wire rope failure modes supplier

In 1998, a crane load line broke while lifting the south topside module of the Petronius platform, dropping the module into the Gulf of Mexico. The cost was estimated to be around 116 million US dollars. Since 1999 more than 60 people have been killed as a result of wire ropes breaking and more than 65 associated injuries.
Not many people appreciate that there are literally thousands of wire rope designs, most of which can be put into a specific category. According to BS ISO 4309 2010 there are currently more than 25 categories of crane wire rope, each with differing characteristics and also different discard criteria. Deterioration can be measured, counted or calculated and the wire rope eventually taken out of service based on sophisticated discard criteria published in chosen standards, codes of practice or users handbooks.
Unfortunately there is no simple answer to either of these questions. All wire ropes will eventually break due to corrosion, wear or fatigue even if they are maintained and used properly. Unpredictable wire rope failures will inevitably occur, quite often when you least expect it if the discard criteria is ignored, or those using the equipment are ignorant of it.
James Dawes of Topeka, Illinois, was killed in 2008 after being struck by the boom of a Link-Belt crane; the accident was caused by the boom hoist wire rope breaking. The crane rope had been inspected, but a report said that the inspector failed to reject the rope showing a high number of visible wire breaks. Premature or unexpected wire rope failures can also be attributed to poor manufacture, incorrect handling and storage, poor installation technique, poor selection or fitting of its termination, infrequent or inadequate inspection and poor maintenance. Of course there is always the possibility that mechanical damage can occur and this is usually attributed to human error.
It is necessary, particularly during offshore operations that frequent inspections are carried out over the whole length of the working part of all steel wire ropes. The frequency of inspections should be based on the severity of use and risk assessment and particular attention should be paid to the critical areas of the wire rope; areas that are frequently running over sheaves, compensating sheaves and the rope termination to name a few.
If a wire rope has not been subjected to an abnormal environmental condition such as excessive heat, chemical attack or any corrosive solution and it has not been the victim of any form of mechanical damage, then trained operatives and inspectors can reasonably predict the length of time the steel wire rope is likely to last. That prediction, of course, will be dependent on the knowledge and experience of those making it coupled with known facts about the rope, its current condition and the application it is running on. The Inspector should be aware of the previous rope’s history, capacities of loads and the reeving systems employed together with the frequency of use etc.
Various standards and codes of practice have been written by recognized bodies and institutes based on the experience of experts or representatives of corporate organizations who have a vested interest. These standards do offer guidance on when a wire rope should be removed from service based on wear, abrasion and fatigue amongst others things, but none of these standards have any legal status except when they are called up by contract. Indeed they can all be supported or overturned in a court of law by an expert.
The users handbook, or more importantly the safe use instructions do have legal status. In many parts of the world these days, suppliers of cranes or any machinery for that matter, issue safe use instructions with new equipment. Modern applications employ modern wire rope and, in some cases, sheaves and pulleys that are made with materials other than steel. Original equipment manufacturers of such applications may impose discard criteria for the wire rope that is stricter than those in chosen standards. By law the user must follow manufacturers’ instructions.
Wire ropes will deteriorate much more quickly if they go dry and are allowed to remain in that condition. Tests have proven that a dry rope will lose up to 60 % of its expected life if it is not re-lubricated. There are differing schools of thought as to how wire rope should be lubricated. Some believe that a thin lubricant should be applied using a paintbrush. It is thought that this method allows the lubricant to penetrate. Experience has proven however, that thin penetrative lubricants will easily drain away or fly off in hot climates.
Another school of thought, and the one I stand on, is that grease should be pressure lubricated into the rope. This method, if applied properly, will ensure that the grease penetrates the rope pushing out the old lubricant with it and any possible corrosive agents such as salt water and sand. Any lubricant that is used must be compatible with the type that was applied previously and it is a good idea to consider the environment as well.
In any event, wire ropes usually announce that they are about to break. A series of individual wire breaks can be heard. These are likely to go on over several seconds and continuing for up to ten minutes before ultimate failure. Therefore, if operatives understand the warning signals, expensive incidents could be avoided.
Figure 2 shows two pieces of the same rope, the bottom portion quite clearly shows a progression of wire breaks. The operator was able to put the load down before disaster struck. The root cause of this fault was core deterioration brought about by internal corrosion.
To answer the other question on accountability, the list is extensive. Usually the first suspect is the wire rope manufacturer and that may be where the problem lies, but very often that is not the case. What if you were supplied the wrong rope for the application? Maybe you ordered the wrong rope or your buyer bought it from a cheap unapproved manufacturing source.
Perhaps your supplier is responsible, maybe he provided you with a rope that was produced to the wrong specifications. Would you know the difference? Perhaps you were sold a rope that had been stored in the suppliers or manufactures stock for a number of years and, whilst it was there, it hadn’t been properly maintained. Maybe the rope had been badly handled or installed incorrectly. The list of possibilities is endless.
In 1999 a ropeway in the French Alps snapped causing 21 deaths. In 2003, a ropeway wire rope snapped and 7 people died and a further 42 were injured. In 2007 a crane wire rope snapped at New Delhi’s metro, the entire structure tumbled down crushing workers underneath, six people were killed and 13 more were injured. In 2009 26 people were killed and 5 people were injured when a rope failed in a mine and a further 6 people were injured when a lift rope broke inside London’s Tower Bridge.
If you find yourself in the unfortunate situation after the unthinkable premature failure of a wire rope, then you might like to know that there are independent analytical services capable of determining probable cause. One of these is Doncaster Analytical Services Ltd (DAS), they have an independent metallurgical laboratory providing factual analysis and testing of wire rope for any reason (contact Mr Shui Lee, Technical Director, Tel +44(0)1302 556063, email: shui.lee@doncasteranalyticalservices. com).
You do not need a wire rope to fail in order to learn. Careful analysis of discarded ropes can also give you valuable information about your application, the way it operates, and the rope you have been using.
Based on this information, a trained, skilled and experienced inspector will be able to advise on a better crane or wire rope design, or to an improvement in maintenance procedures and safety.
Unfortunately, many phone calls into ITI Field Services begins this way, “We have had an incident with a wire rope and we believe the rope failed. How do we determine the cause of failure?”
Fortunately, the calls come in because wire rope users want to determine cause of failure in an effort to improve their crane, rigging and lifting activities.
A wire rope distributor received a hoist rope and sockets from a rubber-tired gantry. The rope and sockets were returned by the customer who believed the rope and sockets failed. The distributor hired ITI Field Services to conduct an analysis on the rope and sockets to determine the cause of the failure and to produce written documentation.
Based on the findings of the examination, fatigue-type breaks in the wires indicated that the wire rope lost significant strength due to vibration. There was no indication that the rope was overloaded. The poured sockets showed no evidence of abnormalities in the pouring method, wire zinc bonding length or the materials used in the speltering process. The conclusion of the inspection is that rope failed due to fatigue.
Wire rope examination is just one of the many services that is offered by ITI Field Services. ITI has some of the most highly-regarded subject-matter experts in the crane and rigging industry with experience in performance evaluations, litigation, accident investigations, manual development and critical lift planning reviews.

Safety should be the top concern of anyone employed in rigging. When working a job where so many lives could be cut short due to carelessness, there is no excuse for laziness or distraction. Rigs should be inspected thoroughly for any potential areas of breakage. It is important for employees to gain a fluency in the causes of wire rope damage and failures so they can spot areas of weakness and fix them before they grow into a dangerous problem.
Corrosion issues in wire ropes are one of the most difficult causes of wire rope damage and failures to identify, which is why it is one of the most dangerous. Wire rope failures due to corrosion are typically the result of poor lubrication. You can measure some amount of the lubrication by looking at the pitted surface of every individual rope, but this tells us little of the damage done to the core. Since it is difficult to identify the full spectrum of corrosion, this break stands apart as mysterious and deadly.
Abrasion-caused failure occurs when the wire rope has been damaged by irregular contact with hoist sheaves and drums or when it awkwardly rubs against an object such as shelving or a crane girder. It is also often caused by poorly grooved drums and sheaves. You know the wire ropes have experienced abrasions when the wire ends are worn thin.
When hoist ropes go through repetitive bending over sheaves, cracks will eventually develop in the individual wires. Sections of the wire that move over the sheaves develop the worst fatigue. The damage can often be seen by the naked eye. Whenever one broken wire appears due to fatigue, more will follow. Since these issues are essentially the result of wear and tear on the rope wire, they are considered a normal part of operating a crane.
Being fluent in safety measures is just as valuable to an employer as competency with cable rigging hardware. People who know how to spot areas for potential failures can keep themselves and their coworkers secure, which saves time, money, and even lives.

Hoisting loads with a wire rope is a simple operation. Hook it up; lift it. Turns out, it’s more complicated than it appears. The details of setting up, inspecting, and maintaining lifts with wire ropes are not complicated, but are critical. A lift that goes awry is dangerous. A bad lift puts workers at risk. In this article, we discuss the causes of wire rope failure and how to avoid them.
Abrasion breaks are caused by external factors such as coming into contact with improperly grooved sheaves and drums. Or just hitting against some object during operation. Worn, broken wire ends is the result of an abrasion break. Common causes of abrasion breaks include:
Core slippage or protrusion is caused by shock load or improper installation of the wire rope. Excessive torque can cause core slippage that forces the outer strands to shorten. The core will then protrude from the rope. Wire ropes designed to be rotation-resistant should be handled carefully so as not to disturb its lay length.
Corrosion breaks cause pitting on the individual wires that comprise the rope. This type of damage is caused by poor lubrication. However, corrosion breaks are also caused by the wire rope coming into contact with corrosive chemicals, such as acid.
There are many ways the strands of a rope can be crushed or flattened. Improper installation is a common cause. To avoid crushing, you’ll want the first layer of the wire rope to be very tight. You’ll also need to properly break-in a new wire rope. Other causes of crushing include cross winding, using a rope of the wrong diameter, or one that it too long.
Cracks to individual wires are caused by fatigue breaks. Fatigue breaks happen because the wire rope is being bent over the sheave over and over again. In time, the constant rubbing of the wire rope against the sheave or drum causes these breaks. Sheaves that are too small will accelerate fatigue breaks because they require more bending. Worn bearings and misaligned sheaves can also cause fatigue. A certain number of broken wires is acceptable. The worker responsible for equipment inspection prior to use should know the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) standard for wire ropes. The ASME standard determines whether the wire rope must be replaced. (https://www.asme.org/)
Selecting the right wire rope for the job is critical. There is never a perfect rope. For example, you will need to make a tradeoff between fatigue resistance and abrasion resistance. There are several aspects to wire rope design to consider, including:
In general, the proper wire rope will have a strength rating high enough to handle the load. (Strength is rated in tons.) It can handle the stress of repeated bending as it passes over sheaves or around drums. How you attach the rope in preparation for the lift matters and should only be handled by properly trained workers.
The wire rope (and all the equipment involved in a lift) should be fully inspected prior to the lift. The worker performing the inspection should be well-versed in the types of damage that can cause a wire rope to fail. Using a checklist is highly recommended. This will ensure that the inspection is complete. Worker and supervisor signoff will increase accountability. Of course, the wire rope must be maintained according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
How a wire rope is stored, the weather conditions in which it is used, and how they are cleaned all affect its useful life. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) provides these recommendations: (Source: https://www.osha.gov/dsg/guidance/slings/wire.html)
Preventing wire rope failures starts with selecting the right one for the job. When in doubt, talk with your local equipment dealer. Be prepared to discuss your specific job requirements. A thorough inspection of the wire rope prior to using it is critical. Finally, properly store your wire rope. The selection, inspection, and care of wire rope is key to job safety.

Due to the wide variety of service conditions for wire ropes, they are susceptible to many types of inadequacies and failures. It is important for consumers to frequently inspect wire ropes for signs of wear and fatigue. Wire ropes will inevitably fail if not used according to manufacturing limitations or when routine inspections for fatigue and wear are not properly performed. Eventually, all wire ropes are removed from service when they meet established discard criteria.

To optimise the life of the rope and minimise the risk of failure, it needs to be carefully selected for its operating environment and must be appropriately maintained and regularly inspected. Thus, the Skuld P&I Club, in contribution with Graham Cooper, Hawkins & Associates, Singapore, has issued advisory on metal wire rope operations.
The correctly selected rope that has been appropriately operated and maintained, has not been damaged and has been regularly inspected should provide safe and trouble free service. However, it must be withdrawn from service before it becomes degraded to the point where its safety becomes compromised.
In order for the rope to work efficiently as part of a lifting or winching system, it needs to be of appropriate strength, construction and diameter. It’s very important that the rope not only has the required minimum braking strength, but is also of the correct size and construction. The diameter of the rope must be matched to the groove dimensions of the sheaves that it will be passing over and it must have appropriate flexibility, which is expressed in terms of its minimum bend radius, to suit the diameter of those sheaves.
As a rule of thumb, the greater the diameter of the rope, the greater it’s minimum bend radius. That means that a larger diameter rope cannot automatically be substituted for a smaller diameter rope, even though it may have a greater breaking strength, since its minimum bend radius may be greater than the radius of the sheaves over which it is required to operate. That will lead to over-bending of the rope, which will increase the fatigue loading on it, reducing its service life. Similarly, if the rope diameter is not correctly matched to the sheave groove dimensions, i.e. it is too large or too small, then the load on the rope will be concentrated at certain points on its circumference, rather than being spread evenly around its circumference. That will also increase the fatigue loading on the rope and so reduce its service life.
Fatigue causes individual wires to break one by one, usually over an extended period of service, rather than causing a sudden, catastrophic failure of the rope. As the number of broken wires increases, the residual strength of the rope is reduced so that it will eventually break under normal service loads. Fortunately, the tell-tale signs of fatigue damage are relatively easy to identify, since broken wires can often be seen with the naked eye or will protrude from the rope. Hence, any rope exhibiting broken or protruding wires should be treated as suspect and removed from service.
Wear and corrosion are both progressive degradation mechanisms that can be very damaging to metal wire ropes and are often the life-limiting factors. Both can be greatly reduced, but not eliminated entirely, by appropriate and regular lubrication of the rope. It is therefore very important that wire ropes are appropriately lubricated and checked on a regular basis, particularly where they are operating in arduous conditions, such as a marine environment. This is quite challenging as the method of lubrication must ensure that the interior of the rope is properly lubricated. Simple greasing of the surface is not adequate and methods such as pressurised grease application need to be used. If this is not done correctly, a rope can suffer significant internal wear, caused by the rubbing together of individual wires as the rope passes over sheaves, drums etc..
Visual assessment of the rope may indicate damage or degradation, such as wear or corrosion, in the outer layer. However, it won’t identify damage or degradation of the internal core. To evaluate the internal condition of the rope, it is necessary to use non-destructive testing techniques.
Any wire rope failure is a serious and potentially life threatening event. Fortunately, such failures are relatively rare, but if a failure does occur, it is important that it is investigated thoroughly to determine the cause and from that, identify what went wrong. To fully investigate a failure, it is necessary to gather as much information as possible at the time. That should include photographing the damage before anything is disturbed, interviewing witnesses and obtaining maintenance records etc.. The rope itself should then be examined by a specialist, which may include laboratory examination and testing, to determine the mode of failure. Once that cause of the failure has been established, it is important that lessons are learned from it and changes to working practices, maintenance procedures etc. are implemented to ensure that it does not happen again.

Wire rope manufacturers produce their products in order to provide a high load capacity, versatile alternative to weaker ropes like manila rope or hemp rope. Wire rope products are used for a wide variety of motion transmission applications, among them: lifting, baling, tie down, hoisting, hauling, towing, mooring, anchoring, rigging, cargo control, guidance and counterbalance. They can also be used as railing, fencing and guardrailing.
Wire rope is a must-have for many heavy duty industrial applications. From mining to forestry to marine and beyond, there’s wire rope for almost every job. Some of the many industries in which wire rope is popular include: construction, agriculture, marine, industrial manufacturing, fitness, sports and recreation (plastic coated cables for outdoor playground equipment and sports equipment), electronics, theater (black powder coated cables for stage rigging), mining, gas and oil, transportation, security, healthcare and consumer goods.
Wire rope as we know it was invented just under 200 years ago, between 1831 and 1834. At that time, the goal was to create a rope strong enough to support work in the mines of the Harz Mountains. Invented by Wilhelm Albert, a German mining engineer, this wire rope consisted on four three-stranded wires. It was much stronger than older rope varieties, such as manila rope, hemp rope and metal chain rope.
While studying at Freiburg School of Mines, a man named L.D.B. Gordon visited the mines in the Harz Mountains, where he met Albert. After he left, Gordon wrote to his friend Robert Stirling Newall, urging him to create a machine for manufacturing wire ropes. Newall, of Dundee, Scotland, did just that, designing a wire rope machine that made wire ropes with four strands, consisting of four wires each. After Gordon returned to Dundee, he and Newall, along with Charles Liddell, formed R.S. Newall and Company. In 1840, Newall received a patent for “certain improvements in wire rope and the machinery for making such rope.”
In 1841, an American manufacturer named John A. Roebling began producing wire rope for suspension bridges. Soon after, another set of Americans, Josiah White and Erskine Hazard, started incorporating wire rope into coal mining and railroad projects, forming Lehigh Coal & Navigation Company (LC&N Co.). In 1848, wire rope from their wire rope factory in Mauch Chunk, Pennsylvania provided the lift cables needed to complete the Ashley Planes Project. This project sought to improve the performance and appearance of the freight railroad that ran through Ashley, Pennsylvania, by adding lift cables. This increased tourism and increased the railroad’s coal capacity. Before, cars took almost four hours to return; after, they took less than 20 minutes.
Wire rope likewise changed the landscape (again) in Germany, in 1874, when an engineering firm called Adolf Bleichert & Co. used wire rope to build Bi-cable aerial tramways. These allowed them to mine the Ruhr Valley. Several years later, they also used wire rope to build tramways for the German Imperial Army and the Wehrmacht. These tramways were wildly successful, opening up roads in Germany and all over Europe and the USA.
Since the 1800s, manufacturers and engineers have found ways to improve wire rope, through stronger materials and material treatments, such as galvanization, and different rope configurations. Today, wire rope makes possible many heavy industrial processes. It has become a necessity of the modern world.
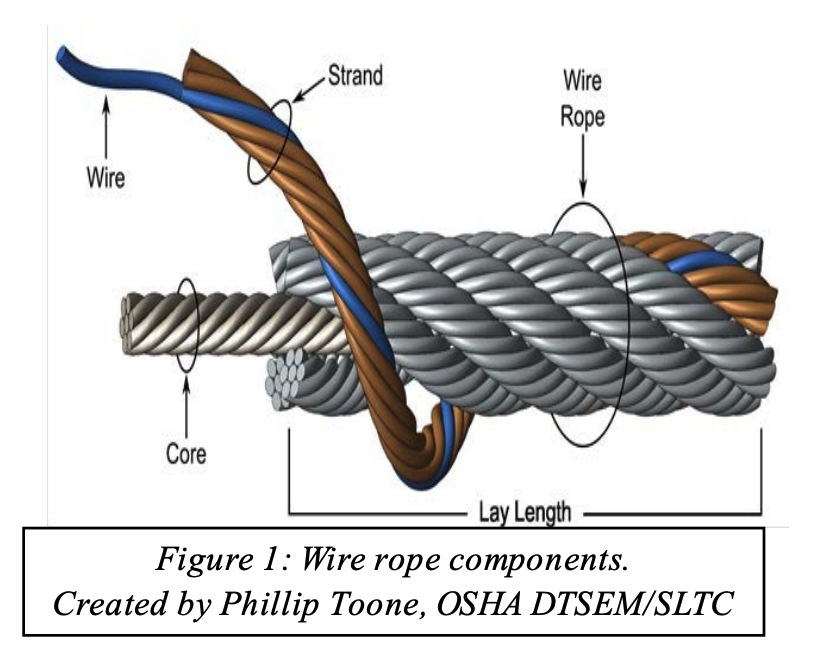
Strands are made by tightly twisting or braiding individual wire together. One strand could have anywhere between two and several dozen wire filaments depending on the necessary strength, flexibility, and weight capacity.
One of the most dynamic elements of wire cables is the inner core. The strands are wrapped around the core, and it can be made of different metals, fibers, or even impregnated fiber materials. For heavy applications, cores are often made of a different strand of wire called an independent wire rope core (IWRC). An IWRC has a considerable amount of flexibility and it is still very strong. In fact, at least 7.5% of the strength increase in a wire rope can be attributed to an IWRC.
While they sometimes use other metals, like aluminum, nickel, copper, titanium, and even bronze for some applications, manufacturers primarily produce wire rope from steel. This is because steel is very strong and stretchable. Among the most common types they use are: galvanized wire, bright wire, stainless steel and cold drawn steel.
Of the wire rope steels, cold drawn carbon steel wire is most popular, although stainless steel wire rope is sometimes employed as well. Stainless steel rope is most popular for its anti-corrosive properties. Bright wire rope, a type of ungalvanized steel wire rope, is also popular. For added strength and durability, galvanized steel wire rope/galvanized steel cables are a very popular choice. Galvanized aircraft cable, for example, is always a must in aerospace.
When choosing or designing a custom wire rope for your application, suppliers consider factors such as: the environment in which the rope will function, required rust resistance, required flexibility, temperature resistance, required breaking strength and wire rope diameter. To accommodate your needs, manufacturers can do special things like: make your rope rotation resistant, color code your rope, or add a corrosion resistant coating. For instance, sometimes they specially treat and coat a cable with plastic or some other compound for added protection. This is particularly important to prevent fraying if the wire rope is often in motion on a pulley.
Manufacturers and distributors identify the differences in wire cable by listing the number of strands and the amount of wires per strand so that anyone that orders understand the strength of the cable. Sometimes they are also categorized by their length or pitch. Common examples of this include: 6 x 19, 6 x 25, 19 x 7, 7 x 19, 7 x 7, 6 x 26 and 6 x 36.
More complex wire rope identification codes connote information like core type, weight limit and more. Any additional hardware like connectors, fasteners, pulleys and fittings are usually listed in the same area to show varying strengths and degrees of fray prevention.
Cable wire rope is a heavy-duty wire rope. To give it its high strength, manufacturers construct it using several individual filaments that are twisted in strands and helically wrapped around the core. A very common example of cable wire rope is steel cable.
Spiral rope is made up an assemblage of wires with round or curved strands. The assemblage features at least one outer layer cord pointed in the opposite direction of the wire. The big advantage of spiral ropes is the fact that they block moisture, water and pollutants from entering the interior of the rope.
Similarly, stranded rope steel wire is made up of an assemblage of spirally wound strands. Unlike spiral rope, though, its wire patterns have crisscrossing layers. These layers create an exceptionally strong rope. Stranded rope may have one of three core material types: wire rope, wire strand or fiber.
Wire rope chain, like all chains, is made up of a series of links. Because it is not solid, wire rope chain is quite flexible. At the same time, it is prone to mechanical failure.
Wire rope slings are made from improved plow wire steel, a strong steel wire that offers superior return loop slings and better security. The plow wire steel also shields rope at its connection points, which extends its working life. Wire rope slings, in general, provide their applications with increased safety, capacity and performance. Wire rope sling is a rope category that encompasses a wide range of sub-products, such as permaloc rope sling, permaloc bridle slings and endless slings. These and other wire rope slings may be accompanied by a wide variety of sling terminations, such as thimbles, chokers and hooks.
Wire rope offers its user many advantages. First, design of even distribution of weight among strands makes it ideal for lifting extremely heavy loads. Second, wire rope is extremely durable and, when matched properly to the application, can withstand great stress and elements like corrosion and abrasion. In addition, it is very versatile. Its many iterations and the ways in which the rope can treated means that users can get rope custom fit for virtually any application.
Depending on the type of wire rope with which you are working and your application, you may want to invest in different accessories. Among these accessories are: wire rope clips, steel carabiners, fittings, fasteners and connections.
To ensure that your wire rope quality remains high, you must regularly inspect them for wear and degradation. The right wire rope should be selected for a particular use. Watch out for performance-impacting damage like: rust, fraying and kinks. To make sure that they stay in tip-top shape, you should also clean and lubricate them as needed. Check for this need as a part of your regular inspection.
Rope care is about more than inspection. It’s also about making an effort to use and store them properly every time you use them. For example, never exceed your rope’s rated load and breaking strength. Doing so will not only cause the weakening of your cable, but it may even cause immediate breakage. In addition, always store your wire rope cable in a dry and warm area, away from those elements that could cause premature rusting or other damage. Finally, always carefully wind your wire rope when you’re done with it, so as to avoid kinks. If you follow all these tips and treat your wire rope assemblies well, they will reward you with a long and productive service life.
Always make sure that you purchase wire rope that matches your industry and regional standards. Some of the most widely referenced standards organizations for wire rope include: ISO, ASTM International and OSHA. Talk over your specifications and application with your wire rope supplier to figure out what’s best for you.
If you’re in the market for a wire rope or a wire rope assembly, the best way to know you’re getting something that will both perform well and be safe if by working with a vetted professional. Find one among the list we’ve provided on this page. Check out their profiles to get an idea of the services and products they offer. Pick out three or four to whom you’d like to speak, and reach out. Talk to them about your specifications, standard requirements and budget. Ask about lead times and delivery options. Once you’ve spoken with all of them, compare and contrast their answers. You’ll know you’ve found the one when you talk to a wire rope company that is willing to go above and beyond for your satisfaction.

Mechanical properties of wire ropes, their chemical composition, and the failure analysis process for them are described. The wires are manufactured from high-carbon, plain carbon steel, with high-strength ropes most often manufactured from AISI Grade 1074. During visual failure examination, the rope, strand, and wire diameters should all be measured. Examination should also address the presence or absence of lubricant, corrosion evidence, and gross mechanical damage. Failed wires can exhibit classic cup-and-cone ductile features, flat fatigue features, and various appearances in-between. However, wires are often mechanically damaged after failure. Most nondestructive evaluation (NDE) techniques are not applicable to wire...




 8613371530291
8613371530291