what is the difference between strand and wire rope made in china

Wire rope and cable are each considered a “machine”. The configuration and method of manufacture combined with the proper selection of material when designed for a specific purpose enables a wire rope or cable to transmit forces, motion and energy in some predetermined manner and to some desired end.
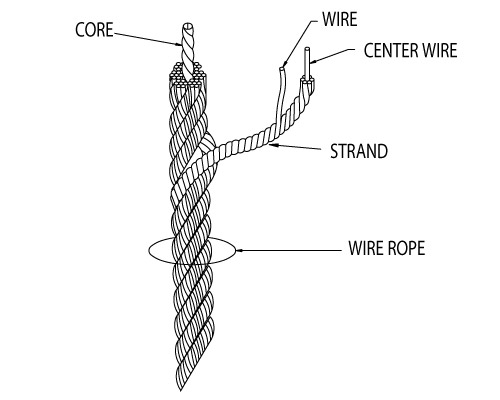
Two or more wires concentrically laid around a center wire is called a strand. It may consist of one or more layers. Typically, the number of wires in a strand is 7, 19 or 37. A group of strands laid around a core would be called a cable or wire rope. In terms of product designation, 7 strands with 19 wires in each strand would be a 7×19 cable: 7 strands with 7 wires in each strand would be a 7×7 cable.
Materials Different applications for wire rope present varying demands for strength, abrasion and corrosion resistance. In order to meet these requirements, wire rope is produced in a number of different materials.
Stainless Steel This is used where corrosion is a prime factor and the cost increase warrants its use. The 18% chromium, 8% nickel alloy known as type 302 is the most common grade accepted due to both corrosion resistance and high strength. Other types frequently used in wire rope are 304, 305, 316 and 321, each having its specific advantage over the other. Type 305 is used where non-magnetic properties are required, however, there is a slight loss of strength.
Galvanized Carbon Steel This is used where strength is a prime factor and corrosion resistance is not great enough to require the use of stainless steel. The lower cost is usually a consideration in the selection of galvanized carbon steel. Wires used in these wire ropes are individually coated with a layer of zinc which offers a good measure of protection from corrosive elements.
Cable Construction The greater the number of wires in a strand or cable of a given diameter, the more flexibility it has. A 1×7 or a 1×19 strand, having 7 and 19 wires respectively, is used principally as a fixed member, as a straight linkage, or where flexing is minimal.
Cables designed with 3×7, 7×7 and 7×19 construction provide for increasing degrees of flexibility but decreased abrasion resistance. These designs would be incorporated where continuous flexing is a requirement.
Selecting Wire Rope When selecting a wire rope to give the best service, there are four requirements which should be given consideration. A proper choice is made by correctly estimating the relative importance of these requirements and selecting a rope which has the qualities best suited to withstand the effects of continued use. The rope should possess:Strength sufficient to take care of the maximum load that may be applied, with a proper safety factor.
Strength Wire rope in service is subjected to several kinds of stresses. The stresses most frequently encountered are direct tension, stress due to acceleration, stress due to sudden or shock loads, stress due to bending, and stress resulting from several forces acting at one time. For the most part, these stresses can be converted into terms of simple tension, and a rope of approximately the correct strength can be chosen. As the strength of a wire rope is determined by its, size, grade and construction, these three factors should be considered.
Safety Factors The safety factor is the ratio of the strength of the rope to the working load. A wire rope with a strength of 10,000 pounds and a total working load of 2,000 pounds would be operating with a safety factor of five.
It is not possible to set safety factors for the various types of wire rope using equipment, as this factor can vary with conditions on individual units of equipment.
The proper safety factor depends not only on the loads applied, but also on the speed of operation, shock load applied, the type of fittings used for securing the rope ends, the acceleration and deceleration, the length of rope, the number, size and location of sheaves and drums, the factors causing abrasion and corrosion and the facilities for inspection.
Fatigue Fatigue failure of the wires in a wire rope is the result of the propagation of small cracks under repeated applications of bending loads. It occurs when ropes operate over comparatively small sheaves or drums. The repeated bending of the individual wires, as the rope bends when passing over the sheaves or drums, and the straightening of the individual wires, as the rope leaves the sheaves or drums, causing fatigue. The effect of fatigue on wires is illustrated by bending a wire repeatedly back and forth until it breaks.
The best means of preventing early fatigue of wire ropes is to use sheaves and drums of adequate size. To increase the resistance to fatigue, a rope of more flexible construction should be used, as increased flexibility is secured through the use of smaller wires.
Abrasive Wear The ability of a wire rope to withstand abrasion is determined by the size, the carbon and manganese content, the heat treatment of the outer wires and the construction of the rope. The larger outer wires of the less flexible constructions are better able to withstand abrasion than the finer outer wires of the more flexible ropes. The higher carbon and manganese content and the heat treatment used in producing wire for the stronger ropes, make the higher grade ropes better able to withstand abrasive wear than the lower grade ropes.
Effects of Bending All wire ropes, except stationary ropes used as guys or supports, are subjected to bending around sheaves or drums. The service obtained from wire ropes is, to a large extent, dependent upon the proper choice and location of the sheaves and drums about which it operates.
A wire rope may be considered a machine in which the individual elements (wires and strands) slide upon each other when the rope is bent. Therefore, as a prerequisite to the satisfactory operation of wire rope over sheaves and drums, the rope must be properly lubricated.
Loss of strength due to bending is caused by the inability of the individual strands and wires to adjust themselves to their changed position when the rope is bent. Tests made by the National Institute of Standards and Technology show that the rope strength decreases in a marked degree as the sheave diameter grows smaller with respect to the diameter of the rope. The loss of strength due to bending wire ropes over the sheaves found in common use will not exceed 6% and will usually be about 4%.
The bending of a wire rope is accompanied by readjustment in the positions of the strands and wires and results in actual bending of the wires. Repetitive flexing of the wires develops bending loads which, even though well within the elastic limit of the wires, set up points of stress concentration.
The fatigue effect of bending appears in the form of small cracks in the wires at these over-stressed foci. These cracks propagate under repeated stress cycles, until the remaining sound metal is inadequate to withstand the bending load. This results in broken wires showing no apparent contraction of cross section.
Experience has established the fact that from the service view-point, a very definite relationship exists between the size of the individual outer wires of a wire rope and the size of the sheave or drum about which it operates. Sheaves and drums smaller than 200 times the diameter of the outer wires will cause permanent set in a heavily loaded rope. Good practice requires the use of sheaves and drums with diameters 800 times the diameter of the outer wires in the rope for heavily loaded fast-moving ropes.
It is impossible to give a definite minimum size of sheave or drum about which a wire rope will operate with satisfactory results, because of the other factors affecting the useful life of the rope. If the loads are light or the speed slow, smaller sheaves and drums can be used without causing early fatigue of the wires than if the loads are heavy or the speed is fast. Reverse bends, where a rope is bent in one direction and then in the opposite direction, cause excessive fatigue and should be avoided whenever possible. When a reverse bend is necessary larger sheaves are required than would be the case if the rope were bent in one direction only.
Stretch of Wire Rope The stretch of a wire rope under load is the result of two components: the structural stretch and the elastic stretch. Structural stretch of wire rope is caused by the lengthening of the rope lay, compression of the core and adjustment of the wires and strands to the load placed upon the wire rope. The elastic stretch is caused by elongation of the wires.
The structural stretch varies with the size of core, the lengths of lays and the construction of the rope. This stretch also varies with the loads imposed and the amount of bending to which the rope is subjected. For estimating this stretch the value of one-half percent, or .005 times the length of the rope under load, gives an approximate figure. If loads are light, one-quarter percent or .0025 times the rope length may be used. With heavy loads, this stretch may approach one percent, or .01 times the rope length.
The elastic stretch of a wire rope is directly proportional to the load and the length of rope under load, and inversely proportional to the metallic area and modulus of elasticity. This applies only to loads that do not exceed the elastic limit of a wire rope. The elastic limit of stainless steel wire rope is approximately 60% of its breaking strength and for galvanized ropes it is approximately 50%.
Preformed Wire Ropes Preformed ropes differ from the standard, or non-preformed ropes, in that the individual wires in the strands and the strands in the rope are preformed, or pre-shaped to their proper shape before they are assembled in the finished rope.
This, in turn, results in preformed wire ropes having the following characteristics:They can be cut without the seizings necessary to retain the rope structure of non-preformed ropes.
They are substantially free from liveliness and twisting tendencies. This makes installation and handling easier, and lessens the likelihood of damage to the rope from kinking or fouling. Preforming permits the more general use of Lang lay and wire core constructions.
Removal of internal stresses increase resistance to fatigue from bending. This results in increased service where ability to withstand bending is the important requirement. It also permits the use of ropes with larger outer wires, when increased wear resistance is desired.
Outer wires will wear thinner before breaking, and broken wire ends will not protrude from the rope to injure worker’s hands, to nick and distort adjacent wires, or to wear sheaves and drums. Because of the fact that broken wire ends do not porcupine, they are not as noticeable as they are in non-preformed ropes. This necessitates the use of greater care when inspecting worn preformed ropes, to determine their true condition.

Wire ropes can be seen everywhere around us, they are made of strands or bundles of individual wires constructed around an independent core, suitable for construction, industrial, fitness, commercial, architectural, agricultural, and marine rigging applications.
Wire rod is made from high carbon steel wires(0.35 to 0.85 percent carbon) in a hot rolling process of a required diameter, usually from 5.5mm to 8 mm.
Wire rod is drawn to the required diameter by the 1st drawing machine after descaling dust and rust, adding mechanical properties suitable for application.
Positioning the wires different or the same size lay in multiple layers and same direction, or cross lay and diameter is maintained by one-third of the rope size.
So in theory, it is very simple to manufacture wire ropes. However there are many more details that must be closely monitored and controlled, and this requires time and experienced personnel since it is a super complicated project you cannot imagine.

This website is using a security service to protect itself from online attacks. The action you just performed triggered the security solution. There are several actions that could trigger this block including submitting a certain word or phrase, a SQL command or malformed data.
Have you ever wondered why aircraft cable is called aircraft cable instead of aircraft strand? Do you use the words cable and wire rope interchangeably when you’re not sure which is correct? The world of manufacturing is chock-full of words to describe wire products, and while it may seem confusing to keep track of them at first, having some background knowledge about cable construction will help you understand each component. Let’s take a moment to differentiate our terms by starting small.
Wire: In its simplest form, wire is a single, flexible, string-like rod. It begins life as a metal such as stainless steel or carbon steel that becomes narrower in diameter as it is drawn through a series of small holes called dies. Used in everything from electrical equipment and coat hangers to art projects and nails, wire is the foundation of many wide and varied items.
Strand: Strand is made of two or more wires laid around a single center wire. In general, “1 by…” products are considered strand, like 1x7 and 1x19, which are two common configurations.
Notice how this 1x7 strand is a unit comprised of individual wires. It is 1 strand of 7 wires.1x19, as another example, is 1 strand of 19 wires. Like wire,strand can exist as its own product, or it can be laid around a core in multiples to become cable or wire rope.
Cable:Cables are made by concentrically wrapping groups of strands. A 7x7 cable, for example, is comprised of seven strands, each made of 7 wires. 7x19 cable, as another example, has seven strands with 19 wires in each one. Wire rope is technically also a group of strands wrapped around a core, which is why the terms cableand wire rope are often used interchangeably. Professions will argue that wire rope is designated for products with a diameter larger than 3/8 inch while cableis designated for all smaller diameters, but in practical application, the terms are somewhat interchageable.
Looking for wire, strand, or cable for your application? Make sure that you specify the size, construction, and material of a product when building your quote on www.strandcore.com. Luckily, Strand Core provides comprehensive data sheets for all our aircraft cable and general purpose wire rope products to help make your selection easier. Visit https://strandcore.com/products/general-purpose-wire-rope/ to start browsing our wire rope products, today.

CIVMATS produces high quality stainless steel wire rope. Our annual production capacity is roughly 8000 tons, among which stainless steel wire rope amounts to 400 tons per month. The tolerance of our stainless steel wire rope can be as small as ±0.01mm. CIVMATS produces strictly according to ISO9001:2000. Every product delivered from CIVMATS is a reputation warranty.
Wire rope can be divided into multi-strand wire rope and single-strand wire rope. It is structured with at least two layers of steel wire or a plurality of strands spirally wound around a center or a core. Stainless steel wire rope refers to a steel wire rope made of stainless steel. In dynamic systems, stainless steel wire ropes are widely applied in the lifting of cranes and elevators, the transmission of mechanical power, the control of automobile cockpit poles and the operation of aircraft control systems, etc. In static systems, stainless steel wire ropes are also employed in various industries such as the stability of the sling bridge"s pulling support tower and the design of new railings.
Stainless steel wire rope features high temperature resistance, good fatigue resistance, excellent breaking force, long service life and durability. It is widely used in coal, petroleum, metallurgy, chemical industry, shipbuilding, bridge, electric power, rubber, military, tourism, water conservancy and light industry. The products can be produced according to ISO, BS, DIN, JIS, ABS, LR and other international and foreign advanced standards
In CIVMATS, all of our stainless steel wire ropes are packaged as per international standard to prevent any possible damage or loss. They are neatly wrapped in accurate length with securely tied rope ends. For enhanced customer experience, we also provide dedicated package as per your special requirements.
By default, we will quote based on sea transportation, such as FOB, CFR, CIF and the like for most enquiries or orders. Quotation based on air transportation is also optional upon your request for urgent demands.
Our main grades for stainless steel wire rope are 304 and 316. We can also customize stainless steel wire rope as per your specified grades and sizes for your reference.
1. Point contact: The adjacent stainless steel wires contact in the form of point in the strands. The diameters of all the stainless steel wires, excluding the central wire are equal, and the strands are formed by layering.
2. Line contact: There is a linear contact between the adjacent layers of stainless steel wire in the strand, and the strands are made of stainless steel wires of different diameters in one process.
4. Point and line contact: There are two kinds of contact forms between the adjacent layers of stainless steel wires in the strand. The strands are made of wires of different diameters.
1. In the equipment reform of chemical, fertilizer, chemical fiber and other industries, stainless steel wire rope was used for the deployment of the updated equipment.
2. Stainless steel wire ropes are used in the applications of popular stainless steel welding rods and a considerable number of stainless steel components, springs, connecting parts, etc.,
5. Stainless steel wire ropes are also extensively used in railway electrification, decoration industry, rigging industry, fishing gear industry, automobile and motorcycle industry and other industries.

Rotation rope and non-rotation rope or rotation resistant rope. Round strand rope, compacted rope, swaged rope. Wire rope with fiber core, wire rope with IWRC(Independent Wire Rope Core). Galvanized wire rope, ungalvanized wire rope or bright wire rope. Wire rope with plastic insert, Wire rope without plastic insert. Wire rope covered with plastic.

Wire rope and cable, is there a difference? The terms are often used interchangeably, but are they different? Each is considered a machine. Wire ropes are usually ⅜” in diameter or larger, while cables or cords are smaller. Though this little distinction exists in aircraft and marine cables, wire ropes and cables are synonymous in most other ways.
A strand is made up of two or more wires twisted around a center wire. Each strand is made up of 7, 19, or 37 wires. Cable or wire rope is made when a group of strands is twisted around a center wire or rope. They are named for the numbers of wires and strands. A 7×7 cable has 7 strands with 7 wires in each strand wrapped around a central core. A 7×19 cable would include 7 strands with 19 wires in each cable.
Different wire rope applications require different demands for abrasion, strength, and corrosion resistance. Different materials are used to meet different needs. Sizes under ⅜ “ are considered aircraft cable, sizes over 3/8 “ in diameter are considered wire rope.Stainless Steel – Type 302, made up of 18% chromium and 8% nickel alloy, is the most common grade because of its high strength and resistance to corrosion. When non-magnetic properties are required, type 305 is employed. Other common types used in wire rope are 304, 305, 316, and 321. Each has specific advantages and disadvantages. Stainless steel is the stronger of the two, so its cost is higher but well worth it.
Galvanized Carbon Steel – To protect from the elements, a coating of zinc is applied to wire ropes used in the making of this wire rope. It is the wire rope of choice when strength is necessary, but corrosion resistance is not significant enough to warrant the use of stainless steel. Galvanized carbon steel is the go-to for cost-effectiveness.
If you require flexibility, you need wires that have more strands, more strands equal more flexibility. Look for 3×7, 7×7, and 7×19; these will give you more flexibility. However, as the degrees of flexibility increase, the abrasion resistance decreases. These cables are most useful where you require continuous flexing. Basic cable construction:
1×19 cable – This cable is still reasonably flexible, yet it resists compressive forces. It is smooth on the outside, and sizes above 3/32” diameter are the strongest.
It is essential to correctly estimate the qualities necessary for the work the wire rope will be doing. To decide the importance of the essential attributes to do the job, you need to look for quality and figure out whether it can withstand how it will be used and the length of time it can be used in this capacity. In choosing a wire rope for the job at hand, these four things must be considered:Sufficient strength to lift the load and then some, keeping safety in mind. Always overestimate.
Whether it is a crane, a pulley, or some other machine, be sure to choose the proper size, construction, and grade of wire rope appropriate for the job.
To find the wire rope or cable you need for the job, contact us atSilver State Wire Ropefor all of your wire rope and rigging needs. We have all sizes of cable and wire rope; whether you need it for aircraft, marine, or land use, we have it all!

As specialist for manufacturing quality steel wire ropes over 20 years, our company can supply strong, durable and reliable ropes that capable to minimize your downtime and maximize cost effectiveness. Decades of experience we owned make us know clearly the work you do and capable to provide professional guidance.
We select the best steel or stainless steel as raw material for wire rope manufacturing. Our products are manufactured under strict quality managements and test before they leave the factory.
Our engineers can provide professional advice about picking up optimal steel wire ropes for their application, installation guidance to ensure maximum return in their wire rope system.
As one of the largest manufacturers in China, we can purchase better materials at a lower price. Then we transmit this saving to our customers by providing the most competitive price.
If you are going to pick up steel wire ropes that suit your project perfectly, you must have an ideal about the construction about them. Our company can supply bright wire rope, galvanized wire rope, stainless steel wire rope, compacted wire rope, rotation resistant wire ropes, mining wire rope, elevator wire rope, crane wire rope and gas & oilfield wire ropes. Here are some details to solve the problem that may puzzle you whether you are browsing the web or picking up steel wire ropes.
Bright steel wire ropes mean no surface treatment is applied to the rope. Therefore, they have the lower price among these three wire ropes. Generally, they are fully lubricated to protect the rope from rust and corrosion.
Galvanized steel wire ropes feature compressed zinc coating for providing excellent corrosion resistance. With higher break strength yet lower price than stainless steel, galvanized steel wire ropes are widely used in general engineering applications such as winches and security ropes.
Stainless steel wire ropes, made of quality 304, 305, 316 steels, are the most corrosive type for marine environments and other places subjected to salt water spray. Meanwhile, bright and shiny appearance can be maintained for years rather than dull as galvanized steel wire ropes.
Steel wire ropes are composed of multiple strands of individual wires that surrounding a wire or fiber center to form a combination with excellent fatigue and abrasion resistance. These wires and strands are wound in different directions to from different lay types as follows:
Beside above lay types, alternative lay ropes which combine regular lay and lang lay together and ideal for boom hoist and winch lines, can also be supplied as your request.
Two main methods about seizing steel wire ropes in conjunction with soft or annealing wire or strands to protect cut ends of the ropes form loosening.

While talking to people at a recent trade show it hit me: There is a lack of information in the marketplace concerning the quality of available wire rope . Most people feel that there is one general level of cable quality, usually based on their experience with imported wire rope. Let"s take a minute to clear up the confusions many people have about wire rope availability and performance.
When I dig a little deeper, I always find out that the cable they are using is low quality import material, often from China, that never seems to perform the way they intended. Short service life, broken wires and low break strength are often tolerated because the wire rope is just so very cheap. And the lowering of quality and performance from your wire rope tends to feed on itself: Inexpensive cable performance is sub-par, so the purchaser becomes conditioned to poor performance. This translates into a buying decision focused solely on the price of the wire rope, which in turn leads to distributors looking for less and less expensive material, which dictates the quality, and so on.
Ultimately, this cycle results in wire rope that is manufactured to just meet the thresholds of performance required by specification, and nothing more. Some applications can accept this material, but the majority of customers would be best served by selecting a higher quality wire rope.
When the performance is a key element of your application, you should be requesting a high quality domestic wire rope. Why should you purchase a domestic rope? Domestic manufacturers work with smaller lot sizes and focus on quality.
It will require a larger investment to purchase and employ the higher quality material, but that will end the downward quality spiral created by using the least expensive cable you can find. You will notice, first and foremost, that your cable will last longer and perform at an improved level. You will also notice that the added cost for purchasing a domestic wire rope is minimal when compared to the extended life you will receive.
So for your next purchase, request a domestic wire rope for your application. Here are some general rules to ensure you receive the best cable available:
1. Not all wire rope is created equal. There are specifications for wire rope, including Federal Specification RR-W-410 and Military Specification MIL-DTL-83420, both detailing the level of quality and performance required for specific applications. When purchasing a wire rope, be sure to reference one of these specifications to ensure you receive a higher quality material.
2. Just because you purchased the rope from a domestic source does not mean that it is domestic.Make sure you specifically request a domestic wire rope.
3. Domestic Wire rope is available.there are several manufacturers that would be more than delighted t quote your requirements. You can find a list of companies on the Domestic Wire Rope Committee web site.

a. Wires: steel wires for wire ropes are normally made of non-alloy carbon steel with a carbon content of 0.4 to 0.95%. The tensile forces and to run over sheaves with relatively small diameters.
b. Strand: the strand is a component of wire rope usually consisting of an assembly of wires of appropriate diamsions laid helically in one or more layers around a central element.
c. Core: the core is the central element, of fiber or steel, around which are laid helically the outer strands of wire rope. The core provides proper support for the strands under normal bending and loading conditions.
d. Wire rope is several strands of metal wire twisted into a helix forming a composite "rope", in a pattern known as "laid rope". Larger diameter wire rope consists of multiple strands.
Mine hoisting, blast furnace hoisting, large casting, oil drilling, forestry and marine industries,all kinds ofelevator, large hoisting, ground cable car ships and offshore facilities, cable railing.
Zinc coated carbon steel offers some corrosion resistance. It remains ductile over long periods of working. Usually higher break strengths than stainless steels.

Steel wire rope is consisted of several strands of metal wire twisted into a helix. It is used for lifting, traction, taut and bearing in the material handling. And it has advantages of high strength, light weight, safe and stable work.
We can produce various of steel wire rope according to our national standards such as GB8919, GB/T20118, GB/T20067 and also international standards ISO, ASTM, EN, JIS and API etc. GotAPI, DNV, LR, BV, CCS, MA and KA certification,which assure good quality control.
The performance of steel wire rope to load is mainly determined by steel wire. Steel wire rope are normally made of carbon steel or alloy steel, which makes it has high strength and toughness. And the surface treatment of it can be finished according to the used environment.
In the cross lay strands, the wires of the different layers cross each other. In the mostly used parallel lay strands, the lay length of all the wire layers is eaqul and the wires of any two superimposed layers are parallel, resulting in linear contact.
The rope core is mainly used to increase the elasticity and thoughness, lubricate steel wire, lighten friction and improve the service life of wire rope. The commonly used types including oganic fibers, such as hemp and cotton, synthetic fiber, asbestos core or soft metal materials.
On how to select different constructions of wire rope, you can refer to GB8918-2006 “ Steel Wire Ropes for Important Purpose ”, and GB/T20018-2006 “ Steel Wire Ropes for General Purposes ”. The technical parameters such as lifting load, safety coefficient, and the lifting capacity of the lifting equipment should be taken into consideration when selecting the strength class of wire rope.

Wire rope is commonly comprised of wire core and strand, which is made using various types of steel including galvanized, coated and non-coated. The steel wire ropes are also named as wire cables and steel wire, which are featured with high strength, flexibility, abrasion resistance, corrosion resistance and rotation resistance. This makes them well-suited for varieties of uses such as pulling, fixing and bearing in the marine, architectural and construction.
The wire ropes can be assembled into steel wire rope slings being used with lifting equipment or winches to meet lifting and rigging needs in different industries.
The wire ropes are classified according to the strand and wires. Shown below are just some typical types of wire ropes. Wire ropes are also available in customized constructions.

Steel wire ropes have important applications in mine lifting, cable-stayed bridges, metallurgy, elevators, and so on. They are widely used due to their high strength, light weight, reliability, and efficiency [1]. Since wire ropes usually work in harsh environments, although they suffer from a variety of types of damage such as broken wire and wear, which affects the safety of production and even threatens the lives of workers [2]. To avoid accidents, manual inspection and regular replacement are generally used in engineering. However, manual inspection is time-consuming and laborious, and regular replacement usually causes great economic waste. According to a survey, more than 70% of replaced wire ropes still have initial breaking strength [3]. Therefore, it is of great importance to develop scientific and effective devices to inspect steel wire ropes.
There are two types of defects of steel wire ropes, loss of metallic cross-sectional area (LMA) and a localized fault (LF), and broken wire is the most typical outcome of LF. Among the various nondestructive testing techniques, magnetic flux leakage (MFL) method is most economical and effective for broken wire detection [4,5,6,7,8]. The basic principle of the MFL method is shown in Figure 1, where the permanent magnet magnetizes part of the wire rope to saturation, and a closed magnetic circuit is formed between the wire rope, the magnet and the yoke. When no damage is present, most of the magnetic induction lines pass through the inside of the wire rope. When there is a damage such as broken wire, the magnetic resistance of the damaged position increases, and part of the magnetic induction line leaks out to form the MFL. Magnetic sensitive elements are placed between the poles of the magnet to sense the MFL signal. The condition of the wire rope can be determined according to the received signal.
For decades, many experts and scholars have done a lot of research on the design of damage detecting sensors based on the MFL method [9,10,11,12,13]. Cao Y.N. et al. [9] proposed an approach for detecting LF of steel wire ropes using an annular array of Hall components. A back propagation (BP) network is used to classify the faults. This method can differentiate the degree and the width of local defects. Zhang J. et al. [10] applied the giant magneto-resistance (GMR) sensor to the detection of LF and LMA of the wire rope. Through the use of compressed sensing wavelet filtering and BP neural network, the accuracy and reliability of MFL sensor is improved. Wu B. [13] designed an MFL sensor based on tunnel magneto-resistive device. A blind hole with dimension of 0.3 mm in both depth and diameter is detectable for the sensor. The axial resolution to two adjacent notches with a width of 0.2 mm of the TMR-based MFL sensor can be less than 2.5 mm. However, arranging annular arrays of Hall components undoubtedly increases the complexity of the signal processing. Using magneto-resistive sensors can improve the sensitivity of the sensor, but it is difficult to be applied to actual inspections due to the micron-level requirements of the lift-off [13]. Therefore, designing a sensor that can be applied to the detection in actual engineering and is both simple and effective, has always been a problem for the condition monitoring of wire ropes.
The magnetic concentrating detection technology provides a new direction for the development of MFL sensors. The detection of wire ropes usually requires the arrangement of a plurality of magnetic sensitive elements. Especially for the large diameter wire ropes, it usually needs dozens of magnetic sensors, which greatly increases the difficulty of signal processing in the later stage. The magnetic concentrating principle can realize the leak-free detection of large diameter wire ropes through a small number of magnetic sensitive elements [14,15]. Kang et al. [14] theoretically analyzed the feasibility of magnetic concentrating detection. It is proved by calculation that the magnetic concentrator can collect the MFL and guide it into the Hall component through the bridge between the concentrators to realize the collection of weak leakage flux. At the same time, it can eliminate the strand-waveform noise of wire ropes and improve signal-to-noise ratio of the MFL signal. Wang et al. [15] analyzed the performance of the magnetic concentrators on collecting the MFL by finite element simulation and proposed the structure which is suitable for collecting the magnetic leakage flux. The structure was verified by experiments, which further promoted the development of the magnetic concentrating detection.
In this study, a sensor, which is constructed of ring-shaped magnets, a yoke, and a magnetic concentrator, is designed to detect broken wires of steel wire ropes. We optimized the structural parameters of the circumferential multi-circuit permanent magnet exciter (CMPME) and analyzed the performance of the magnetic concentrator on collecting MFL through the finite element method. Finally, the proposed sensor is applied in an experiment for broken wire detection. The induced MFL signal can be clearly recognized and the signal-to-noise ratio of the MFL signal is improved by discrete wavelet transform (DWT).
The rest of the paper is organized as follows. Section 2 describes the design principle of the magnetic circuit of the CMPME and the basic theory of magnetic concentrating detection. In Section 3, the structure parameters of the exciter are optimized by simulation, and the performance of the magnetic concentrator on collecting MFL is analyzed. Section 4 illustrates the experimental settings, steps and result analysis. Finally, the conclusions are drawn in Section 5.

Wire rope is often used in slings because of its strength, durability, abrasion resistance and ability to conform to the shape of the loads on which it is used. In addition, wire rope slings are able to lift hot materials.
Wire rope used in slings can be made of ropes with either Independent Wire Rope Core (IWRC) or a fiber-core. It should be noted that a sling manufactured with a fiber-core is usually more flexible but is less resistant to environmental damage. Conversely, a core that is made of a wire rope strand tends to have greater strength and is more resistant to heat damage.
Wire rope may be manufactured using different rope lays. The lay of a wire rope describes the direction the wires and strands are twisted during the construction of the rope. Most wire rope is right lay, regular lay. This type of rope has the widest range of applications. Wire rope slings may be made of other wire rope lays at the recommendation of the sling manufacturer or a qualified person.
Wire rope slings are made from various grades of wire rope, but the most common grades in use are Extra Improved Plow Steel (EIPS) and Extra Extra Improved Plow Steel (EEIPS). These wire ropes are manufactured and tested in accordance with ASTM guidelines. If other grades of wire rope are used, use them in accordance with the manufacturer"s recommendations and guidance.
When selecting a wire rope sling to give the best service, consider four characteristics: strength, ability to bend without distortion, ability to withstand abrasive wear, and ability to withstand abuse.
Rated loads (capacities) for single-leg vertical, choker, basket hitches, and two-, three-, and four-leg bridle slings for specific grades of wire rope slings are as shown in Tables 7 through 15.
Rated loads for a sling in a choker hitch are the values shown in Table 7, 9, 11, 13, 14, or 15, provided that the angle of the choke is 120 degrees or more (Fig. 2). Use the values in Fig. 2 or those from the sling manufacturer or a qualified person for angles of choke less than 120 degrees.
Ensure that slings made of rope with 6×19 and 6x37 classifications and cable slings have a minimum clear length of rope 10 times the component rope diameter between splices, sleeves, or end fittings unless approved by a qualified person,
Ensure that braided slings have a minimum clear length of rope 40 times the component rope diameter between the loops or end fittings unless approved by a qualified person,
Ensure that grommets and endless slings have a minimum circumferential length of 96 times the body diameter of the grommet or endless sling unless approved by a qualified person, and
Perform welding of handles or other accessories to end attachments, except covers to thimbles, before assembly of the sling. Ensure that welded end attachments are proof tested by the manufacturer or a qualified person. Retain the certificates of proof test and make them available for examination.
Do not use wire rope clips to fabricate wire rope slings, except where the application precludes the use of prefabricated slings and where the sling is designed for the specific application by a qualified person,
Although OSHA"s sling standard does not require you to make and maintain records of inspections, the ASME standard contains provisions on inspection records.[3]
Use damaged slings only after they are repaired, reconditioned, and proof tested by the sling manufacturer or a qualified person using the following criteria:
Ensure that wire rope slings have suitable characteristics for the type of load, hitch, and environment in which they will be used and that they are not used with loads in excess of the rated load capacities described in the appropriate tables. When D/d ratios (Fig. 4) are smaller than those listed in the tables, consult the sling manufacturer. Follow other safe operating practices, including:
Ensure that multiple-leg slings are selected according to Tables 7 through 15 when used at the specific angles given in the tables. Ensure that operations at other angles are limited to the rated load of the next lower angle given in the tables or calculated by a qualified person,
When D/d ratios (see Fig. 6) smaller than those cited in the tables are necessary, ensure that the rated load of the sling is decreased. Consult the sling manufacturer for specific data or refer to the WRTB (Wire Rope Technical Board) Wire Rope Sling Users Manual, and
Ensure that all portions of the human body are kept away from the areas between the sling and the load and between the sling and the crane or hoist hook,
When using a basket hitch, ensure that the legs of the sling contain or support the load from the sides, above the center of gravity, so that the load remains under control,
Ensure that the load applied to the hook is centered in the base (bowl) of the hook to prevent point loading on the hook, unless the hook is designed for point loading,
Before initial use, ensure that all new swaged-socket, poured-socket, turnback-eye, mechanical joint grommets, and endless wire rope slings are proof tested by the sling manufacturer or a qualified person.
Permanently remove from service fiber-core wire rope slings of any grade if they are exposed to temperatures in excess of 180 degrees F (82 degrees C).
Follow the recommendations of the sling manufacturer when you use metallic-core wire rope slings of any grade at temperatures above 400 degrees F (204 degrees C) or below minus 40 degrees F (minus 40 degrees C).




 8613371530291
8613371530291