kelly bushing height in stock

Because wells are not always drilled vertically, there may be two “depths” for every given point in a wellbore: the measured depth (MD) measured along the path of the borehole, and the true vertical depth (TVD), the absolute vertical distance between the datum and the point in the wellbore. In perfectly vertical wells, the TVD equals the MD; otherwise, the TVD is less than the MD measured from the same datum. Common datums used are ground level (GL), drilling rig floor (DF), rotary table (RT), kelly bushing (KB) and mean sea level (MSL). [1]
Kelly Bushing Height (KB):The height of the drilling floor above the ground level. Many wellbore depth measurements are taken from the Kelly Bushing. The Kelly bushing elevation is calculated by adding the ground level to the Kelly bushing height.

Because wells are not always drilled vertically, there may be two “depths” for every given point in a wellbore: the measured depth (MD) measured along the path of the borehole, and the true vertical depth (TVD), the absolute vertical distance between the datum and the point in the wellbore. In perfectly vertical wells, the TVD equals the MD; otherwise, the TVD is less than the MD measured from the same datum. Common datums used are ground level (GL), drilling rig floor (DF), rotary table (RT), kelly bushing (KB) and mean sea level (MSL). [1]
Kelly Bushing Height (KB):The height of the drilling floor above the ground level. Many wellbore depth measurements are taken from the Kelly Bushing. The Kelly bushing elevation is calculated by adding the ground level to the Kelly bushing height.

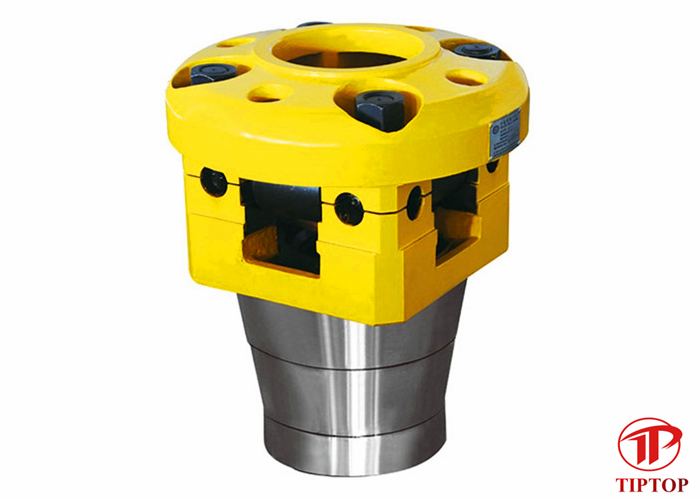
Kelly bushing is that elevated device positioned right on top of the rotary table and used to transmit torque from the rotary table to the kelly. The kelly bushing is designed to be the connection between the rotary table and the kelly. The kelly is a 4 or 6 sided steel pipe.
The purpose of the rotary table is to generate the rotary action (torque) and power necessary to rotate the drillstring and drill a well. The torque generated by the rotary table is useless if it is not transferred to the kelly (the drillstring is connected to the kelly).
Hence, through the kelly bushing the torque generated at the rotary table is transferred to the kelly. To achieve this connection, the inside profile of the kelly bushing matches the outer profile of the kelly so that the kelly fits or “sits” comfortably in the kelly bushing.
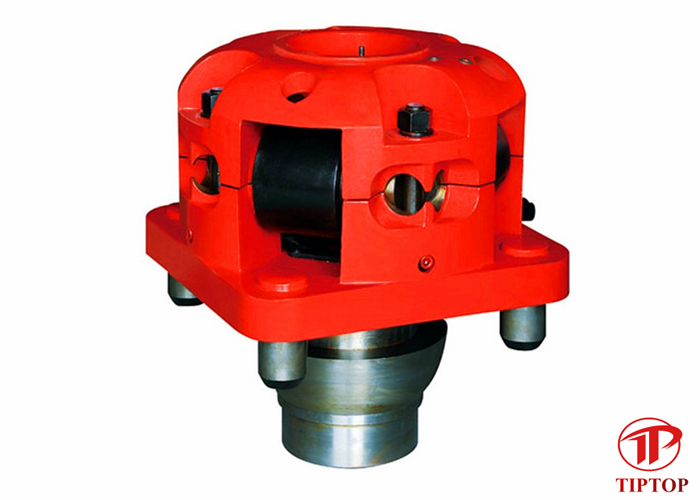
There are various designs for the kelly bushing including the split type, the pin-drive type and the square-drive type. Each of these designs has different ways in which they are connected and disconnected from the rotary table.
The internal diameter of the kelly bushing can be cut into the shape of a square (4-sided) or a hexagon (6-sided) depending on the outer shape of the kelly that will be used. The internals of a Kelly bushing is designed to resemble the outer shape of a Kelly just like the insides of a key lock is cut to exactly match the outer shape of the key.
The kelly bushing is not designed to hold tightly onto the Kelly; the kelly is still permitted to move up and down through the kelly bushing. This requirement is a must since drilling cannot progress if the kelly remains on a fixed spot. As the well is drilled deeper, the kelly also moves downward through the Kelly bushing.
The kelly bushing is sometimes used as a reference point from which depth measurements can be taken. All depths must be recorded with respect to a reference point; the kelly bushing (KB) is one of the depth references used in the oil and gas industry.
The top of the kelly bushing is normally used as the depth reference.For example, 7500ft KB means 7500ft below the kelly bushing or 7500ft measured from the top of the kelly bushing down to that point in the well.
In some other cases, depths could be recorded as 7500ft MDBKB meaning 7500ft measured depth below the kelly bushing. This is mostly used when the measured depth is different from the true vertical depth of the well, common with deviated and horizontal wells.

An adapter that serves to connect the rotary table to the kelly. The kelly bushing has an inside diameter profile that matches that of the kelly, usually square or hexagonal. It is connected to the rotary table by four large steel pins that fit into mating holes in the rotary table. The rotary motion from the rotary table is transmitted to the bushing through the pins, and then to the kelly itself through the square or hexagonal flat surfaces between the kelly and the kelly bushing. The kelly then turns the entire drillstring because it is screwed into the top of the drillstring itself. Depth measurements are commonly referenced to the KB, such as 8327 ft KB, meaning 8327 feet below the kelly bushing.
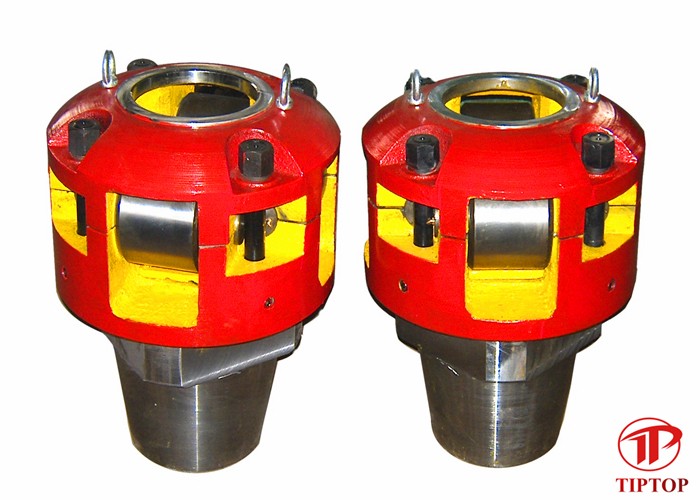

The NOV CUL & CB Casing Bushings are inserted directly into the rotary table and insure that the casing being run is perfectly aligned with the center of the hole. Model CU is a solid bushing and model CB is a split bushing. All of the bushings accept bowls of different sizes to accommodate a wide range of casing. Using CMS-XL or CP-S slips, since these bushings fit into the rotary table, the casing string can be easily rotated during cementing operations.

{"status":1,"html":"\r\n.onlinebox_three{border:2px solid;}\r\n.onlinebox_three .onlinebox_three_list{width: 160px;padding: 10px 0px;}\r\n.onlinebox_three .online-item{margin-bottom: 5px; padding: 0px 17px; position: relative;display: block;color: #666;}\r\n.onlinebox_three .online-item:last-child{margin-bottom: 0px;}\r\n.onlinebox_three .online-item:hover{background: #f8f8f8;}\r\n.onlinebox_three .online-item i{font-size: 16px;}\r\n.onlinebox_three .onlinebox-open{font-size: 22px;display:none;cursor: pointer;padding: 0 10px; font-size: 18px; line-height: 40px;}\r\n.onlinebox.min .onlinebox-open{display:block;padding:0 10px;background:#444;font-size:18px;line-height:40px;color:#fff}\r\n.onlinebox .onlinebox-min{position: relative;top:-4px;}\r\n@media (max-width: 767px){\r\n.onlinebox_three .online-item{font-size: 12px;padding-top: 6px;}\r\n.onlinebox_three .online-item i{font-size: 14px;}\r\n}\r\n<\/style>\r\n
online chating<\/h4>\r\n <\/div>\r\n \r\n \r\n <\/i>\r\n 客服01<\/span>\r\n <\/a>\r\n \r\n <\/i>\r\n 客服02<\/span>\r\n <\/a>\r\n \r\n <\/i>\r\n 客服03<\/span>\r\n <\/a>\r\n <\/div>\r\n

At a previous employer a coworker came to me and told me that a group within our company had asked for all the KB (kelly bushing) elevations for every well in Colorado. I replied that it made no sense and asked my coworker to see if the reference elevations were what they really wanted. The coworker returned the next day and indicated that they had insisted on the KB elevations. We supplied the KB elevations and sure enough, about a week later they came back and asked for the reference elevations.

All CategoriesAdapters (20)B.O.P. (4)Bit Breakers (4)Casing (52)Drill Collars (51)Drill Pipe (77)Downhole/Tubulars (1)Elevators (10)Flanges (13)Heavy Weight Drill Pipe (49)Hooks (5)Insert Bowl (1)Kelly Bushing (5)Kellys (3)Pony Collars (4)Pumps (1)Pup Joints (5)Rams (10)Rotary Tables (1)Spools (6)Stabilizers (1)Stabilizers, Non-Mag (2)Subs, Bits (24)Subs, Cross-Over (43)Subs, Double Pin (22)Subs, Double Pin Kick (2)Subs, Lift (23)Subs, Pump-In Outlet (3)Subs, Saver (4)Tubing (8)Valves (2)Wash Pipe (1)
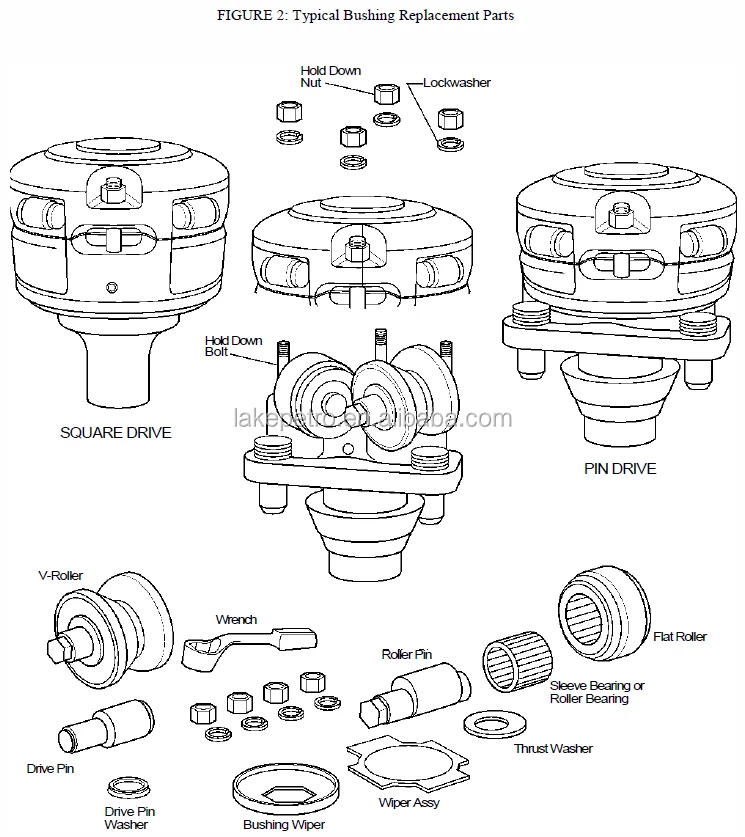
A pit in the ground to provide additional height between the rig floor and the well head to accommodate the installation of blowout preventers, ratholes, mouseholes, and so forth. It also collects drainage water and other fluids for disposal.†
A device fitted to the rotary table through which the kelly passes. It is the means by which the torque of the rotary table is transmitted to the kelly and to the drill stem. Also called the drive bushing.†
The derrickman"s working platform. Double board, tribble board, fourable board; a monkey board located at a height in the derrick or mast equal to two, three, or four lengths of pipe respectively.†
A hole in the rig floor 30 to 35 feet deep, lined with casing that projects above the floor. The kelly is placed in the rathole when hoisting operations are in progress.†
The hose on a rotary drilling rig that conducts the drilling fluid from the mud pump and standpipe to the swivel and kelly; also called the mud hose or the kelly hose.†
The principal component of a rotary, or rotary machine, used to turn the drill stem and support the drilling assembly. It has a beveled gear arrangement to create the rotational motion and an opening into which bushings are fitted to drive and support the drilling assembly.
Wedge-shaped pieces of metal with teeth or other gripping elements that are used to prevent pipe from slipping down into the hole or to hold pipe in place. Rotary slips fit around the drill pipe and wedge against the master bushing to support the pipe. Power slips are pneumatically or hydraulically actuated devices that allow the crew to dispense with the manual handling of slips when making a connection. Packers and other down hole equipment are secured in position by slips that engage the pipe by action directed at the surface.†
The top drive rotates the drill string end bit without the use of a kelly and rotary table. The top drive is operated from a control console on the rig floor.†

LEE C. MOORE, Set back capacity 700 klb. Height to rotary beams 24 ft. Drill Floor Height 30 ft.; Complete with: Catwalk, 1 Set of Skidding Gear, Hydraulic jack up unit

At a previous employer a coworker came to me and told me that a group within our company had asked for all the KB (kelly bushing) elevations for every well in Colorado. I replied that it made no sense and asked my coworker to see if the reference elevations were what they really wanted. The coworker returned the next day and indicated that they had insisted on the KB elevations. We supplied the KB elevations and sure enough, about a week later they came back and asked for the reference elevations.

All CategoriesAdapters (20)B.O.P. (4)Bit Breakers (4)Casing (52)Drill Collars (51)Drill Pipe (77)Downhole/Tubulars (1)Elevators (10)Flanges (13)Heavy Weight Drill Pipe (49)Hooks (5)Insert Bowl (1)Kelly Bushing (5)Kellys (3)Pony Collars (4)Pumps (1)Pup Joints (5)Rams (10)Rotary Tables (1)Spools (6)Stabilizers (1)Stabilizers, Non-Mag (2)Subs, Bits (24)Subs, Cross-Over (43)Subs, Double Pin (22)Subs, Double Pin Kick (2)Subs, Lift (23)Subs, Pump-In Outlet (3)Subs, Saver (4)Tubing (8)Valves (2)Wash Pipe (1)

A pit in the ground to provide additional height between the rig floor and the well head to accommodate the installation of blowout preventers, ratholes, mouseholes, and so forth. It also collects drainage water and other fluids for disposal.†
A device fitted to the rotary table through which the kelly passes. It is the means by which the torque of the rotary table is transmitted to the kelly and to the drill stem. Also called the drive bushing.†
The derrickman"s working platform. Double board, tribble board, fourable board; a monkey board located at a height in the derrick or mast equal to two, three, or four lengths of pipe respectively.†
A hole in the rig floor 30 to 35 feet deep, lined with casing that projects above the floor. The kelly is placed in the rathole when hoisting operations are in progress.†
The hose on a rotary drilling rig that conducts the drilling fluid from the mud pump and standpipe to the swivel and kelly; also called the mud hose or the kelly hose.†
The principal component of a rotary, or rotary machine, used to turn the drill stem and support the drilling assembly. It has a beveled gear arrangement to create the rotational motion and an opening into which bushings are fitted to drive and support the drilling assembly.
Wedge-shaped pieces of metal with teeth or other gripping elements that are used to prevent pipe from slipping down into the hole or to hold pipe in place. Rotary slips fit around the drill pipe and wedge against the master bushing to support the pipe. Power slips are pneumatically or hydraulically actuated devices that allow the crew to dispense with the manual handling of slips when making a connection. Packers and other down hole equipment are secured in position by slips that engage the pipe by action directed at the surface.†
The top drive rotates the drill string end bit without the use of a kelly and rotary table. The top drive is operated from a control console on the rig floor.†

LEE C. MOORE, Set back capacity 700 klb. Height to rotary beams 24 ft. Drill Floor Height 30 ft.; Complete with: Catwalk, 1 Set of Skidding Gear, Hydraulic jack up unit




 8613371530291
8613371530291