uchida hydromatik hydraulic pump free sample

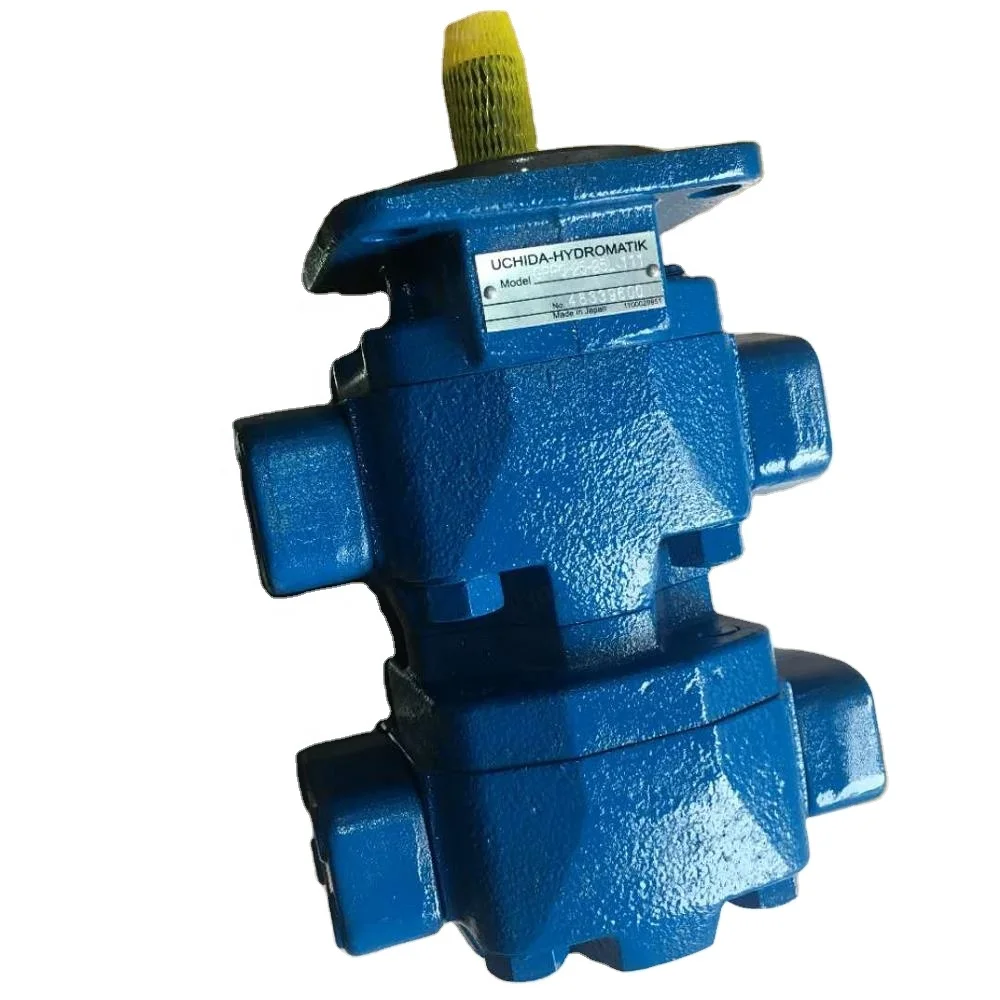
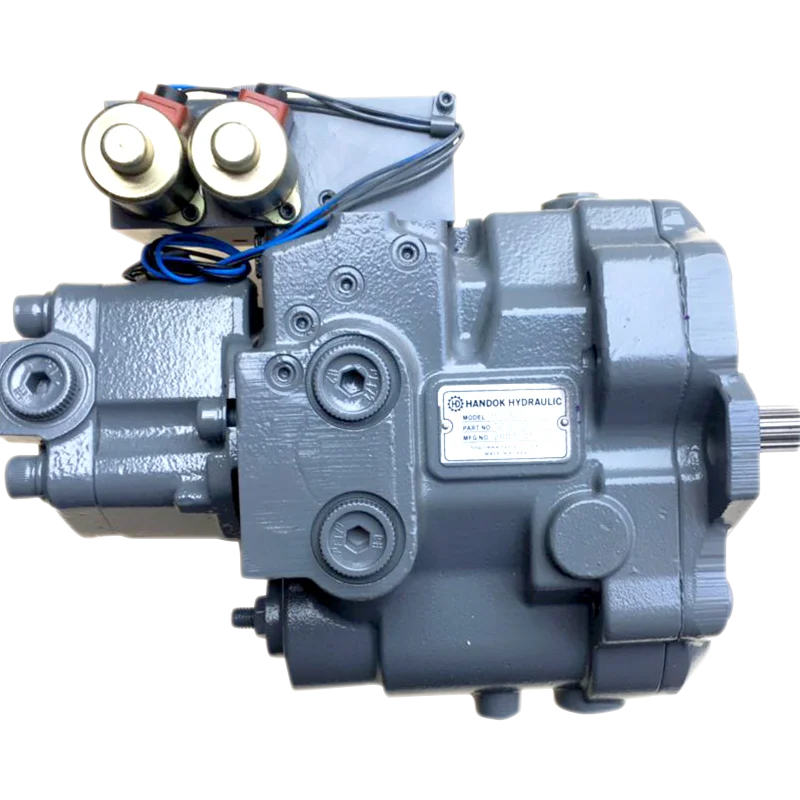
There are many machines that are used in construction work. Excavators, cranes, loaders and tractors are commonly used, and all these have hydraulic systems. A hydraulic system converts mechanical energy into hydraulic energy. The Uchida Hydromatik hydraulic pump is one of the most common systems available on Alibaba.com. This a very efficient pump that is used in various applications. One can also buy various hydraulic pump parts on the site from reputed manufacturers.
The Uchida Hydromatik hydraulic pump uses an axial piston system with a swashplate design. This pump is known for its long life and low noise levels. It has excellent oil absorption features. There are several models of this pump with different capacities to choose from depending on one"s application. The hydraulic pump parts used in the equipment are of the best quality for excellent durability.
The piston of a hydraulic main pump is its most important part. It is the piston that applies pressure on the fluid to discharge it. One must have high-quality pistons for the pump to work efficiently. Customers can buy a hydraulic pump piston of the highest quality on Alibaba.com. The suppliers will deliver the pistons as per the choice of the customer.
Many other parts for the axial piston pump are also sold on Alibaba.com. Customers can buy these with their logos and brand names. Gearboxes, cylinder blocks, rotary motors and other parts for the Uchida Hydromatik hydraulic pump are also available on the site. All parts are made from the best raw materials to ensure proper functioning and durability.

If you are supplying pump supplies, you can find the most favorable prices at Alibaba.com. Whether you will be working with piston type or diaphragm type systems, reciprocating or centrifugal, Alibaba.com has everything you need. You can also shop for different sizes uchida hydromatik hydraulic pump parts wholesale for your metering applications. If you operate a construction site, then you could need to find some concrete pump solutions that you can find at affordable rates at Alibaba.com. Visit the platform and browse through the collection of submersible and inline pump system, among other replaceable models.
Alibaba.com has been an excellent wholesale supplier of uchida hydromatik hydraulic pump parts for years. The supply consists of a vast number of brands to choose from, comes in different sizes, operations, and power sources. You can get a pump for residential and large commercial applications from the collection. Whether you want a water pump for your home, or run a repair and maintenance business, and need a supply of ucida hy dromatically hydraulic products, you can find the product you want from the vast collection of wholesale securityuch at hyibom.ik.raulicther parts want to water the your industry, and you"ll find everything in need.
A uchida hydromatik hydraulic pump parts comes in different makes and sizes, and you buy the tool depending on the application. The pump used by a filling station is not the one you use to fill up your tanks. There are high flow rate low pressure systems used to transfer fluids axially. On the other hand, you can go with radial ones dealing with a low flow rate and high-pressure fluid. The mixed flow pump variety combines radial and axial transfer mechanisms and works with medium flow and pressure fluids. Depending on what it will be pumping, you can then choose the uchida hydromatik hydraulic pump parts of choice from the collection at Alibaba.com.
A gear pump is a type of positive displacement (PD) pump. It moves a fluid by repeatedly enclosing a fixed volume using interlocking cogs or gears, transferring it mechanically using a cyclic pumping action. It delivers a smooth pulse-free flow proportional to the rotational speed of its gears.
Gear pumps use the actions of rotating cogs or gears to transfer fluids. The rotating element develops a liquid seal with the pump casing and creates suction at the pump inlet. Fluid, drawn into the pump, is enclosed within the cavities of its rotating gears and transferred to the discharge. There are two basic designs of gear pump: external and internal(Figure 1).
An external gear pump consists of two identical, interlocking gears supported by separate shafts. Generally, one gear is driven by a motor and this drives the other gear (the idler). In some cases, both shafts may be driven by motors. The shafts are supported by bearings on each side of the casing.
As the gears come out of mesh on the inlet side of the pump, they create an expanded volume. Liquid flows into the cavities and is trapped by the gear teeth as the gears continue to rotate against the pump casing.
No fluid is transferred back through the centre, between the gears, because they are interlocked. Close tolerances between the gears and the casing allow the pump to develop suction at the inlet and prevent fluid from leaking back from the discharge side (although leakage is more likely with low viscosity liquids).
An internal gear pump operates on the same principle but the two interlocking gears are of different sizes with one rotating inside the other. The larger gear (the rotor) is an internal gear i.e. it has the teeth projecting on the inside. Within this is a smaller external gear (the idler –only the rotor is driven) mounted off-centre. This is designed to interlock with the rotor such that the gear teeth engage at one point. A pinion and bushing attached to the pump casing holds the idler in position. A fixed crescent-shaped partition or spacer fills the void created by the off-centre mounting position of the idler and acts as a seal between the inlet and outlet ports.
As the gears come out of mesh on the inlet side of the pump, they create an expanded volume. Liquid flows into the cavities and is trapped by the gear teeth as the gears continue to rotate against the pump casing and partition.
Gear pumps are compact and simple with a limited number of moving parts. They are unable to match the pressure generated by reciprocating pumps or the flow rates of centrifugal pumps but offer higher pressures and throughputs than vane or lobe pumps. Gear pumps are particularly suited for pumping oils and other high viscosity fluids.
Of the two designs, external gear pumps are capable of sustaining higher pressures (up to 3000 psi) and flow rates because of the more rigid shaft support and closer tolerances. Internal gear pumps have better suction capabilities and are suited to high viscosity fluids, although they have a useful operating range from 1cP to over 1,000,000cP. Since output is directly proportional to rotational speed, gear pumps are commonly used for metering and blending operations. Gear pumps can be engineered to handle aggressive liquids. While they are commonly made from cast iron or stainless steel, new alloys and composites allow the pumps to handle corrosive liquids such as sulphuric acid, sodium hypochlorite, ferric chloride and sodium hydroxide.
External gear pumps can also be used in hydraulic power applications, typically in vehicles, lifting machinery and mobile plant equipment. Driving a gear pump in reverse, using oil pumped from elsewhere in a system (normally by a tandem pump in the engine), creates a hydraulic motor. This is particularly useful to provide power in areas where electrical equipment is bulky, costly or inconvenient. Tractors, for example, rely on engine-driven external gear pumps to power their services.
Gear pumps are self-priming and can dry-lift although their priming characteristics improve if the gears are wetted. The gears need to be lubricated by the pumped fluid and should not be run dry for prolonged periods. Some gear pump designs can be run in either direction so the same pump can be used to load and unload a vessel, for example.
The close tolerances between the gears and casing mean that these types of pump are susceptible to wear particularly when used with abrasive fluids or feeds containing entrained solids. However, some designs of gear pumps, particularly internal variants, allow the handling of solids. External gear pumps have four bearings in the pumped medium, and tight tolerances, so are less suited to handling abrasive fluids. Internal gear pumps are more robust having only one bearing (sometimes two) running in the fluid. A gear pump should always have a strainer installed on the suction side to protect it from large, potentially damaging, solids.
Generally, if the pump is expected to handle abrasive solids it is advisable to select a pump with a higher capacity so it can be operated at lower speeds to reduce wear. However, it should be borne in mind that the volumetric efficiency of a gear pump is reduced at lower speeds and flow rates. A gear pump should not be operated too far from its recommended speed.
For high temperature applications, it is important to ensure that the operating temperature range is compatible with the pump specification. Thermal expansion of the casing and gears reduces clearances within a pump and this can also lead to increased wear, and in extreme cases, pump failure.
Despite the best precautions, gear pumps generally succumb to wear of the gears, casing and bearings over time. As clearances increase, there is a gradual reduction in efficiency and increase in flow slip: leakage of the pumped fluid from the discharge back to the suction side. Flow slip is proportional to the cube of the clearance between the cog teeth and casing so, in practice, wear has a small effect until a critical point is reached, from which performance degrades rapidly.
Gear pumps continue to pump against a back pressure and, if subjected to a downstream blockage will continue to pressurise the system until the pump, pipework or other equipment fails. Although most gear pumps are equipped with relief valves for this reason, it is always advisable to fit relief valves elsewhere in the system to protect downstream equipment.
Internal gear pumps, operating at low speed, are generally preferred for shear-sensitive liquids such as foodstuffs, paint and soaps. The higher speeds and lower clearances of external gear designs make them unsuitable for these applications. Internal gear pumps are also preferred when hygiene is important because of their mechanical simplicity and the fact that they are easy to strip down, clean and reassemble.
Gear pumps are commonly used for pumping high viscosity fluids such as oil, paints, resins or foodstuffs. They are preferred in any application where accurate dosing or high pressure output is required. The output of a gear pump is not greatly affected by pressure so they also tend to be preferred in any situation where the supply is irregular.
A gear pump moves a fluid by repeatedly enclosing a fixed volume within interlocking cogs or gears, transferring it mechanically to deliver a smooth pulse-free flow proportional to the rotational speed of its gears. There are two basic types: external and internal. An external gear pump consists of two identical, interlocking gears supported by separate shafts. An internal gear pump has two interlocking gears of different sizes with one rotating inside the other.
Gear pumps are commonly used for pumping high viscosity fluids such as oil, paints, resins or foodstuffs. They are also preferred in applications where accurate dosing or high pressure output is required. External gear pumps are capable of sustaining higher pressures (up to 7500 psi) whereas internal gear pumps have better suction capabilities and are more suited to high viscosity and shear-sensitive fluids.

Engineering Technology Services (ETS) offers pump and motor units in many different ways. ETS stocks over 3800 GENUINE New and Service Exchange units that are ready for same day shipment. If the pump, motor, or valve units needed are not in stock, we can repair your core within 1-3 days, fully tested with a one-year warranty.
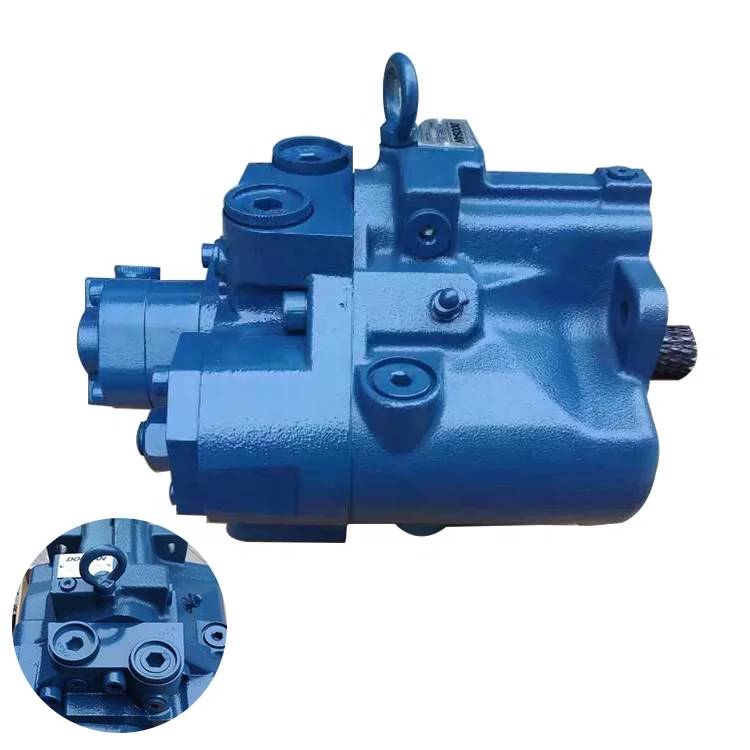

We have the largest variety of Bosch Rexroth, Uchida, Hydromatik & Brueninghaus original service exchange pumps & motors including A2FO, A2FM, A2FE, A2FLM, A2FSL, A3V, A4FO, A4FM, AA4V, AA4VG, AA4VS, A4VSG, AA6VM, A6VE, AA7VO, A7VTO, A7VSL, A8V, AA10VSO, AA10VO, AA10VG, A10FM, A10VM, A10VE, AA11VLO, A11VO, A11VG, AA20V, A22V, as well as S.A.E. & Metric models of pumps and motors. By using ETS as your provider, you have access to the largest Bosch Rexroth pump and motor inventory in the United States. We also carry genuine Bosch Rexroth valve spare parts, proportional valves, servo valves and more for Bosch, Rexroth, Uchida, Hydromatik and Brueninghaus motor and pump models. Stop wasting time by searching for a replacement part, service exchange unit or for a new motor or pump. We have over $35M in genuine Bosch Rexroth parts, units and valves, including complete rotary groups as well as individual spare parts. ETS has a parts inventory for the following Rexroth A2F, A2V, A3V, A4V, A4VG, A4VS, A5V, A6V, A7V, A8V, A10V, A11V, A20V and A22V units. Come to ETS for your Bosch, Rexroth, Uchida, Hydromatik and Brueninghaus motor or pump needs.

The main pump is actually a double axial piston pump, that uses a single ten-bore barrel (five pistons for each pump), with the kidney pressure ports arranged in two rings. The valve plate
swashplate of the piston pump is biased by a very strong double coil spring, and if you look at the end cover, you"ll see that it is destroked not by one, but by three servo-pistons,
pump machined into it! The tiny pump sends the oil to the relief vlave, mounted inside the piston pump end cover, and feeds the two solenoid operated valves mounted on the end cover as well (picture).




 8613371530291
8613371530291