wire rope inspection standards pricelist
A competent person must begin a visual inspection prior to each shift the equipment is used, which must be completed before or during that shift. The inspection must consist of observation of wire ropes (running and standing) that are likely to be in use during the shift for apparent deficiencies, including those listed in paragraph (a)(2) of this section. Untwisting (opening) of wire rope or booming down is not required as part of this inspection.
Significant distortion of the wire rope structure such as kinking, crushing, unstranding, birdcaging, signs of core failure or steel core protrusion between the outer strands.
In running wire ropes: Six randomly distributed broken wires in one rope lay or three broken wires in one strand in one rope lay, where a rope lay is the length along the rope in which one strand makes a complete revolution around the rope.
In rotation resistant ropes: Two randomly distributed broken wires in six rope diameters or four randomly distributed broken wires in 30 rope diameters.
In pendants or standing wire ropes: More than two broken wires in one rope lay located in rope beyond end connections and/or more than one broken wire in a rope lay located at an end connection.
If a deficiency in Category I (see paragraph (a)(2)(i) of this section) is identified, an immediate determination must be made by the competent person as to whether the deficiency constitutes a safety hazard. If the deficiency is determined to constitute a safety hazard, operations involving use of the wire rope in question must be prohibited until:
If the deficiency is localized, the problem is corrected by severing the wire rope in two; the undamaged portion may continue to be used. Joining lengths of wire rope by splicing is prohibited. If a rope is shortened under this paragraph, the employer must ensure that the drum will still have two wraps of wire when the load and/or boom is in its lowest position.
If a deficiency in Category II (see paragraph (a)(2)(ii) of this section) is identified, operations involving use of the wire rope in question must be prohibited until:
The employer complies with the wire rope manufacturer"s established criterion for removal from service or a different criterion that the wire rope manufacturer has approved in writing for that specific wire rope (see § 1926.1417),
If the deficiency is localized, the problem is corrected by severing the wire rope in two; the undamaged portion may continue to be used. Joining lengths of wire rope by splicing is prohibited. If a rope is shortened under this paragraph, the employer must ensure that the drum will still have two wraps of wire when the load and/or boom is in its lowest position.
If the deficiency (other than power line contact) is localized, the problem is corrected by severing the wire rope in two; the undamaged portion may continue to be used. Joining lengths of wire rope by splicing is prohibited. Repair of wire rope that contacted an energized power line is also prohibited. If a rope is shortened under this paragraph, the employer must ensure that the drum will still have two wraps of wire when the load and/or boom is in its lowest position.
Where a wire rope is required to be removed from service under this section, either the equipment (as a whole) or the hoist with that wire rope must be tagged-out, in accordance with § 1926.1417(f)(1), until the wire rope is repaired or replaced.
The inspection must include any deficiencies that the qualified person who conducts the annual inspection determines under paragraph (c)(3)(ii) of this section must be monitored.
Wire ropes on equipment must not be used until an inspection under this paragraph demonstrates that no corrective action under paragraph (a)(4) of this section is required.
At least every 12 months, wire ropes in use on equipment must be inspected by a qualified person in accordance with paragraph (a) of this section (shift inspection).
The inspection must be complete and thorough, covering the surface of the entire length of the wire ropes, with particular attention given to all of the following:
Exception: In the event an inspection under paragraph (c)(2) of this section is not feasible due to existing set-up and configuration of the equipment (such as where an assist crane is needed) or due to site conditions (such as a dense urban setting), such inspections must be conducted as soon as it becomes feasible, but no longer than an additional 6 months for running ropes and, for standing ropes, at the time of disassembly.
If the deficiency is localized, the problem is corrected by severing the wire rope in two; the undamaged portion may continue to be used. Joining lengths of wire rope by splicing is prohibited. If a rope is shortened under this paragraph, the employer must ensure that the drum will still have two wraps of wire when the load and/or boom is in its lowest position.
If the qualified person determines that, though not presently a safety hazard, the deficiency needs to be monitored, the employer must ensure that the deficiency is checked in the monthly inspections.
All documents produced under this section must be available, during the applicable document retention period, to all persons who conduct inspections under this section.

Wire rope isa type of cablewhich is made up of several strands of metal wirelaid or twisted into a braid or helix.Do you know how often your wire rope needs to be inspected? Wire rope inspections are vital to industries that use wire rope.
One of the most important purposes of carrying out wire rope inspections or testing is to oversee the process of depreciation in the wire rope. When any depreciation or deterioration is identified these wire ropes can cease to be used immediatelybefore it becomes a hazard. A great advantage of conducting these examinations is to analyse and identify if there is unexpected corrosion and destruction.
Commonly, there is a constant increase rate in the amount of wire rope breaks, during the lifespan of that wire rope. Wire ropes need to be inspected and tested as they have a limited life, like all consumable products. Early in the life of the wire rope (when it is starting to be used), the wires and strands of the rope settle into position and the breaking strength increases. Once it has hit its maximum, the breaking strength then decreases rapidly.
Wire rope inspections should only be carried out by highly trained professionals. There are 2 ways that these inspections are carried out on crane wire rope: Visual and Non-Destructive. Visual and no-destructive examinations are equally as important but a non-destructive wire rope test is a lot less frequent than a visual wire rope inspection. Destructive testing only takes place when specifically required by a company to find out what type of wire rope something is that has not been labelled and is not common practice in the general testing/inspections.
Visual inspection of wire ropeThe visual method is a simple yet effective method to check for external damage to a crane wire rope. Visually inspecting the entire length of rope is very important. The rope should be inspected 2 to 3 feet at a time and examined carefully at each stop. Whilst inspecting the wire rope it also cleaned with Lanotec and a wire brush.
Although tedious, it can determine many visual signs of wire rope damage, such as; kinks, bird caging, cutting, knots, flattening, crushing & heat damage (burn marks, discolouration of the metal). Wearing heavy duty gloves, an inspector will grab the rope and lightly move a rag slowly along the length of rope. Broken wires will often stick out (porcupine) and will therefore snag on the rag. Should the rag snag on a wire, the inspector should the stop and visually assess the rope condition. Broken wires do not always ‘porcupine’. Visual inspections should not be the only method relied on for inspecting crane wire ropes.
Due to the composition of a wire rope, the outer layer only represents approximately 40% of the metallic cross section of the rope and only approximately half of this is visible due to the strand twisting inside and out. That means you are only able to visually examine approximately 20% of the entire rope composition. You can only assume that the other 80% is in good condition.
Although the external 20% may look in good condition it may be concealing a great number of wire breaks and internal damage. Wire ropes with internal damage that have no signs of external damage can be extremely dangerous. This is why an internal wire rope inspection should also be completed. Internal deterioration is the primary cause of many rope failures, mainly due to corrosion and the normal progress of fatigue. Single-layer stranded ropes may be opened up slightly to allow an assessment of their internal condition, provided that they are at zero tension; though, some restrictions occur with large rope sizes. Permanent damage can be caused to multi-layer wire ropes if they are opened.
Internal inspection should always be carried out by a capable person. The method of inspection consists of firmly attaching two clamping jaws of appropriate size at a suitable distance apart to the rope. During the inspection of sections of rope adjacent to terminations, it is adequate to use a single clamping jaw, since the end anchorage system, or a bar suitably located through the end portion of the termination, may be used as the second clamp.
By the application of a force to the clamping jaws in the opposite direction to the rope lay, the outer strands separate and move away from the core. Care should be taken during the opening process to ensure that the clamping jaws do not slip about the outside of the rope. The strands should not be displaced excessively. When a limited opening is achieved, a small probe, such as a screwdriver, may be used to remove grease or debris that could obstruct observation of the interior of the rope. The crucial points that should be observed are as follows:
After inspection, a service dressing should be introduced into the opened part and the clamping jaws rotated with moderate force to ensure correct replacement of the strands around the core. After removal of the jaws, the outer surface of the rope should be greased. Since it is impossible to inspect the interior of the wire rope over the whole of its length, suitable sections shall be selected.
For wire ropes that wind onto a drum, or pass over pulleys or rollers, it is recommended that the lengths that engage the pulley grooves when the appliance is in a loaded condition be inspected. Those localised lengths in which shock forces are arrested (i.e., adjacent to drum and jib head pulleys) and those lengths that are particularly exposed to the weather for long periods should be inspected. Attention should be given to the length of rope close to its termination, and this is particularly important for fixed ropes, such as stays or pendants. This is where a visual inspection is complimented by a non-destructive test. .
Any wire rope in use should be inspected on a regular basis. You have too much at stake in lives and equipment to ignore thorough examination of the rope at prescribed intervals.
The purpose of inspection is to accurately estimate the service life and strength remaining in a rope so that maximum service can be had within the limits of safety. Results of the inspection should be recorded to provide a history of rope performance on a particular job.
On most jobs wire rope must be replaced before there is any risk of failure. A rope broken in service can destroy machinery and curtail production. It can also kill.
Because of the great responsibility involved in ensuring safe rigging on equipment, the person assigned to inspect should know wire rope and its operation thoroughly. Inspections should be made periodically and before each use, and the results recorded.
When inspecting the rope, the condition of the drum, sheaves, guards, cable clamps and other end fittings should be noted. The condition of these parts affects rope wear: any defects detected should be repaired.
To ensure rope soundness between inspections, all workers should participate. The operator can be most helpful by watching the ropes under his control. If any accident involving the ropes occurs, the operator should immediately shut down his equipment and report the accident to his supervisor. The equipment should be inspected before resuming operation.
The Occupational Safety and Health Act has made periodic inspection mandatory for most wire rope applications. If you need help locating the regulations that apply to your application, please give our rigging experts a call.

Wire rope is a preferred lifting device for many reasons. Its unique design consists of multiple steel wires that form individual strands laid in a helical pattern around a core. Wire rope comes in a variety of strand patterns including single layer, filler wire, seale, warrington, and combination. Wire rope strands can be laid around the core in different configurations including regular lay wire rope, lang lay wire rope, and alternate lay wire rope. There also many types of grades of wire rope, including: improved plow steel (IPS), extra improved plow steel (EIPS), and extra extra improved plow steel (EEIPS). Some types of wire rope is preferred over others due to the unique properties, including: rotation resistant wire rope, compacted strand wire rope, swaged wire rope, plastic coated wire rope, plastic impregnated (PI) wire rope.
There is no denying that wire ropes are one of the most used materials in the industrial landscape. According to Statista, in 2020 itself, the production volume of steel wire ropes in Japan amounted to approximately 240.32 thousand tons. Their necessity is evident, and the wire rope sling manufacturers are increasingly deploying their solutions in marine environments or for rigging purposes. However, as wire ropes face considerable loads, they suffer massive mechanical damage.
As suggested by the leading steel wire rope manufacturers, some well-known reasons for wire rope failure are corrosion, excess deterioration, improper usage, and lack of maintenance resulting in reduced safety, increased replacement costs, and early discard. Do you want to know the professional ways steel wire rope manufacturers inspect wire ropes? Then here"s a guide for you!
All wire ropes must be inspected visually on daily basis before starting the operation. This safety guideline can ensure maximum security. Although it"s daunting to determine the exact service span of the ropes, close analysis on a more frequent basis can help get a more precise estimation of their predictive life cycle. Also, note that calculating the precise times when the ropes have been in use during the mooring/tidal conditions, load pressures, etc., can be the answer. A competent person shall carry out an overall, thorough periodical inspection of the wire rope.
You can use the rag-and-visual process to check for any external damage. All you need to do is grab the rope lightly with a rag or cotton cloth. Then move the rag along the wire, and if there are any broken wires, they will stick out and snag on the rag. If the cloth catches broken wires, you can stop and assess the rope visually. Also, make sure to visually inspect the wire without any rag because some wire breaks don"t stick out.
Measure the diameter of the rope and compare the diameter with the original values. When the measurements are different, the change implies internal or external rope conditions.
When a steel wire rope passes over the drum and sheaves or any other metallic equipment component, abrasion takes place. Hence, it is important that all components must be in proper working order and of the appropriate diameter for the rope. A badly corrugated or worn-out sheave or drum will significantly damage a new rope, resulting in premature rope replacement.
In addition, try to look for corrosion, pitting, abrasions, end fitting conditions, wire breakage (if any), and lubrication inside the rope. Wire rope should be inspected to check for any abnormality like External damage, Kink, Strand looseness, Core protrusion, or Bird-caging.
While sometimes the damage can be easily identified on the surface, in other cases, the fracture might occur inside the wires. Therefore, ensure that the ropes are maintained, manufactured, and inspected by competent professionals. Searching for the best wire rope sling manufacturers and inspecting company that focuses stringently on quality checks? Usha Martin can be your one-stop solution!

This 12-page brochure presents important guidelines for inspecting wire rope systems or installations. It provides a clear and concise approach to assisting wire rope users" needs to comply with industry and governmental regulations that require inspections of individual ropes, fittings and attachments, as well as entire operating systems at regularly scheduled intervals. It is very useful for conducting safety meetings and training sessions. In addition to information and criteria, the brochure includes a blank Inspection Form, which may be easily copied for recording results of regular inspections for the permanent, written files required by many regulations.

European Standards and partners need your consent to the use of individual data so that they can, among other things, show you information about your interests. Click on the "OK" box to give your consent.
The CSIR is the recognised custodian of in-service mine rope technology, and performs the bulk of the statutory tests required for hoist ropes in the mining industry.As a National Key Point, the Wire Rope Testing Laboratory also maintains the largest historical database of rope tests in Africa.
Access to rope test data and certificates are provided via a user-friendly web-based system. Through this facility clients can get direct access to their test results, and the Department of Minerals and Energy can draw lists of tests performed by the various mines. Registered users can follow the link below to access the rope test database. (Rope Certificates) The rope test prices are also provided.
Safety is a crucial factor in the profitability of the mining industry. With thousands of workers transported up and down mine shafts each day, measuring the safety of hoisting ropes form an integral part of mine management.Strict laws cover the maintenance and testing of steel wire ropes.The Wire Rope Testing Laboratory focuses mainly on the destructive testing of these ropes.
For each hoist rope tested, the customer is provided with a detailed report that includes the breaking force, absorbed strain energy, force vs. elongation curve and an assessment of the condition of individual strands and wires at the point of failure.The report also alerts the customer to rope characteristics that breach, or are approaching, accepted performance standards. For example, a breaking force that is 90% or less than the new rope-breaking force. An assessment of corrosion and general rope lubrication is also provided.
The Laboratory is an advanced technology facility housing state of the art wire rope testing equipment.The machines used in the destructive testing of steel wire ropes have capacities ranging from 1 MN for small diameter ropes, to 15 MN for ropes up to 160 mm in diameter.
A 15 MN MFL tensile test machine which is able to accommodate large-diameter ropes as used in the oil drilling, bridge and shipping industries.It also caters for tensile tests on conveyor belts up to 1.2m wide and large-link chains as used on coal mine draglines and;
The CSIR Wire Rope Testing Laboratory is the government approved facility for statuary testing of winding ropes. Because of the CSIRs impartiality, professionalism and technical expertise, rope manufacturers locally and abroad also choose to have their wire rope samples tested by the CSIR. Existing clients include, but are not limited to, the following:

Yes, it is absolutely safe to buy Wire Rope Inspection Guidelines (25/pack) from desertcart, which is a 100% legitimate site operating in 164 countries. Since 2014, desertcart has been delivering a wide range of products to customers and fulfilling their desires. You will find several positive reviews by desertcart customers on portals like Trustpilot, etc. The website uses an HTTPS system to safeguard all customers and protect financial details and transactions done online. The company uses the latest upgraded technologies and software systems to ensure a fair and safe shopping experience for all customers. Your details are highly secure and guarded by the company using encryption and other latest softwares and technologies.

Abrasion damage may occur when the rope contacts an abrasive medium or simply when it passes over the drum and sheaves. Therefore it is vital that all components be in proper working order and of the appropriate diameter for the rope. A badly corrugated or worn sheave or drum will seriously damage a new rope, resulting in premature rope replacement.
Corrosion is very difficult to evaluate but is a more serious cause of degradation than abrasion. Usually signifying a lack of lubrication, corrosion will often occur internally before there is any visible external evidence on the rope’s surface. A slight discoloration caused by rusting usually indicates a need for lubrication which should be tended to immediately. If this condition persists, it will lead to severe corrosion which promotes premature fatigue failures in the wires and strands, necessitating the rope’s immediate removal from service.
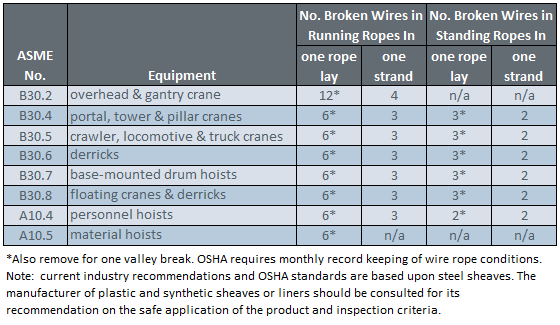
The table below shows the number of allowable wire breaks per crane type. The inspector must know the ASME standard for the equipment being inspected. The number of broken wires on the outside of the wire rope is an indication of its general condition and whether or not it must be considered for replacement. The inspector may use a type of spike to gently probe the strands for any wire breaks that do not protrude. Check as the rope runs at a slow speed over the sheaves, where crown (surface) wire breaks may be easier to see. Also examine the rope near the end connections. Keeping a detailed inspection record of the wire breaks and other types of damage will help the inspector determine the elapsed time between breaks. Note the area of the breaks and carefully inspect these areas in the future. Replace the rope when the wire breaks reach the total number allowable by ASME or other applicable specifications.
Valley breaks, or breaks in between strands, must be taken very seriously at all times!When two or more valley breaks are found in one lay-length, immediately replace the rope. Valley breaks are difficult to see; however, if you see one you can be assured that there are a few more hidden in the same area. Crown breaks are signs of normal deterioration, but valley breaks indicate an abnormal condition such as fatigue or breakage of other wires such as those in the core.
Once crown and valley breaks appear, their number will steadily and quickly increase as time goes on. The broken wires should be removed as soon as possible by bending the broken ends back and forth with a pair of pliers. In this way the wire is more likely to break inside the rope where the ends will be tucked away. If the broken wires are not removed they may cause further damage. The inspector must obey the broken wire standard; pushing the rope for more life will create a dangerous situation.
It is important to check and record a new rope’s actual diameter when under normal load conditions. During the life of the rope the inspector should periodically measure the actual diameter of the rope at the same location under equivalent loading conditions. If followed carefully, this procedure reveals a common rope characteristic—after an initial reduction, the overall diameter will stabilize and slowly decrease in diameter during the course of the rope’s life. This condition is normal. However, if diameter reduction is isolated to one area or happens quickly, the inspector must immediately determine (and correct, if necessary) the cause of the diameter loss, and schedule the rope for replacement.
Crushing or flattening of the strands can be caused by a number of different factors. These problems usually occur on multilayer spooling conditions but can occur by simply using the wrong wire rope construction. Most premature crushing and/or flattening conditions occur because of improper installation of the wire rope. In many cases failure to obtain a very tight first layer (the foundation) will cause loose or “gappy” conditions in the wire rope which will cause rapid deterioration. Failure to properly break-in the new rope, or worse, to have no break-in procedure at all, will cause similar poor spooling conditions. Therefore, it is imperative that the inspector knows how to inspect the wire rope as well as how that rope was installed.
Shock loading (bird-caging) of the rope is another reason for replacement of the rope. Shock loading is caused by the sudden release of tension on the wire rope and its resultant rebound from being overloaded. The damage that occurs can never be corrected and the rope must be replaced.
High stranding may occur for a number of reasons such as failure to properly seize the rope prior to installation or maintain seizing during wedge socket installation. Sometimes wavy rope occurs due to kinks or a very tight grooving problem. Another possibility is simply introducing torque or twist into a new rope during poor installation procedures. This condition requires the inspector to evaluate the continued use of the rope or increase the frequency of inspection.

Stock up on every variety of steel wire rods at the Alibaba metalworking store. Our listings feature wholesale steel rods from a network of dependable Chinese manufacturing partners. If you need to source steel rods for construction projects, you"ll find products that are robust and durable. And if you need welding rods, they are easy to find via our search engine. Track down the steel wire rope price you need at affordable prices at Alibaba.com.
What can you do with the steel wire rods available from Alibaba"s wholesale store? One common use for steel rods is in the welding sector. Steel works well as a welding rod material thanks to its high ductility, meaning that welds are relatively strong and long-lasting. Choose a low carbon rod and you"ll be all set for successful welds in industrial settings and workshops alike. However, steel wire also has applications beyond welding. You can use it as wiring in electronic circuits and power distribution systems and it works especially well in high temperature settings as armored cabling. Find the ideal steel wire rope price for every industrial use at Alibaba.com.
Steel wire rods also have applications in everyday life. For example, you can use coils of steel wire to construct fences and barriers both inside and outside homes. It"s a common material in agricultural businesses thanks to its toughness and resistance to oxidation. Use it to create reinforcement cages, enclosures for equipment, or add it to concrete to add extra strength where it really matters. From welding to concrete reinforcement, steel wire rope price will always find a use. And whether you need small batches or huge bulk orders, our metallic materials catalog is the ideal place to look.




 8613371530291
8613371530291