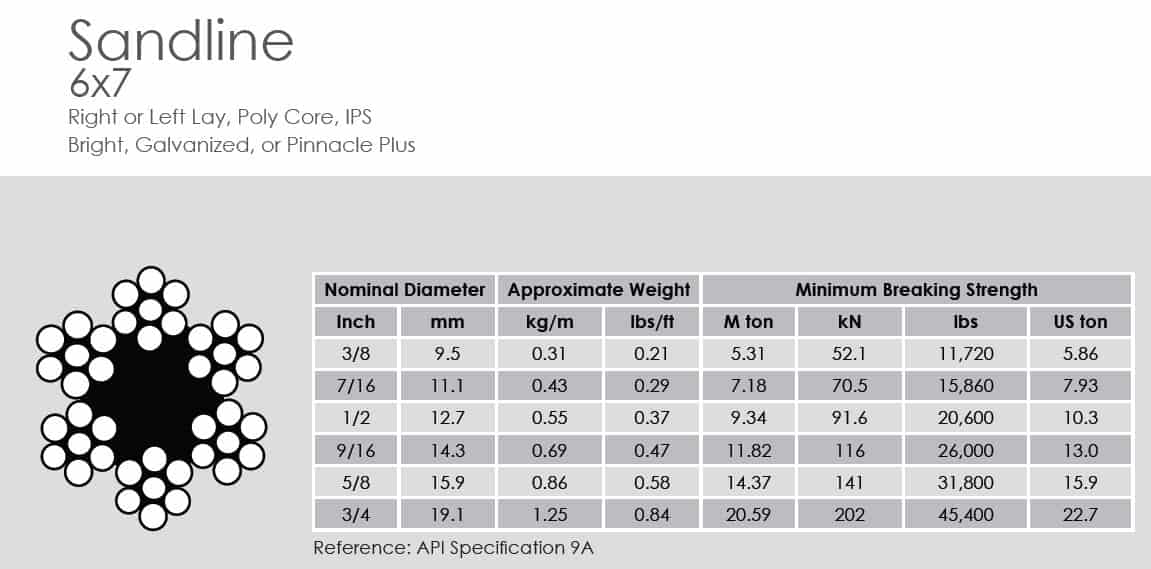
wire rope ips pricelist
.jpg)
The 6x19 galvanized wire rope provides an excellent balance between fatigue and wear resistance. For use in lifting and rigging, securement, and general purpose, the 6x19 wire rope class comprises either a wire rope core or a fiber core.
The wire rope core is its own wire rope construction, most commonly 7x7. This is known as IWRC (Independent Wire Rope Core), meaning it moves independent to the outer strands. The 6x19 has larger outer wires, and is therefore more abrasion resistant, though its fatigue resistance is decreased—but overall, it"s is a good rope for withstanding abrasion or crushing on the drum. Galvanized wire rope (steel) features a compressed zinc coating for providing excellent corrosion resistance. With higher break strength, yet lower price than stainless steel, galvanized steel wire rope is widely used in general engineering applications such as winches and security ropes.
The 6x19 wire rope class is made up of six strands of between 16 and 26 wires per strand for additional wire rope strength and durability, with a maximum breaking strength of 69 tons. The 6x19 features IPS (Improved Plowed Steel), EIPS (Extra Improved Plowed Steel), or EEIPS (Extra Extra Improved Plowed Steel) grade wire rope. Also available in USA-made.

The 6x36 galvanized wire rope is a flexible general engineering wire rope with an equal lay construction and achieves a superior breaking load to the 6x19 construction range. The 6x36 is available with either a fiber core or IWRC (Independent Wire Rope Core) and is used in a wide range of applications, including, but not limited to, wire rope slings, crane ropes, winch ropes, hoist ropes, lifeboat falls, mooring ropes, pursing wires, luffing ropes, and tow ropes.
Galvanized wire rope (steel) features a compressed zinc coating for providing excellent corrosion resistance. With higher break strength, yet lower price than stainless steel, galvanized steel wire rope is widely used in general engineering applications.
The 6x36 wire rope class is made up of six strands of between 27 and 49 wires per strand for additional wire rope strength and durability. The 6x36 features IPS (Improved Plowed Steel), EIPS (Extra Improved Plowed Steel), or EEIPS (Extra Extra Improved Plowed Steel) grade wire rope. Also available in USA-made.

Interested in becoming a distributor for Miami Cordage/Florida Wire & Rigging Works? Whether you have a brick-and-mortar store or are an on-line retailer, we offer substantial discounts to our loyal distributors. Click here to find out more information.
.jpg)
Interested in becoming a distributor for Miami Cordage/Florida Wire & Rigging Works? Whether you have a brick-and-mortar store or are an on-line retailer, we offer substantial discounts to our loyal distributors. Click here to find out more information.
Wire Rope Material: The lifting slings are made from independent wire rope core (IWRC) offering less stretch and resistance to crushing while maintaining sling flexibility. Wire rope slings are fabricated from extra improved plow steel (EIPS).
A low quality wire rope sling can cause injury and damage. A look-alike wire rope sling often found at lower prices is also often advertised to conform to the same safety standards (if at all). Be aware that it may refer to safety ratings in effect decades ago. So for example under the same safety standard a decade ago, a wire rope sling may be rated to 100% without proof load testing while today it may be 300% with proof load testing. Be assured that we only sell the highest quality wire rope slings and our advertised safety standards conform to the current ASME standards.
Working load limits (capacity) of the wire rope lifting slings vary depending on the angle of use. The capacity is reduced as the angle of use declines. See drawing below how a 1,000 lbs sling capacity is reduced as the angle of use declines. The capacity of the sling is always highest at a 90 degree angle of use and smallest at an angle of 30 degrees (or less).
The wire rope sling is not quite as durable. The wire rope sling is not as flexible as chain but its greater stiffness can be an advantage if it has to be inserted through a small opening or beneath a load. However, when wrapped around a load, the wire rope sling often tends to deform permanently to the shape of the load. Wire rope suitable for slings comes in a variety of grades and constructions. In most cases looping back and securing the loop with a metal sleeve terminates the rope. This forms a loop or soft eye, the simplest form of sling end. Thimbles are used to support and protect the eye from abrasion. Wire rope is generally cheaper and lighter than chain which can be a plus, particularly for applications that require long sling lengths.
The nylon and polyester slings have the advantage of being lightweight in comparison to chain and wire rope slings. They are very flexible and relatively soft; therefore, they are suitable in applications were minimal damage to the load"s surface finish is important. The rope is made endless or terminated with an eye by means of a handmade splice. Similar to a wire rope sling, various terminal fittings are available. Without adequate protection, nylon and poly slings are susceptible to being severed when impinging on even a relatively moderate sharp edge.
Wire rope is often commonly referred to as cable; they are one in the same. Wire rope is composed of wires, strands, and a core. The basic unit is the wire, which is formed into strands. The strands are wound around the core. Various types of wire rope exist to meet a range of uses and operating conditions. These types are designated by the number of strands; the number, sizes and arrangement of the wires in each strand; and the way in which the wires and strands are wound, or laid, about each other.
Important characteristics of wire rope relate to the number and size of the outer wires. A small number of large outer wires result in better resistance to wear and corrosion. A large number of small wires result in better flexibility and resistance to fatigue.
The core acts as the axial member about which the strands are laid. Wire rope cores are made in two different forms. The one used most extensively is a wire rope of suitable size to serve as a core. It is called as independent wire rope core (IWRC). IWRC has increased tensile strength, offers less stretch, and is resistant to crushing; however, is less flexible. The other type is a wire strand core (WSC). This consists of a multiple-wire strand, and may be the same construction as the main rope strands.
Two grades of carbon steel wire are offered. The bulk of commercial wire rope lifting sling is made from improved plow steel (IPS) or extra improved plow steel (EIPS) which has a higher tensile strength.
Hand Splicing:Because no metal sleeve is required to secure the eye in the hand spliced sling, it exhibits more flexibility than mechanically splice slings of equal diameter. They have a more narrow profile and therefore can fit through tight spaces. Without benefit of a metal sleeve, lifts must be limited to applications where the wire rope sling is restrained from rotation and possible unlaying of the sling body.
Mechanical Splicing:Mechanically spliced eyes do not suffer the limitations of hand splicing, are economical, and offer the highest rated capacity of any spliced wire rope sling. This wire rope sling is fabricated by unlaying the rope body into two parts, one containing half the number of strands, the other having the remaining strands and core. The rope is unlayed far enough back to allow the eye to be formed by looping one part in one direction and the other part in the opposite direction and laying the rope back together. The strands are rolled back around the rope body and a metal sleeve is slipped over the ends and pressed (or swaged) to secure the ends to the body of the wire rope sling.
MAX Groups Marine is one of the most trusted suppliers of stainless steel and galvanised wire ropes/cables. Wire ropes consist of several strands of metal wire twisted into a helix form, forming extremely durable wire ropes for various marine purposes. Wire ropes are exposed to high fluctuation of contradicting forces, wear and tear or even corrosion in some cases. Thus, the quality of wire rope has to be taken very seriously.
Constant eye inspection and tests should be carried out to make sure the wire ropes are performing as they should. In MAX, all manufacturing of wire ropes are supervised and tested by professional technicians at all times.
Commonly used types of wire ropes may be of a fiber core (FC), Wire Strand core (WSC) or an Independent Wire Rope Core (IWRC). Usually IWRC core ropes are more durable whereas fibre core wire ropes are more elastic. The choice of wire rope core mostly depends on the usage and situation.
Most wire ropes are made from high-carbon steel, iron, stainless steel, bronze and more. Carbon steel wire ropes are graded from IPS (Improved Plow Steel), EIPS (Extra Improved Plow Steel to EEIPS (Extra Extra Improved Plow Steel), with each grade signifying its nominal strength. The most popular MAX steel wire ropes are of EIPS grade.
It doesn’t matter whether the lay direction is right (Z) or left (S), ordinary lay or langlay, MAX wire ropes are designed to have high durability and tensile strength for heavy industry usage.
For wire rope slings, you may opt for thimble eye (where a thimble if fixed inside the loop to preserve the natural loop shape and prevent direct contact that will damage the cable) or soft eye. Besides, rope ends with machine swaged with ferrules or sockets is a better option than hand spliced slings as it offers more protection.
Do you experience a short lifespan for your steel wire ropes? Deal with a supplier who is slow in responding & customer service? Or did you pay high prices for average quality products that fails you all the time? 83% of our clients claim that these made them search for a better option and subsequently worked with us since.
.jpg)
Wire rope is a preferred lifting device for many reasons. Its unique design consists of multiple steel wires that form individual strands laid in a helical pattern around a core. Wire rope comes in a variety of strand patterns including single layer, filler wire, seale, warrington, and combination. Wire rope strands can be laid around the core in different configurations including regular lay wire rope, lang lay wire rope, and alternate lay wire rope. There also many types of grades of wire rope, including: improved plow steel (IPS), extra improved plow steel (EIPS), and extra extra improved plow steel (EEIPS). Some types of wire rope is preferred over others due to the unique properties, including: rotation resistant wire rope, compacted strand wire rope, swaged wire rope, plastic coated wire rope, plastic impregnated (PI) wire rope.
A wire rope is a type of cable that includes several wire strands laced together to form a single wire. Generally, both the terms “wire” and “rope” are used interchangeably with “wire rope”; however, according to the technical definition, to be labeled a wire rope, the cable must have a thickness of at least 9.52 mm. As a versatile, high load capacity alternative to natural fiber ropes such as hemp and manila, wire rope provides motion transmission through nearly all angles, tie down, counterbalance, guidance, control, or lift.
Modern wire rope was invented by Wilhelm Albert, a German mining engineer, between 1831 and 1834. He developed them in order for work in the mines in the Harz Mountains. This rope replaced weaker natural fiber ropes, like hemp rope and manila rope, and weaker metal ropes, like chain rope.
Albert’s rope was constructed of four three-stranded wires. In 1840, a Scot named Robert Stirling Newall improved upon this model. A year later in the United States, American manufacturer John A. Roebling started producing wire rope, aimed at his vision of suspension bridges. From there, other interested Americans, such as Erskine Hazard and Josiah White, used wire rope in railroad and coal mining applications. They also applied their wire rope techniques to provide lift ropes for something called the Ashley Planes project, which allowed for better transportation and increased tourism in the area.
Approximately twenty-five years later, back in Germany in 1874, the engineering firm Adolf Bleichert & Co. was founded. They used wire rope to build bicable aerial tramways for mining the Ruhr Valley. Years later they built tramways for both the Wehrmacht and the German Imperial Army. Their wire rope systems spread all across Europe, and then migrated to the USA, concentrating at Trenton Iron Works in New Jersey.
Over the years, engineers and manufacturers have created materials of all kinds to make wire rope stronger. Such materials include stainless steel, plow steel, bright wire, galvanized steel, wire rope steel, electric wire, and more. Today, wire rope is a staple in most heavy industrial processes. Wherever heavy duty lifting is required, wire rope is there to facilitate.
Wire rope is strong, durable, and versatile. Even the heaviest industrial loads may be lifted with a well-made wire rope because the weight is distributed evenly among constituent strands.
There are three basic elements of which wire ropes are composed: wire filaments, strands, and cores. Manufacturers make wire rope by taking the filaments, twisting or braiding them together into strands, and then helically winding them around a core. Because of this multiple strand configuration, wire rope is also often referred to as stranded wire.
The first component, the filaments, are cold drawn rods of metal materials of varying, but relatively small diameter. The second component, the strands, can individually consist of as few as two or as many as several dozen filaments. The last component, the core, is the central element around which strands are wrapped; wire rope cores maintain a considerable amount of flexibility, while increasing strength by at least 7.5% over the strength of fiber core wire ropes.
The helical winding of the strands around the core is known as the lay. Ropes may be right hand lay, twisting strands clockwise, or they may be left hand lay, twisting strands counter-clockwise. In an ordinary lay, the individual strands are twisted in the opposite direction of the lay of the entire rope of strands to increase tension and to prevent the rope from coming unwound. Though this is most common Lang"s lay has both the strands and the rope twisted in the same direction while alternate lays, as the name suggests alternate between ordinary and Lang style lays. While alternative rope designs are available, the helical core design is often favored, as it allows a wire cable to hold a lot of weight while remaining ductile.
There are many design aspects that wire rope manufacturers consider when they are creating custom wire rope assemblies. These include: strand gauge (varies based on application strength, flexibility, and wear resistance requirements), wire rope fittings (for connecting other cables), lay, splices, and special coatings. Specially treated steel cable and plastic coated cables, for instance, are common to many application specific variations of wire rope such as push pull cable assemblies used in transferring motion between two points.
Suppliers typically identify wire cable by listing both the number of strands and the amount of wires per strand respectively, though stranded cable may alternatively be measured by their lay and length or pitch. For example, a door-retaining lanyard wire rope is identified by its 7 x 7 construction, and wire rope used for guying purposes is identified by its 1 x 19 construction. The most common types are 6 x 19, 6 x 25, 19 x 7, 7 x 7, 7 x 19, 6 x 26, and 6 x 36.
An ungalvanized steel wire rope variety. This uncoated wire rope can also be designed to resist spinning or rotating while holding a load; this is known as rotation resistant bright wire rope.
Also called a coiled wire rope, a coiled cable is a rope made from bundles of small metal wires, which are then twisted into a coil. Wire rope and cable can come in a huge variety of forms, but coiled cables specifically provide the benefits of easy storage and tidiness. Unlike other wire ropes, coiled cables do not require a spool for storage. Because it has been coiled, the cable will automatically retract into its spring-like shape when it is not in use, making it incredibly easy to handle.
A type of high strength rope, made of several individual filaments. These filaments are twisted into strands and helically wrapped around a core. One of the most common types of wire rope cable is steel cable.
Wire rope made not as one solid piece, but as a piece made up of a series of metal links. Wire rope chain is flexible and strong, but it is more prone to mechanical failure than wire rope.
Push pull cables and controls are a particular type of control cable designed for the positive and precise transmission of mechanical motion within a given system. Unlike their counterpart pull-pull cables, these wire rope assemblies offer multidirectional control. Additionally, their flexibility allows for easy routing, making them popular in a number of industrial and commercial applications.
Iron and steel are the two most common materials used in producing wire ropes. A steel wire is normally made from non-alloy carbon steel that offers a very high strength and can support extreme stretchable forces. For even more strength and durability, manufacturers can make stainless steel wire rope or galvanized steel wire rope. The latter two are good for applications like rigging and hoisting.
Technically, spiral ropes are curved or round strands with an assemblage of wires. This gathering of wires has at least one cord situated in the opposite direction of the wire in the outer layer of the rope. The most important trait of this rope is that all the wires included are round. The biggest benefit of this category of rope is that it does not allow the entrance of pollutants, water, or moisture.
Contain an assemblage of strands placed spirally around a core. Stranded rope steel wire patterns have different layers that cross each other to form an even stronger cable or rope. Stranded ropes contain one of three types of core: a fiber core, a wire strand core, or a wire rope core.
Provide an added level of security to a manufacturing production application. Wire rope slings are made from improved plow steel wire ropes that, apart from offering added security, also provide superior return loop slings. Plow steel wire ropes improve the life of a mechanism by shielding the rope at its connection points. The key objective of wire rope slings is to enhance the safety of an application while increasing its capacity and performance. Rope slings are also available in various sling termination options, such as hook type, chokers, and thimbles.
The eye in this rope sling is made using the Flemish Splice method. Just like a typical sling, a Permaloc rope sling improves safety and provides reverse strength meaning that the uprightness of the eye does not depend on the sleeves of the metal or alloy. Additionally, permaloc rope slings offer an abrasion resistance feature that makes them long lasting.
These slings have all the features that most other slings offer. However, compared to their counterparts, Permaloc bridle slings provide better load control, wire rope resistant crushing, robust hooks and links that work for a longer duration, and help save on maintenance requirements.
Manufacturers produce wire rope for many different reasons; from cranes to playground swings, wire ropes have something for everyone. Among the many applications of wire rope are hoisting, hauling, tie down, cargo control, baling, rigging, anchoring, mooring, and towing. They can also serve as fencing, guardrails, and cable railing, among other products.
Some of the industries that make use of wire rope include industrial manufacturing, construction, marine, gas and oil, mining, healthcare, consumer goods, and transportation. Others include the fitness industry, which uses plastic coated cable products in weight machines, the theater industry, which uses black powder coated cables for stage rigging, the recreation industry, which uses plastic coated cables for outdoor playground equipment, and the electronics industry, which uses miniature wire rope for many types of electronic equipment and communications devices.
Wire ropes are typically made from cold drawn steel wire, stainless steel wire, or galvanized wire. They may also be made from a wide variety of less popular metals, including aluminum, nickel alloy, bronze, copper, and titanium. However, nearly all wire ropes, including control cables, are made from strands of cold drawn carbon steel wires. Stainless steel rope and cables are subbed in for highly corrosive environments. Galvanized cables and galvanized wire rope are popular for their increased strength and durability; these qualities are important to specialized ropes like galvanized aircraft cable.
A core may be composed of metal, fiber or impregnated fiber materials depending on the intended application. Cores may also be another strand of wire called an independent wire rope core (IWRC).
Wire rope, depending on its application, is subject to many standard requirements. Among the most common of these are the standards detailed by OSHA, ASTM International, and ISO. Per your application and industry, you’ll likely have others you need to consider. To get a full list, talk to your service provider.
To determine the safety factor, which is a margin of security against risks, the first step involves knowing the type of load that the rope will be subjected to. The load must consider the shock loads and blowing wind effects. The safety factor is characterized in ratios; typical are 4:1 and 5:1. If a ratio is 5:1, then the tensile strength of a wire rope must be five times of the load it will be subjected to. In some applications, the ratios can go up to 10:1.
By weighing all these factors carefully, the wire rope that you will buy will be safe to use and last considerably. For the best advice and guidance, though, don’t go it alone! Find a great wire rope supplier that you can trust. You’ll know you’ve found the right supplier for you when you talk to one that can not only fulfill your requirements, but shows that they are excited to go the extra mile for you. For a company like this, browse the list near the top of the page.
As the cables play an integral role in the safety of many operations and structures, careful analysis of a wire rope and all of its capabilities and features is vital. Important qualities and physical specifications you must consider include wire rope diameter, breaking strength, resistance to corrosion, difficulty of flattening or crushing, bendability, and average lifespan.
Each of the aforementioned considerations should be compatible with the specific application for which the rope is intended as well as the environment in which such operations are undertaken. Temperature and corrosive environments often require specially coated wire ropes with increased durability.
When you use your industrial wire rope, the first thing to remember is to not exceed your rope’s rated load and breaking strength. If you do not stay within these parameters, you risk causing your rope to weaken or even break.
Rust, kinks, fraying and even carefully performed splicing will all have an impact on the performance of wire ropes. To maintain the integrity of your wire rope assembly, you need to inspect them regularly and clean and lubricate them as needed. In addition, you need to store them out of the wet and cold as much as possible. Also wrap them up properly, so they are not kinked.
A high-carbon steel having a tensile strength of approximately 260,000 psi that is roughly fifteen percent stronger than Plow Steel. Most commercial wires are made from IPS.
A low carbon steel wire of approximately 10,000 psi, which is pliable and capable of repeated stresses from bending around small sheaves. This grade is effective for tillers, guys and sash ropes.
The manner in which the wires are helically wound to form rope. Lay refers specifically to the direction of the helical path of the strands in a wire rope; for example, if the helix of the strands are like the threads of a right-hand screw, the lay is known as a right lay, or right-hand, but if the strands go to the left, it is a left lay, or left-hand.
A classification of wire rope according to its breaking strength. The rank of grades according to increasing breaking strengths is as follows: Iron, Traction, Mild Plow Steel, Plow Steel, Improved Steel, Extra Improved Steel.
The act of fastening a termination to a wire rope through physical deformation of the termination about the rope via a hydraulic press or hammering. The strength is one hundred percent of the wire rope rating.
A grade of rope material that has a tensile strength range of 180,000 to 190,000 psi. Traction steel has great resistance to bending fatigue with a minimum of abrasive force on sheaves and drums, which contributes to its long use in elevators, from which the steel gets its name.
It is composed of wire strands that are braided together. Wire braid is similar to stranded wire. The difference between the two is the fact that stranded wire features strands that are bundled together, rather than braided.
Essential parts of cable assemblies, wire rope assemblies and wire rope slings that assist spliced or swaged rope ends in connecting to other cables and keeping cables and rope from unraveling.
A wire rope cable assembly is a metallic rope consisting of bundles of twisted, spiraled, or bonded wires. While the terms wire rope and cable are often used interchangeably, cables are typically designated as smaller diameter wire ropes, specifically wire ropes with a diameter less than 3/8 inch. Therefore, wire rope cable assemblies are typically utilized for lighter duty applications.
Or cable assemblies, are cables which are composed of many spiraled bundles of wire. These cables are used to support hanging objects, connect objects, pull or lift objects, secure items, and much more.
Wire rope wholesalers can sell an extensive range of wire rope and wire rope accessories at a very affordable rate as well as in bulk. Many of the additional wire rope equipment that wire rope wholesalers provide include: swivel eye pulleys, eye nuts, eye bolts, slip hooks, spring hooks, heavy duty clips, clevis hooks, turnbuckle hooks, anchor shackle pins, s hooks, rigging blocks, and much more. Wire rope fittings will generally improve the versatility of the wire and also prevent fraying.

Galvanized wire rope is an excellent choice for that added protection from moisture and corrosion. The 6x37 class wire rope (actual 6x36 configuration) offers superior flexibility than the 6x19 class. However, it is more susceptable to abrasion as added amount of wires per strand but the strand diameter remaining the same means the individual wires are smaller in diameter. Made of EIPS (Extra Improved Plowed Steel), our IWRC wire rope core provides added support to the outer strands. The extra support adds to the durability and strength of the wire rope assemblies. We also carry coils of wire rope in 2500" and 5000" lengths. Quantity ordered will be in a continuous roll. Specific lengths can be ordered for additional charges. Please call our sales team for pricing and availability.
Galvanized wire rope is an excellent choice for that added protection from moisture and corrosion. The 6x37 class wire rope (actual 6x36 configuration...
Galvanized wire rope is an excellent choice for that added protection from moisture and corrosion. The 6x37 class wire rope (actual 6x36 configuration) offers superior flexibility than the 6x19 class. However, it is more susceptable to abrasion as added amount of wires per strand but the strand diameter remaining the same means the individual wires are smaller in diameter. Made of EIPS (Extra Improved Plowed Steel), our IWRC wire rope core provides added support to the outer strands. The extra support adds to the durability and strength of the wire rope assemblies. We also carry coils of wire rope in 2500" and 5000" lengths. Quantity ordered will be in a continuous roll. Specific lengths can be ordered for additional charges. Please call our sales team for pricing and availability.

US Producer Price Index: Metals and Metal Products: Ferrous Wire Rope, Cable, Forms Strand is at a current level of 373.00, unchanged from 373.00 last month and up from 313.99 one year ago. This is a change of 0.00% from last month and 18.79% from one year ago.

Choosing the right wire rope for a job will be based on many factors: application, required strength, and environment, to name a few. Understanding the basic terminology and the abbreviations associated with wire rope can help you decide which will work best for you.Size
Displayed as inch or fractional inch measurements, the size indicates the diameter of the rope. Industry standards measure the rope at its widest point. A wide range of sizes are available.
The numbers used in describing wire rope indicate its construction. For example: a 6 x 19 construction wire rope, the first number is the number of strands (6); the second number is how many wires make up one strand (19).
Regular lay:Also known as a right lay or ordinary lay, this indicates that the strands pass from left to right across the rope and the wires in the rope are laid in opposite direction to the lay of the strands. This type of construction is the most common and offers the widest range of applications for the rope.
Lang lay:This indicates that the wires are twisted in the same direction as the strands. These ropes are generally more flexible and have increased wearing surface per wire than right lay ropes. Because the outside wires lie at an angle to the rope’s axis, internal stress is reduced making it more resistant to fatigue from bending. This type of rope is often used in construction, excavating, and mining applications.
Fiber cores are made of vegetable (sisal, etc.) or synthetic (polypropylene, etc.) fiber and offer more elasticity. Independent wire rope cores offer more support to the outer strands, and has a higher resistance to crushing and heat. Independent wire rope core also has less stretch and more strength.

Galvanized wire rope is categorized by number of strands in its construction. We supply most of them but we concentrate on the two major categories of galvanized (and ungalvanized or bright) wire rope. These “classes” are referred to as 6x19 and 6x36. Within each category of galvanized wire rope there are different “constructions” illustrated in the tables below.
Wire rope, galvanized and ungalvanized is used for many kinds of projects and applications. No matter the application galvanized wire rope must be used properly to insure the safest working conditions. All of our galvanized wire rope is manufactured to meet or exceed Federal Specification RRW-410 and is mill certified.
All of these general purpose wire ropes are available in full reels, custom cut sizes or as part of a custom made wire rope sling. Contact us today for more information.
Galvanized wire rope also comes in different strength categories (IPS and EIPS) and different cores (FC or fiber core and IWRC or independent wire rope core). Relevant data for each is listed in the table below.




 8613371530291
8613371530291