kelly bushing diagram made in china

The roller kelly bushing is formed by cutting and forging hexagon bar. These bushings with different thread types are also available. The material is high-quality alloy steel with heat treatment. And there are two types, pin drive and square drive. As a threaded fitting, the roller kelly bushing is used to connect pipelines with different bores. This tool plays an irreplaceable role in the pipeline connection. In China, bushings are usually known as hexagonal nipples with inside and outside threaded.
When a different caliber is needed in the water pipe, for example, the caliber of DN15 water pipe is changed to DN20, roller kelly bushing is a must. The threaded outside of DN15 water pipe is connected to the threaded inside of bushing; the threaded inside of DN20 is joint with threaded outside of bushing. However, if DN20 water pipe is with a threaded outside, we can use a short connector with a threaded inside between DN20 pipe and bushing. Threaded connection is very convenient for any water instrument and valve. Therefore, the application of the roller kelly bushing to change calibers is very common both in industry and life.
As a professional China roller kelly bushing manufacturer and supplier, Jiangsu Kayson Petrol- Machinery Co., Ltd possesses strong technical force, excellent production equipments and complete test facilities. After several years of research and innovation, we"ve now formed many product series like: bushings, bottleneck elevator, manual tongs, spiders, slips, inserts and bit breakers.

Roller Kelly Bushings are designed and manufactured as per API Spec 7K "Drilling and Well Servicing Equipment" for driving Kelly in the drilling operation.
Roller kelly bushings are constructed in upper body half, low body half, rollers, rollers pin and etc., can be available in square drive or pin drive. Square drive roller kelly bushing designed with taper contact surface in low body half, while pin drive roller kelly bushing designed with pin to be installed in low body half.
According to torque of drilling, roller kelly bushing can be available in heavy duty, medium duty and light duty, heavy duty bushings are for high torque and high speed drilling operations while medium duty and light duty are for medium or shadow depth drilling operations.
Roller kelly bushings can accommodate square Kelly or hex Kelly, for square Kelly, the bushing is designed with four flat rollers, and for hex Kelly, the bushing is designed with two V-shaped rollers and two flat rollers. By changing roller size, roller kelly bushing can accommodate square Kelly from 2½" to 5¼" or hex Kelly from 3" to 6", and can be installed in rotary table range from 17½" to 37½".

Pin drive bushingsPin drive bushings consist of lower body half, upper body half, roller and roller pin, etc. when the bushing is installed to square kelly or hex kelly, the square part of the lower body half can be fitted in the square of the master bushing. When operating, the rotary table drives master bushing and master bushing drives roller kelly bushings ...
Square drive bushingSquare drive bushing is also referred to as roller bushing or roller kelly bushing. This roller bushing is an essential drilling tool. Square drive bushing is used for 17 1/2-49 1/2 inch rotary tables. It"s designed and manufactured according to API Spec 7K. The roller kelly bushing works with master bushing to drive dril...
This roller kelly bushing is an essential drilling tool. The bushings are designed with two drive methods, i.e. square rolling and pin shaft rolling. And according to type, there are heavy, medium and light-duty kelly bushings. The roller kelly bushing can be equipped with turntable slips to drive the square or hexagon kelly bar.
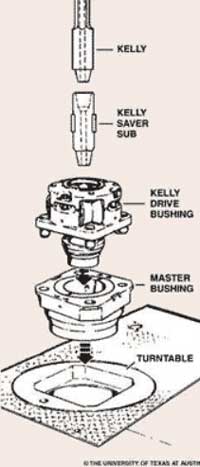
Kelly bushings consist of top cover, base, axis, needle bearing, sealing body, roller, binding bolt, and refuel cup. The needle bearing within the roller is installed on axis whose both ends are compact between top cover and base. The refuel cup lying on axis end injects grease into needle bearing at regular intervals. In order to prevent the sealing body from penetrating and protect the needle bearing, the inner-outer O type circle must be installed on the both ends of the roller. Fasten pin lying on the top of sealing body prevents it from rotating, and inlays are inside seam allowance of up base.
To produce kelly bushings and other drilling tools, the company possesses strong technical force, excellent production equipments and complete test facilities. And we"re focusing on new products making and market expanding all the time. Now Jiangsu Saifu Petrol- Machinery Co., Ltd becomes a first-level supply member of Chinese Petroleum & Natural Gas Consortium. At the same time, it"s also the member of China Petrochemical Material Resources Market.

Product Description: Roller Kelly Bushings can be classed as two types based on different ways of drive, square drive and pin drive. Also they can be classed as three types based on different style, heavy, medium and light-duty. They are used for 17.1/2 to 49.1/2inch rotary tables. They are designed and manufactured...

According to the drive method, this range of roller kelly bushing is classified into square drive and pin drive types. Based on the capacity, the product is divided into heavy duty, medium duty and light duty types.
These roller kelly bushings are applicable for rotary tables with diameter between 171/2 and 491/2 inches. They are designed and manufactured in accordance with API Spec 7K specifications for drilling and well servicing equipment.

A device fitted to the rotary table through which the kelly passes. It is the means by which the torque of the rotary table is transmitted to the kelly and to the drill stem. Also called the drive bushing.†
A hole in the rig floor 30 to 35 feet deep, lined with casing that projects above the floor. The kelly is placed in the rathole when hoisting operations are in progress.†
The hose on a rotary drilling rig that conducts the drilling fluid from the mud pump and standpipe to the swivel and kelly; also called the mud hose or the kelly hose.†
The principal component of a rotary, or rotary machine, used to turn the drill stem and support the drilling assembly. It has a beveled gear arrangement to create the rotational motion and an opening into which bushings are fitted to drive and support the drilling assembly.
Wedge-shaped pieces of metal with teeth or other gripping elements that are used to prevent pipe from slipping down into the hole or to hold pipe in place. Rotary slips fit around the drill pipe and wedge against the master bushing to support the pipe. Power slips are pneumatically or hydraulically actuated devices that allow the crew to dispense with the manual handling of slips when making a connection. Packers and other down hole equipment are secured in position by slips that engage the pipe by action directed at the surface.†
The top drive rotates the drill string end bit without the use of a kelly and rotary table. The top drive is operated from a control console on the rig floor.†

• Kelly is manufactured strictly according to API Spec7-1 standard. Manufactured from AISI 4145H-modified, fully heat-treated alloy steel with aBrinell hardness range of 285-341 and a minimum average Charpy impact value of 40 ft-lbs.

A 27-year-old gas drilling rig worker died on May 23, 2003 from blunt force trauma to the head, neck, and chest during a cleanout operation at the well. At the time of the incident, the victim was working within eight feet of the kelly on the drilling rig floor. Compressed air was used to blow out the conductor pipe, but due to a lack of communication, the compressor was turned on before the valves were prepared to control the flow of debris out of the hole. The excess pressure caused the kelly bushing, drillpipe slips, and debris to be blown out of the rotary table. The victim was struck by these objects and was pronounced dead on arrival to the hospital.
A 27-year-old gas drilling rig worker died on May 23, 2003 from blunt force trauma to the head, neck, and chest after he was struck by the kelly bushing and drillpipe slips. OKFACE investigators reviewed the death certificate, related local news articles, and reports from the sheriff’s office, Medical Examiner, Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA),
At the time of the incident, the rig floor and working surfaces were level and dry; the weather was warm with light to no wind. The victim was working with four other crew members on a gas drilling rig, wearing the necessary personal protective equipment (e.g., steel toe boots, hard hat, eye protection). Prior to the incident, the decedent was assigned the task of driller and was asked to find the bottom of the conductor hole with the kelly (Figure 2). The kelly is used to transmit power (rotary motion) from the rotary table and kelly bushing to the drillstring (Table 1). After unlatching the brake handle, the driller allowed the kelly to free fall to the bottom. The uncontrolled fall caused the kelly to become jammed with debris, such as water, mud, and other material, that had collected in the conductor hole since the time it was originally drilled for the well. As a result, a cleanout operation became necessary. Cleanout procedures involving air or mud drilling fluid are acceptable norms in the oil and gas drilling industry; however, drilling fluid is more commonly used than compressed air.
a long square or hexagonal steel bar with a hole drilled through the middle for a fluid path; goes through the kelly bushing, which is driven by the rotary table
After the kelly became jammed, a senior driller was assigned to take over the brake handle and kelly; however, the decedent remained approximately eight feet away on the rig floor. A newly hired, yet experienced, derrickman had the job of running the air compressor. While the drillers were switching positions, the derrickman realized that he had not started that particular type of compressor in quite some time and left the rig floor to seek help from another driller onsite.
In normal cleanout operation procedures, certain valves are closed prior to turning on the compressed air, which allows control over the flow of debris out of the hole and into a catch pond. Once the valves are prepared, the driller indicates to the derrickman that the area is ready for the compressed air. At some point between the senior driller preparing for cleanout and the derrickman leaving the floor to turn on the air compressor, there was a lack of communication and the air compressor was activated without the senior driller’s knowledge, prior to the prescribed valves being shut. After starting the air compressor, the derrickman returned to the rig floor and, as he walked to his next assignment, the rotary table erupted. The pressure normally used to complete the cleanout work is a minimum of 20 pounds per square inch. Within minutes, the kelly had pressurized well beyond this point to 150 pounds per square inch. The victim, who was still on the rig floor in close proximity to the kelly, was also unaware that the air compressor had been turned on. The compressed air, at full pressure with no valves closed to control or direct the flow, blew the kelly bushing, drillpipe slips, and debris out of the rotary table; all of which struck and landed on the victim.
The JOTKB MODEL 27 PDHD OR 20 PDHD are developed for pin drive master bushing for rotary table sizes from 27-1/2" to 49-1/2" having 25-3/4" and 23" dia pin center. This unit is used for heavy duty drilling operations and high torque conditions on off shore as well as on shore drilling operations, and handle Kelly sizes from 3" to 6" Square or Hexagonal.

The kelly is a primary link between the drilling rig’s surface equipment and the bit, and is therefore a critical component of the rotary system. Although top drive systems have replaced kelly/rotary table combinations on many rigs, some knowledge of their manufacture and operation is useful.
Their angled surfaces, or drive flats, are designed to fit into a drive roller assembly on the kelly bushing, so that as the rotary table turns to the right, the kelly turns with it. To allow for normal right-hand rotation of the drill string, kellys have right-hand threads on their bottom connections and left-hand threads on their top connections.
The American Petroleum Institute has established manufacturing and design standards for kellys, and has included them in the follwoing publications:API RP 7G, Recommended Practice for Drill Stem Design and Operating Limits.
For a kelly to be efficient in turning the drill string, the clearance between its drive flat surfaces and the rollers in the kelly bushing must be kept to a minimum. Kellys most often wear out due to a rounding-off of the drive corners, as shown in Figure 1 (new kelly with new drive assembly) and Figure 2 (worn kelly with worn drive assembly).
For minimal rounding, there must be a close fit between the kelly and the roller assembly, with the rollers fitting the largest spot on the kelly flats. Manufacturing techniques and rig operating practices play important roles in determining this fit.
Both square and hexagonal kellys are manufactured either from bars with an “as-forged” drive section, or from bars with fully-machined drive sections. Forged kellys are cheaper to manufacture. But machined kellys tend to last longer because:Unlike forged kellys, machined kellys are not subject to the metallurgical process of decarburization, which leaves a relatively soft layer of material on the drive surface that can accelerate the rounding process and increase the potential for fatigue cracks;
To minimize rounding, rig personnel should follow these guidelines (Brinegar, 1977):Always use new drive-bushing roller assemblies to break in a new kelly.
Frequently inspect and periodically replace drive assemblies to ensure that clearance and contact angle between the kelly and the rollers is held to a minimum;
Fatigue failures are seldom a problem with kellys because of the high-quality steels used in their manufacture. Nevertheless, kellys should be regularly inspected for cracks and other signs of wear, particularly within the threaded connections, in the areas where the flats join the upper and lower upsets and in the center of the drive section.
In general, the stress level for a given tensile load is less in the drive section of a hexagonal kelly than in the drive section of a square kelly of comparable size. Hexagonal kellys are thus likely to last longer than square kellys before failing under a given bending load.
Kellys can become crooked or bent due to improper handling. Examples of mishandling include dropping the kelly, misaligning it in the rathole and thereby exerting a side pull, using poor tie-down practices during rig moves, not using the kelly scabbard and improper loading or unloading techniques. Depending on where a bend is located, it may cause fatigue damage not only to the kelly but to the rest of the drill string, and can also result in uneven wear on the kelly bushing.
Unusual side motions or swaying of the swivel are good indicators of a crooked kelly. A good field service shop has equipment for straightening bent kellys, making this an easily-corrected problem.
A kelly saver subshould always be run between the kelly and the top joint of drill pipe. This protects the kelly’s lower connection threads from wear, as joints of drill pipe are continually made up and broken out. A saver sub is much less expensive and much easier to replace than the kelly itself, and it can also be equipped with a rubber protector to help keep the kelly centralized and to protect the top joint of casing against wear.
A kelly cock is a valve installed above or below the kelly, which prevents fluid from escaping through the drill string if the well should begin to flow or “kick.” As an extra well control precaution, an upper kelly cock (having left-hand threads) should be installed directly above the kelly, while a lower kelly cock (having right-hand threads) should be installed below the kelly. Installing two kelly cocks ensures that at least one of them is always accessible, regardless of the kelly’s position.
Automatic check valves, designed to close when the mud pumps are shut off, are also available, and can be installed below the kelly to prevent mud from spilling onto the rig floor during connections.




 8613371530291
8613371530291