what is breaking strength of wire rope quotation

Some of our calculators and applications let you save application data to your local computer. These applications will - due to browser restrictions - send data between your browser and our server. We don"t save this data.
Google use cookies for serving our ads and handling visitor statistics. Please read Google Privacy & Terms for more information about how you can control adserving and the information collected.
Rope strength is a misunderstood metric. One boater will talk about tensile strength, while the other will talk about working load. Both of these are important measurements, and it’s worth learning how to measure and understand them. Each of these measurements has different uses, and here we’re going to give a brief overview of what’s what. Here’s all you need to know about rope strength.
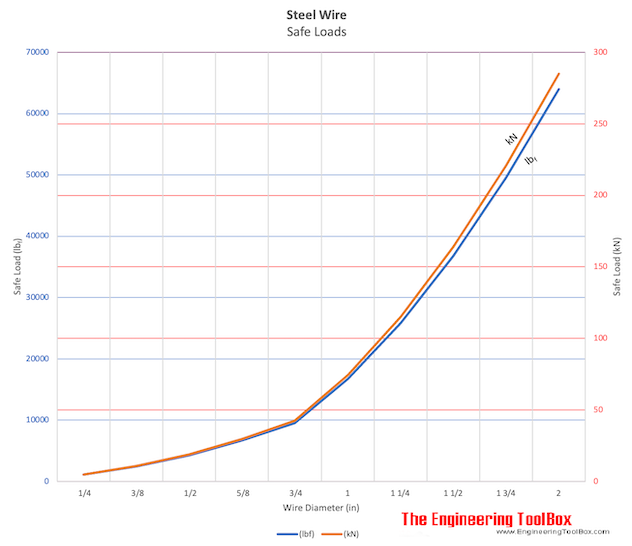
Each type of line, natural fiber, synthetic and wire rope, have different breaking strengths and safe working loads. Natural breaking strength of manila line is the standard against which other lines are compared. Synthetic lines have been assigned “comparison factors” against which they are compared to manila line. The basic breaking strength factor for manila line is found by multiplying the square of the circumference of the line by 900 lbs.
When you purchase line you will buy it by its diameter. However, for purposes of the USCG license exams, all lines must be measured by circumference. To convert use the following formula.
As an example, if you had a piece of ½” manila line and wanted to find the breaking strength, you would first calculate the circumference. (.5 X 3.14 = 1.57) Then using the formula above:
To calculate the breaking strength of synthetic lines you need to add one more factor. As mentioned above, a comparison factor has been developed to compare the breaking strength of synthetics over manila. Since synthetics are stronger than manila an additional multiplication step is added to the formula above.
Using the example above, letÂ’s find the breaking strength of a piece of ½” nylon line. First, convert the diameter to the circumference as we did above and then write the formula including the extra comparison factor step.
Knots and splices will reduce the breaking strength of a line by as much as 50 to 60 percent. The weakest point in the line is the knot or slice. However, a splice is stronger than a knot.
Just being able to calculate breaking strength doesn’t give one a safety margin. The breaking strength formula was developed on the average breaking strength of a new line under laboratory conditions. Without straining the line until it parts, you don’t know if that particular piece of line was above average or below average. For more information, we have discussed the safe working load of ropes made of different materials in this article here.
It’s very important to understand the fundamental differences between the tensile strength of a rope, and a rope’s working load. Both terms refer to rope strength but they’re not the same measurement.
A rope’s tensile strength is the measure of a brand-new rope’s breaking point tested under strict laboratory-controlled conditions. These tests are done by incrementally increasing the load that a rope is expected to carry, until the rope breaks. Rather than adding weight to a line, the test is performed by wrapping the rope around two capstans that slowly turn the rope, adding increasing tension until the rope fails. This test will be repeated on numerous ropes, and an average will be taken. Note that all of these tests will use the ASTM test method D-6268.
The average number will be quoted as the rope’s tensile strength. However, a manufacturer may also test a rope’s minimum tensile strength. This number is often used instead. A rope’s minimum tensile strength is calculated in the same way, but it takes the average strength rating and reduces it by 20%.
A rope’s working load is a different measurement altogether. It’s determined by taking the tensile strength rating and dividing it accordingly, making a figure that’s more in-line with an appropriate maximum load, taking factors such as construction, weave, and rope longevity into the mix as well. A large number of variables will determine the maximum working load of a rope, including the age and condition of the rope too. It’s a complicated equation (as demonstrated above) and if math isn’t your strong point, it’s best left to professionals.
However, if you want to make an educated guess at the recommended working load of a rope, it usually falls between 15% and 25% of the line’s tensile strength rating. It’s a lotlower than you’d think. There are some exceptions, and different construction methods yield different results. For example, a Nylon rope braided with certain fibers may have a stronger working load than a rope twisted out of natural fibers.
For safety purposes, always refer to the information issued by your rope’s manufacturer, and pay close attention to the working load and don’t exceed it. Safety first! Always.
If you’re a regular sailor, climber, or arborist, or just have a keen interest in knot-tying, be warned! Every knot that you tie will reduce your rope’s overall tensile strength. Some knots aren’t particularly damaging, while others can be devastating. A good rule of thumb is to accept the fact that a tied knot will reduce your rope’s tensile strength by around 50%. That’s an extreme figure, sure, but when it comes to hauling critical loads, why take chances?
Knots are unavoidable: they’re useful, practical, and strong. Splices are the same. They both degrade a rope’s strength. They do this because a slight distortion of a rope will cause certain parts of the rope (namely the outer strands) to carry more weight than others (the inner strand). In some cases, the outer strands end up carrying all the weight while the inner strands carry none of it! This isn’t ideal, as you can imagine.
Some knots cause certain fibers to become compressed, and others stretched. When combined together, all of these issues can have a substantial effect on a rope’s ability to carry loads.
Naturally, it’s not always as drastic as strength loss of 50% or more. Some knots aren’t that damaging, some loads aren’t significant enough to cause stress, and some rope materials, such as polypropylene, Dyneema, and other modern fibers, are more resilient than others. Just keep in mind that any knots or splices will reduce your rope’s operations life span. And that’s before we talk about other factors such as the weather or your rope care regime…

Understand that most of the people out from the industry always face the problem of having no idea with the terms of wire rope when receiving quotation. In this update, we will explain in the most simple way and hopefully it is applicable to anyone.
6X36 = Construction of wire rope (There are quite a lot different constructions available for different application for example like, 6X25, 6X29, 6X31, 4X39, 19X7, 8X26 etc.)
RHOL = Right hand ordinary lay, it is the wire lay direction and very important to select the right direction of wire when dealing with multi-reeving, crane and hoist application.
EIPS (1960) = Extra improved plow steel and 1960 stands for the tensile strength 1960N/mm2. The figure is telling you the grade of wire rope, lower or higher tensile strength will result in different breaking strength.
UNGALVD = Ungalvanized, the surface finishing of wire rope. Galvanized and Ungalvanized are the basic surface finishing selection with different grade of lubrication.
G411 THIMBLE EYE = Thimble eye model. Soft eye will be stated with the effective working length and the size of soft eye is based on nominal diameter x 15times according to EN131411 standard.
MECH SPLICED = Mechanical splicing is the process of using hydraulic pressure to press the aluminum sleeve or metal sleeve and a loop is formed. This phrase is always telling you the terminal of both end wire rope. It can be plain, socketed, fuse tapered or eye formed.
Wire rope could have a lot of variation upon the application which I will cover in the next update. The essay above is good enough to tell the basic and hope it helps for procurement department while dealing with steel wire rope. Last but not least, selecting the right wire rope is crucial to your company"s long term expenditure and safety purposes. Do not take the risk because of cheap.
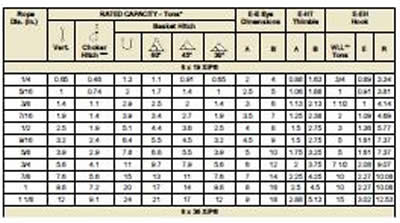
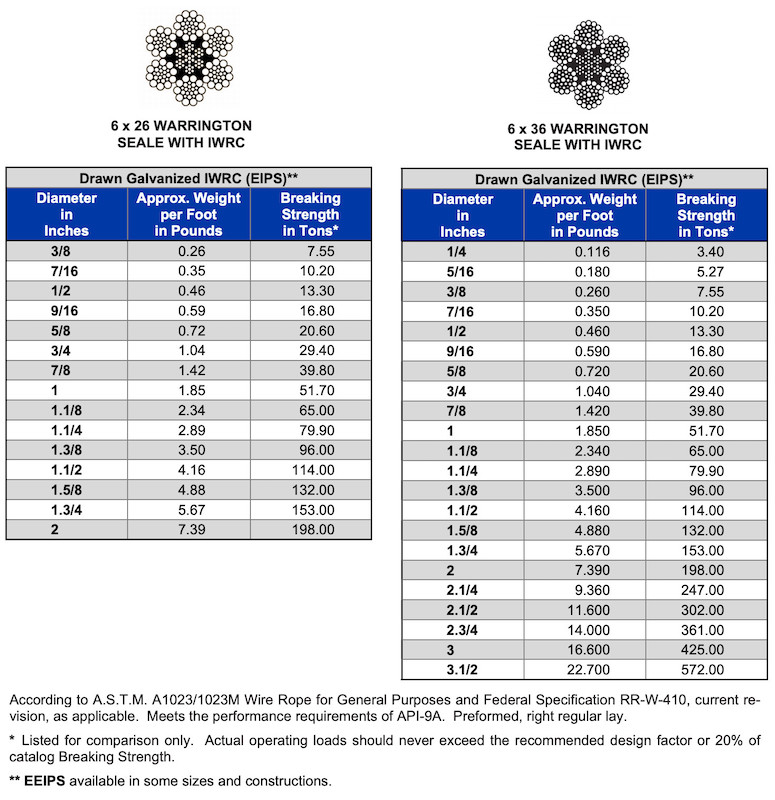
METRIC WIRE ROPES- 6 x 36 wire rope is a more flexible cable wire than 6 x 19 wire rope since it has a higher number of wires per strand. Some of the most common uses are winch lines, choker and boom lines, and works well in marine environments.
* EIPS (Extra Improved Plowed Steel) wire rope has roughly 10% more strength than regular IPS. Independent wire rope core ( IWRC ) provides added strength, reduces the amount of stretch. IWRC wire rope also is resistance to heat and provides extra corrosion resistance over a typical bright wire finish.
As a wire rope is used, the outer wires wear through abrasion and so the rope suffers loss of cross-sectional area – this obviously reduces the breaking strength of the wire rope. Resistance to abrasive wear is therefore an important property of a wire rope.
Abrasion resistance is directly related to the design of the rope, in particular the design of the strands of the rope. In general, ropes with fewer larger wires will be more abrasion resistant than a similar rope made up of smaller wires – a 6 x 19 rope will therefore be more abrasion resistant than a 6 x 36 rope.
In a later article in this technical series we will discuss fatigue resistance in great detail but for the purposes of this discussion, we must recognise that a cyclic stress reversal occurs when a body is subjected to alternating tensile and compressive loads.
In a drilling operation, wire ropes run through sheaves constantly and so are constantly subjected to alternating tensile and compressive loads – i.e. cyclic stress reversals.
Figure 1 illustrates a wire rope bending over a sheave. It is clear that the outer parts of the rope running over the sheave are in tension and the inner parts of the rope running over the sheave are in compression and as the rope moves over the sheave these stresses reverse.
It should be obvious that the smaller the diameter of the sheave the greater the magnitude (amplitude) of the stress reversal and so the more rapidly fatigue will occur in the rope.
Wire ropes experience external forces that will tend to alter or distort the shape of the rope. Crushing prevents wires and strands moving easily over one another during normal operation and this can lead to accelerated wear and reduced rope life.

The Wire Rope Tensile Strength reported in terms of Minimum Breaking Strength (MBS). It achieves this rating based on destruction testing at the factory. In general – every batch will exceed its rating by some amount. This is done for safety purposes. A more detailed discussion of
Please note that MBS is NOT the safe working load (SWL) or maximum working load (MWL) that the wire is rated at for a given purpose. Basically, the SWL depends on the MBS and a safety factor chosen by the Design Engineer.
Some wire is coated, and some is naked




 8613371530291
8613371530291