wire rope construction chart factory
Wire rope is a complex mechanical device that has many moving parts all working in tandem to help support and move an object or load. In the lifting and rigging industries, wire rope is attached to a crane or hoist and fitted with swivels, shackles or hooks to attach to a load and move it in a controlled matter. It can also be used to lift and lower elevators, or as a means of support for suspension bridges or towers.
Wire rope is a preferred lifting device for many reasons. Its unique design consists of multiple steel wires that form individual strands laid in a helical pattern around a core. This structure provides strength, flexibility, and the ability to handle bending stresses. Different configurations of the material, wire, and strand structure will provide different benefits for the specific lifting application, including:Strength
However, selecting the proper wire rope for your lifting application requires some careful thought. Our goal is to help you understand the components of a wire rope, the construction of wire rope, and the different types of wire rope and what they might be used for. This will allow you to select the best performing and longest-lasting wire rope for the job at hand.
A wire rope is, in reality, a very complicated machine. A typical 6 x 25 rope has 150 wires in its outer strands, all of which move independently and together in a very complicated pattern around the core as the rope bends. Clearances between wires and strands are balanced when a rope is designed so that proper bearing clearances will exist to permit internal movement and adjustment of wires and strands when the rope has to bend. These clearances will vary as bending occurs, but are of the same range as the clearances found in automobile engine bearings.
Understanding and accepting the “machine idea” gives a rope user a greater respect for rope, and enables them to obtain better performance and longer useful life from rope applications. Anyone who uses a rope can use it more efficiently and effectively when they fully understand the machine concept.
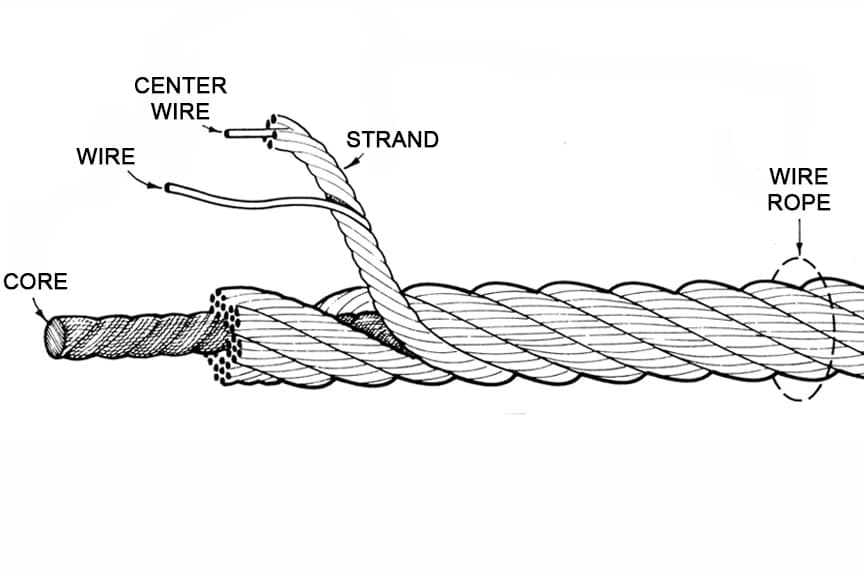
Wires are the smallest component of wire rope and they make up the individual strands in the rope. Wires can be made from a variety of metal materials including steel, iron, stainless steel, monel, and bronze. The wires can be manufactured in a variety of grades that relate to the strength, resistance to wear, fatigue resistance, corrosion resistance, and curve of the wire rope.
Strands of wire rope consist of two or more wires arranged and twisted in a specific arrangement. The individual strands are then laid in a helical pattern around the core of the rope.
The core of a wire rope runs through the center of the rope and supports the strands and helps to maintain their relative position under loading and bending stresses. Cores can be made from a number of different materials including natural or synthetic fibers and steel.
Lubrication is applied during the manufacturing process and penetrates all the way to the core. Wire rope lubrication has two primary benefits:Reduces friction as the individual wires and strands move over each other
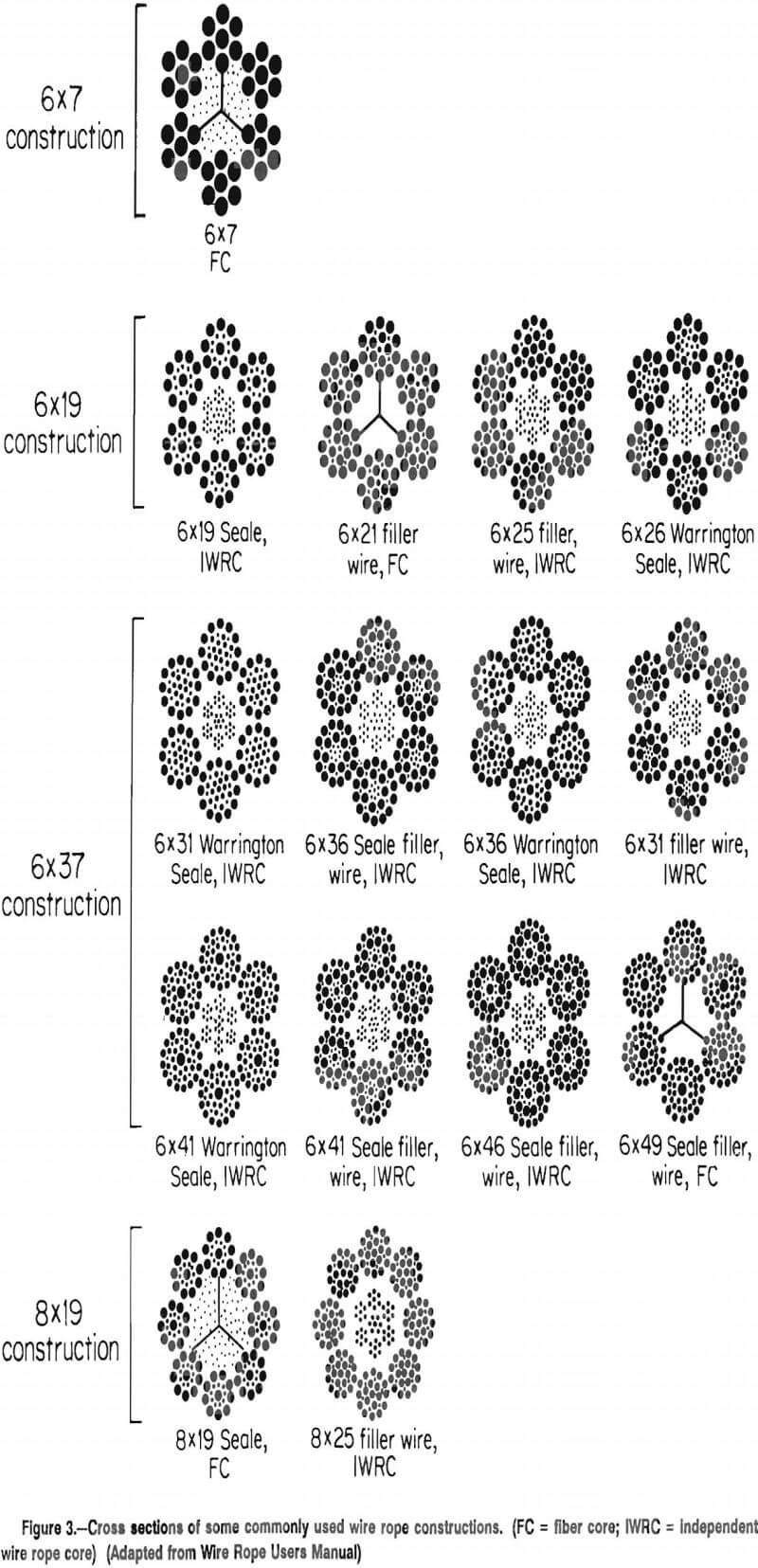
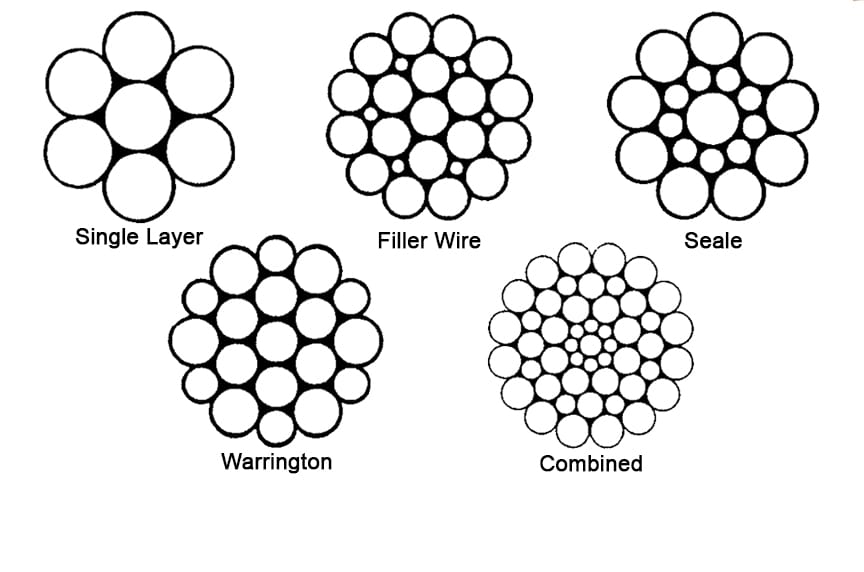
The number of layers of wires, the number of wires per layer, and the size of the wires per layer all affect the strand pattern type. Wire rope can be constructed using one of the following patterns, or can be constructed using two or more of the patterns below.Single Layer – The most common example is a 7 wire strand with a single-wire center and six wires of the same diameter around it.
Filler Wire – Two layers of uniform-size wire around a center with the inner layer having half the number of wires as the outer layer. Small filler wires, equal to the number in the inner layer, are laid in valleys of the inner wire.
Seale – Two layers of wires around a center with the same number of wires in each layer. All wires in each layer are the same diameter. The large outer wires rest in the valleys between the smaller inner wires.
Warrington – Two layers of wires around a center with one diameter of wire in the inner layer, and two diameters of wire alternating large and small in the outer later. The larger outer-layer wires rest in the valleys, and the smaller ones on the crowns of the inner layer.
On a preformed wire rope, the strands and wires are formed during the manufacturing process to the helical shape that they will take in a finished wire rope.
Preformed rope can be advantageous in certain applications where it needs to spool more uniformly on a drum, needs greater flexibility, or requires more fatigue-resistance when bending.
Direction and type of lay refer to the way the wires are laid to form a strand (either right or left) and how the strands are laid around the core (regular lay, lang lay, or alternate lay).Regular Lay – The wires line up with the axis of the rope. The direction of the wire lay in the strand is opposite to the direction of the strand lay. Regular lay ropes are more resistant to crushing forces, are more naturally rotation-resistant, and also spool better in a drum than lang lay ropes.
Lang Lay– The wires form an angle with the axis of the rope. The wire lay and strand lay around the core in the same direction. Lang Lay ropes have a greater fatigue-resistance and are more resistant to abrasion.
A steel core can be an independent wire rope or an individual strand. Steel cores are best suited for applications where a fiber core may not provide adequate support, or in an operating environment where temperatures could exceed 180° F.
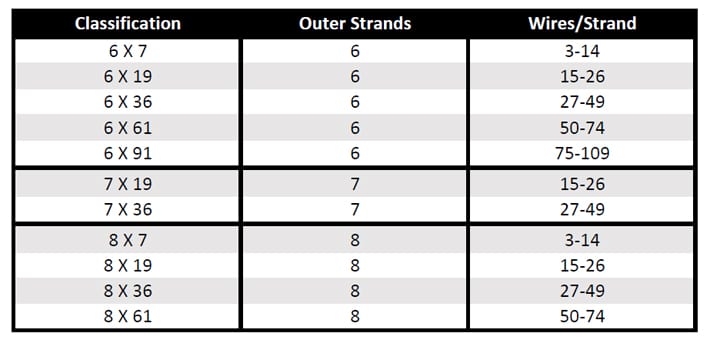
The classifications of wire rope provide the total number of strands, as well as a nominal or exact number of wires in each strand. These are general classifications and may or may not reflect the actual construction of the strands. However, all wire ropes of the same size and wire grade in each classification will have the SAME strength and weight ratings and usually the same pricing.
Besides the general classifications of wire rope, there are other types of wire rope that are special construction and designed for special lifting applications.
Some types of wire rope, especially lang lay wire rope, are more susceptible to rotation when under load. Rotation resistant wire rope is designed to resist twisting, spinning, or rotating and can be used in a single line or multi-part system.
Special care must be taken when handling, unreeling, and installing rotation resistant wire rope. Improper handling or spooling can introduce twist into the rope which can cause uncontrolled rotation.
Compacted strand wire rope is manufactured using strands that have been compacted, reducing the outer diameter of the entire strand, by means of passing through a die or rollers. This process occurs prior to closing of the rope.
This process flattens the surface of the outer wires in the strand, but also increases the density of the strand. This results in a smoother outer surface and increases the strength compared to comparable round wire rope (comparing same diameter and classification), while also helping to extend the surface life due to increased wear resistance.
A swaged wire rope differs from a compacted strand wire rope, in that a swaged wire rope’s diameter is compacted, or reduced, by a rotary swager machine after the wire rope has been closed. A swaged wire rope can be manufactured using round or compacted strands.
The advantages of a swaged wire rope are that they are more resistant to wear, have better crushing resistance, and high strength compared to a round strand wire rope of equal diameter and classification. However, a swaged wire rope may have less bending fatigue resistance.
A plastic coating can be applied to the exterior surface of a wire rope to provide protection against abrasion, wear, and other environmental factors that may cause corrosion. However, because you can’t see the individual strands and wires underneath the plastic coating, they can be difficult to inspect.
Plastic filled wire ropes are impregnated with a matrix of plastic where the internal spaces between the strands and wires are filled. Plastic filling helps to improve bending fatigue by reducing the wear internally and externally. Plastic filled wire ropes are used for demanding lifting applications.
This type of wire rope uses an Independent Wire Rope Core (IWRC) that is either filled with plastic or coated in plastic to reduce internal wear and increase bending fatigue life.
Remember, wire rope is a complex piece of mechanical machinery. There are a number of different specifications and properties that can affect the performance and service life of wire rope. Consider the following when specifying the best type of wire rope for your lifting application:Strength
When you select a piece of rope that is resistant to one property, you will most likely have a trade-off that affects another property. For example, a fiber core rope will be more flexible, but may have less crushing resistance. A rope with larger diameter wires will be more abrasion resistant, but will offer less fatigue resistance.
At Mazzella Companies, we offer all different kinds of wire rope from all of the leading manufacturers. We sell the highest-quality domestic and non-domestic rigging products because product quality and operating safety go hand-in-hand. We have one of the largest and most complete inventories of both domestic and non-domestic rigging and lifting products to suit your lifting needs.
If you’re looking for a standard or custom specified wire rope for your lifting project, contact a Lifting Specialist at a Mazzella Companies location near you.
We stock well over 2,000,000 feet of wire rope in our various locations … ready for immediate delivery! We provide wire rope assemblies, and manufacture bridge cables, crane cables, steel mill cables, and thousands of OEM assemblies.
Understanding the basics of wire rope will help guide you on how to choose the right wire rope for your job. Application, required strength, and environmental conditions all play a factor in determining the type of wire rope that is best for you.
But when it comes to buying wire rope, the various numbers and abbreviations that describe the different types of wire rope can be confusing. EIPS wire rope, 6X19 IWRC wire rope, and lang lay wire rope are just some of the many variations available. But what does it all mean?
Displayed as inch or fractional inch measurements, the size indicates the diameter of the rope. Industry standards measure the rope at its widest point. A wide range of sizes are available from 1/8” wire rope to 2-1/2” wire rope. Thicker sized wire rope has a higher break strength. For example, our Wire Rope has a 15,100 lb. break strength while our Wire Rope has a 228,000 lb. break strength.
The numbers indicate its construction. For example: in wire rope, as shown above the first number is the number of strands (6); the second number is how many wires make up one strand (19).
When it comes to wire rope basics, regular lay also refers to right lay or ordinary lay. This indicates that the strands pass from left to right across the rope and the wires in the rope lay in opposite direction to the lay of the strands. This type of construction is the most common and offers the widest range of applications for the rope.
This term indicates that the wires twist in the same direction as the strands. These ropes are generally more flexible and have increased wearing surface per wire than right lay ropes. Because the outside wires lie at an angle to the rope’s axis, internal stress is reduced making it more resistant to fatigue from bending. This type of rope is often used in construction, excavating, and mining applications.
Independent wire rope cores offer more support to the outer strands and have a higher resistance to crushing and heat. Independent wire rope core also has less stretch and more strength.
Many of our customers use our rope and our wire rope clips to create rope assemblies. Check out of video blog on Wire Rope Clips to Wire Rope Assemblies to learn more.
For any questions on our wire rope products, call (877) 923-0349 or email customerservice@uscargocontrol.com to speak with one of our product experts.
Wire rope is a collection of metal strands that have been twisted and wound to form the shape of a helix with the purpose of supporting and lifting heavy loads and performing tasks that are too rigorous for standard wire. On shipping docks, rigging, and load bearing equipment, wire rope is attached to swivels, shackles, or hooks to lift a load in a controlled, even, and efficient manner.
The uses for wire rope include adding support to suspension bridges, lifting elevators, and serving as additional reinforcement for towers. The design of wire rope, with its multiple strands wrapped around a stable core, provides strength, flexibility, and ease of handling for applications that have bending stress.
Individual designs of wire rope involve different materials, wire, and strand configurations as a means for supporting and assisting in the completion of lifting or supportive applications.
The term wire rope encompasses a wide range of mechanical tools that are made to perform heavy and extreme lifting jobs. Wire rope is a complicated and complex tool with multiple moving parts capable of moving in unison. A 6 by 25 wire rope has 150 outer strands that move as one in an intricate pattern supported by a flexible core.
An essential part of the design of wire rope is the required clearance between the strands to give each stand the freedom to move and adjust when the rope bends. It is this unique feature that differentiates wire rope from solid wire and other forms of cable.
The basic element of wire rope is wire that is used to configure, shape, and form the rope. Typically, steel, stainless steel, and galvanized wires are the first choice with aluminum, nickel alloy, bronze, copper, and titanium being second possibilities. The choice of wire is dependent on the type of work the wire is going to be used to perform with strength, flexibility, and abrasion resistance being the major determining factors.
Stainless steel wire rope has all of the basic qualities of galvanized and general wire rope with the added benefits of corrosion and rust resistance; this makes it the ideal choice for harsh and stressful conditions.
Steel wire rope is classified as general purpose wire rope and comes in a wide variety of sizes, diameters, and strengths. It is the most common type of wire rope and is used for several industrial, manufacturing, and construction applications.
Before going further into the discussion of how wire rope is made, it is important to understand the numbers used to describe each type. All wire ropes have a core around which wires are wound. The various styles of cores vary according to the construction and design of the requirements of the wire rope that is being produced.
Wire rope is classified by the number of strands it has as well as the number of wires in each strand. The most common classification is a seven wire rope that has one strand in the center and six around its circumference. This type of wire rope is lightweight with a very simple construction. The majority of wire ropes are more complex and intricate with multiple intertwining strands and wires.
What must be understood about wire rope is that it has a complicated configuration. It is actually wires wrapped around wires to form bundles that are wrapped around other bundles. In the case of a seven wire wire rope, the core has bundles of wires wound around it; this can be seen in the image below.
The first step in wire rope creation is the production of wire strands where wires are wound around a single core wire. The number of wires included in the strand is dependent on the specified strength, flexibility, and size requirements of the rope. Once the strand is completed, it is straightened before being moved to wire rope construction.
Like wire ropes, strands have different patterns; patterns are the arrangements of the wires and their diameters. Though most strands have a core, there are strand patterns that have three or four wires without a core that are referred to as centerless strands. The design of each strand pattern is meant to enhance the strength of the wire rope and improve its performance.
For a multiple layer strand, the layers of wire are placed over one another in successive order. The placement of the wires on top of each other must be such that they fit smoothly and evenly.
The Warrington pattern is like the multiple layer pattern with one variation. Like the multiple layer pattern, the inner wires and the core are the same and have the same diameter. The difference is in the outer layer, which has wires of alternating sizes of large and small with larger diameter wires laying in the valleys of the inner wires.
All of the wires of a filler pattern are the same size. What makes this pattern unique is the insertion of small wires in the valleys of the inner wires to fill the gap between the inner and outer layer.
The flattened strand pattern is also known as the triangular strand, which can be triangular or oval. Three round wires form the core. The outer flattened surface has a greater sectional metallic area; this makes this pattern stronger and longer lasting.
The core of a wire rope runs through the center of the rope and can be composed of a variety of materials, which include synthetic fibers, natural fibers, a single strand, or another wire rope. The core supports the wound strands, helps maintain their position, is an effective lubricant carrier, and provides support.
Wire ropes with fiber cores are restricted to light loads and are not used in severe, harsh, or stressful conditions. Polypropylene and nylon are types of synthetic fiber cores and can be used in conditions where there is exposure to chemicals.
Cores made of wire are classified as independent wire cores. The core of a wire rope with a wire core is actually a wire rope with another wire rope serving as the core, as can be seen in the diagram below. These types of wire ropes are used where the rope will be exposed to exceptional resistance and crushing.
A strand, or wire strand core, is exactly like the rest of the strands of the wire rope with wires of the same diameter and size as the other strands.
The choice of core and creation of the strands are the simplest yet most essential parts of wire rope construction. Wire rope lays, the method used to wind the strands, is more complex and involves several choices.
Lay is a term used to describe three of the main characteristics of wire rope: direction, relationship, and linear distance. The strands can be wrapped around the core going right or left. Right or left refers to the direction of the strands wrapped around the core and the wires within the strands. The linear distance is how far a strand moves when it is making a revolution around the core.
In a regular lay, the wires and strands spiral in opposite directions. With a right hand regular lay, the wires spiral to the left and the strands to the right. In the left hand regular lay, the wires spiral to the right and the strands to the left. This type of lay is easy to handle but wears out quickly because the crown wires are in contact with the bearing surface.
In the Lang, or Albert, lay, the wires and strands spiral in the same direction with right hand lay being the most common. The wires in a Lang lay appear to run parallel to the center line of the rope. The difficulty with Lang lay wire ropes is handling since they tend to kink, twist, and crush.
Wire rope is an exceptionally strong tool that has been configured and designed to withstand the stress placed upon it through rigorous and continual use. In most applications, wire rope has to endure extreme stress and strain. It is for these reasons that coatings have been developed to protect wire rope from abrasions, corrosion, UV rays, and harmful and damaging chemicals.
Three main types of coatings are used to protect wire rope: polyvinyl chloride (PVC), polypropylene, and nylon. Of the three types, PVC is the most popular.
In cases where there are severe and hazardous working conditions, polypropylene is the recommended choice since it is capable of protecting wire rope against corrosion and chemical leaching. Additionally, it is resistant to impact damage and abrasion. Polypropylene is a tough, rigid, and crystalline thermoplastic that is made from a propene monomer and is resilient as well as inexpensive.
Braided wires are electrical conductors made up of small wires that are braided together to form a round tubular braid. The braiding and configuration of braided wire makes them very sturdy such that they do not break when flexed or bent. Braided wires are widely used as conductors, are commonly made from copper due to copper"s exceptional conductivity, and can be bare or coated depending on the application.
Braided wire can be round and tubular or flat. Round tubular braids fit in most spaces where flat braided wire will not. Flat braided wire begins as round braided wire which is flattened on a capstan. They are exceptionally strong and designed for medical and aircraft applications.
Metals used to make wire rope are various grades of stainless steel, bright steel, and galvanized steel. Though the majority of wire rope manufacturers use these three metals, other metals such as copper, aluminum, bronze, and monel are also used on a limited basis.
The most important aspect of wire rope is the wire and the metal from which it is made. The strength and resilience of wire rope is highly dependent on the quality of metal used to make it, and these are essential factors to be considered when purchasing it.
Bright steel wire does not have a coating and is rotation resistant, (designed to not rotate when lifting a load). It is drawn from hot rolled rods that are put through a die to match its specific dimensional tolerances, mechanical properties, and finish. Bright wire is used as a single line in conditions that require a rope that will resist cabling.
Galvanized steel has a zinc coating for corrosion resistance and has the same strength and durability as bright steel. Environmental conditions determine the use of galvanized steel. In mildly severe and slightly harsh conditions, galvanized steel wire is an economical replacement for stainless steel.
In the manufacturing process, galvanized wire goes through the process of galvanization, a method of coating steel wire with a protective and rust resistant metal. Galvanized wire is exceptionally strong, rust resistant, and flexible enough to meet the needs of a variety of applications.
Wire rope made from copper is mostly used for electrical applications due to its exceptional electrical characteristics. The benefits of copper wire rope are its durability, flexibility, and resilience compared to standard copper wire. The strength of copper wire rope is seen in its use in applications where there are vibrations and shaking.
The wire rope lubrication process begins during its fabrication and continues during its use. Lubrication of wire rope is designed to lower the amount of friction it endures and provide corrosion protection. Continued lubrication increases the lifespan of wire rope by preventing it from drying up, rusting, and breaking.
The types of lubricants for wire rope are penetrating or coating with coatings covering and sealing the outside of the rope. Penetrating lubricants go deep into the rope and seep into the core where they evaporate to form a thick coating or film.
The application of the lubricant is dependent on the type of core. Fiber cores absorb the lubricant and serve as a reservoir that retains the lubricant for an extended period of time. With metal cores, the lubricant is applied as the wire is twisted into strands to give complete saturation and coverage of the wires.
There are several types of greases that are used as wire rope lubricating agents and are made up of oil, a thickener, and additives. The essential components are the base oil and additives, which influence the behavior of the grease. The thickener holds the base oil and additives together. The amount of base oil in a grease is between 70% and 95% with an additive of 10%.
The additive in grease enhances the positive properties of the oil and suppresses the negative properties. Common additives are oxidation and rust inhibitors as well as pressure, wear, and friction reducing agents.
Of the many choices for lubricants, vegetable oil is the easiest to use and penetrates the deepest. The design of the additives for vegetable oils gives them the necessary qualities required to penetrate deep into a wire rope. The exceptional penetration provides protection against wear and corrosion. Since vegetable oil is a fluid, it helps in washing the wire rope to remove external abrasive contaminants.
Wire rope is widely used in machines, structures, and varied lifting applications. Its type, size, and requirements are determined by how it will be used. Regardless of its use, wire rope guarantees exceptional strength and provides high quality and excellent performance.
The lifting of heavy loads for centuries involved the use of hemp rope or chains, neither of which was a guaranteed or substantial method. Early in the 18th Century, between 1824 and 1838, Wilhelm Albert, a German mining engineer, combined the twisting of hemp and strength of chains to create today‘s wire rope.
The most common use of wire rope is as a part of a crane hoist wherein it is attached to the hook of the hoist and wrapped around a grooved drum. The tensile strength and durability of wire rope makes an ideal tool for lifting and keeping loads secure. Though it is used in several industries, it is very popular for production environments wherein materials need to be lifted quickly and efficiently.
In addition to its many lifting applications, the strength and stability of wire rope is useful in other applications, especially in the aerospace industry. Pedals, levers, and connectors in the cockpit of an aircraft are connected with wire rope. The wires provide for the passage of power between systems and mechanisms; this allows control of the aircraft. Wire rope is used to control propeller pitch, cowl flaps, and the throttle. It also assists in lowering and minimizing vibrations.
Tires are reinforced with wire rope to increase their durability and strength. All automotive production environments make use of wire ropes for supplying materials, moving heaving loads, and positioning equipment. Wire rope can be found in the production of steering wheels, cables, exhausts, springs, sunroofs, doors, and seating components.
As surprising as it may seem, the place that wire rope has the greatest use is in the home, where its strength, long life, endurance, and resilience provide guaranteed protection and performance. The main reason wire ropes are so popular for home use is cost.
Inexpensive, easy to obtain, easy to install, and easy to maintain, wire ropes provide an additional method for performing home repairs and structural support. Their excellent flexibility and sturdiness combined with their invisibility has made wire rope an ideal solution to several home maintenance issues. It is used to support staircases, fences, decks, and hang plants.
The search and production of crude oil has relied on wire ropes for centuries to lift drill bits, insert shafts, and support oil rigs on land and the water. When equipment, machinery, and tools have to be lowered into the depths of the earth and sea, wire ropes are the tool that the oil industry relies on to do the job.
Many of the tasks of oil production require tools that are capable of enduring severe and harsh conditions. Wire ropes have to withstand enormous pressure, extraordinary stress, and a wide range of temperatures. The use of wire rope includes maintaining oil rig stability and moorings for offshore rigs.
Wire rope has long been a standard component for the transportation industry, from the cable cars of San Francisco to the lift chairs for ski resorts. For many years, cable cars have relied on heavy duty cables (wire ropes) to be pulled by a central motor from multiple locations. It is a method of transportation that has existed for centuries.
In Europe, funiculars use cables that hang from a support to move cars up and down a mountain with cables moving in opposite directions. The word funicular is from the French word funiculaire, meaning railway by cable. The terms wire rope and cable are used interchangeably when discussed by professionals. The first part of funicular, or funiculaire, is from the Latin word "funis," meaning rope.
The major use for wire ropes in the food and beverage industries is as a means for lifting and moving heavy loads. Wine barrels and containers full of ingredients are lifted and placed through use of cranes and wire ropes. They are also part of conveyor systems that move products from one station to another.
From the beginnings of amusement rides up to the present, wire ropes have been an essential part of attraction construction and safety. They pull cars on roller coasters, hold cabins that swing, and move carriages through haunted houses. The main concern of amusement parks is safety. The strength, stability, and guaranteed performance of wire ropes ensures that people who attend amusement parks will have a good time and stay safe.
The rigging used to complete the stunts in modern movies depends on wire rope for safety. Much like in amusement rides, wire ropes protect performers from injury and harm as they hang above a scene or carry out an impossible move.
The live theater industry uses wire ropes to raise and lower curtains, support overhead rigging, and hold backdrops and scenery pieces. During a production, rapid and efficient movement is a necessity that is facilitated by the use of wire ropes.
Wire rope is a tool that we tend to envision as indestructible, unable to succumb to any form of damage. Though it is exceptionally sturdy and strong as well as capable of enduring constant use, it is just as susceptible to breakdown as any other tool.
To avoid serious harm and damage, wire ropes should be scheduled for regular inspections. There are situations that can damage or break a wire rope; these should be understood prior to the problem arising.
Guide rollers have the potential to damage and cause abrasions on wire rope if they become rough and uneven. Of the various elements of a crane and lift, guide rollers have the greatest contact with the mechanism‘s wire rope. Regular inspection of guide rollers will ensure they are not damaging the rope or causing abrasions.
Bending is normally a regular part of wire rope usage; this occurs repetitively as the rope passes through a sheave. As a wire rope traverses the sheave, it is continually bent and develops cracks or breaks. The cracking and breaking are exacerbated by movement on and off the groove of the drum. Normally, the breakage happens on the surface and is visible. Once it appears, it accelerates to the core of the rope.
A bird cage is caused by a sudden release of tension and a rebound of the rope. This type of break requires that the rope be replaced since the place of the break will not return to its normal condition.
Wire ropes are multi-layered; this makes them flexible and torque balanced. The layering inside and outside creates flexibility and wear resistance. Relative motion between the wires causes wear over time, which leads to internal breakage. The detection of these breaks can be indicated by an electromagnetic inspection that calculates the diameter of the rope.
Kinked wire rope is caused by pulling a loop on a slack line during installation or operation; this causes a distortion in the strands and wires. This is a serious condition that necessitates rope replacement.
Corrosion damage is the most difficult cause of wire rope damage to identify, which makes it the most dangerous. The main reason for corrosion is poor lubrication that can be seen in the pitted surface of the rope.
The types of damage and problems listed here are only a small portion of the problems that can be caused if a wire rope is not regularly lubricated and inspected. Various regulatory agencies require that wire ropes be inspected weekly or monthly and provide a list of factors to examine.
As with any type of heavy duty equipment, wire rope is required to adhere to a set of regulations or standards that monitor and control its use for safety and quality reasons. The two organizations that provide guidelines for wire rope use are the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) and the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA).
All wire rope manufacturers and users closely follow the standards and guidelines established by OSHA and ASME. In the majority of cases, they will identify the specific standards they are following in regard to their products.
OSHA‘s regulations regarding wire rope fall under sections 1910, 1915, and 1926, with the majority of the stipulations listed in 1926 under material handling, storage, use, and disposal.
"Running rope in service shall be visually inspected daily, unless a qualified person determines it should be performed more frequently. The visual inspection shall consist of observation of all rope that can reasonably be expected to be in use during the day‘s operations. The inspector should focus on discovering gross damage that may be an immediate hazard."
"The inspection frequency shall be based on such factors as rope life on the particular installation or similar installations, severity of environment, percentage of capacity lifts, frequency rates of operation, and exposure to shock loads. Inspections need not be at equal calendar intervals and should be more frequent as the rope approaches the end of its useful life. Close visual inspection of the entire rope length shall be made to evaluate inspection and removal criteria."
ASTM A1023 covers the requirements for steel wire ropes with specifications for various grades and constructions from ¼ in. (6 mm) to 31/2 in. (89 mm) manufactured from uncoated or metallic coated wire. Included are cord products from 1/32 in. (0.8 mm) to 3/8 in. (10 mm) made from metallic coated wire.
United States Federal Spec RR W 410 covers wire ropes and wire seizing strands but does not include all types, classes, constructions, and sizes of wire rope and strands that are available. The purpose of Spec RR W 410 is to cover more common types, classes, constructions, and sizes suitable for federal government use.
Wire rope and wire seizing strand covered by United States Federal Spec RR W 410 are intended for use in general hauling, hoisting, lifting, transporting, well drilling, in passenger and freight elevators, and for marine mooring, towing, trawling, and similar work, none of which are for use with aircraft.
API 9A lists the minimum standards required for use of wire rope for the petroleum and natural gas industries. The types of applications include tubing lines, rod hanger lines, sand lines, cable-tool drilling and clean out lines, cable tool casing lines, rotary drilling lines, winch lines, horse head pumping unit lines, torpedo lines, mast-raising lines, guideline tensioner lines, riser tensioner lines, and mooring and anchor lines. Well serving wire ropes such as lifting slings and well measuring are also included in API 9A.
Wire rope is a collection of metal strands that have been twisted and wound to form the shape of a helix with the purpose of supporting and lifting heavy loads and performing tasks that are too rigorous for standard wire.
Individual designs of wire rope involve different materials, wire, and strand configurations as a means for supporting and assisting in the completion of a lifting or supportive task.
Rope diameter is specified by the user and is generally given in the equipment manufacturer’s instruction manual accompanying the machine on which the rope is to be used.
Rope diameters are determined by measuring the circle that just touches the extreme outer limits of the strands— that is, the greatest dimension that can be measured with a pair of parallel-jawed calipers or machinist’s caliper square. A mistake could be made by measuring the smaller dimension.
The right way to unreel.To unreel wire rope from a heavy reel, place a shaft through the center and jack up the reel far enough to clear the floor and revolve easily. One person holds the end of the rope and walks a straight line away from the reel, taking the wire rope off the top of the reel. A second person regulates the speed of the turning reel by holding a wood block against the flange as a brake, taking care to keep slack from developing on the reel, as this can easily cause a kink in the rope. Lightweight reels can be properly unreeled using a vertical shaft; the same care should be taken to keep the rope taut.
The wrong way to unreel.If a reel of wire rope is laid on its flange with its axis vertical to the floor and the rope unreeled by throwing off the turns, spirals will occur and kinks are likely to form in the rope. Wire rope always should be handled in a way that neither twists nor unlays it. If handled in a careless manner, reverse bends and kinks can easily occur.
The right way to uncoil.There is only one correct way to uncoil wire rope. One person must hold the end of the rope while a second person rolls the coil along the floor, backing away. The rope is allowed to uncoil naturally with the lay, without spiraling or twisting. Always uncoil wire rope as shown.
The wrong way to uncoil.If a coil of wire rope is laid flat on the floor and uncoiled by pulling it straight off, spirals will occur and kinking is likely. Torsions are put into the rope by every loop that is pulled off, and the rope becomes twisted and unmanageable. Also, wire rope cannot be uncoiled like hemp rope. Pulling one end through the middle of the coil will only result in kinking.
Great stress has been placed on the care that should be taken to avoid kinks in wire rope. Kinks are places where the rope has been unintentionally bent to a permanent set. This happens where loops are pulled through by tension on the rope until the diameter of the loop is only a few inches. They also are caused by bending a rope around a sheave having too severe a radius. Wires in the strands at the kink are permanently damagedand will not give normal service, even after apparent “re-straightening.”
When wire rope is wound onto a sheave or drum, it should bend in the manner in which it was originally wound. This will avoid causing a reverse bend in the rope. Always wind wire rope from the top of the one reel onto the top of the other.Also acceptable, but less so, is re-reeling from the bottom of one reel to the bottom of another. Re-reeling also may be done with reels having their shafts vertical, but extreme care must be taken to ensure that the rope always remains taut. It should never be allowed to drop below the lower flange of the reel. A reel resting on the floor with its axis horizontal may also be rolled along the floor to unreel the rope.
Wire rope should be attached at the correct location on a flat or smooth-faced drum, so that the rope will spool evenly, with the turns lying snugly against each other in even layers. If wire rope is wound on a smooth-face drum in the wrong direction, the turns in the first layer of rope will tend to spread apart on the drum. This results in the second layer of rope wedging between the open coils, crushing and flattening the rope as successive layers are spooled.
A simple method of determining how a wire rope should be started on a drum. The observer stands behind the drum, with the rope coming towards him. Using the right hand for right-lay wire rope, and the left hand for left lay wire rope, the clenched fist denotes the drum, the extended index finger the oncoming rope.
Clips are usually spaced about six wire rope diameters apart to give adequate holding power. They should be tightened before the rope is placed under tension. After the load is placed on the rope, tighten the clips again to take care of any lessening in rope diameter caused by tension of the load. A wire rope thimble should be used in the eye of the loop to prevent kinking.
U-bolt Clips.There is only one correct method for attaching U-bolt clips to wire rope ends, as shown in TheRightWayimage below. The base of the clip bears on the live end of the rope; the “U” of the bolt bears on the dead end.
Compare this with the incorrect methods. Five of the six clips shown are incorrectly attached—only the center clip in the top view is correct. When the “U” of the clip bears on the live end of the rope, there is a possibility of the rope being cut or kinked, with subsequent failure.
Proper seizing and cutting operations are not difficult to perform, and they ensure that the wire rope will meet the user’s performance expectations. Proper seizings must be applied on both sides of the place where the cut is to be made. In a wire rope, carelessly or inadequately seized ends may become distorted and flattened, and the strands may loosen. Subsequently, when the rope is operated, there may be an uneven distribution of loads to the strands; a condition that will significantly shorten the life of the rope.
Either of the following seizing methods is acceptable. Method No. 1 is usually used on wire ropes over one inch in diameter. Method No. 2 applies to ropes one inch and under.
Method No. 1: Place one end of the seizing wire in the valley between two strands. Then turn its long end at right angles to the rope and closely and tightly wind the wire back over itself and the rope until the proper length of seizing has been applied. Twist the two ends of the wire together, and by alternately pulling and twisting, draw the seizing tight.
The Seizing Wire. The seizing wire should be soft or annealed wire or strand. Seizing wire diameter and the length of the seize will depend on the diameter of the wire rope. The length of the seizing should never be less than the diameter of the rope being seized.
Proper end seizing while cutting and installing, particularly on rotation-resistant ropes, is critical. Failure to adhere to simple precautionary measures may cause core slippage and loose strands, resulting in serious rope damage. Refer to the table below ("Suggested Seizing Wire Diameters") for established guidelines. If core protrusion occurs beyond the outer strands, or core retraction within the outer strands, cut the rope flush to allow for proper seizing of both the core and outer strands.
The majority of wire rope problems occurring during operation actually begin during installation, when the rope is at its greatest risk of being damaged. Proper installation procedures are vital in the protection and performance of wire rope products.
Until the rope is installed it should be stored on a rack, pallet or reel stand in a dry, well-ventilated storage shed or building. Tightly sealed and unheated structures should be avoided as condensation between rope strands may occur and cause corrosion problems. If site conditions demand outside storage, cover the rope with waterproof material and place the reel or coil on a support platform to keep it from coming directly in contact with the ground.
While lubrication is applied during the manufacturing process, the wire rope must still be protected by additional lubrication once it is installed. Lubricants will dry out over a period of time and corrosion from the elements will occur unless measures are taken to prevent this from happening. When the machine becomes idle for a period of time, apply a protective coating of lubricant to the wire rope. Moisture (dew, rain, and snow) trapped between strands and wires will create corrosion if the rope is unprotected. Also apply lubricant to each layer of wire rope on a drum because moisture trapped between layers will increase the likelihood of corrosion.
Always use the nominal diameter as specified by the equipment manufacturer. Using a smaller diameter rope will cause increased stresses on the rope and the probability of a critical failure is increased if the rated breaking strength does not match that of the specified diameter. Using a larger diameter rope leads to shorter service life as the rope is pinched in the sheave and drum grooves which were originally designed for a smaller diameter rope. Just as using a different diameter rope can create performance problems, so can the use of an excessively undersized or oversized rope.
Measure the wire rope using a parallel-jawed caliper as discussed in Measuring Rope Diameter at the top of this page. If the rope is the wrong size or outside the recommended tolerance, return the rope to the wire rope supplier. It is never recommended nor permitted by federal standards to operate cranes with the incorrect rope diameter. Doing so will affect the safety factor or reduce service life and damage the sheaves and drum. Note that in a grooved drum application, the pitch of the groove may be designed for the rope’s nominal diameter and not the actual diameter as permitted by federal standards.
Wire rope can be permanently damaged by improper unreeling or uncoiling practices. The majority of wire rope performance problems start here.Improper unreeling practices lead to premature rope replacement, hoisting problems and rope failure.
Place the payout reel as far away from the boom tip as is practical, moving away from the crane chassis. Never place the payout reel closer to the crane chassis than the boom point sheave. Doing so may introduce a reverse bend into the rope and cause spooling problems. Follow the guidelines highlighted under Unreeling and Uncoiling and Drum Winding. Take care to determine whether the wire rope will wind over or under the drum before proceeding. If the wire rope supplier secured the end of the rope to the reel by driving a nail through the strands, ask that in the future a U-bolt or other nondestructive tie-down method be used; nails used in this manner damage the rope.
Take extra precaution when installing lang lay, rotation-resistant, flattened strand or compacted ropes. Loss of twist must be avoided to prevent the strands from becoming loosened, causing looped wire problems.
The end of the rope must be securely and evenly attached to the drum anchorage point by the method recommended by the equipment manufacturer. Depending on the crane’s regulatory requirements, at least two to three wraps must remain on the drum as dead wraps when the rope is unwound during normal operations. Locate the dead end rope anchorage point on the drum in relation to the direction of the lay of the rope. Do not use an anchorage point that does not correspond with the rope lay. Mismatching rope lay and anchorage point will cause the wraps to spread apart from each other and allow the rope to cross over on the drum. Very gappy winding will occur resulting in crushing damage in multilayer applications.
Back tension must be continually applied to the payout reel and the crewman installing the rope must proceed at a slow and steady pace whether the drum is smooth or grooved.Regardless of the benefits of a grooved drum, tension must be applied to ensure proper spooling. An improperly installed rope on a grooved drum will wear just as quickly as an improperly installed rope on a smooth drum. If a wire rope is poorly wound and as a result jumps the grooves, it will be crushed and cut under operating load conditions where it crosses the grooves.
Every wrap on the first or foundation layer must be installed very tightly and be without gaps. Careless winding results in poor spooling and will eventually lead to short service life. The following layers of rope must lay in the grooves formed between adjacent turns of the preceding layer of rope. If any type of overwind or cross-winding occurs at this stage of installation and is not corrected immediately, poor spooling and crushing damage will occur.
On a multilayer spooling drum be sure that the last layer remains at least two rope diameters below the drum flange top. Do not use a longer length than is required because the excess wire rope will cause unnecessary crushing and may jump the flange. Loose wraps that occur at any time must be corrected immediately to prevent catastrophic rope failure.
The use of a mallet is acceptable to ensure tight wraps, however a steel-faced mallet should be covered with plastic or rubber to prevent damage to the rope wires and strands.
Rotation-resistant ropes of all constructions require extra care in handling to prevent rope damage during installation. The lay length of a rotation-resistant rope must not be disturbed during the various stages of installation. By introducing twist or torque into the rope, core slippage may occur—the outer strands become shorter in length, the core slips and protrudes from the rope. In this condition the outer strands become over- loaded because the core is no longer taking its designed share of the load. Conversely, when torque is removed from a rotation-resistant rope core slippage can also occur. The outer strands become longer and the inner layers or core become overloaded, reducing service life and causing rope failure.
The plain end of a wire rope must be properly secured. If the entire cross section of the rope is not firmly secured, core slippage may occur, causing the core to pull inside the rope’s end and allowing it to protrude elsewhere, either through the outer strands (popped core) or out the other end of the line. The outer layer of the outside strands may also become overloaded as there is no complete core-to-strand support.
Secure the ends of the rope with either seizing or welding methods as recommended under Seizing Wire Rope. It is imperative that the ends be held together tightly and uniformly throughout the entire installation procedure, including attaching the end through the wedge socket and the drum dead end wedge
When installing a new line, connect the old line to the new line by using a swivel-equipped cable snake or Chinese finger securely attached to the rope ends. The connection between the ropes during change-out must be very strong and prevent torque from the old rope being transferred into the new rope.Welding ropes together or using a cable snake without the benefit of a swivel increases the likelihood of introducing torque into the new rope. A swivel-equipped cable snake is not as easy as welding the ropes, but this procedure can be mastered with a little patience and practice.

Wire rope forms an important part of many machines and structures. It is comprised of continuous wire strands wound around a central core. There are many kinds of wire rope designed for different applications. Most of them are steel wires made into strands wound with each other. The core can be made of steel, rope or even plastics.
Wire ropes (cables) are identified by several parameters including size, grade of steel used, whether or not it is preformed, by its lay, the number of strands and the number of wires in each strand.
A typical strand and wire designation is 6x19. This denotes a rope made up of six strands with 19 wires in each strand. Different strand sizes and arrangements allow for varying degrees of rope flexibility and resistance to crushing and abrasion. Small wires are better suited to being bent sharply over small sheaves (pulleys). Large outer wires are preferred when the cable will be rubbed or dragged through abrasives.
There are three types of cores. An independent wire rope core (IWRC) is normally a 6x7 wire rope with a 1x7 wire strand core resulting in a 7x7 wire rope. IWRCs have a higher tensile and bending breaking strength than a fiber core rope and a high resistance to crushing and deformation.
A wire strand core (WSC) rope has a single wire strand as its core instead of a multistrand wire rope core. WSC ropes are high strength and are mostly used as static or standing ropes.
Wire ropes also have fiber cores. Fiber core ropes were traditionally made with sisal rope, but may also use plastic materials. The fiber core ropes have less strength than steel core ropes. Fiber core ropes are quite flexible and are used in many overhead crane applications.
The lay of a wire rope is the direction that the wire strands and the strands in the cable twist. There are four common lays: right lay, left lay, regular lay and lang lay. In a right lay rope the strands twist to the right as it winds away from the observer. A left lay twists to the left. A regular lay rope has the wires in the strands twisted in the opposite direction from the strands of the cable. In a lang lay rope, the twist of the strands and the wires in the strands are both twisted the same way. Lang lay ropes are said to have better fatigue resistance due to the flatter exposure of the wires.
Wire ropes are made mostly from high carbon steel for strength, versatility, resilience and availability and for cost consideration. Wire ropes can be uncoated or galvanized. Several grades of steel are used and are described in Table 1.
Steel cable wire is stiff and springy. In nonpreformed rope construction, broken or cut wires will straighten and stick out of the rope as a burr, posing a safety hazard. A preformed cable is made of wires that are shaped so that they lie naturally in their position in the strand, preventing the wires from protruding and potentially causing injury. Preformed wire ropes also have better fatigue resistance than nonpreformed ropes and are ideal for working over small sheaves and around sharp angles.
Lubricating wire ropes is a difficult proposition, regardless of the construction and composition. Ropes with fiber cores are somewhat easier to lubricate than those made exclusively from steel materials. For this reason, it is important to carefully consider the issue of field relubrication when selecting rope for an application.
There are two types of wire rope lubricants, penetrating and coating. Penetrating lubricants contain a petroleum solvent that carries the lubricant into the core of the wire rope then evaporates, leaving behind a heavy lubricating film to protect and lubricate each strand (Figure 2). Coating lubricants penetrate slightly, sealing the outside of the cable from moisture and reducing wear and fretting corrosion from contact with external bodies.
Both types of wire rope lubricants are used. But because most wire ropes fail from the inside, it is important to make sure that the center core receives sufficient lubricant. A combination approach in which a penetrating lubricant is used to saturate the core, followed with a coating to seal and protect the outer surface, is recommended. Wire rope lubricants can be petrolatum, asphaltic, grease, petroleum oils or vegetable oil-based (Figure 3).
Petrolatum compounds, with the proper additives, provide excellent corrosion and water resistance. In addition, petrolatum compounds are translucent, allowing the technician to perform visible inspection. Petrolatum lubricants can drip off at higher temperatures but maintain their consistency well under cold temperature conditions.
Various types of greases are used for wire rope lubrication. These are the coating types that penetrate partially but usually do not saturate the rope core. Common grease thickeners include sodium, lithium, lithium complex and aluminum complex soaps. Greases used for this application generally have a soft semifluid consistency. They coat and achieve partial penetration if applied with pressure lubricators.
Petroleum and vegetable oils penetrate best and are the easiest to apply because proper additive design of these penetrating types gives them excellent wear and corrosion resistance. The fluid property of oil type lubricants helps to wash the rope to remove abrasive external contaminants.
Wire ropes are lubricated during the manufacturing process. If the rope has a fiber core center, the fiber will be lubricated with a mineral oil or petrolatum type lubricant. The core will absorb the lubricant and function as a reservoir for prolonged lubrication while in service.
If the rope has a steel core, the lubricant (both oil and grease type) is pumped in a stream just ahead of the die that twists the wires into a strand. This allows complete coverage of all wires.
After the cable is put into service, relubrication is required due to loss of the original lubricant from loading, bending and stretching of the cable. The fiber core cables dry out over time due to heat from evaporation, and often absorb moisture. Field relubrication is necessary to minimize corrosion, protect and preserve the rope core and wires, and thus extend the service life of the wire rope.
If a cable is dirty or has accumulated layers of hardened lubricant or other contaminants, it must be cleaned with a wire brush and petroleum solvent, compressed air or steam cleaner before relubrication. The wire rope must then be dried and lubricated immediately to prevent rusting. Field lubricants can be applied by spray, brush, dip, drip or pressure boot. Lubricants are best applied at a drum or sheave where the rope strands have a tendency to separate slightly due to bending to facilitate maximum penetration to the core. If a pressure boot application is used, the lubricant is applied to the rope under slight tension in a straight condition. Excessive lubricant application should be avoided to prevent safety hazards.
Some key performance attributes to look for in a wire rope lubricant are wear resistance and corrosion prevention. Some useful performance benchmarks include high four-ball EP test values, such as a weld point (ASTM D2783) of above 350 kg and a load wear index of above 50. For corrosion protection, look for wire rope lubricants with salt spray (ASTM B117) resistance values above 60 hours and humidity cabinet (ASTM D1748) values of more than 60 days. Most manufacturers provide this type of data on product data sheets.
Cable life cycle and performance are influenced by several factors, including type of operation, care and environment. Cables can be damaged by worn sheaves, improper winding and splicing practices, and improper storage. High stress loading, shock loading, jerking heavy loads or rapid acceleration or deceleration (speed of the cable stopping and starting) will accelerate the wear rate.
Corrosion can cause shortened rope life due to metal loss, pitting and stress risers from pitting. If a machine is to be shut down for an extended period, the cables should be removed, cleaned, lubricated and properly stored. In service, corrosion and oxidation are caused by fumes, acids, salt brines, sulfur, gases, salt air, humidity and are accelerated by elevated temperatures. Proper and adequate lubricant application in the field can reduce corrosive attack of the cable.
Abrasive wear occurs on the inside and outside of wire ropes. Individual strands inside the rope move and rub against one another during normal operation, creating internal two-body abrasive wear. The outside of the cable accumulates dirt and contaminants from sheaves and drums. This causes three-body abrasive wear, which erodes the outer wires and strands. Abrasive wear usually reduces rope diameter and can result in core failure and internal wire breakage. Penetrating wire rope lubricants reduce abrasive wear inside the rope and also wash off the external surfaces to remove contaminants and dirt.
Many types of machines and structures use wire ropes, including draglines, cranes, elevators, shovels, drilling rigs, suspension bridges and cable-stayed towers. Each application has specific needs for the type and size of wire rope required. All wire ropes, regardless of the application, will perform at a higher level, last longer and provide greater user benefits when properly maintained.
Lubrication Engineers, Inc. has found through years of field experience, that longer wire rope life can be obtained through the use of penetrating lubricants, either alone or when used in conjunction with a coating lubricant. Practical experience at a South African mine suggests that life cycles may be doubled with this approach. At one mine site, the replacement rate for four 44-mm ropes was extended from an average 18.5 months to 43 months. At another mine, life cycles of four 43-mm x 2073 meter ropes were extended from an average 8 months to 12 months.
In another study involving 5-ton and 10-ton overhead cranes in the United States that used 3/8-inch and 5/8-inch diameter ropes, the average life of the ropes was doubled. The authors attribute this increased performance to the ability of the penetrating lubricant to displace water and contaminants while replacing them with oil, which reduces the wear and corrosion occurring throughout the rope. A good spray with penetrating wire rope lubricant effectively acts as an oil change for wire ropes.
In these examples, the savings in wire rope replacement costs (downtime, labor and capital costs) were substantial and dwarfed the cost of the lubricants. Companies who have realized the importance of proper wire rope lubrication have gained a huge advantage over those who purchase the lowest priced lubricant, or no lubricant at all, while replacing ropes on a much more frequent basis.




 8613371530291
8613371530291