that could cause premature rusting or other damage. Finally, always carefully wind your wire rope when you’re done with it, so as to avoid kinks. If you follow all these tips and treat your wire rope assemblies well, they will reward you with a long and productive service life.
Always make sure that you purchase wire rope that matches your industry and regional standards. Some of the most widely referenced standards organizations for wire rope include: ISO, ASTM International and OSHA. Talk over your specifications and application with your wire rope supplier to figure out what’s best for you.
If you’re in the market for a wire rope or a wire rope assembly, the best way to know you’re getting something that will both perform well and be safe if by working with a vetted professional. Find one among the list we’ve provided on this page. Check out their profiles to get an idea of the services and products they offer. Pick out three or four to whom you’d like to speak, and reach out. Talk to them about your specifications, standard requirements and budget. Ask about lead times and delivery options. Once you’ve spoken with all of them, compare and contrast their answers. You’ll know you’ve found the one when you talk to a wire rope company that is willing to go above and beyond for your satisfaction.

Large structures and equipment needing stabilization and support require specially-fabricated wire rope products. These assemblies usually fit swaged or poured terminations to wire rope. Assemblies like these used on boom cranes are referred to as either pennant or boom lines. Similarly-made products are also frequently used in structures such as large awnings and support cables for bridges.
The proper application of these types of assemblies requires careful consideration of capacity, length, plane, and type of termination. The capacity of the socketed assembly will be determined by the diameter and grade of wire rope. Trinity Sling offers a wide variety of wire ropes suitable for socketed and threaded wire rope terminations. The length of a socketed or threaded wire rope assembly requires exacting measurements. These usually are ordered in pairs and require length matching. Due to the differences in stretch inherent in different batches of wire rope, it is not recommended that new socketed slings be matched to used assemblies. The lengths will be mismatched under load.
At Trinity Sling we have years of experience with the various types of socket terminations. The terminations most commonly come with one of three types of connections; open socket (female), closed socket (male), and threaded ends. An open socket looks like a fork with a pin that can be inserted to close and secure the end fitting to the opening of the fork. A closed socket has an eye. The eye of the closed socket is designed to accept the pin of the open socket so they can be linked together. Threaded wire rope end fittings can be made with any type of thread pitch or thread length required for the application.
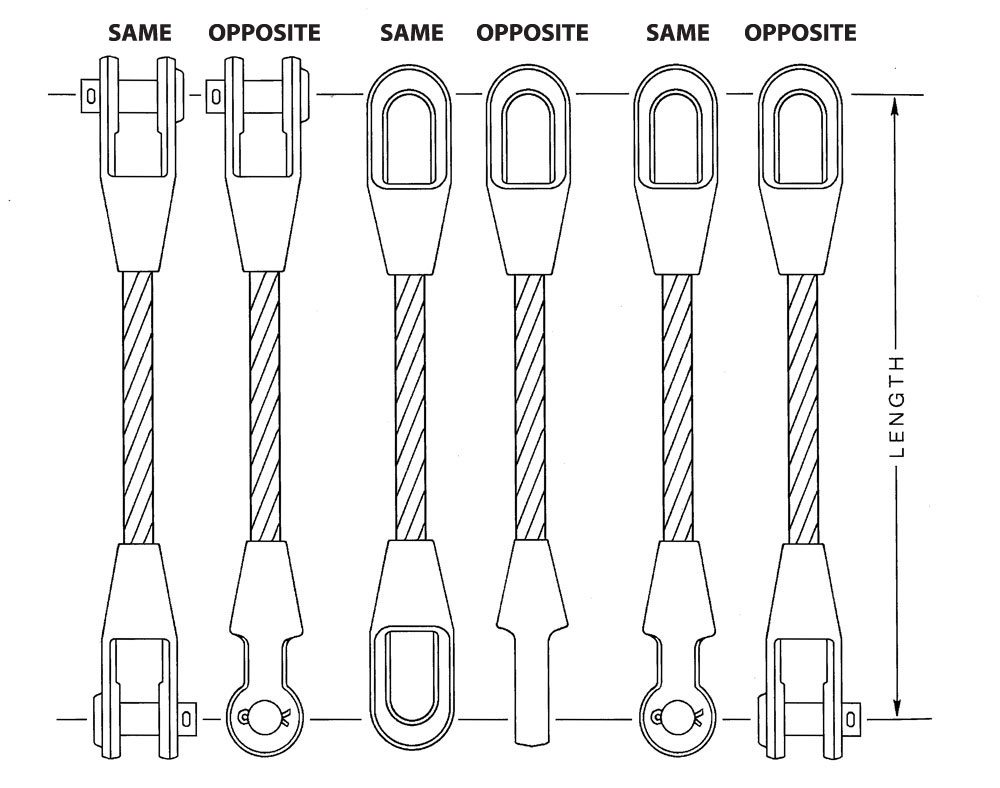
With open and closed socket wire rope terminations the plane of the attachment to the wire rope is also important. The plane of the assembly is determined by the degree relative to each end to which the terminations are attached. Consult the diagram from the Wire Rope Sling User’s Manual for reference to same and opposite planes.
Whether a job requires poured sockets or swaged sockets, well-built assemblies will carry up to 98% of the rated break strength of the rope. Poured sockets are usually set with an epoxy covering the broomed wires inside the socket, while swaged end fittings are attached by forming the shank of the end fitting over the wire rope with a press. Poured socket wire rope end fittings feature flexibility of assembly.
With a properly-trained person and the right equipment, poured sockets can be made in the field. Field installation should not be used in critical or overhead lifting or supporting applications, however, as those applications cannot be proof tested in the field.

Our fork and jaw end fittings must be machine swaged for proper hold strength. Lexco takes pride in our assembly work and will quote any assembly you need per your specification or design print.
Lexco® Cable supplies both commercial grade and MIL SPEC (MS20667) fork ends. Typically machined from 304 stainless steel, they are available in various sizes to accommodate cable from 1/16” to 1” in diameter.
Commercial and military grade fork ends must be machine swaged for proper hold strength. Please contacta Lexco® sales representative to receive an assembly quote.




 8613371530291
8613371530291