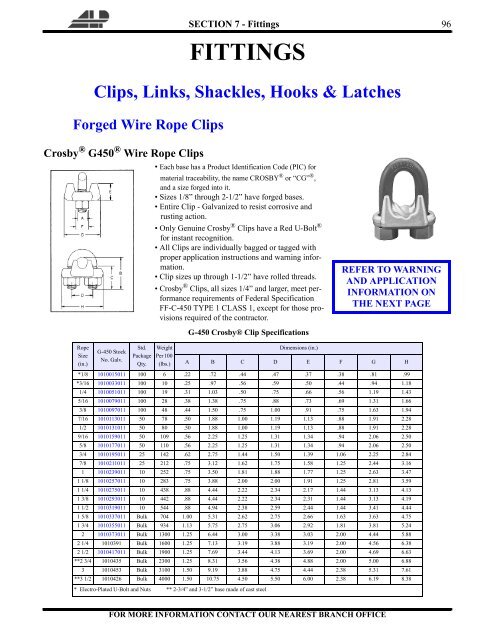
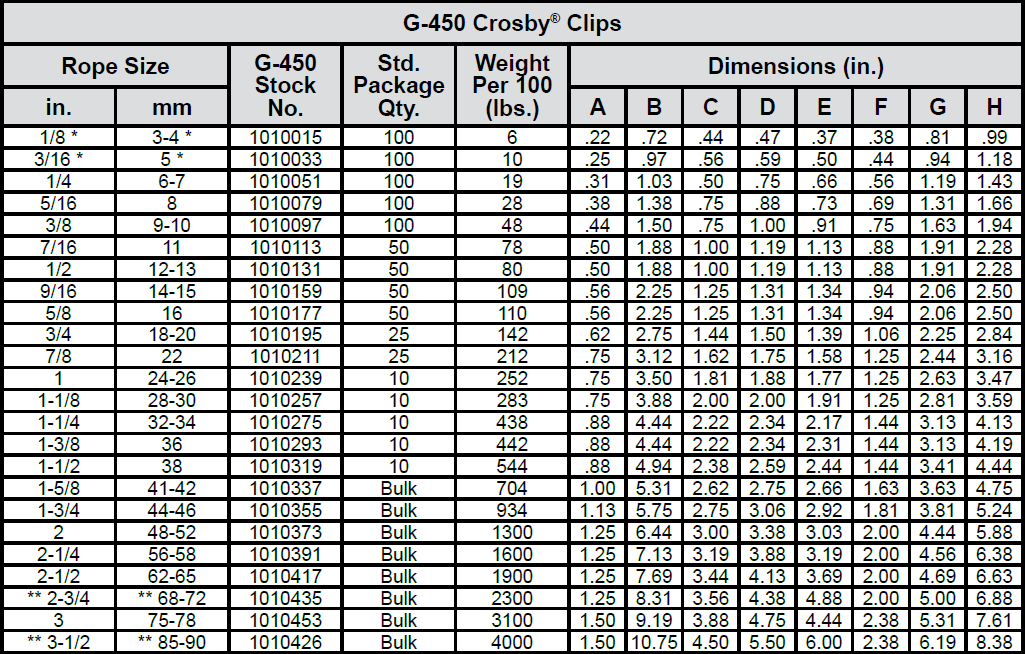
wire rope clip spacing formula in stock

Wire Rope Clip a.k.a Bulldog Clip or U-Bolt Clip which used to clamp the loose end of wire rope by looping the wire rope back and form eye to create a bearing point. The termination efficiency of forged wire rope clip shall be 80%.
According to EN 13411-5, grip secured eye termination wire rope is only suitable in suspending static load and single use lifting operation (one time use lifting operation with proper safetyfactor consideration). To use with spiral rope or use it in general lifting sling make is not recommended.
Proper secure of wire rope clip, the distance, d between wire rope clip and the distance of wire rope clip to tail have to be at least 1.5 times and not more than 3 times of the wire rope clip base width. Collar nut shall be secured with proper torque value according to size of the wire rope clip to prevent crushing the wire rope if the torque value is too large or wire rope slip over uf the torque value is below the proper or recommended collar nut pre-load value.
The number of malleable wire rope clip used in securing eye termination shall be one more than the forged wire rope clip used in same size of wire rope.
Proof load value of Grip Secured eye termination shall is 20% of the wire rope Minimum Breaking Strength, the collar nut needs to be re-torque to proper value after the proof load testing.
U-bolt Clips.There is only one correct method for attaching U-bolt clips to wire rope ends, as shown in TheRightWayimage below. The base of the clip bears on the live end of the rope; the “U” of the bolt bears on the dead end.
Compare this with the incorrect methods. Five of the six clips shown are incorrectly attached—only the center clip in the top view is correct. When the “U” of the clip bears on the live end of the rope, there is a possibility of the rope being cut or kinked, with subsequent failure.
Wire rope is an extremely versatile mechanical device that can be used to help support and move an object or load. Whether for use on cranes or for other lifting applications, it’s important to have a solid understanding of the rigging components that are being used to attach to and lift a load.
As a rigger or end-user of wire rope, it’s necessary to understand the types of wire rope end termination, or treatments that can be used at the ends of a length of wire rope—one of the most common being wire rope clips.
Wire rope clips can be used to form a load bearing eye at the end of a cable or wire rope, or to connect two cables together with a lap splice. Wire rope clips are popular because they can be installed in the field and provide 80-90% efficiency of the rope breaking strength, depending on the diameter of the wire rope.
As a general guideline, they are NOT to be used for making slings, as ASME B30.9 Slingsstandard states: “Mechanical wire rope terminations requiring periodic adjustment to maintain efficiency shall not be used to fabricate slings.”
There are two main types of wire rope clips—U-Bolt and double saddle clips. U-Bolt wire rope clips are the most common and may be made of forged or malleable metal.
This type of wire rope clip is essentially a U-bolt, two nuts, and a metal base (saddle) that can be made from forged steel or cast iron. Careful consideration and attention must be given to the way U-bolt type wire rope clips are installed.
The base of the wire rope clip is made from forged steel. Forged clips are heated and hammered into the desired shape—resulting in a consistent grain structure in the steel. Forged wire rope clips are used for critical, heavy-duty, overhead loads such as winch lines, crane hoist lines, support lines, guy lines, towing lines, tie downs, scaffolds, etc.
Malleable wire rope clips are used for making eye termination assemblies only with right regular lay wire rope and only for light duty uses with small applied loads, such as hand rails, fencing, guard rails, etc. The base of the wire rope clips is made from malleable cast iron, which may fracture under heavy use and does not have the desirable metal properties of steel, or the beneficial grain structure that a forged base has.
Unfortunately, it is not uncommon to see a wire rope clip applied incorrectly. Some of the most common mistakes include:Not torquing to the manufacturer’s expectations
Wire rope clips require the use of a torque wrench in order to function properly. Torquing the nuts on the clips too much or too little can cause the clip to fail. If the clip is over-torqued, it could damage the threads of the wire rope. If the clip is under-torqued, the holding power of the clip is diminished and the wire rope could slip through.
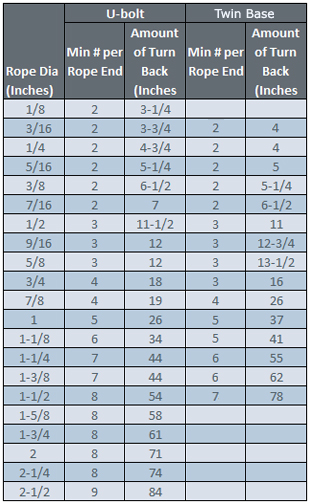
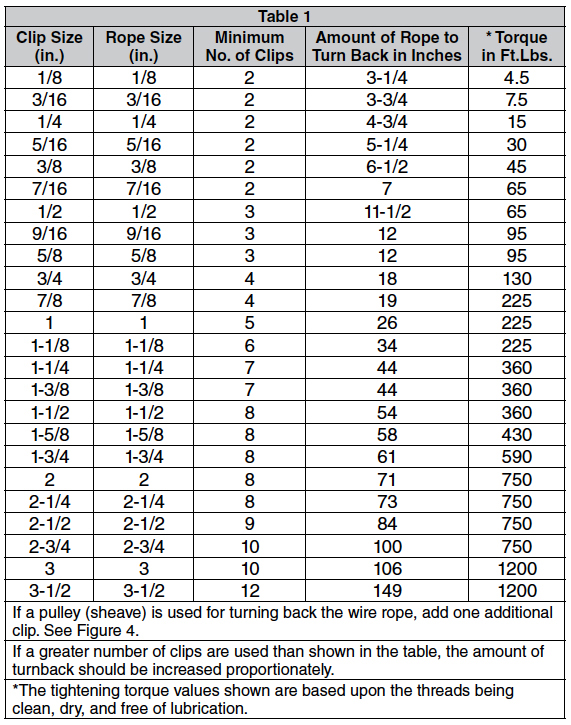
There are a minimum number of clips required for use related to the wire rope diameter. Using less than the number of specified clips could result in decreased efficiency and possible failure.
Depending on the number and size of the wire rope clips, there is a proportional amount of space required between the placement on each clip on the rope.
There are two sides of a U-Bolt style wire rope clip: the saddle and the U-Bolt. When securing a wire rope eye, it is important to place the clip on the correct end of the rope.
A saying commonly used in rigging to help remember this is: “Never saddle a dead horse!” In other words, never put the saddle on the dead end of the rope.
The turnback is the portion of the wire rope eye that runs from the end of the bearing eye to the live end. Having less than the suggested amount of turnback will decrease the efficiency of the wire rope eye and could lead to failure.
It is important to be sure you are using the correct wire rope clip—forged or malleable wire rope clips—for the application. Malleable clips can only be used for non-critical uses, such as tension rope to form a perimeter around a parking lot.
If the use is critical—an application where, if there is a failure, you have potential injury or loss of life or damage to property—a forged clip must be used.
The clip size used—whether it be 1/8”, 3”, or otherwise—must match the diameter size of the wire rope. If it doesn’t, the wire rope could slip out of the clip.
After installing clips, it is necessary to regularly cycle the rope and retighten the clips. Monitoring the torque on the nuts is important, as they will loosen over repeated use.
Basic steps for installing a wire rope clip include:First, wrap the wire rope around the thimble or to form the eye, and turn back the correct amount of rope—as specified by the manufacturer.
Apply the first wire rope clip at the end of the dead end, with one base width of space. Use a torque wrench to tighten the nuts on the wire rope clip.
When applying the second clip (if required), place it as close to the eye loop or thimble as possible. Again, be sure to properly tighten the nuts of the clip with a torque wrench.
Wire rope clips are a common and necessary piece of rigging hardware when it comes to using wire rope and forming end terminations. They are used to form a wire rope eye or to connect two cables together. It’s important to understand how to correctly install a wire rope clip, as incorrect installation leads to decreased efficiency in the wire rope assembly.

Wire rope clip is otherwise known as a wire rope clamp, wire cable clamp, wire clamp, wire clip, U-bolt, etc. It is widely used for making eye-loop connections or join two wire rope cable ends together. The traditional styles of wire rope clips usually have three components: a U-shaped bolt, a forged or cast iron saddle, and two nuts.
The wire rope clips are available in a range of sizes and finishes, while you can easily find the difference from the appearance, traditional wire clips with u bolt, saddle and nuts, fist grip, stamped cable clamp.
Cast and malleable wire rope clips can only be used under light duty loads applications with relatively light loads, such as handrails, fencing, guard rails, etc.
While the drop forged wire rope clip variety is recommended for important, critical or sustaining overhead loads, such as guy lines, support lines, scaffolding, etc. The drop forged wire rope clips can be used in critical suspending, guying, and tie-down applications for the die forging process make them strong and more durable and the heating and hammering steps make their structure to be consistent and conform to the shape of the forged item.
Simplex and duplex cable clamps are also known as single stamped wire clip and double stamped cable clip are composed of stamping plate, saddle, and bolts, feature an aesthetic design, used for outdoor light duty applications.
Wire rope clips are available in a variety of materials and finishes but basically three types of materials, carbon steel, cast, malleable iron, and stainless steel.
Carbon steel wire rope cable clamps are galvanized, or hot dipped galvanized, the galvanised metal wire clamp has an added zinc layer to prevent rusting and protect against scratching and the addition of carbon corresponds with an increase in the hardness and strength of wire rope cable clamps. G, but stainless steel wire rope clamps are the best choice for corrosion-resistant applications that can be used for saltwater environments.
Commonly wire rope clamp installation is very simple, there’s a well-known saying can help you remember how to attach wire rope clips, that reads “never saddle a dead horse.” Just follow the recommendation ways:
Keep three or more wire rope clips attached at the end of the wire rope dead end, space between each wire rope clip should be at least 6 times the wire rope diameter.
You can see the correct and incorrect ways of installation from the following pictures and find how many wire rope clips to use at one wire rope loop.
The saddle shall be placed on the live end of the wire rope, with the U-bolt on the dead-end side—Remember the well-known saying: “Never saddle a dead horse.” Use at least two or three wire rope clips to secure the ends properly to the length of the rope, and tighten nuts evenly one by one until reaching the recommended torque.
If you have any wire rope clips questions, you can contact us by email at info@hilifting.com. We will be glad to share with you more useful information.
U-bolt on the bitter (dead) end, not on the standing part of the wire rope. If clips are attached incorrectly, the standing part (live end) of the wire rope will be distorted or have mashed spots. A rule of thumb when attaching a wire rope is to NEVER saddle a dead horse.
Another type of wire rope clip is the twin-base clip, often referred to as the universal or two clamp (fig. 6-56). Both parts of this clip are shaped to fit the wire rope, so the clip cannot be attached incorrectly. The twin-base clip allows for a clear 360-degree swing with the wrench when the nuts are being tightened.
THIMBLE. - When an eye is made in a wire rope, a metal fitting, called a thimble, is placed in the eye, as shown in figure 6-55. The thimble protects the eye against wear. Wire rope eyes with thimbles and wire rope clips can hold approximately 80 percent of the wire rope strength.
After the eye made with clips has been strained, the nuts on the clips must be re-tightened. Checks should be made now and then for tightness or the clips will cause damage to the rope.
SWAGED CONNECTIONS. - Swaging makes an efficient and permanent attachment for wire rope, as shown in figure 6-57. A swaged connection is made by compressing a steel sleeve over the rope by using a hydraulic press. When the connection is made properly, it provides 100 percent capacity of the wire rope.
Careful inspection of the wires leading into these connections is important because of the pressure put upon the wires in this section. If one broken wire is found at the swaged connection or a crack in the swage, replace the fitting.
HOOKS AND SHACKLES. - Hooks and shackles are handy for hauling or lifting loads without tying them directly to the object with line, wire rope, or chain. They can be attached to wire rope, fiber line, blocks, or chains. Shackles should be used for loads too heavy for hooks to handle.
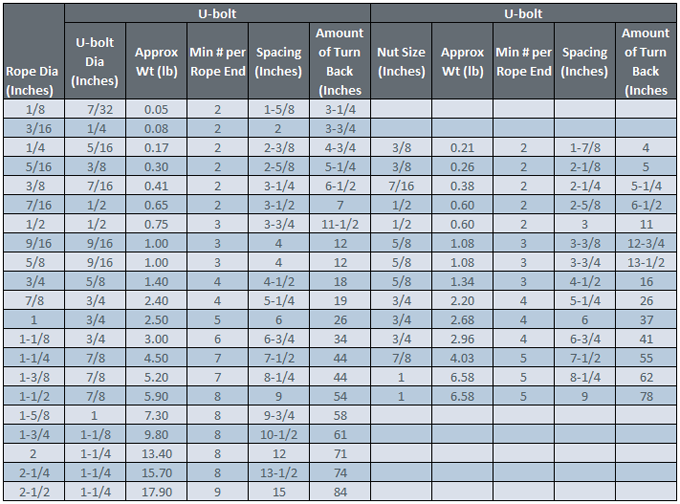
Refer to the chart above in following these instructions. Turn back specified amount of rope from thimble or loop. Apply first clip one base width from dead end of rope. Apply U-bolt over dead end of wire rope - live end rests in saddle. Tighten nuts evenly, alternate from one nut to the other until reaching the recommended torque.
When two clips are required, apply the second clip as near the thimble or loop as possible. Tighten nuts evenly, alternating until reaching the recommended torque. When more than two clips are required, apply the second clip as near the loop or thimble as possible, turn nuts on second clip firmly, but do not tighten. Proceed to Step 3.
When three or more clips are required, space additional clips equally between the first two - take up rope slack - tighten nuts on each U-bolt evenly, alternating from one nut to the other until reaching the recommended torque.
Apply an initial load equal to loads expected in use. Inspect for proper orientation and spacing of clips and re-tighten the nuts to recommended torque.

Northern Strands, safety is one of our top priorities. Therefore, knowing how to properly clip wire rope using Crosby clips is very important in order to practice safe rigging. Keep in mind that the wire rope clip must be the correct size for the diameter of the rope that is being used and that there is a specific number of clips that are required according to rope size.
A quick rule of thumb for proper clip installation is, "Never Saddle a Dead Horse". This refers to the live end of the wire rope that rests in the saddle of the forged wire clip and the U-bolt that is placed on the dead end of the wire rope.
Refer to chart above in following these instructions. Turn back specified amount of rope from thimble or loop. Apply first clip one base width from dead end of rope. Tighten nuts evenly, alternating from one nut to the other until reaching the recommended torque.
When two clips are required, apply the second clip as near the loop or thimble as possible. Tighten nuts evenly, alternating until reaching the recommended torque. When more than two clips are required, apply the second clip as near the loop or thimble as possible, turn nuts on second clip firmly, but do not tighten.
When three or more clips are required, space additional clips between first two—take up rope slack—tighten nuts on all clips, alternating from one nut to the other until reaching the recommended torque.

Wire rope is often used in slings because of its strength, durability, abrasion resistance and ability to conform to the shape of the loads on which it is used. In addition, wire rope slings are able to lift hot materials.
Wire rope used in slings can be made of ropes with either Independent Wire Rope Core (IWRC) or a fiber-core. It should be noted that a sling manufactured with a fiber-core is usually more flexible but is less resistant to environmental damage. Conversely, a core that is made of a wire rope strand tends to have greater strength and is more resistant to heat damage.
Wire rope may be manufactured using different rope lays. The lay of a wire rope describes the direction the wires and strands are twisted during the construction of the rope. Most wire rope is right lay, regular lay. This type of rope has the widest range of applications. Wire rope slings may be made of other wire rope lays at the recommendation of the sling manufacturer or a qualified person.
Wire rope slings are made from various grades of wire rope, but the most common grades in use are Extra Improved Plow Steel (EIPS) and Extra Extra Improved Plow Steel (EEIPS). These wire ropes are manufactured and tested in accordance with ASTM guidelines. If other grades of wire rope are used, use them in accordance with the manufacturer"s recommendations and guidance.
When selecting a wire rope sling to give the best service, consider four characteristics: strength, ability to bend without distortion, ability to withstand abrasive wear, and ability to withstand abuse.
Rated loads (capacities) for single-leg vertical, choker, basket hitches, and two-, three-, and four-leg bridle slings for specific grades of wire rope slings are as shown in Tables 7 through 15.
Ensure that slings made of rope with 6×19 and 6x37 classifications and cable slings have a minimum clear length of rope 10 times the component rope diameter between splices, sleeves, or end fittings unless approved by a qualified person,
Ensure that braided slings have a minimum clear length of rope 40 times the component rope diameter between the loops or end fittings unless approved by a qualified person,
Do not use wire rope clips to fabricate wire rope slings, except where the application precludes the use of prefabricated slings and where the sling is designed for the specific application by a qualified person,
Ensure that wire rope slings have suitable characteristics for the type of load, hitch, and environment in which they will be used and that they are not used with loads in excess of the rated load capacities described in the appropriate tables. When D/d ratios (Fig. 4) are smaller than those listed in the tables, consult the sling manufacturer. Follow other safe operating practices, including:
When D/d ratios (see Fig. 6) smaller than those cited in the tables are necessary, ensure that the rated load of the sling is decreased. Consult the sling manufacturer for specific data or refer to the WRTB (Wire Rope Technical Board) Wire Rope Sling Users Manual, and
Before initial use, ensure that all new swaged-socket, poured-socket, turnback-eye, mechanical joint grommets, and endless wire rope slings are proof tested by the sling manufacturer or a qualified person.
Permanently remove from service fiber-core wire rope slings of any grade if they are exposed to temperatures in excess of 180 degrees F (82 degrees C).
Follow the recommendations of the sling manufacturer when you use metallic-core wire rope slings of any grade at temperatures above 400 degrees F (204 degrees C) or below minus 40 degrees F (minus 40 degrees C).




 8613371530291
8613371530291