wire rope load calculator made in china
Some of our calculators and applications let you save application data to your local computer. These applications will - due to browser restrictions - send data between your browser and our server. We don"t save this data.
Wire rope is often used in slings because of its strength, durability, abrasion resistance and ability to conform to the shape of the loads on which it is used. In addition, wire rope slings are able to lift hot materials.
Wire rope used in slings can be made of ropes with either Independent Wire Rope Core (IWRC) or a fiber-core. It should be noted that a sling manufactured with a fiber-core is usually more flexible but is less resistant to environmental damage. Conversely, a core that is made of a wire rope strand tends to have greater strength and is more resistant to heat damage.
Wire rope may be manufactured using different rope lays. The lay of a wire rope describes the direction the wires and strands are twisted during the construction of the rope. Most wire rope is right lay, regular lay. This type of rope has the widest range of applications. Wire rope slings may be made of other wire rope lays at the recommendation of the sling manufacturer or a qualified person.
Wire rope slings are made from various grades of wire rope, but the most common grades in use are Extra Improved Plow Steel (EIPS) and Extra Extra Improved Plow Steel (EEIPS). These wire ropes are manufactured and tested in accordance with ASTM guidelines. If other grades of wire rope are used, use them in accordance with the manufacturer"s recommendations and guidance.
When selecting a wire rope sling to give the best service, consider four characteristics: strength, ability to bend without distortion, ability to withstand abrasive wear, and ability to withstand abuse.
Rated loads (capacities) for single-leg vertical, choker, basket hitches, and two-, three-, and four-leg bridle slings for specific grades of wire rope slings are as shown in Tables 7 through 15.
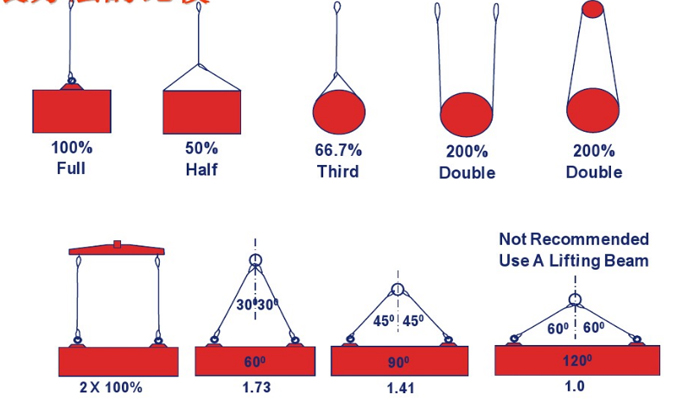
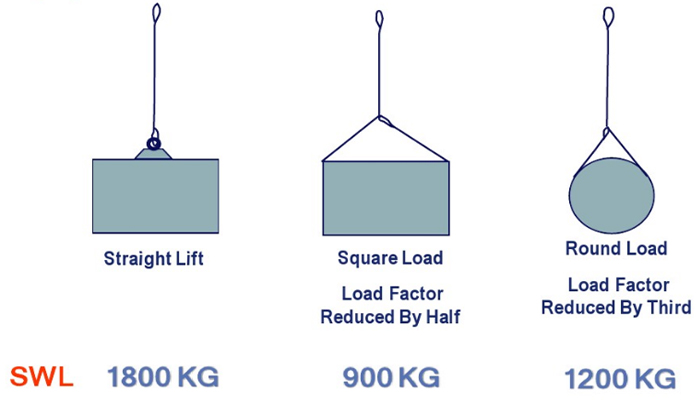
Rated loads for a sling in a choker hitch are the values shown in Table 7, 9, 11, 13, 14, or 15, provided that the angle of the choke is 120 degrees or more (Fig. 2). Use the values in Fig. 2 or those from the sling manufacturer or a qualified person for angles of choke less than 120 degrees.
Ensure that slings made of rope with 6×19 and 6x37 classifications and cable slings have a minimum clear length of rope 10 times the component rope diameter between splices, sleeves, or end fittings unless approved by a qualified person,
Ensure that braided slings have a minimum clear length of rope 40 times the component rope diameter between the loops or end fittings unless approved by a qualified person,
Do not use wire rope clips to fabricate wire rope slings, except where the application precludes the use of prefabricated slings and where the sling is designed for the specific application by a qualified person,
Ensure that wire rope slings have suitable characteristics for the type of load, hitch, and environment in which they will be used and that they are not used with loads in excess of the rated load capacities described in the appropriate tables. When D/d ratios (Fig. 4) are smaller than those listed in the tables, consult the sling manufacturer. Follow other safe operating practices, including:
Ensure that multiple-leg slings are selected according to Tables 7 through 15 when used at the specific angles given in the tables. Ensure that operations at other angles are limited to the rated load of the next lower angle given in the tables or calculated by a qualified person,
When D/d ratios (see Fig. 6) smaller than those cited in the tables are necessary, ensure that the rated load of the sling is decreased. Consult the sling manufacturer for specific data or refer to the WRTB (Wire Rope Technical Board) Wire Rope Sling Users Manual, and
Ensure that all portions of the human body are kept away from the areas between the sling and the load and between the sling and the crane or hoist hook,
When using a basket hitch, ensure that the legs of the sling contain or support the load from the sides, above the center of gravity, so that the load remains under control,
Ensure that the load applied to the hook is centered in the base (bowl) of the hook to prevent point loading on the hook, unless the hook is designed for point loading,
Before initial use, ensure that all new swaged-socket, poured-socket, turnback-eye, mechanical joint grommets, and endless wire rope slings are proof tested by the sling manufacturer or a qualified person.
Permanently remove from service fiber-core wire rope slings of any grade if they are exposed to temperatures in excess of 180 degrees F (82 degrees C).
Follow the recommendations of the sling manufacturer when you use metallic-core wire rope slings of any grade at temperatures above 400 degrees F (204 degrees C) or below minus 40 degrees F (minus 40 degrees C).
(a) Wire rope slings must be made from new or unused regular lay wire rope. The wire rope must be manufactured and tested in accordance with ASTM A 1023-02 and ASTM A 586.
(f) Wire rope clips, if used, must be installed and maintained in accordance with the recommendations of the clip manufacturer or a qualified person, or in accordance with the provisions of ASME B30.26-2010.
(g) You must not use slings made with wire rope clips as a choker hitch.Note:If using wire rope clips under these conditions, follow the guidance given in Table 5.
Number, Torque Values, and Turn Back Requirements for U-Bolt Wire Rope ClipsNumber, Torque Values, and Turn Back Requirements for Double Saddle (Fist Grip) Wire Rope Clips
•Slings made of rope with 6x19 and 6x36 classification.A minimum clear length of rope 10 times the rope diameter between splices, sleeves, or end fittings (see Figure 4, Minimum Sling Length) unless approved by a qualified person.
•Braided slings.A minimum clear length of rope 40 times the component rope diameter between the loops or end fittings (see Figure 5, Minimum Braided Sling Length) unless approved by a qualified person.
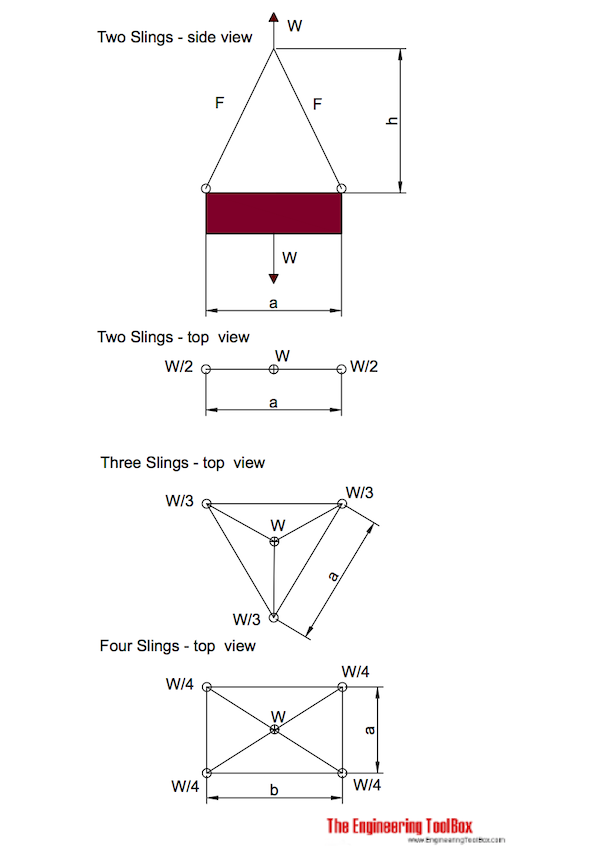
(b) You must rate slings with the load capacity of the lowest rated component of the sling. For example, if you use fittings that are rated lower than the sling material itself, identify the sling with the lower rated capacity.
(3) Identification information. All wire rope slings must have legible identification information attached to the sling which includes the information below, see sample tag in Figure 6. For slings in use that are manufactured before the effective date of this rule, the information below must be added before use or at the time the periodic inspection is completed.
Sample Wire Rope Sling ID TagNote:Sample tag for a 1/2" single-leg sling 6x19 or 6x36 classification, extra improved plow steel (EIPS) grade fiber core (FC) wire rope with a mechanical splice (ton = 2,000 lb).
(6) Proof load tests. You must make sure the sling manufacturer or a qualified person proof load tests the following slings before initial use, according to Table 8:
(c) For single- or multiple-leg slings and endless slings, each leg must be proof loaded according to the requirements listed in Table 8 based on fabrication method. The proof load test must not exceed 50% of the component ropes" or structural strands" minimum breaking strength;
•Swaged socket and poured socket slings.Each leg to at least two times, but not more than two and 1/2 times, the single-leg vertical hitch rated load.
Note: For mechanical splice, swaged socket and poured socket slings follow the rope manufacturer"s recommendations for proof load testing provided that it is within the above-specified proof load range, including (c) of this subsection.
(a) You must use wire rope slings within the rated loads shown in Tables 7 through 15 in ASME B30.9-2010. For angles that are not shown in these tables, either use the rated load for the next lower angle or have a qualified person calculate the rated load.
(c) Rated loads for slings used in a choker hitch must conform to the values shown in the above referenced tables, provided that the angle of choke is 120 degrees or greater. See Figure 9 and Table 10, Angle of Choke.
(d) You must use either Figure 9 and Table 10, the manufacturer, or a qualified person to determine the rated load if the angle of choke in a choker hitch is less than 120 degrees.
(e) You must decrease the rated load of the sling when D/d ratios (Figure 8) smaller than 25 to one. Consult the sling manufacturer for specific data or refer to the Wire Rope Sling User"s Manual (wire rope technical board).
Wire rope and cable are each considered a “machine”. The configuration and method of manufacture combined with the proper selection of material when designed for a specific purpose enables a wire rope or cable to transmit forces, motion and energy in some predetermined manner and to some desired end.
Two or more wires concentrically laid around a center wire is called a strand. It may consist of one or more layers. Typically, the number of wires in a strand is 7, 19 or 37. A group of strands laid around a core would be called a cable or wire rope. In terms of product designation, 7 strands with 19 wires in each strand would be a 7×19 cable: 7 strands with 7 wires in each strand would be a 7×7 cable.
Materials Different applications for wire rope present varying demands for strength, abrasion and corrosion resistance. In order to meet these requirements, wire rope is produced in a number of different materials.
Stainless Steel This is used where corrosion is a prime factor and the cost increase warrants its use. The 18% chromium, 8% nickel alloy known as type 302 is the most common grade accepted due to both corrosion resistance and high strength. Other types frequently used in wire rope are 304, 305, 316 and 321, each having its specific advantage over the other. Type 305 is used where non-magnetic properties are required, however, there is a slight loss of strength.
Galvanized Carbon Steel This is used where strength is a prime factor and corrosion resistance is not great enough to require the use of stainless steel. The lower cost is usually a consideration in the selection of galvanized carbon steel. Wires used in these wire ropes are individually coated with a layer of zinc which offers a good measure of protection from corrosive elements.
Cable Construction The greater the number of wires in a strand or cable of a given diameter, the more flexibility it has. A 1×7 or a 1×19 strand, having 7 and 19 wires respectively, is used principally as a fixed member, as a straight linkage, or where flexing is minimal.
Selecting Wire Rope When selecting a wire rope to give the best service, there are four requirements which should be given consideration. A proper choice is made by correctly estimating the relative importance of these requirements and selecting a rope which has the qualities best suited to withstand the effects of continued use. The rope should possess:Strength sufficient to take care of the maximum load that may be applied, with a proper safety factor.
Strength Wire rope in service is subjected to several kinds of stresses. The stresses most frequently encountered are direct tension, stress due to acceleration, stress due to sudden or shock loads, stress due to bending, and stress resulting from several forces acting at one time. For the most part, these stresses can be converted into terms of simple tension, and a rope of approximately the correct strength can be chosen. As the strength of a wire rope is determined by its, size, grade and construction, these three factors should be considered.
Safety Factors The safety factor is the ratio of the strength of the rope to the working load. A wire rope with a strength of 10,000 pounds and a total working load of 2,000 pounds would be operating with a safety factor of five.
It is not possible to set safety factors for the various types of wire rope using equipment, as this factor can vary with conditions on individual units of equipment.
The proper safety factor depends not only on the loads applied, but also on the speed of operation, shock load applied, the type of fittings used for securing the rope ends, the acceleration and deceleration, the length of rope, the number, size and location of sheaves and drums, the factors causing abrasion and corrosion and the facilities for inspection.
Fatigue Fatigue failure of the wires in a wire rope is the result of the propagation of small cracks under repeated applications of bending loads. It occurs when ropes operate over comparatively small sheaves or drums. The repeated bending of the individual wires, as the rope bends when passing over the sheaves or drums, and the straightening of the individual wires, as the rope leaves the sheaves or drums, causing fatigue. The effect of fatigue on wires is illustrated by bending a wire repeatedly back and forth until it breaks.
The best means of preventing early fatigue of wire ropes is to use sheaves and drums of adequate size. To increase the resistance to fatigue, a rope of more flexible construction should be used, as increased flexibility is secured through the use of smaller wires.
Abrasive Wear The ability of a wire rope to withstand abrasion is determined by the size, the carbon and manganese content, the heat treatment of the outer wires and the construction of the rope. The larger outer wires of the less flexible constructions are better able to withstand abrasion than the finer outer wires of the more flexible ropes. The higher carbon and manganese content and the heat treatment used in producing wire for the stronger ropes, make the higher grade ropes better able to withstand abrasive wear than the lower grade ropes.
Effects of Bending All wire ropes, except stationary ropes used as guys or supports, are subjected to bending around sheaves or drums. The service obtained from wire ropes is, to a large extent, dependent upon the proper choice and location of the sheaves and drums about which it operates.
A wire rope may be considered a machine in which the individual elements (wires and strands) slide upon each other when the rope is bent. Therefore, as a prerequisite to the satisfactory operation of wire rope over sheaves and drums, the rope must be properly lubricated.
Loss of strength due to bending is caused by the inability of the individual strands and wires to adjust themselves to their changed position when the rope is bent. Tests made by the National Institute of Standards and Technology show that the rope strength decreases in a marked degree as the sheave diameter grows smaller with respect to the diameter of the rope. The loss of strength due to bending wire ropes over the sheaves found in common use will not exceed 6% and will usually be about 4%.
The bending of a wire rope is accompanied by readjustment in the positions of the strands and wires and results in actual bending of the wires. Repetitive flexing of the wires develops bending loads which, even though well within the elastic limit of the wires, set up points of stress concentration.
The fatigue effect of bending appears in the form of small cracks in the wires at these over-stressed foci. These cracks propagate under repeated stress cycles, until the remaining sound metal is inadequate to withstand the bending load. This results in broken wires showing no apparent contraction of cross section.
Experience has established the fact that from the service view-point, a very definite relationship exists between the size of the individual outer wires of a wire rope and the size of the sheave or drum about which it operates. Sheaves and drums smaller than 200 times the diameter of the outer wires will cause permanent set in a heavily loaded rope. Good practice requires the use of sheaves and drums with diameters 800 times the diameter of the outer wires in the rope for heavily loaded fast-moving ropes.
It is impossible to give a definite minimum size of sheave or drum about which a wire rope will operate with satisfactory results, because of the other factors affecting the useful life of the rope. If the loads are light or the speed slow, smaller sheaves and drums can be used without causing early fatigue of the wires than if the loads are heavy or the speed is fast. Reverse bends, where a rope is bent in one direction and then in the opposite direction, cause excessive fatigue and should be avoided whenever possible. When a reverse bend is necessary larger sheaves are required than would be the case if the rope were bent in one direction only.
Stretch of Wire Rope The stretch of a wire rope under load is the result of two components: the structural stretch and the elastic stretch. Structural stretch of wire rope is caused by the lengthening of the rope lay, compression of the core and adjustment of the wires and strands to the load placed upon the wire rope. The elastic stretch is caused by elongation of the wires.
The structural stretch varies with the size of core, the lengths of lays and the construction of the rope. This stretch also varies with the loads imposed and the amount of bending to which the rope is subjected. For estimating this stretch the value of one-half percent, or .005 times the length of the rope under load, gives an approximate figure. If loads are light, one-quarter percent or .0025 times the rope length may be used. With heavy loads, this stretch may approach one percent, or .01 times the rope length.
The elastic stretch of a wire rope is directly proportional to the load and the length of rope under load, and inversely proportional to the metallic area and modulus of elasticity. This applies only to loads that do not exceed the elastic limit of a wire rope. The elastic limit of stainless steel wire rope is approximately 60% of its breaking strength and for galvanized ropes it is approximately 50%.
Preformed Wire Ropes Preformed ropes differ from the standard, or non-preformed ropes, in that the individual wires in the strands and the strands in the rope are preformed, or pre-shaped to their proper shape before they are assembled in the finished rope.
This, in turn, results in preformed wire ropes having the following characteristics:They can be cut without the seizings necessary to retain the rope structure of non-preformed ropes.
They are substantially free from liveliness and twisting tendencies. This makes installation and handling easier, and lessens the likelihood of damage to the rope from kinking or fouling. Preforming permits the more general use of Lang lay and wire core constructions.
Removal of internal stresses increase resistance to fatigue from bending. This results in increased service where ability to withstand bending is the important requirement. It also permits the use of ropes with larger outer wires, when increased wear resistance is desired.
Outer wires will wear thinner before breaking, and broken wire ends will not protrude from the rope to injure worker’s hands, to nick and distort adjacent wires, or to wear sheaves and drums. Because of the fact that broken wire ends do not porcupine, they are not as noticeable as they are in non-preformed ropes. This necessitates the use of greater care when inspecting worn preformed ropes, to determine their true condition.
Wire ropes are largely used in marine environment or for rigging purposes. They receive considerable loads and thus suffer a great deal of mechanical damage throughout their service life. Moreover, research has shown that the major cause of wire rope failure is excessive deterioration and corrosion, lack of maintenance and inspection, and wrong usage resulting in early discarding, reduced safety and replacement cost increase.
Sometimes damage can be easily detected, while in other cases fractured wires may occur on the inside. Hence, wire ropes should be inspected and maintained by the right person (competent person assigned by the company), to assure they’re in perfect condition. Regular inspectionsensure high rope performance, long service lifetime , safety of personnel and equipment, and reduced operating costs.
All ropes (synthetic, high modulus and wire ropes) should be inspected before and after an operation. This guideline ensures maximum safety for both a ship’s personnel and equipment. Even though it’s difficult to determine the exact service life span of ropes, there is a way to have a more precise estimation about their efficient lifecycle. Calculating the exact time ropes have been in use (e.g mooring time, mooring conditions, weather and tidal conditions) is the answer. All in all, rope inspections should occur at least once a year.
Inspecting wire ropes in particular, comes with great responsibility. Inspection results should be recorded, and any defects noticed have to be reported and addressed properly. Some defects can be repaired, while in some cases replacing a wire rope is inevitable.
Periodical inspections ofvessel deck equipment is also crucial for maintaining the good condition of wire ropes. The condition of the drum, chocks, bitts, rollers, sheaves, cable clamps and other end fittings, affect the rope’s performance, threads and cords. Make sure to mark these parts during your overall inspection.
In order to help marine officers and staff conduct successful wire rope inspections – and keep an up-to-date record of them – we have created an inspection solution that helps in maintaining and monitoring a ship’s ropes and deck equipment.
When calculating mass using F = Minimum Breaking Force, according to the wire rope’s diameter, you can determine the Minimum Breaking Massand therefore the wire’s max strength. When calculating mass using F = Safe Load according to the wire rope’s diameter, you can determine the Safe Load Mass,which is the advised load for this rope diameter.
The strands of a wire rope absorb the majority of the tensile force applied on the rope. Their design and manufacturing standards affect the level of fatigue resistance and resistance to abrasion. An easy way to understand which rope design is suitable for each purpose, is the wire rope classification.
Wire ropes are classified according to the number of strands in each construction and the number of wires in each strand. For example, a classification of 6X19 means that a wire rope of this type always has six strands, but its wires could be 15-26 per strand. This is because 19 is not the exact number of wires, but the classification of a wire number range.
Visual inspections are a common and fast way to assess wire rope condition. Both the standard and rotation resistant wire rope inspectionprocesscomply with the same four steps of examination. A ship’s crew can perform them as follows:
Steel wire rope distortion is obvious in most cases and can easily be identified by the inspector or the ship‘s crew. It usually occurs if load is suddenly applied or abruptly released (shock loading), or even if swift torque is forcefully induced.
Although not all of these deformations make the rope absolutely dangerous to use, they all may cause ropes to wear unevenly in time. This means inspections should take place more often, and distorted ropes should be handled with caution.
The rag and visual inspection is a good method for regular inspection intervals. The inspector pulls a rag along the rope trying to find broken wire cords. If the rug gets snagged by the rope, the inspector has to stop and assess the wire rope’s condition. Extreme caution should be exercised during the visual inspection, and under no circumstances should this method be the only one used to inspect wire ropes.
Tip: When you encounter a protruding wire end, bend it back and forth manually, until it separates from the wire. This will protect neighboring wires from wearing out.
Diameter reduction is a critical factor in steel wire rope wear and if not properly taken care of, it can result in rope breakage. Excessive abrasion, loss of core mass, corrosion or inner wire failure are all factors that contribute to diameter reduction.
To get an accurate measurement of the rope’s diameter, measure the rope at three different points at least 5 feet apart. Take the average of these three measurements to determine the true diameter.
Any measurements showing a reduction of ⅓ or more, indicate that a replacement should follow without delay. A diameter reduction of less than 1/3 still requires attention, and the inspector or the ship’s crew should be on guard in the next scheduled wire rope inspection.
Failure from abrasion or corrosion is a result of deficient deck equipment inspection or insufficient wire rope lubrication respectively. Internal corrosive damage is more difficult to identify than any other types of degradation. In most cases, the damage has progressed more than the external signs suggest.
Wire rope storage plays a significant role in the rope’s operation life.Wire rope corrosion and pitting can be avoided if ropes are safely stored in a clean, cool, dry and well-ventilated place. Steel wire ropes should not by any means rest on the floor, and should be protected from water, dust or any chemical fumes. Long term storage requires periodic greasing, turning the reel upside down for preventing grease dripping and possibly re-winding to another reel with larger inner tube diameter.
Wire ropes should be maintained with periodical lubrication. In order to prevent internal corrosion, a pressure lubricator is suggested to be used. In this case, a small amount of grease is used to lubricate the rope internally, while the deck stays grease-clean. Pressure lubricators clean the rope before they grease it so that the new grease enters a clean rope. The type of grease used is very important for maximum protection and greasing efficiency.
Steel wire ropes exposed to dirt, grime and other contaminants, have to be cleaned with a wire brush and petroleum (unless a pressure lubricator is used). Optimal cleaning of wire ropes can extend their service life and guarantee safe operations.
The reeling process is of high importance for the longevity of wire ropes. To protect them from being damaged, it is important that the surface of the drum is clean, smooth and dry. Improper reeling may cause wire-rope strands to spread or get flattened, when in contact with one another, as successive layers are being spooled and upper layers apply pressure on the lower ones.
Katradis S.A. offers a wide range of top quality wire ropes for shipping (mooring and hoisting operations), fishing and construction purposes. Our wire ropes have greater resistance to fatigue, and they distribute tension force equally among the rope strands. They are less likely to kink, providing higher staff safety and assuring operation success.
Look to Enidine for high performance Wire Rope Isolators and Compact Wire Rope Isolators. The wire rope isolators have stainless steel cable and RoHS compliant aluminum retaining bars, which provides excellent vibration isolation. The isolators are corrosion resistant, which makes them environmentally stable and high-performance in a variety of applications. The isolators are completely unaffected by oil, chemicals, abrasives, ozone, and temperature extremes.
The compact wire rope isolator is smaller than a traditional wire rope and can absorb shock and vibration in small spaces. Single point mounting offers flexibility for integration into existing products.
Both compact wire rope isolators and wire rope isolators can be used on galley components where motors and fans produce vibrations onto surrounding structures. They can also be used to control vibration and thermal expansion.




 8613371530291
8613371530291