single vs double acting hydraulic pump brands

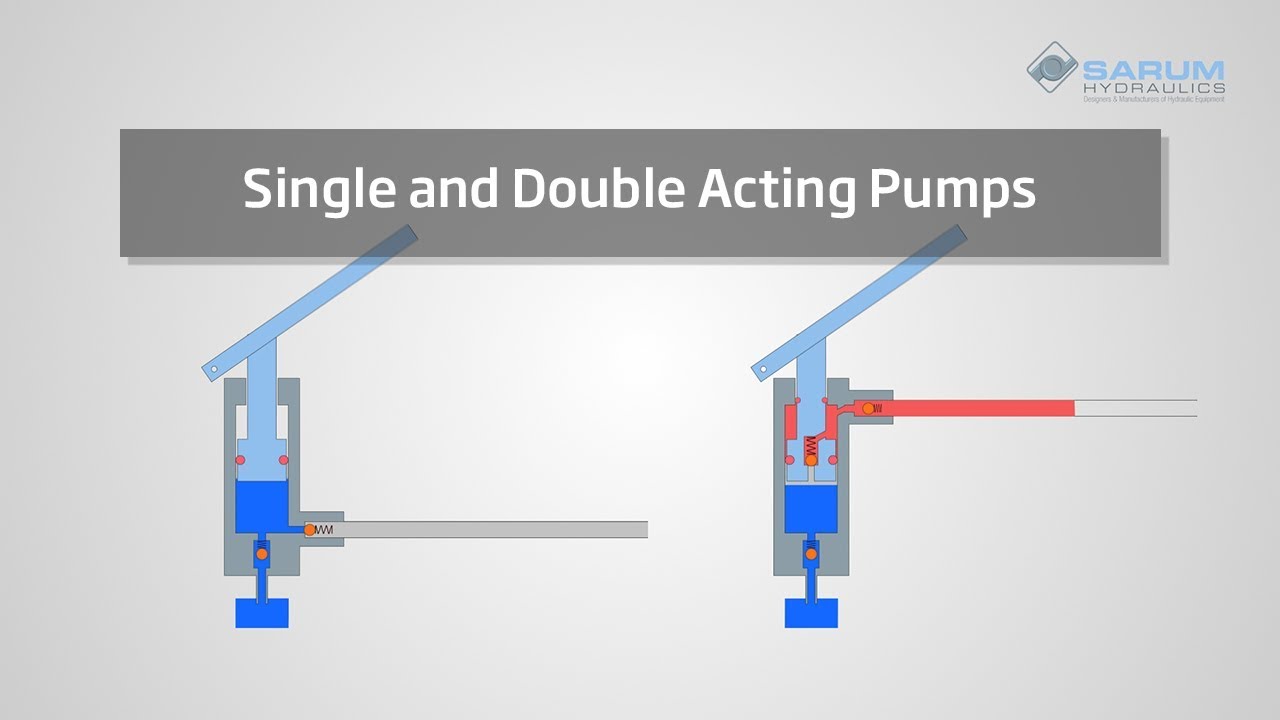
When comparing single-acting vs double-acting hydraulic cylinders, the most visible difference is the number of couplers or connection ports. A single-acting hydraulic cylinder includes just one port. This is where the hydraulic fluid enters and forces the plunger out in one direction. A double-acting cylinder includes two ports. One for the hydraulic fluid to enter and extend the plunger, and the other for retracting the cylinder.
The plunger in a single-acting hydraulic cylinder extends when hydraulic fluid under high pressure is pumped into the cylinder. When it is time to retract the cylinder, depending upon the cylinder design, the plunger can be retracted using a return spring, by the load, or simply by gravity.
In a double-acting hydraulic cylinder, the plunger retracts when hydraulic fluid is pumped under high pressure into the top port, forcing the plunger back to its original position. This can be done quickly, if required, or very gradually with precise control.
The single-acting cylinder is simpler than its double-acting counterpart. With fewer components, there is much less to go wrong, which is good news when it comes to maintenance.
Single-acting cylinders are ideal for straightforward jobs – especially when fast or controlled retraction isn’t essential. Hollow plunger versions including a thread are also available to handle pulling applications.
Double-acting hydraulic cylinders have the ability to pump hydraulic fluid to both sides of the plunger. Connection ports positioned near both ends allow the piston rod to move both forwards and backwards. The extra port also allows more control of the plunger during retraction and ensures it always returns back to its starting point.

The weight of a car is heavy, and it is very difficult to lift a car by muscle power alone, let alone to repair it while suspended in the air. This is the reason why hydraulic systems exist. When you want to work with dump trucks, RVs, boat lifts, lift gates, etc., a hydraulic pump is a must-have tool that allows you to easily complete jobs that are difficult to reach with human power. For some light work, we recommend choosing a 12 volt hydraulic pump, which is a tool of both size and power. Then before buying you"d better choose the type of hydraulic pump you need according to your needs. Next I will give you information about hydraulic pumps you should know.
A hydraulic pump is a machine that works with liquid fluid power, using an incompressible fluid, usually a derivative of petroleum and additives, as the working fluid to convert mechanical energy into hydraulic energy. Should hydraulic pumps be non-sparking due to potentially explosive environments? Keep in mind that most operating fluids are derivatives of petroleum, but there are non-sparking options available. Fluid selection should be determined by the operating environment/temperature.
This hydraulic energy can make a relatively small device very powerful and versatile. In the automotive industry, hydraulic pumps are used in combination with jacks and engine hoists to lift vehicles, platforms, heavy loads and pull engines. They can also be used in production facilities for conveyors, mixers, forklifts, etc.
Electric hydraulic pumps are generally divided into single-acting and double-acting. The most obvious difference is the number of couplers or connection ports. Single-acting hydraulic pumps include only one port. This port is where the hydraulic fluid is allowed to enter and force the plunger to extend in one direction. Double-acting hydraulic pumps have two such ports. The difference is that the first port is where the "push" (extension) hydraulic hose fitting will connect, and the second port is where the "retract" hydraulic hose fitting will connect.
When high pressure hydraulic fluid is pumped into a hydraulic pump, the plunger in the single acting hydraulic cylinder extends. When the cylinder needs to be retracted, depending on the cylinder design, the plunger is retracted by either a load weight or a built-in spring. Single-acting hydraulic pumps have fewer components and less potential for error, which facilitates maintenance of the hydraulic pump. Single-acting is ideal for this simple task when fast or controlled retraction is not required.
In a double-acting hydraulic pump, the plunger retracts as the hydraulic fluid is pumped into the top port at high pressure, forcing the plunger back to its original position. The double-acting principle of operation enables hydraulic oil to be pumped to both sides of the plunger. Connection ports located near each end allow the piston rod to move back and forth. The additional ports also allow for more fine control of the plunger during retraction. Faster and predictable retraction makes double-acting hydraulic pumps a better choice for projects requiring repeatable accuracy.
For lightweight applications, such as rear fender lifts on commercial passenger vehicles, where a low power output is required, a 12v miniature hydraulic power unit is a good choice because the 12v motor can be connected to a standard vehicle circuit for the rear fender lift function. There are other application scenarios such as dump trucks, RVs, boat lifts, lift gates, trailers, clearance trucks, car porters, agricultural equipment, snow plow equipment, and a variety of other applications that require powerful and compact hydraulic pumps.

Hydraulic cylinders provide the unidirectional force required to power your industrial equipment for heavy lifting. Telescopic hydraulic cylinders, which are ideal for dump trailers and platform truck trailers, give the extended stroke lengths required for a range of versatile purposes. When purchasing telescopic hydraulic cylinders, consumers are frequently faced with the decision between single-acting and double-acting hydraulic cylinders. Learn what distinguishes the two types of telescopic cylinders to determine which cylinder is appropriate for your high-power hydraulic requirements.
The hydraulic cylinder is the industrial world’s workhorse. Learn about the benefits and drawbacks of single and double-acting hydraulic cylinders. The function of your cylinder decides whether you should choose a single-acting or double-acting hydraulic cylinder.
Single-acting cylinders generate force exclusively in one direction, whether it is a push or pull action. These are also referred to as “plunger” cylinders. They are utilized in lifting operations where hydraulic pump pressure stretches the hydraulic cylinder and a mass or spring retracts it. Single-acting cylinders contain only one port through which the hydraulic pump’s pressurized oil passes. This causes the piston to extend in one direction, compressing the piston’s spring. After releasing the air via the cylinder port where it entered, the spring or associated mass will retract the piston rod.
Single-acting cylinders are classified into two types: push and pull cylinders. The push-type, as the name implies, will allow the air entering to push the piston out of the cylinder. The pull-type hydraulic cylinder allows the oil entering the cylinder to pull the piston inside the cylinder. For one-way linear movement, single-acting cylinders are ideal. They are commonly seen in hydraulic jacks and forklifts.
The lower manufacture, installation, and repair costs of single-acting hydraulic cylinders are an advantage. With only one port to operate instead of two, both piping and valve costs are significantly reduced.
The spring mechanism in single-action cylinder interiors necessitates venting, which provides the unit with an outlet to the outside world. Particles, on the other hand, can enter the cylinder and create potential malfunctions or a slow loss in performance if not adequately monitored.
Single-acting hydraulic cylinders are ideal for use with smaller equipment due to their single port and compact structure. Most of the time, if a smaller equipment design allows for ports, fluid transmission, and venting, then this cylinder will be extremely suitable.
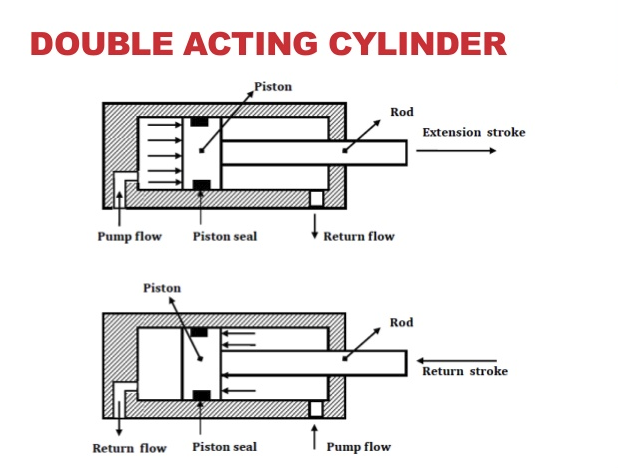
Pressure flows from two ports in double-acting hydraulic cylinders. The “advance” hydraulic hose fitting connects to one of the ports. The pump’s hydraulic power forces the cylinder to extend via the first port. The “retract” hydraulic hose fitting is connected to the second port. Hydraulic power is used to extend and retract the cylinder in a double-acting hydraulic cylinder. In contrast to the single-acting cylinder, which produces force in only one direction, force is generated in both directions. As a result, the cylinder may both push and pull.
The piston rod moves due to the push and pulls forces created by the pressurized fluid that alternates between both sides of the piston. These hydraulic cylinders have more control over their movement in the application where they are installed. Using 2-, 3-, or 4-way position valves, different levels of movement can be produced. Double-acting hydraulic cylinders are utilized in mobile applications such as a TLB’s boom or to control the steering of an excavator.
Though this hydraulic cylinder is not appropriate for small places, double-acting hydraulics are extremely versatile. Two ports provide hydraulic power in both directions and are readily operated with a push-and-pull motion. As a result, they are the most popular hydraulic cylinder.
Unlike single-acting variants, double-acting cylinders are sealed from the outside world. As a consequence, you will not require repairs as a result of particles invading inside pipes and valves.
Precision work that needs hydraulic pistons to stop at specific lengths regularly can stretch and deform the hydraulics over time. However, double-acting hydraulic cylinders are constructed with exact, very precise dual ports, enhancing the product’s longevity.
The choice between a double-acting and a single-acting cylinder is frequently a matter of control. How precisely do you need to be while exerting force in your hydraulic system? A single-acting cylinder may be sufficient if you need to produce a large force to move a load in a single direction, such as in heavy lifting applications. However, if you need to direct a load in two directions or have more control over the cylinder’s movements, a double-acting cylinder will provide you with more control.

There’s been some confusion as to how to configure and use either system effectively without causing damage to the equipment, load, or to the user. Some of this confusion results from misunderstanding the difference between single-acting or double-acting cylinders and being unsure of when either should be used. Hopefully, we can clear the air in this department.
A pump, a hose, and a cylinder round out the basic setup of a hydraulic system, often times referred to as a port-a power. Without each of these components, this system cannot be operated at all.
A single-acting cylinder is one in which the hydraulic fluid performs on just one side of the piston only. Since hydraulic oil does not compress, when applying force via a hand, electric or gas powered pump, the piston rod of the cylinder will extend. More specifically, the pump forces oil into the hose which flows into the bottom connection port of the cylinder, resulting in the ability for pushing, tensioning or jacking applications. The single-acting pump and cylinder are both equipped with one connection port at the lower portion of the cylinder body, for the oil to both advance the piston rod, and when retracting it, allow the oil to flow back into the reservoir of the pump. Many of the single-acting cylinders have springs built in to assist in the retraction process, but if not, they may be a bit more challenging to retract. The pump that you select also plays a role in the retraction process. Some manufacturers have pumps that will pull the oil back into it, rather than allow it to just flow back into the reservoir. The last consideration in selecting either single or double-acting, is whether the cylinder is considered a load-return type. Meaning, that in order for retraction to occur, the load, or a significant force is required, in addition to the pump for it to retract completely. So be careful, if you have an application that requires several complete stroke cycles, such as a jack and crib operation, you will likely want a double-acting cylinder for that task. Most single-acting cylinders are more commonly-used in light industrial and commercial applications. This of course is not an exclusive list, but the majority of single-acting cylinders in use today tend to be on the lower end of the capacity spectrum.
On the other hand, the double-acting cylinder is one in which the hydraulic fluid performs on both sides of an apron portion of the piston. The double-acting pump and cylinder are both equipped with two connection ports; one at the lower portion, the other at the top portion of the cylinder body. This system requires hoses for each port. When advancing the piston rod, oil flows in through the lower connection port. When you have achieved your desired pressure or stroke requirements, putting the pump in the neutral position will hold the cylinder at that resting point, until it is time to either continuing to advance, or when you would begin retracting operations. Double-acting cylinders are more commonly-used in heavy industrial and construction applications, such as lifting bridges to perform bearing maintenance. The majority of double-acting cylinders in use today tend to be on the higher end of the capacity spectrum.

In a single acting hydraulic cylinder, the fluid applies pressure only on a single side of the piston. Because the hydraulic fluid is oil, it does not compress. This means that whenever a force is applied either through your hands, or a gas or electric pump, the cylinder shaft will extend. The oil is pumped by the force into the cylinder’s bottom port, allowing for jacking, pushing, and tensioning applications.
Single acting cylinders have a connection port at the bottom part allowing the hydraulic oil to push the piston rod which flows back to its original position during retraction. Some single acting cylinders have a mechanism to allow the oil to flow back automatically whereas other cylinders redirect it into the reservoir.
The advantages of using a single acting hydraulic cylinder lie in its ruggedness and simplicity. They are easier to maintain and with only one-directional force being applied, the piston rod is retracted with the help of a spring or external force. They are commonly used in light commercial and industrial applications.
In a double acting hydraulic cylinder, the hydraulic fluid is used to apply pressure on both sides of the piston rod. This allows for both extension and retraction without the aid of a spring or external force.
This type of cylinder has two connection ports (and so does the pump), one at the top and the other at the bottom of the cylinder’s body. By connecting hoses to both ports, the hydraulic fluid applies the desired stroke or pressure from the lower end of the cylinder. When the required pressure is achieved, the pump goes into a neutral position, holding the cylinder in place. Likewise, the pump generates the optimum pressure to pull back the extension and cause the rod to collapse back into its pre-extended phase.
The double acting cylinders strength lies in its control and maneuverability. Each cylinder has its own unique strengths and benefits based on the type of operations.
Whether it is single acting or double acting, we manufacture a wide range of custom built hydraulic cylinders based entirely on your specifications. Contact us now to place your order and obtain the highest quality hydraulic cylinders in the market.
... two stage hydraulic hand pumps, easy to handle and use, with very high oil flow rates to operate a wide range of hydraulic cylinders or equipment.
... pneumohydraulic pumps that are compact and easy-to-use. It has a standard reservoir of 2.5L in plastic, and 5 or 10L in steel. The pump can be attached with a threaded G¼" fitting to ...
A compact lightweight pump, the Power Team 60 series is designed for rugged applications and low voltage starting. Experiencing a long, trouble-free life in the most demanding work environments, the 60 ...
... hand pumps come in a variety of configurations to meet the requirements of your application. Along with various oil capacities and flow rates, you can choose from the following options:
... lightweight and portable the Power Team PA6D series pumps are single-speed pumps for driving double-acting cylinders. The PA6D series pumps operate at ...
... : industrial tools, lifting systems, car repair, clamping systems, hydraulic equipment (presses, jacks, …), tire changers, bead breakers, automotive.
The HP-AP pump, like all HP Series pumps, can be installed in any hydraulic applications which requires high working pressures and moderate and controllable oil flow. Our HP Series air-hydraulic ...
... this, PN pumps are extremely handy and stand out due to a very low effort on their handle. The practical pedal locking hook allows to use the lever as a handle during transport by holding it in the correct position in ...
... pneumohydraulic pump incorporates a double-acting pneumatic motor. The pump operates on compressed air with 2 to 7 bar pressure for construction of circuits that demand ...
... for use with either single or double acting cylinders and tools. The HP range offers the ideal solution for applications where completely independent, portable hydraulic power is required. ...
Double-acting, single-stage air-powered compact pump. Standard with a 3/8” NPT female thread and compressed air connector. Excluding coupler, hoses and pressure gauge.
the hydraulic single-port hand-pump range is tailored for use with Equalizer international hydraulic equipment. Certified for use in the hazardous areas ll 2 G ex h T5 GB llB, ll 2D ex ...
Air hydraulic pumps, working pressure 700 bar, using a pressure multiplicator. Recommanded solution to replace hand pumps. For single and double acting ...

There are several sections you can look at within hydraulic cylinders that would allow you to tell them apart. We’re here to help you figure out which is which and get the most out of your components.
These hydraulic cylinders have only one port available for the user to connect hydraulic cylinders or hose fittings to. As a result of there being the single port, this is also where the hydraulic fluid enters the system which then extends the rod due to the area difference. To return the piston rod an external force or gravity function is used.
Single acting cylinders are simpler than their double counterparts and require less maintenance throughout their life, due to their actions being determined by the pressure only being on one line.
Double acting hydraulic cylinders have two separate ports. The first port is where advanced (extending) hydraulic hose fittings will be attached to the cylinder. Whereas the second port is where the retracting hydraulic hose fittings are attached. In this case hydraulic fluid is supplied for both the retraction and extension actions within the hydraulic cylinder, so to return the piston rod an external force is not needed.
With the double acting cylinder the user needs to have full control of the mechanism as the component is moving in two separate directions without the need for manual returns on the piston rod. This means that the hydraulic cylinder needs to be checked regularly and monitored more closely than the single acting cylinder.
For those needing to eject parts off of a conveyor belt then the single acting cylinder could be for you. Need speed and force? Then the double acting cylinder would be better suited for the application you have in mind.
If you are still unsure about which cylinder is the best one for you, then get in contact with our expert team. They’ll offer technical advice and even find you the perfect hydraulic cylinder for you today!

Premium Supply is the leader in tilt and hydraulic dump trailer build products. We specialize in trailer hoists, hydraulic pumps & accessories, hydraulic cylinders, and top quality battery maintenance products. When you shop from Premium Supply, you can be sure that you’re getting top quality products and exemplary customer service.
People prefer them for some of their advantages: no requirement for compressed air, electricity, or hydrostatic flow. Those pumps can be used anywhere, provided that there is somebody that can work with the handle. You can leverage the power of hand pumps while lifting a heavy load and feel like a superman. This is accomplished by transforming mechanical energy into fluid energy. In this way, manual hand pumps differ from pneumatic hand pumps, as the latter generates air pressure instead of non-compressible fluid.
Hydraulic hand pumps are suitable for work where you would need up to 10,000 of pressure. Manual hand pumps are perfect for fieldwork since they are easy to carry and don’t require electric power. They are ideal for places where flammable liquid or gas is present, as they don’t need any electrical power.
When you buy any product, you look for some characteristics according to your needs. This is also the case for hydraulic hand pumps. Here are the top three reasons to choose them:In transferring energy from one form to another, efficiency is crucial. By simply moving the handle, you can move a heavy load.
If you want to achieve an accurate result, manual hand pumps are products you should be seeking. They are engineered to have the highest degree of precision and apply pressure of 10,000 PSI.
During the production process, any stability issues are resolved and maintained accordingly. Therefore, stability is the nature of hydraulic hand pumps.
Magister Hydraulics already has all of those mentioned above. A responsible company with a reliable crew that has the privilege of owning an ISO 9001:2015 certificate. To keep up with the requirements of the certificate, we are delivering high-quality products. All of our products are shipped via FedEx within one business day. We can accomplish this as we have storage facilities all over the USA.

There are two most commonly used types of hydraulic cylinder: single acting and double acting cylinders. One type of cylinder is not innately better than the other and the decision is not normally an either/or choice.
Rather, both single and double acting cylinders have their uses and applications where they are better suited than the other type. In this article we take a brief look at each type, explaining how they work and the applications they are found in.
In a single acting hydraulic cylinder, fluid pressure is exerted on one side of the piston only, so that the piston rod acts like a hydraulic ram, pushing outwards but not pulling back on the retract movement. These cylinders need an external force to retract the piston rod, such as a pump, motor or set of internal springs.
While high quality single acting hydraulic cylinders are reliable units, those equipped with retractable springs are vulnerable to component failure as the springs wear out. This manifests as a gradual reduction in force on the retract movement. They are also more difficult to seal and can become damaged over time through exposure to corrosive fluids.
A double acting cylinder is capable of pressure being exerted on either side of the piston alternatively. This means that both outward and retraction movements can be achieved under the cylinder’s own pressure without an external source of power. This can be used simply to return the piston to its starting position, or to apply an alternating force on both sides of the cylinder – for instance to operate a crankshaft.
The decision between a double acting or single acting cylinder often boils down to one of control. How much precision is required when exerting force in your hydraulic system? If you need to exert a large force to move a load in a single direction – e.g. for heavy lifting applications – a single acting cylinder may be sufficient. However, if you need to direct a load in two directions or have greater flexibility over the movements of the cylinder, a double acting cylinder will give you more control.
We have a range of single acting and double acting hydraulic cylinders available for immediate dispatch from our extensive stock. Click here to check our current availability. For questions and product enquiries, please call 01299 896953.

Double-acting hydraulic cylinders have pressure flowing from two ports. One of the ports is where the “advance” hydraulic hose fitting connects to. The hydraulic power of the pump causes the cylinder to extend through that first port. Attached to the second port is the “retract” hydraulic hose fitting. The double-acting hydraulic cylinder uses hydraulic power to extend and retract the cylinder. Force is generated in both directions, unlike the single-acting cylinder that produces force in only one direction. This gives the cylinder the ability to both push and pull.
Pressurised fluid alternates between both sides of the piston, creating the push and pull forces that move the piston rod. The application in which these hydraulic cylinders are installed has more control over its movement. Different levels of movement are achieved by using 2-, 3-, or 4-way position valves. Double-acting hydraulic cylinders are used in mobile applications like the boom of a TLB or to control the steering in an excavator.

1/2 hp pump, continuous duty with 2 gallon thermoplastic reservoir, 9500 double-acting valve. The 17 series hydraulic pumps are designed to have a maximum of 690 bar (10,000 psi) at a flow rate of 278 cc/min (17 cu. in/min).

Ningbo Target Hydraulics is your reliable hydraulic components supplier. We offer you high-quality dc12v hydraulic pump single acting and double acting. There are many different industrial applications for hydraulic pump unit systems.
dc12v hydraulic pump motor combo is the most common electrical hydraulic pump system. They come with dc motor, hydraulic gear pump, and some other hydraulic components such as a hydraulic oil tank ,hydraulic manifold blocks, some hydraulic valves.
Hydraulic AC power packs are widely used in industrial applications. They are designed with AC voltage electric power supply, so, they can work with AC motors. Some of them are designed with standard B14 flange mounted AC motors, It is easy to find flange type AC motors from your local market.
Dump trailers and forklifts are very common applications of DC12 voltage hydraulic pumps. Most of them are designed and manufactured with single-acting hydraulic pump schematics. They work Power up/gravity down.
DC voltage hydraulic pump packs are designed for mobile hydraulic applications. So, they are also called mobile hydraulic power packs. Some of them are double acting hydraulic pumps, Power Up/power down hydraulic systems.Some of others are single acting,power up/gravity down hydraulic pumps.
Target Hydraulics products are used in different hydraulic applications. Electric dump pump is the most popular application. They complete with a dc motor, hydra-gear pump, and some valves that are assembly in center hydraulic block manifolds, also a button remote and cable.
DC hydraulic pumps are most work with mobile hydraulic applications, so, the mounting size is very compact. That is why compact size power packs are designed with such small sizes. They are designed and manufactured for mini and compact mounting size.
Our hydraulic cartridge valves and hydraulic valve manifold blocks are widely used in DC hydraulic power units, AC hydraulic power units, and hydraulic manifold designs.

Hydraulic pumps are mechanisms in hydraulic systems that move hydraulic fluid from point to point initiating the production of hydraulic power. Hydraulic pumps are sometimes incorrectly referred to as “hydrolic” pumps.
They are an important device overall in the hydraulics field, a special kind of power transmission which controls the energy which moving fluids transmit while under pressure and change into mechanical energy. Other kinds of pumps utilized to transmit hydraulic fluids could also be referred to as hydraulic pumps. There is a wide range of contexts in which hydraulic systems are applied, hence they are very important in many commercial, industrial, and consumer utilities.
“Power transmission” alludes to the complete procedure of technologically changing energy into a beneficial form for practical applications. Mechanical power, electrical power, and fluid power are the three major branches that make up the power transmission field. Fluid power covers the usage of moving gas and moving fluids for the transmission of power. Hydraulics are then considered as a sub category of fluid power that focuses on fluid use in opposition to gas use. The other fluid power field is known as pneumatics and it’s focused on the storage and release of energy with compressed gas.
"Pascal"s Law" applies to confined liquids. Thus, in order for liquids to act hydraulically, they must be contained within a system. A hydraulic power pack or hydraulic power unit is a confined mechanical system that utilizes liquid hydraulically. Despite the fact that specific operating systems vary, all hydraulic power units share the same basic components. A reservoir, valves, a piping/tubing system, a pump, and actuators are examples of these components. Similarly, despite their versatility and adaptability, these mechanisms work together in related operating processes at the heart of all hydraulic power packs.
The hydraulic reservoir"s function is to hold a volume of liquid, transfer heat from the system, permit solid pollutants to settle, and aid in releasing moisture and air from the liquid.
Mechanical energy is changed to hydraulic energy by the hydraulic pump. This is accomplished through the movement of liquid, which serves as the transmission medium. All hydraulic pumps operate on the same basic principle of dispensing fluid volume against a resistive load or pressure.
Hydraulic valves are utilized to start, stop, and direct liquid flow in a system. Hydraulic valves are made of spools or poppets and can be actuated hydraulically, pneumatically, manually, electrically, or mechanically.
The end result of Pascal"s law is hydraulic actuators. This is the point at which hydraulic energy is transformed back to mechanical energy. This can be accomplished by using a hydraulic cylinder to transform hydraulic energy into linear movement and work or a hydraulic motor to transform hydraulic energy into rotational motion and work. Hydraulic motors and hydraulic cylinders, like hydraulic pumps, have various subtypes, each meant for specific design use.
The essence of hydraulics can be found in a fundamental physical fact: fluids are incompressible. (As a result, fluids more closely resemble solids than compressible gasses) The incompressible essence of fluid allows it to transfer force and speed very efficiently. This fact is summed up by a variant of "Pascal"s Principle," which states that virtually all pressure enforced on any part of a fluid is transferred to every other part of the fluid. This scientific principle states, in other words, that pressure applied to a fluid transmits equally in all directions.
Furthermore, the force transferred through a fluid has the ability to multiply as it moves. In a slightly more abstract sense, because fluids are incompressible, pressurized fluids should keep a consistent pressure just as they move. Pressure is defined mathematically as a force acting per particular area unit (P = F/A). A simplified version of this equation shows that force is the product of area and pressure (F = P x A). Thus, by varying the size or area of various parts inside a hydraulic system, the force acting inside the pump can be adjusted accordingly (to either greater or lesser). The need for pressure to remain constant is what causes force and area to mirror each other (on the basis of either shrinking or growing). A hydraulic system with a piston five times larger than a second piston can demonstrate this force-area relationship. When a force (e.g., 50lbs) is exerted on the smaller piston, it is multiplied by five (e.g., 250 lbs) and transmitted to the larger piston via the hydraulic system.
Hydraulics is built on fluids’ chemical properties and the physical relationship between pressure, area, and force. Overall, hydraulic applications allow human operators to generate and exert immense mechanical force with little to no physical effort. Within hydraulic systems, both oil and water are used to transmit power. The use of oil, on the other hand, is far more common, owing in part to its extremely incompressible nature.
Pressure relief valves prevent excess pressure by regulating the actuators’ output and redirecting liquid back to the reservoir when necessary. Directional control valves are used to change the size and direction of hydraulic fluid flow.
While hydraulic power transmission is remarkably useful in a wide range of professional applications, relying solely on one type of power transmission is generally unwise. On the contrary, the most efficient strategy is to combine a wide range of power transmissions (pneumatic, hydraulic, mechanical, and electrical). As a result, hydraulic systems must be carefully embedded into an overall power transmission strategy for the specific commercial application. It is necessary to invest in locating trustworthy and skilled hydraulic manufacturers/suppliers who can aid in the development and implementation of an overall hydraulic strategy.
The intended use of a hydraulic pump must be considered when selecting a specific type. This is significant because some pumps may only perform one function, whereas others allow for greater flexibility.
The pump"s material composition must also be considered in the application context. The cylinders, pistons, and gears are frequently made of long-lasting materials like aluminum, stainless steel, or steel that can withstand the continuous wear of repeated pumping. The materials must be able to withstand not only the process but also the hydraulic fluids. Composite fluids frequently contain oils, polyalkylene glycols, esters, butanol, and corrosion inhibitors (though water is used in some instances). The operating temperature, flash point, and viscosity of these fluids differ.
In addition to material, manufacturers must compare hydraulic pump operating specifications to make sure that intended utilization does not exceed pump abilities. The many variables in hydraulic pump functionality include maximum operating pressure, continuous operating pressure, horsepower, operating speed, power source, pump weight, and maximum fluid flow. Standard measurements like length, rod extension, and diameter should be compared as well. Because hydraulic pumps are used in lifts, cranes, motors, and other heavy machinery, they must meet strict operating specifications.
It is critical to recall that the overall power generated by any hydraulic drive system is influenced by various inefficiencies that must be considered in order to get the most out of the system. The presence of air bubbles within a hydraulic drive, for example, is known for changing the direction of the energy flow inside the system (since energy is wasted on the way to the actuators on bubble compression). Using a hydraulic drive system requires identifying shortfalls and selecting the best parts to mitigate their effects. A hydraulic pump is the "generator" side of a hydraulic system that initiates the hydraulic procedure (as opposed to the "actuator" side that completes the hydraulic procedure). Regardless of disparities, all hydraulic pumps are responsible for displacing liquid volume and transporting it to the actuator(s) from the reservoir via the tubing system. Some form of internal combustion system typically powers pumps.
While the operation of hydraulic pumps is normally the same, these mechanisms can be split into basic categories. There are two types of hydraulic pumps to consider: gear pumps and piston pumps. Radial and axial piston pumps are types of piston pumps. Axial pumps produce linear motion, whereas radial pumps can produce rotary motion. The gear pump category is further subdivided into external gear pumps and internal gear pumps.
Each type of hydraulic pump, regardless of piston or gear, is either double-action or single-action. Single-action pumps can only pull, push, or lift in one direction, while double-action pumps can pull, push, or lift in multiple directions.
Vane pumps are positive displacement pumps that maintain a constant flow rate under varying pressures. It is a pump that self-primes. It is referred to as a "vane pump" because the effect of the vane pressurizes the liquid.
This pump has a variable number of vanes mounted onto a rotor that rotates within the cavity. These vanes may be variable in length and tensioned to maintain contact with the wall while the pump draws power. The pump also features a pressure relief valve, which prevents pressure rise inside the pump from damaging it.
Internal gear pumps and external gear pumps are the two main types of hydraulic gear pumps. Pumps with external gears have two spur gears, the spurs of which are all externally arranged. Internal gear pumps also feature two spur gears, and the spurs of both gears are internally arranged, with one gear spinning around inside the other.
Both types of gear pumps deliver a consistent amount of liquid with each spinning of the gears. Hydraulic gear pumps are popular due to their versatility, effectiveness, and fairly simple design. Furthermore, because they are obtainable in a variety of configurations, they can be used in a wide range of consumer, industrial, and commercial product contexts.
Hydraulic ram pumps are cyclic machines that use water power, also referred to as hydropower, to transport water to a higher level than its original source. This hydraulic pump type is powered solely by the momentum of moving or falling water.
Ram pumps are a common type of hydraulic pump, especially among other types of hydraulic water pumps. Hydraulic ram pumps are utilized to move the water in the waste management, agricultural, sewage, plumbing, manufacturing, and engineering industries, though only about ten percent of the water utilized to run the pump gets to the planned end point.
Despite this disadvantage, using hydropower instead of an external energy source to power this kind of pump makes it a prominent choice in developing countries where the availability of the fuel and electricity required to energize motorized pumps is limited. The use of hydropower also reduces energy consumption for industrial factories and plants significantly. Having only two moving parts is another advantage of the hydraulic ram, making installation fairly simple in areas with free falling or flowing water. The water amount and the rate at which it falls have an important effect on the pump"s success. It is critical to keep this in mind when choosing a location for a pump and a water source. Length, size, diameter, minimum and maximum flow rates, and speed of operation are all important factors to consider.
Hydraulic water pumps are machines that move water from one location to another. Because water pumps are used in so many different applications, there are numerous hydraulic water pump variations.
Water pumps are useful in a variety of situations. Hydraulic pumps can be used to direct water where it is needed in industry, where water is often an ingredient in an industrial process or product. Water pumps are essential in supplying water to people in homes, particularly in rural residences that are not linked to a large sewage circuit. Water pumps are required in commercial settings to transport water to the upper floors of high rise buildings. Hydraulic water pumps in all of these situations could be powered by fuel, electricity, or even by hand, as is the situation with hydraulic hand pumps.
Water pumps in developed economies are typically automated and powered by electricity. Alternative pumping tools are frequently used in developing economies where dependable and cost effective sources of electricity and fuel are scarce. Hydraulic ram pumps, for example, can deliver water to remote locations without the use of electricity or fuel. These pumps rely solely on a moving stream of water’s force and a properly configured number of valves, tubes, and compression chambers.
Electric hydraulic pumps are hydraulic liquid transmission machines that use electricity to operate. They are frequently used to transfer hydraulic liquid from a reservoir to an actuator, like a hydraulic cylinder. These actuation mechanisms are an essential component of a wide range of hydraulic machinery.
There are several different types of hydraulic pumps, but the defining feature of each type is the use of pressurized fluids to accomplish a job. The natural characteristics of water, for example, are harnessed in the particular instance of hydraulic water pumps to transport water from one location to another. Hydraulic gear pumps and hydraulic piston pumps work in the same way to help actuate the motion of a piston in a mechanical system.
Despite the fact that there are numerous varieties of each of these pump mechanisms, all of them are powered by electricity. In such instances, an electric current flows through the motor, which turns impellers or other devices inside the pump system to create pressure differences; these differential pressure levels enable fluids to flow through the pump. Pump systems of this type can be utilized to direct hydraulic liquid to industrial machines such as commercial equipment like elevators or excavators.
Hydraulic hand pumps are fluid transmission machines that utilize the mechanical force generated by a manually operated actuator. A manually operated actuator could be a lever, a toggle, a handle, or any of a variety of other parts. Hydraulic hand pumps are utilized for hydraulic fluid distribution, water pumping, and various other applications.
Hydraulic hand pumps may be utilized for a variety of tasks, including hydraulic liquid direction to circuits in helicopters and other aircraft, instrument calibration, and piston actuation in hydraulic cylinders. Hydraulic hand pumps of this type use manual power to put hydraulic fluids under pressure. They can be utilized to test the pressure in a variety of devices such as hoses, pipes, valves, sprinklers, and heat exchangers systems. Hand pumps are extraordinarily simple to use.
Each hydraulic hand pump has a lever or other actuation handle linked to the pump that, when pulled and pushed, causes the hydraulic liquid in the pump"s system to be depressurized or pressurized. This action, in the instance of a hydraulic machine, provides power to the devices to which the pump is attached. The actuation of a water pump causes the liquid to be pulled from its source and transferred to another location. Hydraulic hand pumps will remain relevant as long as hydraulics are used in the commerce industry, owing to their simplicity and easy usage.
12V hydraulic pumps are hydraulic power devices that operate on 12 volts DC supplied by a battery or motor. These are specially designed processes that, like all hydraulic pumps, are applied in commercial, industrial, and consumer places to convert kinetic energy into beneficial mechanical energy through pressurized viscous liquids. This converted energy is put to use in a variety of industries.
Hydraulic pumps are commonly used to pull, push, and lift heavy loads in motorized and vehicle machines. Hydraulic water pumps may also be powered by 12V batteries and are used to move water out of or into the desired location. These electric hydraulic pumps are common since they run on small batteries, allowing for ease of portability. Such portability is sometimes required in waste removal systems and vehiclies. In addition to portable and compact models, options include variable amp hour productions, rechargeable battery pumps, and variable weights.
While non rechargeable alkaline 12V hydraulic pumps are used, rechargeable ones are much more common because they enable a continuous flow. More considerations include minimum discharge flow, maximum discharge pressure, discharge size, and inlet size. As 12V batteries are able to pump up to 150 feet from the ground, it is imperative to choose the right pump for a given use.
Air hydraulic pumps are hydraulic power devices that use compressed air to stimulate a pump mechanism, generating useful energy from a pressurized liquid. These devices are also known as pneumatic hydraulic pumps and are applied in a variety of industries to assist in the lifting of heavy loads and transportation of materials with minimal initial force.
Air pumps, like all hydraulic pumps, begin with the same components. The hydraulic liquids, which are typically oil or water-based composites, require the use of a reservoir. The fluid is moved from the storage tank to the hydraulic cylinder via hoses or tubes connected to this reservoir. The hydraulic cylinder houses a piston system and two valves. A hydraulic fluid intake valve allows hydraulic liquid to enter and then traps it by closing. The discharge valve is the point at which the high pressure fluid stream is released. Air hydraulic pumps have a linked air cylinder in addition to the hydraulic cylinder enclosing one end of the piston.
The protruding end of the piston is acted upon by a compressed air compressor or air in the cylinder. When the air cylinder is empty, a spring system in the hydraulic cylinder pushes the piston out. This makes a vacuum, which sucks fluid from the reservoir into the hydraulic cylinder. When the air compressor is under pressure, it engages the piston and pushes it deeper into the hydraulic cylinder and compresses the liquids. This pumping action is repeated until the hydraulic cylinder pressure is high enough to forcibly push fluid out through the discharge check valve. In some instances, this is connected to a nozzle and hoses, with the important part being the pressurized stream. Other uses apply the energy of this stream to pull, lift, and push heavy loads.
Hydraulic piston pumps transfer hydraulic liquids through a cylinder using plunger-like equipment to successfully raise the pressure for a machine, enabling it to pull, lift, and push heavy loads. This type of hydraulic pump is the power source for heavy-duty machines like excavators, backhoes, loaders, diggers, and cranes. Piston pumps are used in a variety of industries, including automotive, aeronautics, power generation, military, marine, and manufacturing, to mention a few.
Hydraulic piston pumps are common due to their capability to enhance energy usage productivity. A hydraulic hand pump energized by a hand or foot pedal can convert a force of 4.5 pounds into a load-moving force of 100 pounds. Electric hydraulic pumps can attain pressure reaching 4,000 PSI. Because capacities vary so much, the desired usage pump must be carefully considered. Several other factors must also be considered. Standard and custom configurations of operating speeds, task-specific power sources, pump weights, and maximum fluid flows are widely available. Measurements such as rod extension length, diameter, width, and height should also be considered, particularly when a hydraulic piston pump is to be installed in place of a current hydraulic piston pump.
Hydraulic clutch pumps are mechanisms that include a clutch assembly and a pump that enables the user to apply the necessary pressure to disengage or engage the clutch mechanism. Hydraulic clutches are crafted to either link two shafts and lock them together to rotate at the same speed or detach the shafts and allow them to rotate at different speeds as needed to decelerate or shift gears.
Hydraulic pumps change hydraulic energy to mechanical energy. Hydraulic pumps are particularly designed machines utilized in commercial, industrial, and residential areas to generate useful energy from different viscous liquids pressurization. Hydraulic pumps are exceptionally simple yet effective machines for moving fluids. "Hydraulic" is actually often misspelled as "Hydralic". Hydraulic pumps depend on the energy provided by hydraulic cylinders to power different machines and mechanisms.
There are several different types of hydraulic pumps, and all hydraulic pumps can be split into two primary categories. The first category includes hydraulic pumps that function without the assistance of auxiliary power sources such as electric motors and gas. These hydraulic pump types can use the kinetic energy of a fluid to transfer it from one location to another. These pumps are commonly called ram pumps. Hydraulic hand pumps are never regarded as ram pumps, despite the fact that their operating principles are similar.
The construction, excavation, automotive manufacturing, agriculture, manufacturing, and defense contracting industries are just a few examples of operations that apply hydraulics power in normal, daily procedures. Since hydraulics usage is so prevalent, hydraulic pumps are unsurprisingly used in a wide range of machines and industries. Pumps serve the same basic function in all contexts where hydraulic machinery is used: they transport hydraulic fluid from one location to another in order to generate hydraulic energy and pressure (together with the actuators).
Elevators, automotive brakes, automotive lifts, cranes, airplane flaps, shock absorbers, log splitters, motorboat steering systems, garage jacks and other products use hydraulic pumps. The most common application of hydraulic pumps in construction sites is in big hydraulic machines and different types of "off-highway" equipment such as excavators, dumpers, diggers, and so on. Hydraulic systems are used in other settings, such as offshore work areas and factories, to power heavy machinery, cut and bend material, move heavy equipment, and so on.
Fluid’s incompressible nature in hydraulic systems allows an operator to make and apply mechanical power in an effective and efficient way. Practically all force created in a hydraulic system is applied to the intended target.
Because of the relationship between area, pressure, and force (F = P x A), modifying the force of a hydraulic system is as simple as changing the size of its components.
Hydraulic systems can transfer energy on an equal level with many mechanical and electrical systems while being significantly simpler in general. A hydraulic system, for example, can easily generate linear motion. On the contrary, most electrical and mechanical power systems need an intermediate mechanical step to convert rotational motion to linear motion.
Hydraulic systems are typically smaller than their mechanical and electrical counterparts while producing equivalents amounts of power, providing the benefit of saving physical space.
Hydraulic systems can be used in a wide range of physical settings due to their basic design (a pump attached to actuators via some kind of piping system). Hydraulic systems could also be utilized in environments where electrical systems would be impractical (for example underwater).
By removing electrical safety hazards, using hydraulic systems instead of electrical power transmission improves relative safety (for example explosions, electric shock).
The amount of power that hydraulic pumps can generate is a significant, distinct advantage. In certain cases, a hydraulic pump could generate ten times the power of an electrical counterpart. Some hydraulic pumps (for example, piston pumps) cost more than the ordinary hydraulic component. These drawbacks, however, can be mitigated by the pump"s power and efficiency. Despite their relatively high cost, piston pumps are treasured for their strength and capability to transmit very viscous fluids.
Handling hydraulic liquids is messy, and repairing leaks in a hydraulic pump can be difficult. Hydraulic liquid that leaks in hot areas may catch fire. Hydraulic lines that burst may cause serious injuries. Hydraulic liquids are corrosive as well, though some are less so than others. Hydraulic systems need frequent and intense maintenance. Parts with a high factor of precision are frequently required in systems. If the power is very high and the pipeline cannot handle the power transferred by the liquid, the high pressure received by the liquid may also cause work accidents.
Even though hydraulic systems are less complex than electrical or mechanical systems, they are still complex systems that should be handled with caution. Avoiding physical contact with hydraulic systems is an essential safety precaution when engaging with them. Even when a hydraulic machine is not in use, active liquid pressure within the system can be a hazard.
Inadequate pumps can cause mechanical failure in the place of work that can have serious and costly consequences. Although pump failure has historically been unpredictable, new diagnostic technology continues to improve on detecting methods that previously relied solely on vibration signals. Measuring discharge pressures enables manufacturers to forecast pump wear more accurately. Discharge sensors are simple to integrate into existing systems, increasing the hydraulic pump"s safety and versatility.
Hydraulic pumps are devices in hydraulic systems that move hydraulic fluid from point to point, initiating hydraulic power production. They are an important device overall in the hydraulics field, a special kind of power transmission that controls the energy which moving fluids transmit while under pressure and change into mechanical energy. Hydraulic pumps are divided into two categories namely gear pumps and piston pumps. Radial and axial piston pumps are types of piston pumps. Axial pumps produce linear motion, whereas radial pumps can produce rotary motion. The construction, excavation, automotive manufacturing, agriculture, manufacturing, and defense contracting industries are just a few examples of operations that apply hydraulics power in normal, daily procedures.

We provide a variety of high-quality single and double-acting 12V hydraulic pumps. Choose from a selection of poly or steel reservoir sizing options. Our pumps are ideal for application with Dump Trailers and more. Browse our shop today and find the right hydraulic pump for your hydraulic circuit needs!




 8613371530291
8613371530291